Microscopy of clinical specimens
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Purpose: Primarily used for rapid microscopic examination of
fresh specimens such as vaginal secretions to detect
budding yeast cells, hyphae, and pseudohyphae.
Saline Wet Mount
Application: Useful in candidiasis diagnosis.
Saline Wet Mount
Limitations: Does not kill organisms; structures may move,
and stain contrast is minimal.
Saline Wet Mount
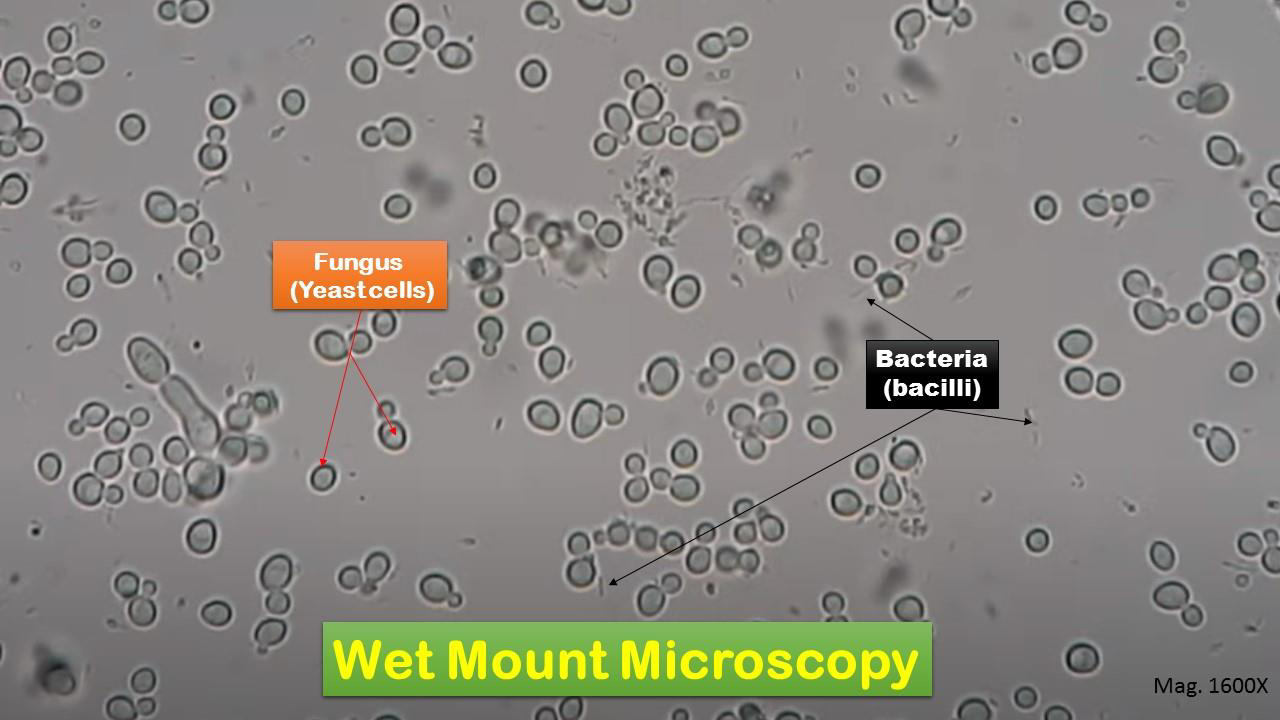
Saline Wet Mount
Purpose: Ideal for staining and mounting cultured fungi, especially filamentous molds.
Lactophenol Cotton Blue (LPCB)
Components and Functions: Lactophenol Cotton Blue (LPCB)
•Phenol:
•Lacid:
•Cotton blue:
Kills organisms.
Preserves and clears fungal elements.
Stains chitin in fungal cell walls.
Application: Tease mounts and Scotch tape preparations are commonly made using LPCB to visualize structural features like
conidia, conidiophores, and hyphae.
