Female Pelvis and Reproductive System
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
What are the components of the female external genitalia?
Clitoris, labia majora, labia minora, vestibule, mons pubis, vaginal orifice.
What are the internal reproductive organs of the female?
Ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, cervix, vagina.
How do structures enter the pelvis from the posterior abdominal wall?
Through the greater sciatic foramen, under the piriformis muscle (e.g., sciatic nerve, pudendal nerve).

How do structures enter the pelvis from the anterior abdominal wall?
Through the inguinal canal (e.g., round ligament of uterus); via vascular and lymphatic routes.
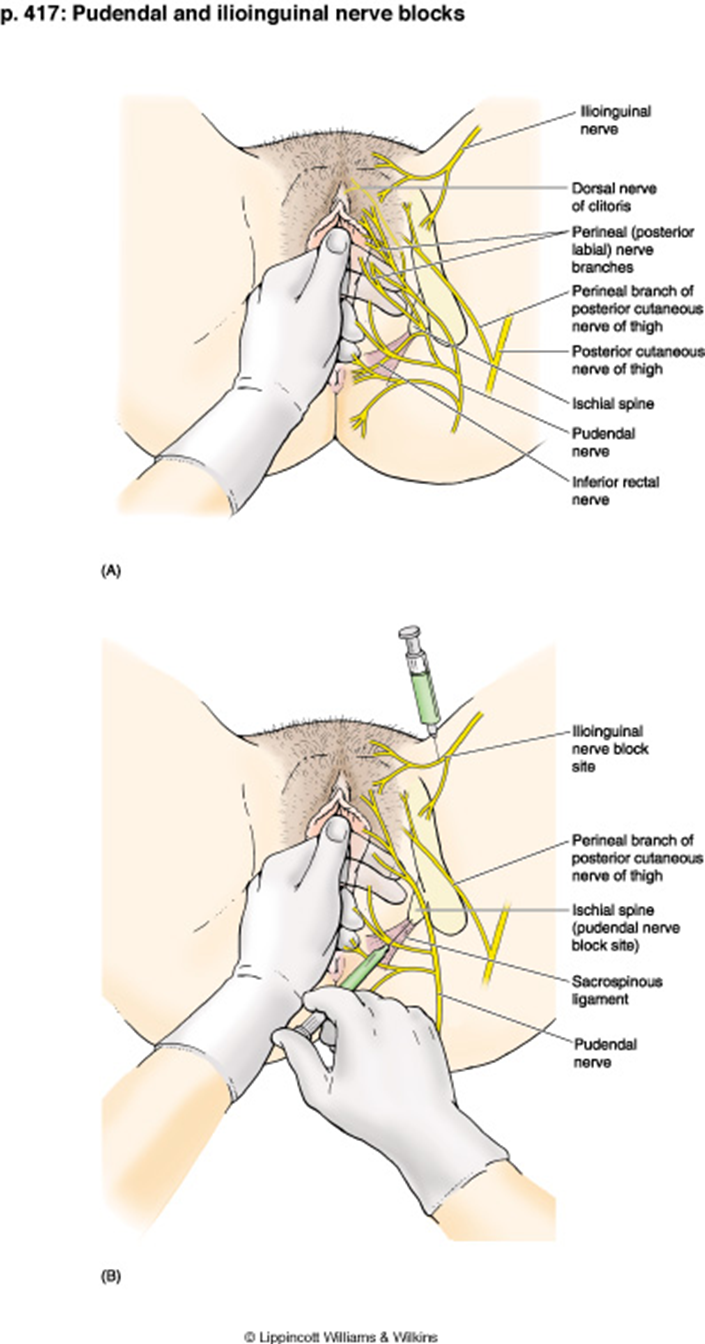
What is the course of the pudendal nerve?
Exits pelvis via greater sciatic foramen, wraps around sacrospinous ligament, re-enters via lesser sciatic foramen.
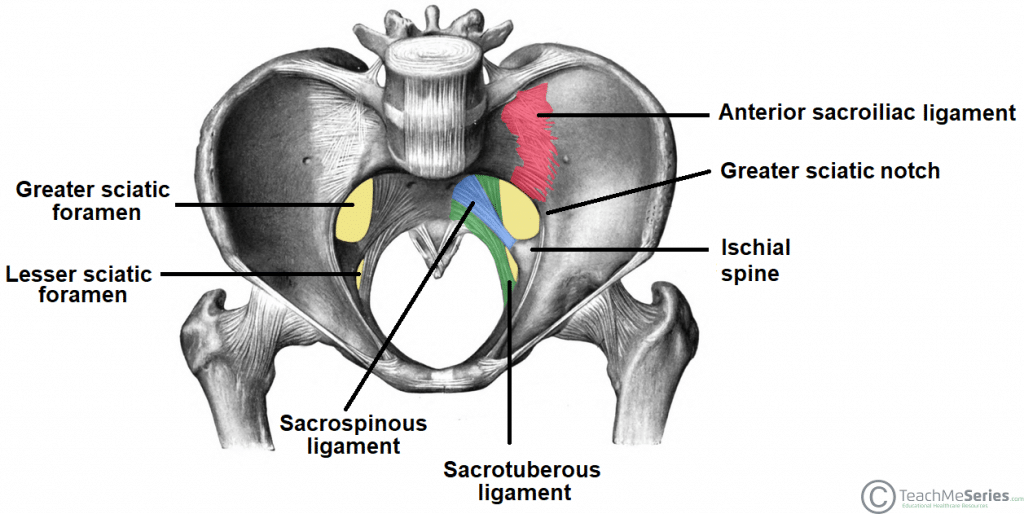

What landmark is used for pudendal nerve block?
Ischial spine palpated transvaginally; needle inserted near sacrospinous ligament.
