ISP 205 Exam 2
1/42
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What will happen to the temperature of an opaque gas cloud when it shrinks?
Increase
Transit Method
Technique for discovering exoplanets by detecting the periodic dimming of a star's light as a planet passes in front of it.
Why is the sky blue?
Earth's atmosphere scatters shorter, high-frequency wavelengths of light, like blue, more than longer wavelengths, like red.
Planetary orbits in our solar system are
fairly circular and in the same plane.
The composition of the solar nebula was 98%
hydrogen and helium.
Solar Nebula
A rotating disk of gas and dust that is the origin of our solar system.
Comet
Leftover ice-rich planetesimals
Asteroid
a small rocky body orbiting the sun made of rock and metal
Meteorite
A meteor that survives the Earth’s atmosphere and strikes the ground.
Which of the following did NOT occur during the collapse of the solar nebula?
Concentrating denser materials nearer the Sun
Which lists the major steps of solar system formation in the correct order?
Collapse, condensation, accretion
How many of the planets orbit the Sun in the same direction as Earth does?
All
What is Jupiter's main ingredients?
hydrogen and helium
Are there any exceptions to the rule that planets rotate with small axis tilts and in the same direction as they orbit the Sun?
Venus and Uranus are exceptions.
True or False: Our Moon is about the same size as moons of the other terrestrial planets.
False
Doppler Effect
Change in a wave’s frequency due to relative motion between the wave's source and it’s observer.
What can the transit method tell us about a planet?
Its size
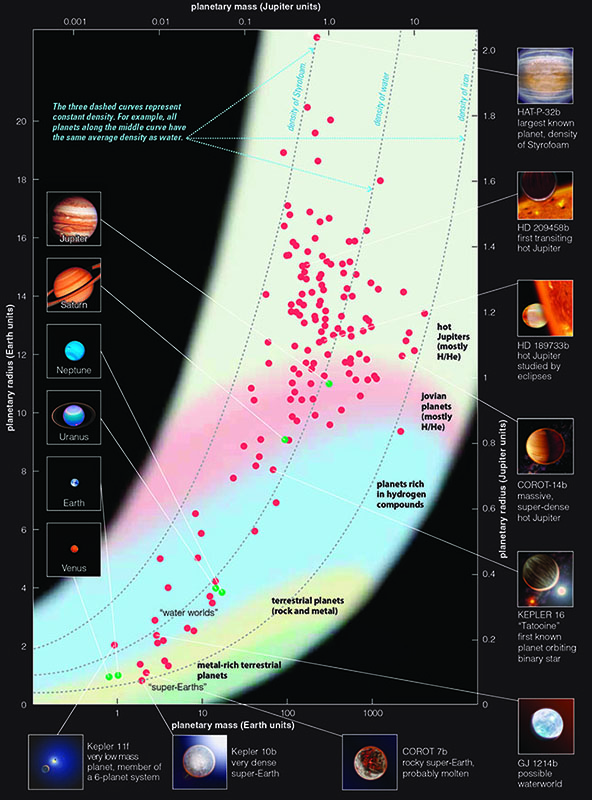
Based on the model types shown in the figure above, a planet made almost entirely of hydrogen compounds would be considered a
Water world
Planetary systems appear to be present around what percentage of stars?
Very common, 99%
What's the best explanation for the location of hot Jupiters?
They formed farther out like Jupiter but then migrated inward.
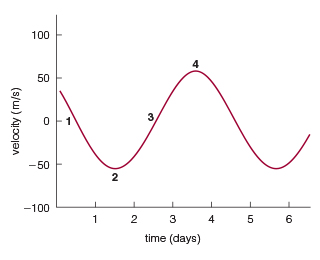
How long does it take the star and planet to complete one orbit around their center of mass?
4 days
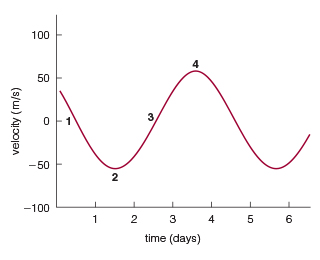
What maximum velocity does the star attain?
50 m/s
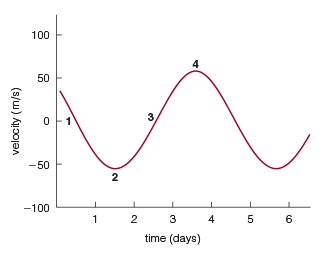
How would the plot change if the planet were more massive (but remained at the same orbital distance)?
The peaks and valleys would get significantly larger (greater positive and negative velocities) because of larger gravitational tugs.
The larger the decrease in the star's brightness as the planet transits in front of a star, _______.
The larger the size of the planet
The asteroid belt lies between the orbits of
Mars and Jupiter.
Terrestrial Planet
A planet with a solid surface and a metallic core.
Dwarf Planet
A planet that is nearly round but has not been able to clear its orbit of debris.
Jovian Planet
A planet with a gaseous surface made of hydrogen, helium, and ice.
Jupiter nudges the asteroids through the influence of
Orbital resonances.
Can an asteroid be pure metal?
Yes, it must have been the core of a shattered asteroid.
Did a large terrestrial planet ever form in the region of the asteroid belt?
No, because Jupiter prevented one from accreting.
How big an object causes a typical shooting star?
A grain of sand
About how often does a 1-kilometer object strike the Earth?
every million years
What would happen if a 1-kilometer object struck the Earth?
It would cause widespread devastation and climate change.
Which have the most elliptical and tilted orbits?
Oort cloud comets
Which are thought to have formed farthest from the Sun?
Kuiper belt comets
What does Pluto most resemble?
a comet
Which statement about asteroids, Kuiper belt and Oort cloud objects is true?
The asteroid belt and Kuiper belt orbit the Sun in nearly the same plane as the planets, but Oort cloud objects do not.
What is NOT true of all comets in our solar system?
Comets always have tails.
Which direction do a comet's dust and plasma tails point?
away from the sun
According to current evidence, Pluto is best explained as ______.
a member of the Kuiper belt