Starch leaves practical
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Invesigate the need for light and chlorophyll in photosynthesis by testing plant leaves for starch
Plants need light for light for photosynthesis. Plants convert glucose produced in photosynthesis into starch.
What can be used to test for starch
Iodine soultuon
What is the colour change of iodine solution
Yellow-brown to blue-black

Word equation for photosynthesis

Banced chemical equation for photosynthesis

Prior to investigation
Plants needs to destarched before to show if starch has been produced during the investigation
Place the plant in dark cupboard for 48 hours
Then put dark strips over one of its leaves before being placed in bright light for 24 hours prior to the ray of the investigation
Safety
Wear safety glasses.
Take care when using Iodine.
Take care when using ethanol.
Take care when using hot water.
Apparatus and materials
The geranium plant that has a dark strip placed over one of its leaves (that had been destarched and then placed in bright light for 24 hours)
Heatproof mat
250 cm3 beaker Hot water
Boiling tube rack
Boiling tube containing 15cm3 of ethanol
Petri dish/white tilelodine solution
Forceps/glass rod
Safety glasses
Methanol
Remove the leaf covered with a strip of dark card from the plant.
Answer Question 1(a) below.
Place a 250 cm§ beaker on a heatproof mat on your bench and carefully half fill the beaker
with hot waterCarefully remove the dark card from the plant.
Using forceps, place the leaf into the beaker of hot water for one minute.
Using forceps, remove the leaf from the hot water.
Using forceps. gently place the leaf into the ethanol in the boiling tube in the boiling tube rack. Take care not to break the leaf.
Immediately place the boiling tube into the beaker of hot water and leave until the green pigment has been removed from the leaf.
Using forceps carefully remove the leaf from the boiling tube and dip it into the beaker of hot water for approximately 10 seconds.
Place the leaf in a Petri dish or on a white tile making sure the leaf is spread out fully.
Cover the leaf with iodine solution.
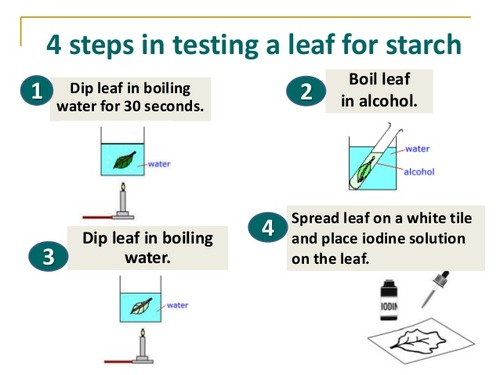
Adding a leaf to boiling water during a starch test
Kills the leaf to prevent any further reactions that might break down starch or affect its presence
Adding hot ethanol during a starch test
Causes the leaf to become decoloured, so iodine results can be easily visualised
Washing the leaf before examination during a starch test
Softens the leaf
Risk of starch tests
Water baths can be made using bunsen burners, however ethanol is also used to remove pigments from the plant, ethanol is very flammable and should be kept away from flames

Starch results for plants kept in light conditions
Plants store glucose as starch in the leaves, plants that are kept in the light will photosynthesise and store starch so their leaves will change colour to blue-black

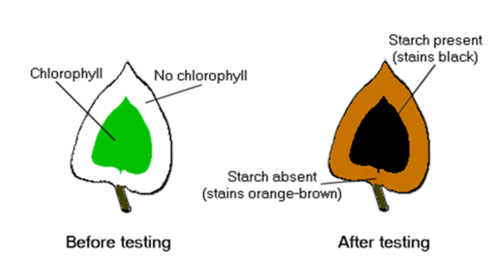
Starch results for variegated leaves
Leaves that are variegated have patches absent of chlorophyll, these regions will not cause iodine to change colour as photosynthesis cannot occur here
what is the dependent variable
The variable that is measured, in this case the presence of starch or colour of iodine test

Independent variable
The variable that is changed such as the type or source of leaf, leaves could be tested that have been kept in the light or in the dark, leaves could also be tested that are either variegated or not variegated
Control variables
The variables that are kept the same, such as the species of plant, the availability of water, temperature, soil mineral or pH content, the amount of time that leaves have been submerged in ethanol or hot water