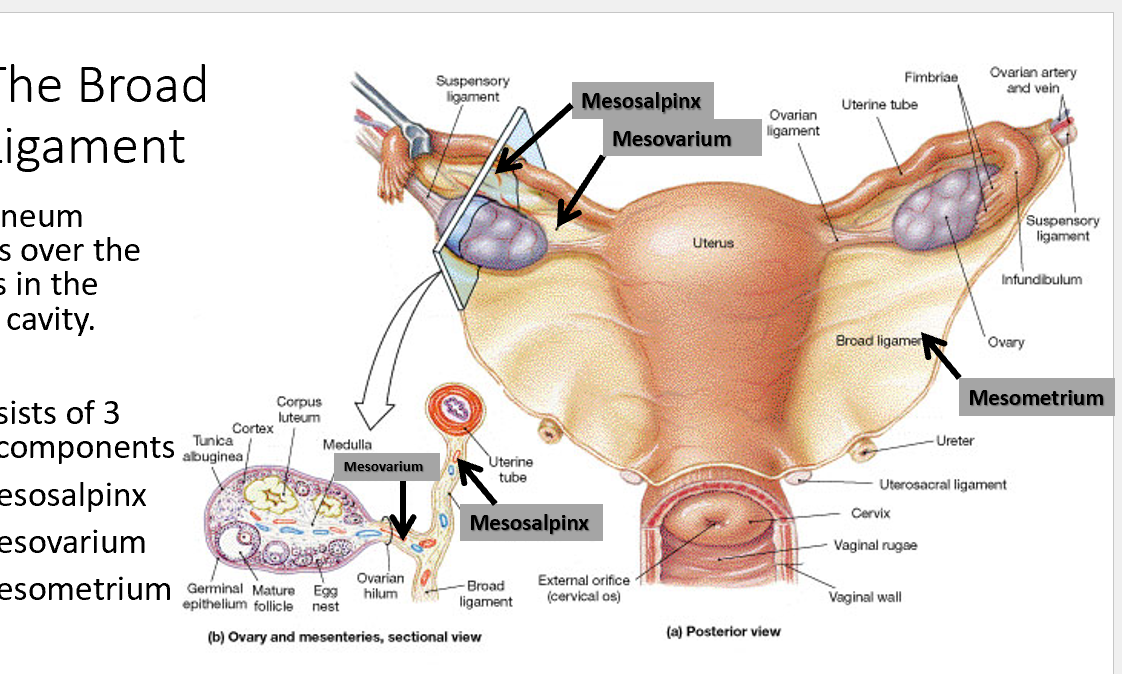
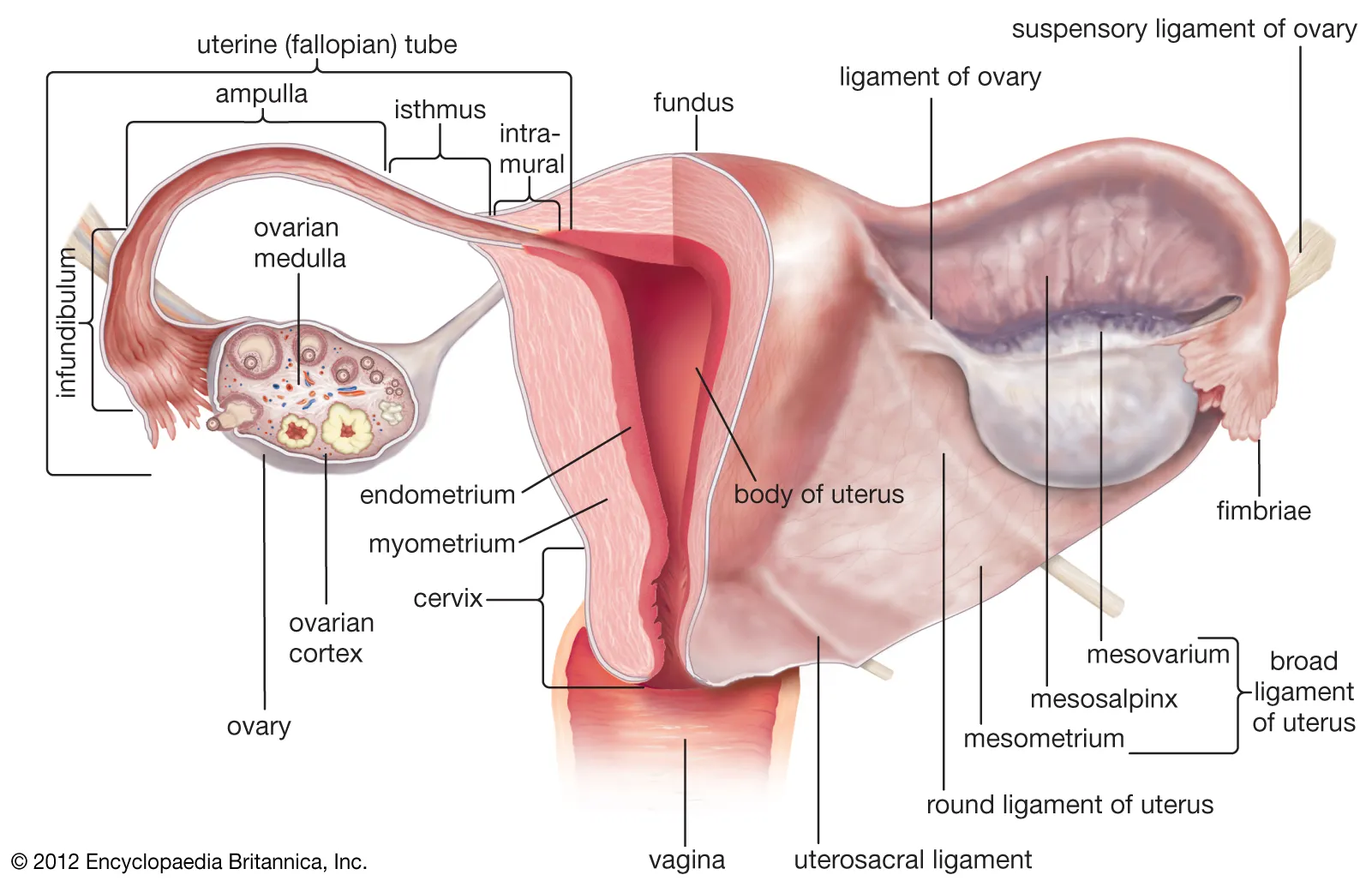
What are the folds of peritoneum in the female pelvis? (think of broad folds)
Broad ligament (mesometrium, mesosalpinx, mesovarium), suspensory ligament of ovary, round ligament.
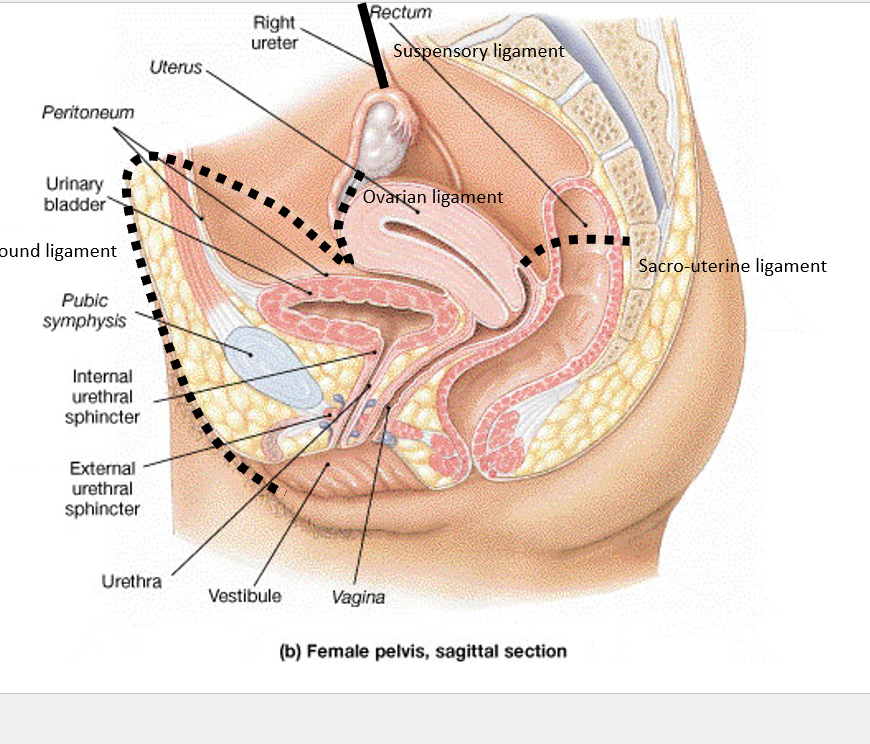

What are the peritoneal pouches in the female pelvis?
