2. Acetylcholine & Amino acids
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
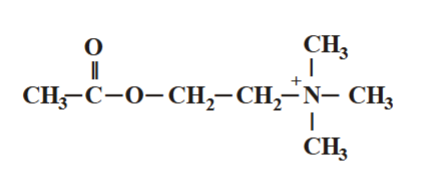
what is that
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Significance of Acetylcholine (ACh) as an NT
The first molecule to be implicated as a NT
What is the history of Acetylcholine (ACh) as an NT

Synthesis of ACh occurs where
Synthesis happens in the cytosol of the nerve terminus
ACh is a combination of what 2 molecules
Acetyl CoA & Choline
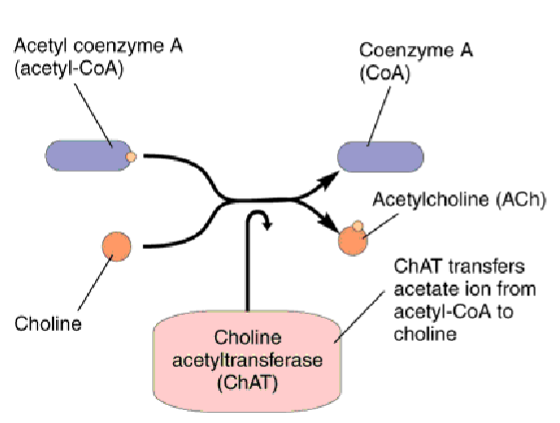
How is ACh synthesised
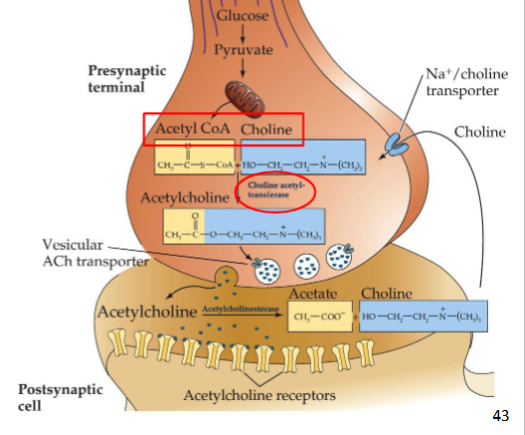
What transfers the acetate ion from Acetyl CoA to choline
ChAT (Choline acetyltransferase)
(ChAT tells Acetyl to chat to choline)
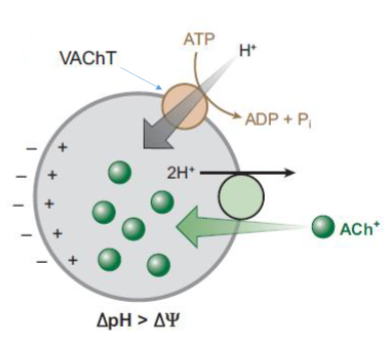
What transports ACh into synaptic vesicles for storage
Vesicular ACh Transporter (VAChT)
Where is VAChT located?
VAChT is embedded in the membrane of synaptic vesicles.
How does VAChT move ACh into vesicles?
VAChT uses a proton (H⁺) gradient established by a vesicular proton pump to drive ACh uptake into vesicles.
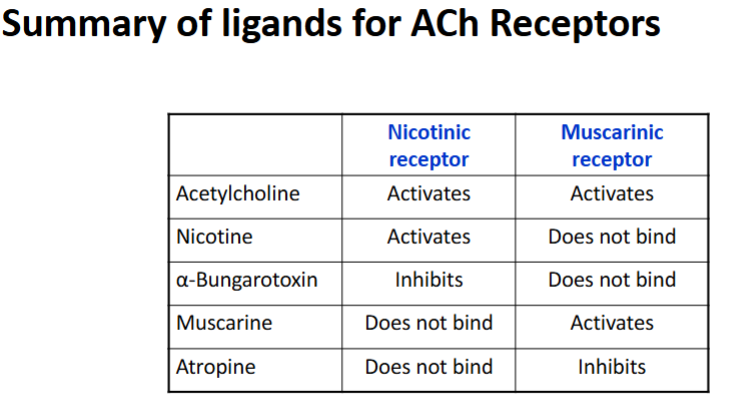
Acetylcholine can bind to what receptor type(s)
Ionotropic: Nicotinic receptor
Metabotropic: Muscarinic receptor
The structure of the nicotinic ACh receptor channel is made up of how many subunits
Receptor is made of 5 subunits: 2α, β, γ, δ
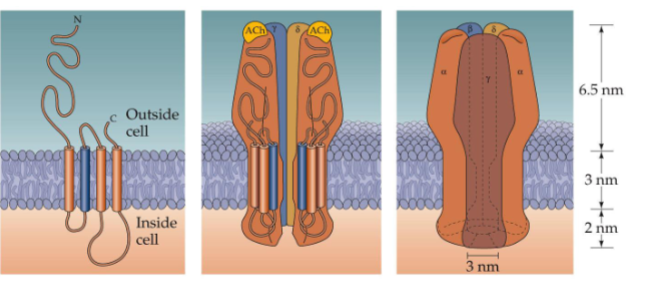
How many binding sites for ACh does each Nicotinic ACh receptor (ionotropic) have
Each nAChR complex has 2 binding sites for ACh
On what subunits does ACh usually bind to nicotinic receptors
Mostly on α-subunits, though partial involvement of δ and γ subunits
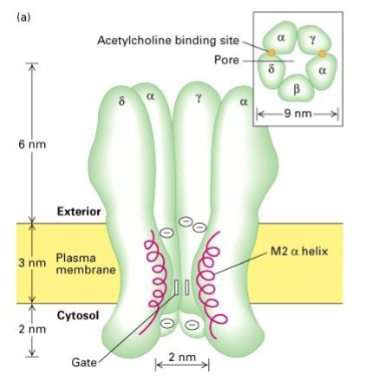
Why can’t calcium ions go through the nicotinic ACh receptor
They’re too big
What ion moves when the nicotinic ACh receptor opens
There is an influx of Na+
Agonist vs antagonist

Name 2 agonists to the nicotinic AChR (acetylcholine receptor)
Acetylcholine is the endogenous agonist
Nicotine is an agonist of ACh ionotropic receptor (a plant alkaloid identified in 1914)
Name an antagonist to the nicotinic AChR (acetylcholine receptor)
α-bungarotoxin is an antagonist of ACh ionotropic receptor (from snake venom)
How many different Muscarinic AChRs are there - name them
5: M1, M2, M3, M4, M5