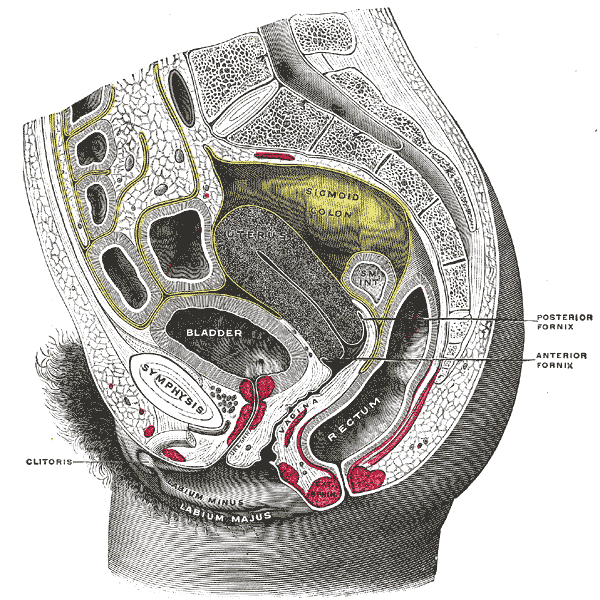
Vesicouterine pouch (between bladder and uterus), rectouterine pouch (Pouch of Douglas, between uterus and rectum).
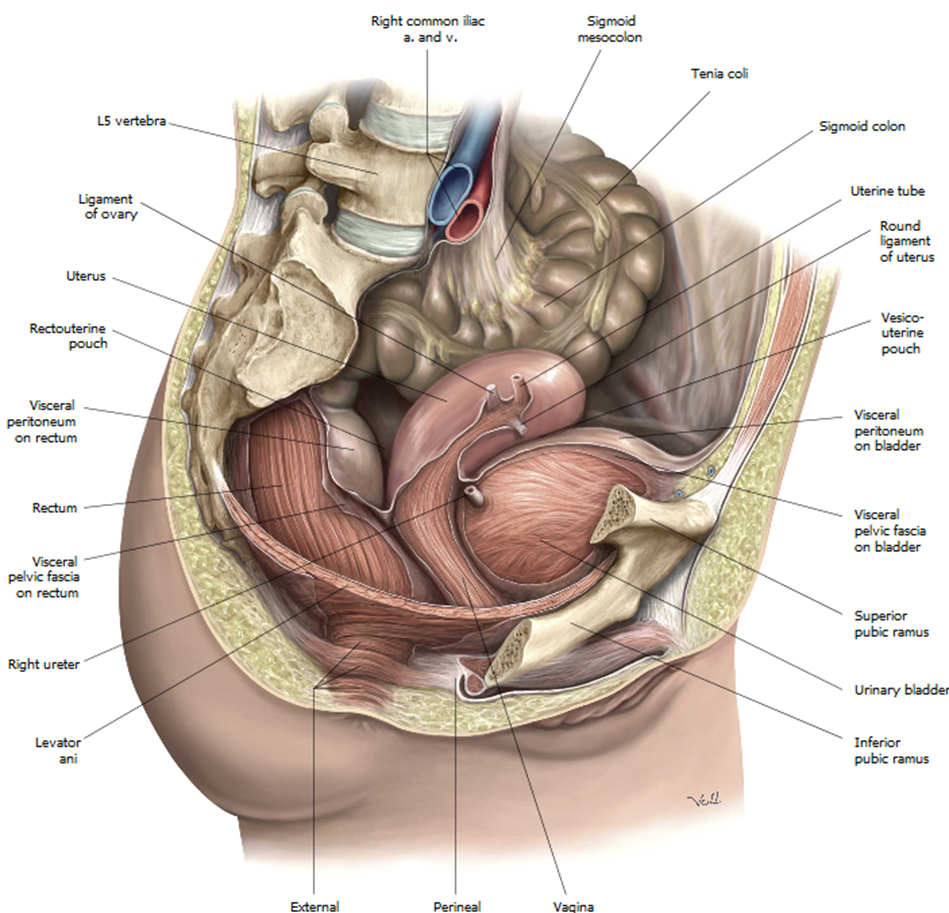
What is the clinical relevance of the rectouterine pouch?
Lowest point in female peritoneal cavity; site of fluid accumulation, accessed via posterior fornix.
What are retroperitoneal spaces in the female pelvis?
Prevesical, retrovesical, presacral spaces; contain vessels, nerves, and connective tissue.
What is the visceral relationship of the uterus?
Anterior: bladder; Posterior: rectum; Superior: loops of small intestine.
What is the visceral relationship of the ovaries?
Posterolateral to uterus; adjacent to lateral pelvic wall and ureters.
What is the pelvic diaphragm? (diaphrams need muscles)
Levator ani (puborectalis, pubococcygeus, iliococcygeus) + coccygeus; forms muscular hammock supporting pelvic organs.
What is the function of the pelvic diaphragm?
Supports pelvic viscera, maintains continence, resists intra-abdominal pressure.
What causes pelvic organ prolapse?
Weakening of pelvic diaphragm and connective tissue; leads to descent of uterus, bladder (cystocele), or rectum (rectocele).
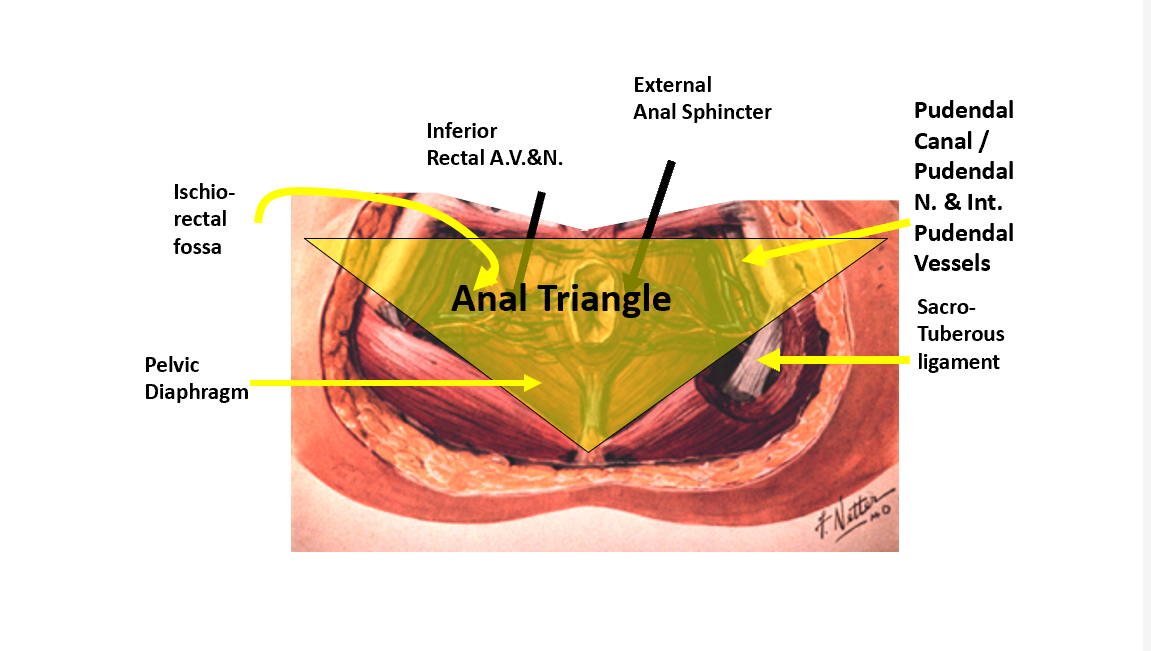
What is the urogenital triangle?
Anterior half of perineum; bounded by pubic symphysis and ischial tuberosities.
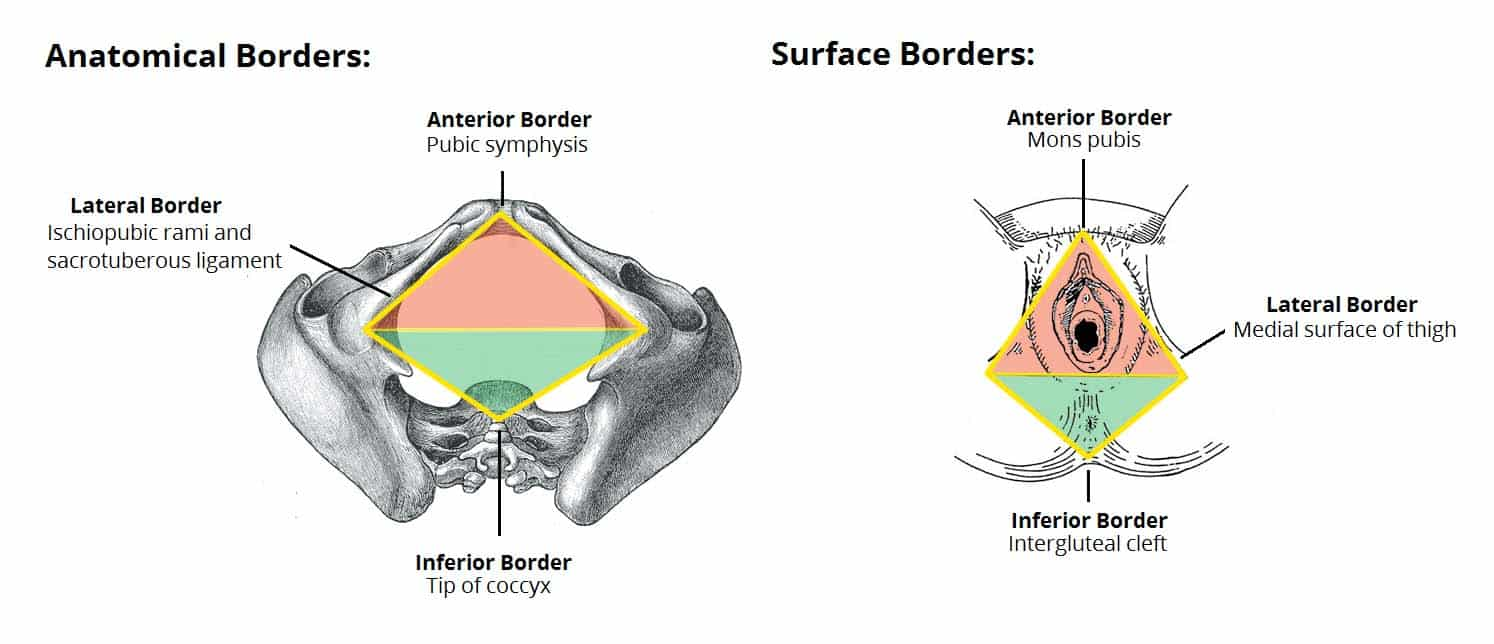

How is the urogenital triangle divided?
Perineal membrane separates it into superficial pouch (inferior) and deep pouch (superior).
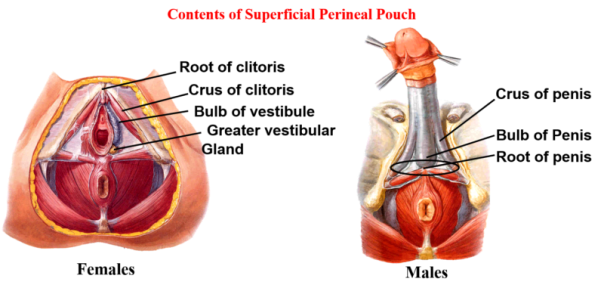
What structures are in the superficial perineal pouch?