There are 5 different mAChRs that can activate different G proteins that link to different signalling systems. Which of the 5 activate which G proteins which link to which signalling systems
M1, M3, M5: Activate phospholipase C (PLC) via Go or Gq
M2, M4: Inhibit adenylate cyclase via Gi & stimulate a K+ channel via Gs
Where in the body are MAChR found & what are they doing there
mAChR present in striatum and in peripheral nervous system. They also mediate autonomic functions acting on heart, smooth muscle and exocrine glands
Name an agonist that binds to Muscarinic AChRs
Muscarine: Fungal alkaloid that binds with high affinity
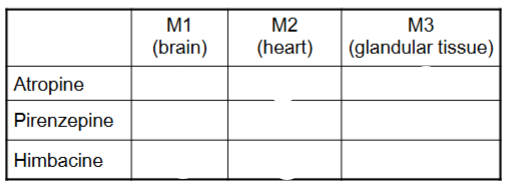
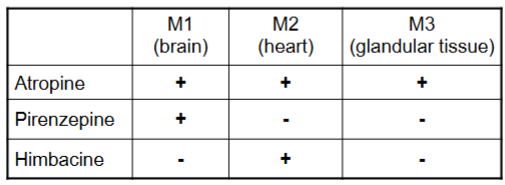
Fill this in and explain
Atropine:
Non-selective muscarinic antagonist
Blocks M1, M2, and M3 → affects brain, heart, and glands
Broad parasympathetic-blocking effects (dry mouth, increased heart rate, CNS effects)
Pirenzepine:
Selective M1 antagonist
Blocks M1 in the brain (and stomach’s gastric glands)
Himbacine:
Blocks M2 (heart)
Mainly affects heart rate (can prevent parasympathetic slowing of the heart)
How is ACh inactivated
Enzymatic degradation - Degraded by acetylcholinesterase in synaptic cleft where ACh is at high concentration
Catalytic rate of acetylcholinesterase
104 – 105 mols per sec
One of the most rapid enzymes known
What happens when ACh is inactivated
Choline is taken back up into the nerve terminal by high affinity Na+- dependent uptake system
Name some drugs that inhibit Acetylcholinesterase
Sarin nerve gas – lethal dose is 0.5 mg (weapon of war)
Organophosphates – used in insecticides (can’t stop contraction of muscles - kills the insects)
Neostigmine, donezepil (used in treatment of Alzheimer’s disease as ACh is depleted at junctions in the brain)
At what location is ACh degraded
In the synaptic cleft
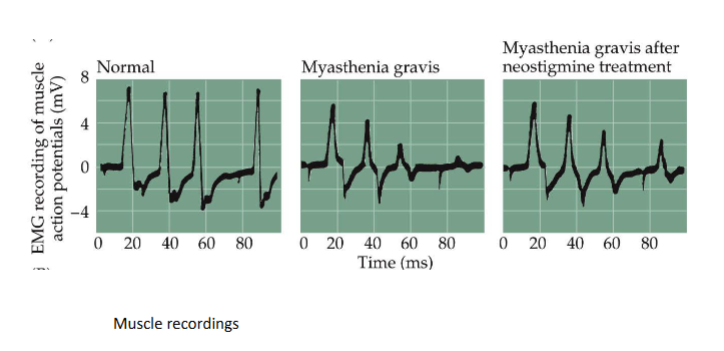
Name an ACh neurotransmission disease
Myasthenia gravis
What does Myasthenia gravis present as
Muscle weakness
What kind of disease is Myasthenia gravis
Autoimmune disorder - Patients’ sera contain antibodies directed against their own nicotinic AChRs → decreased number of functional AChRs on muscle cells → defective neuromuscular transmission leading to muscle weakness
What can be used as treatment against Myasthenia Gravis
Neostigmine treatment