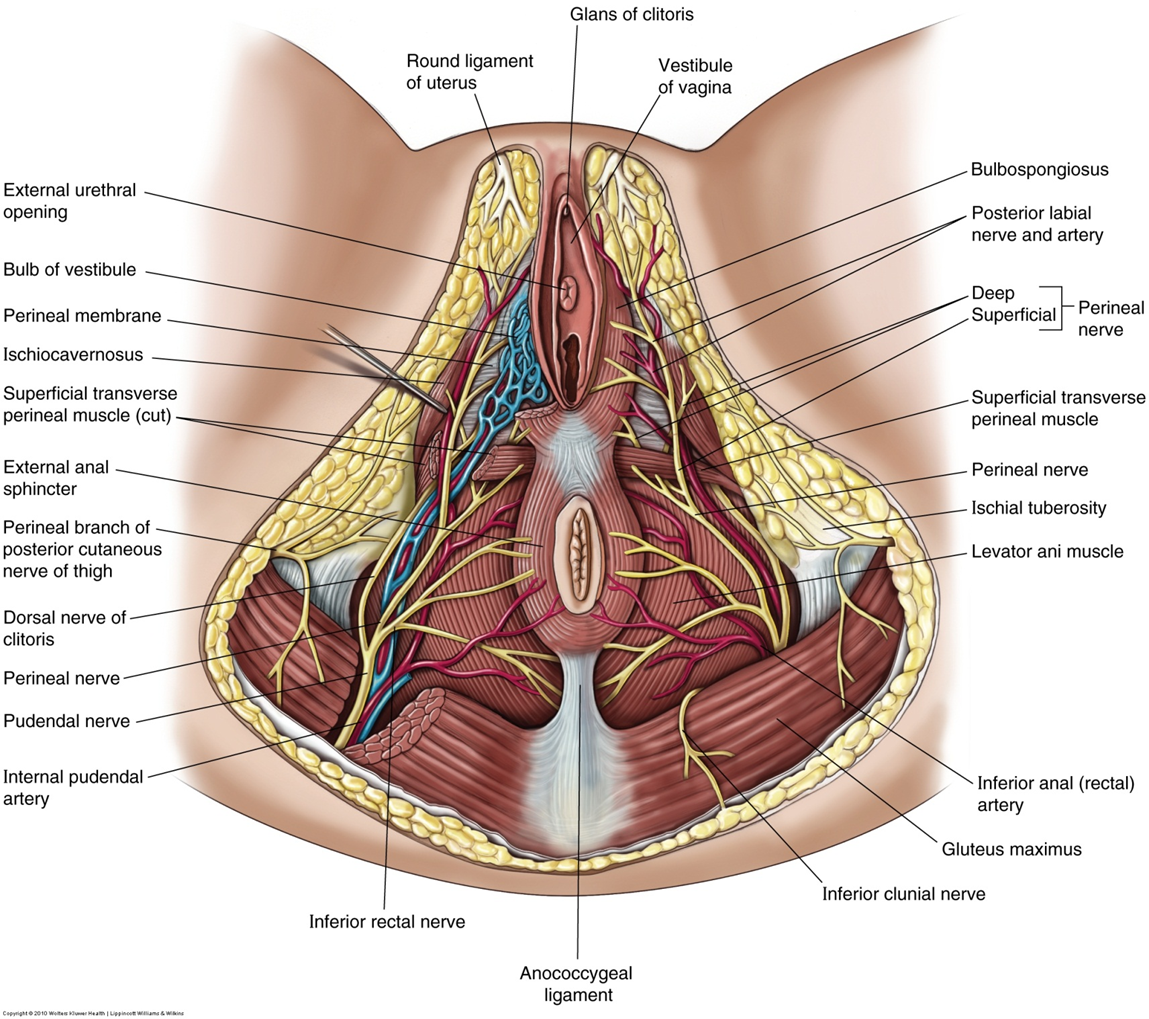
Erectile tissues (bulb of vestibule, clitoris), superficial perineal muscles, Bartholin glands.
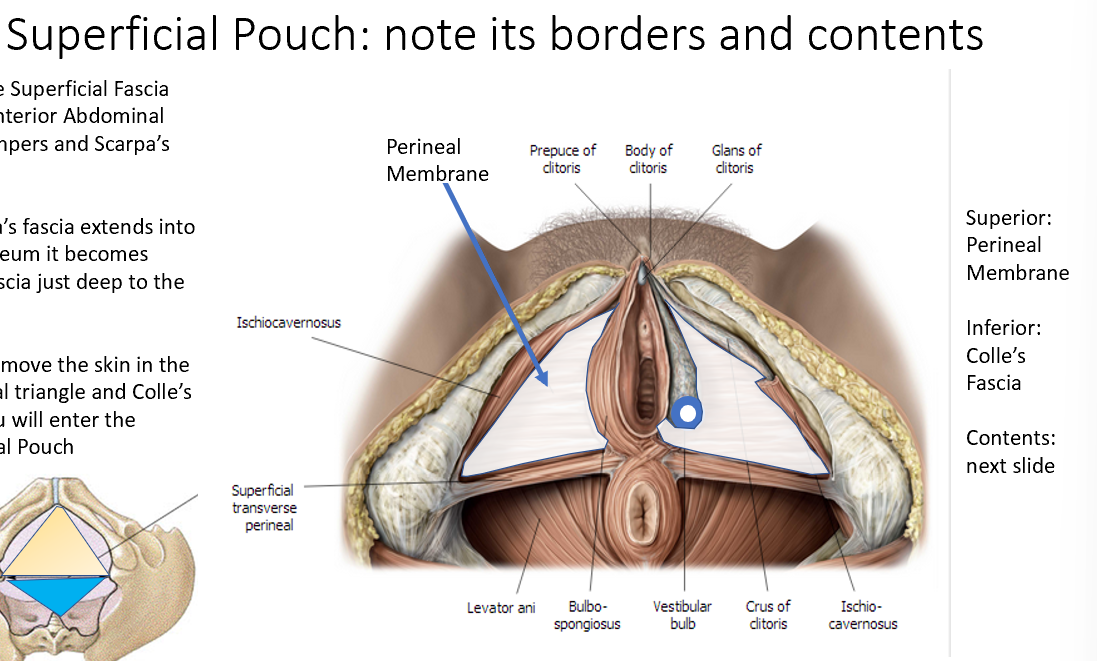

What structures are in the deep perineal pouch?
External urethral sphincter, compressor urethrae, deep transverse perineal muscle, neurovascular elements.
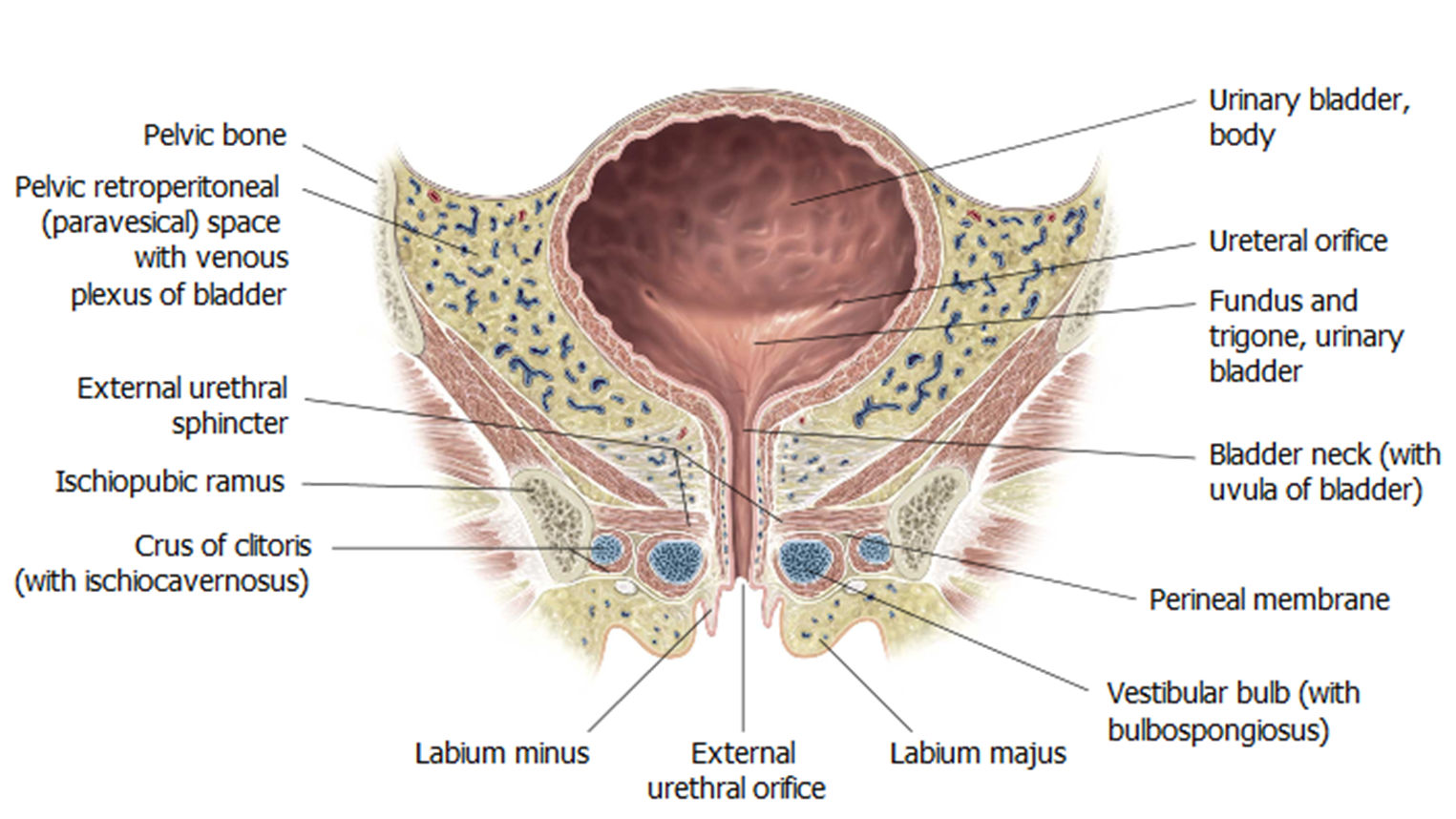
What muscles form the pelvic diaphragm? (Use my PPi’s in my pelvic diaphragm)
Levator ani group (puborectalis, pubococcygeus, iliococcygeus) and coccygeus.
What muscles are in the deep perineal pouch but not part of the pelvic diaphragm?
External urethral sphincter, deep transverse perineal muscle, compressor urethrae.
What is the main arterial supply to female pelvic organs?
Internal iliac artery and its branches: uterine, vaginal, ovarian, internal pudendal arteries.
What is the relationship between uterine artery and ureter?
Uterine artery crosses over ureter near cervix (“water under the bridge”).
Why is the uterine artery-ureter relationship clinically important?
At risk during hysterectomy; ureter injury can cause urine leakage or obstruction.
What is the blood supply to the ovaries?
Ovarian arteries from abdominal aorta; travel in suspensory ligament of ovary.
What is the venous drainage of the ovaries?
Right ovarian vein → IVC; Left ovarian vein → left renal vein.
Where does fertilization occur?
In the ampulla of the uterine tube.
What hormones sustain early pregnancy?
hCG from trophoblast maintains corpus luteum → progesterone production; later placenta produces progesterone and estrogen.
What is the role of progesterone in pregnancy?
Maintains endometrial lining, inhibits uterine contractions, supports placental development.
What is the role of estrogen in pregnancy?
Stimulates uterine growth, increases blood flow, prepares breasts for lactation.
What is the role of hCG?
Maintains corpus luteum in early pregnancy; used as marker in pregnancy tests.
What is the role of the corpus luteum?
Produces progesterone to maintain endometrium until placenta takes over hormone production.
What is the frenulum of the labia minora?
Posterior union of labia minora, also called the fourchette.
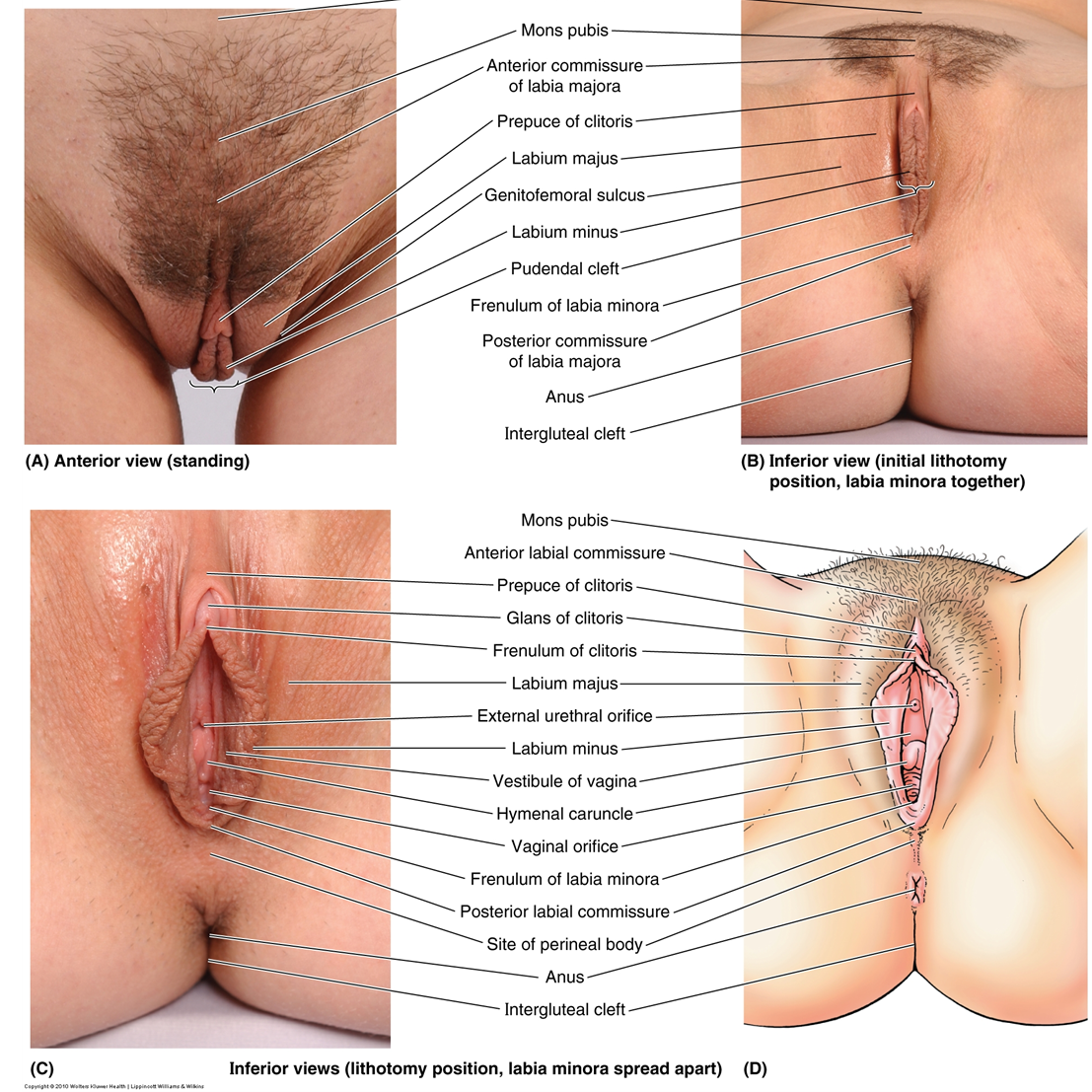
What is the glans clitoris?
Visible portion of clitoris; covered by prepuce; homologous to glans penis.
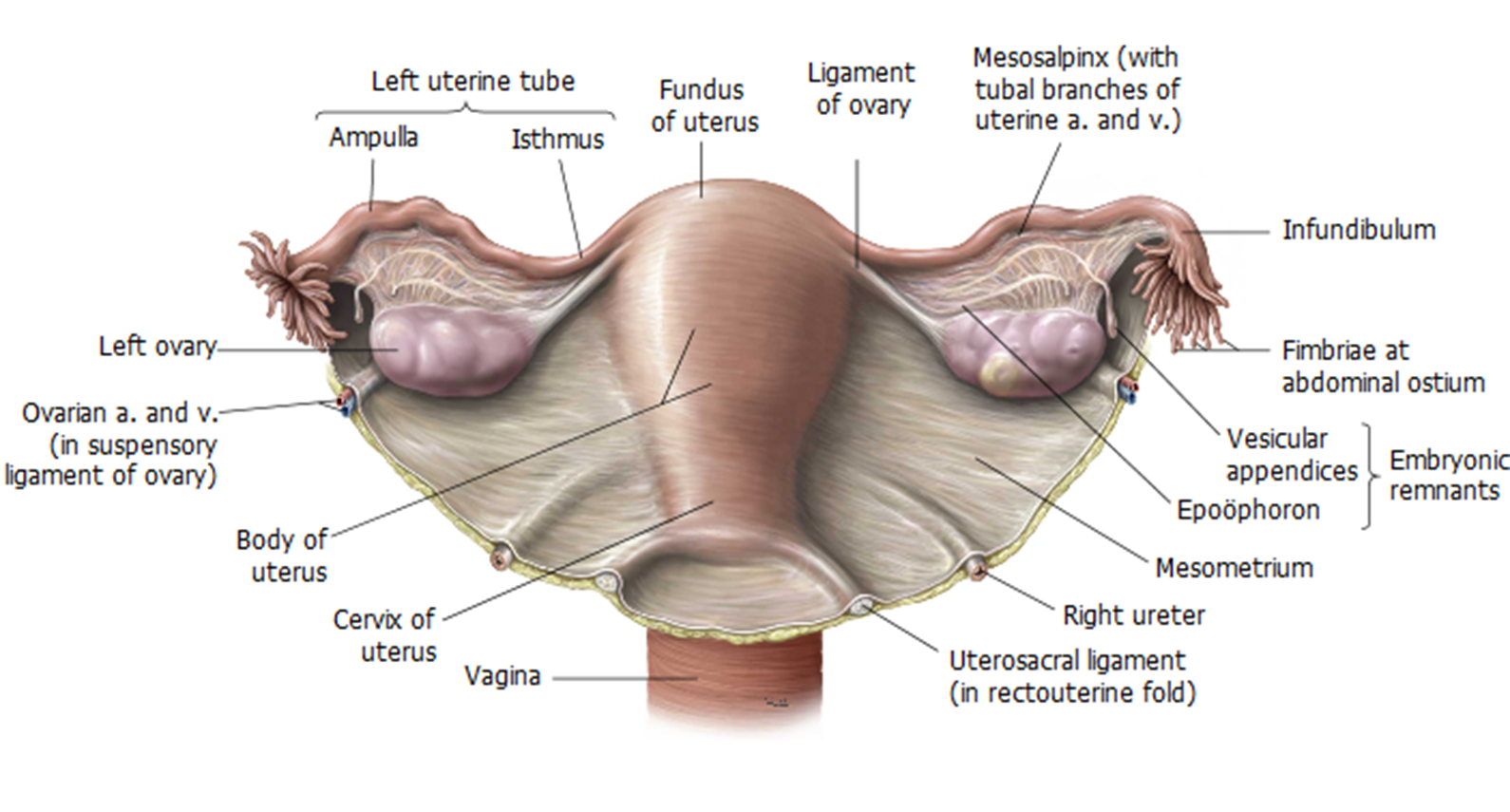
What is the uterosacral ligament?
Connects cervix to sacrum; provides posterior support to uterus.

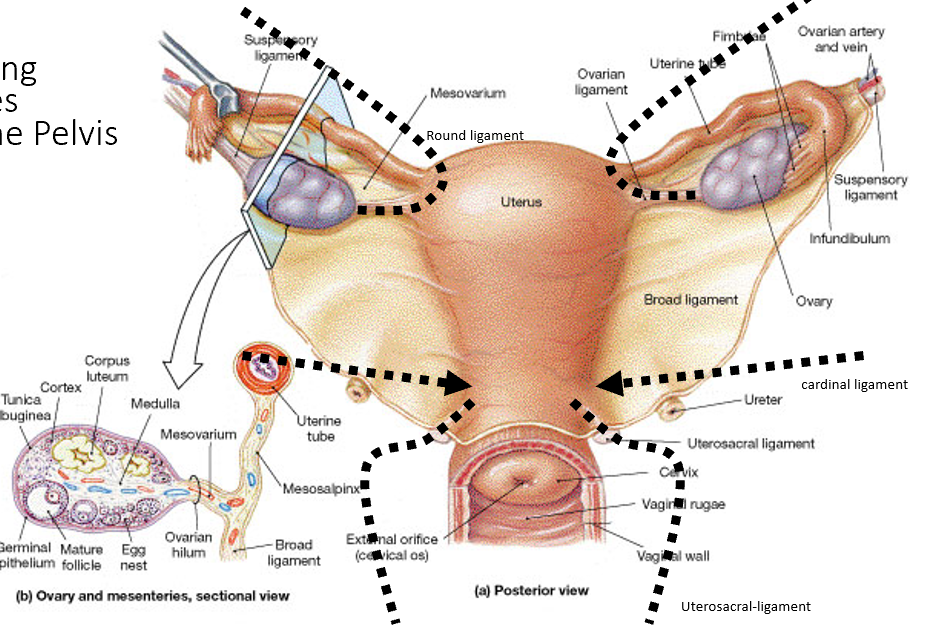
What is the relationship of the ovary to the ureter?
Ovarian vessels cross anterior to ureter in suspensory ligament; ureter lies posterior.

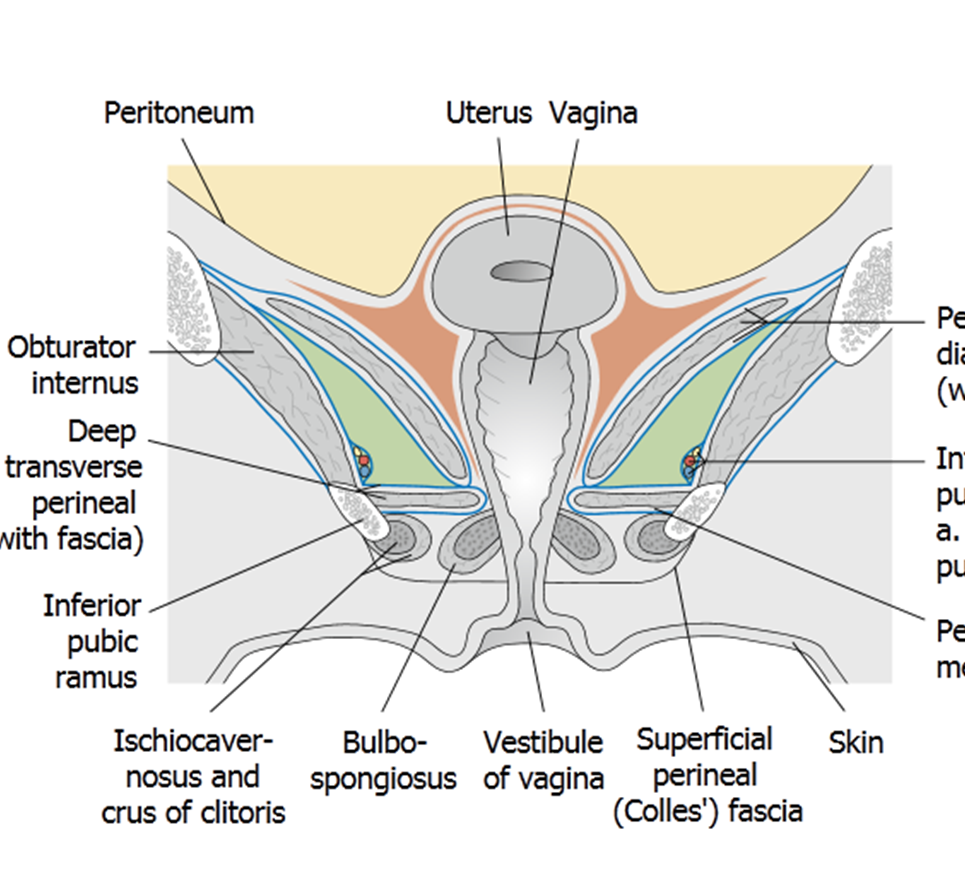
Perineal membrane. Superificial (bottom=colles fascia, roof=perineal membrane) and Deep(bottom=perineal membrane, roof=pelvic diaphragm)
Clitoris, bulbs of vestibule, Bartholin glands, superficial perineal muscles.

Endometrium (mucosa), myometrium (smooth muscle), perimetrium (serosa).

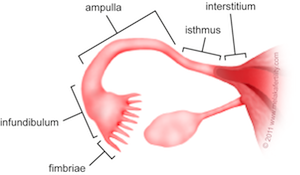
What are the segments of the uterine tube? Fun In An Island Inlet
Fimbriae, infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus, intramural/intersitium portion. FIAII Fun In A Island Inlet

Recess surrounding cervix; divided into anterior, posterior, and lateral fornices.
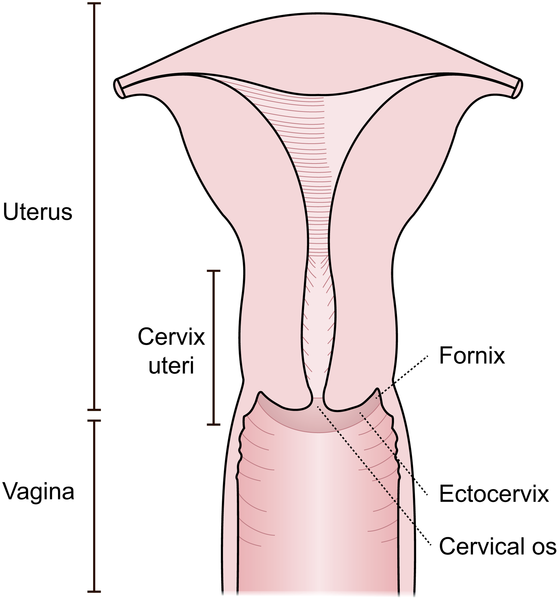

Adjacent to ureter and uterine artery; important in surgical procedures.

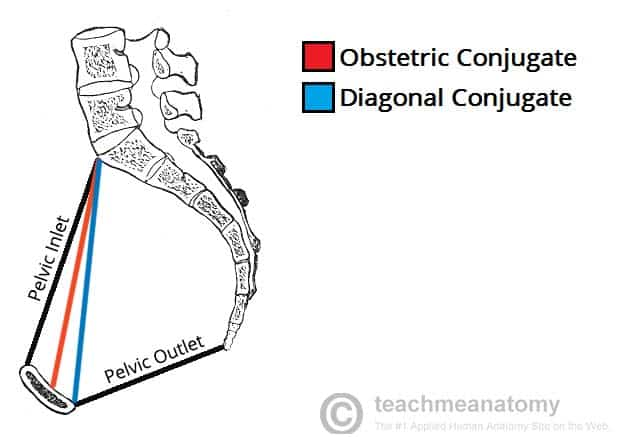
Distance from sacral promontory to pubic symphysis; narrowest fixed AP diameter of pelvic inlet.