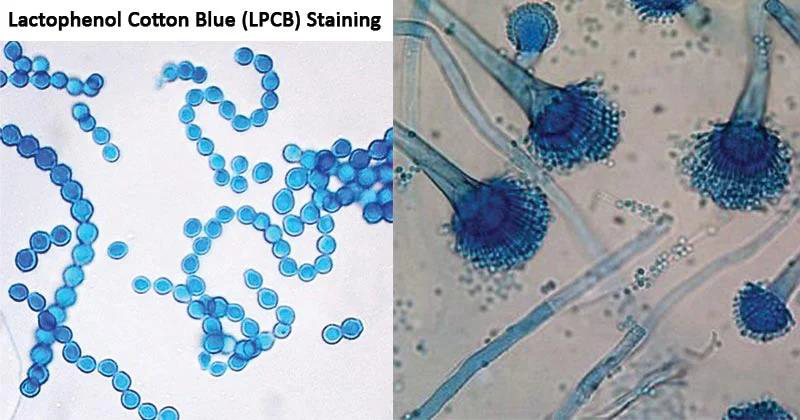
LPCB
Purpose: Used for direct detection of fungal elements in keratinized tissue like skin, hair, and nails
Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) Preparation
Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) Preparation IS ENHANCED BY
Addition of Calcofluor white or Parker ink improves visualization
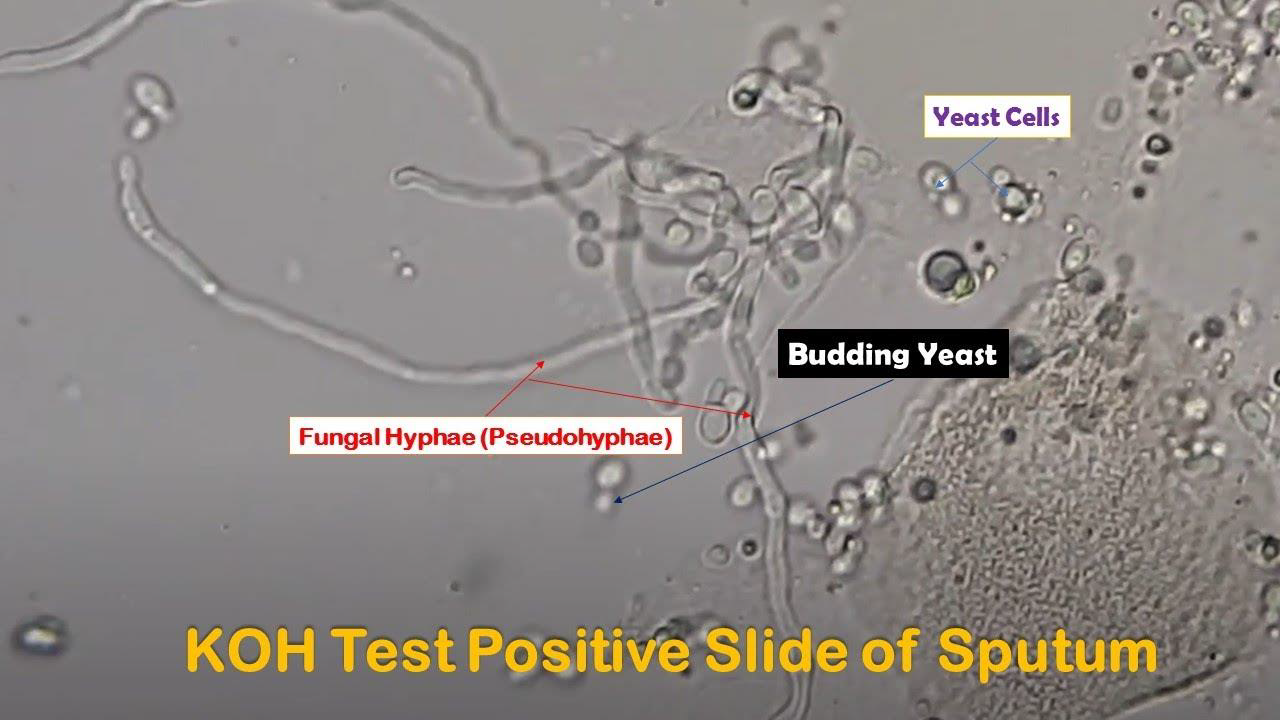
KOH
Purpose: Detects yeasts and pseudohyphae, particularly Candida spp
Use: Especially helpful in blood, sputum, and CSF samples for yeast detection.
Gram Stain
Appearance: Fungi generally appear
Gram-positive
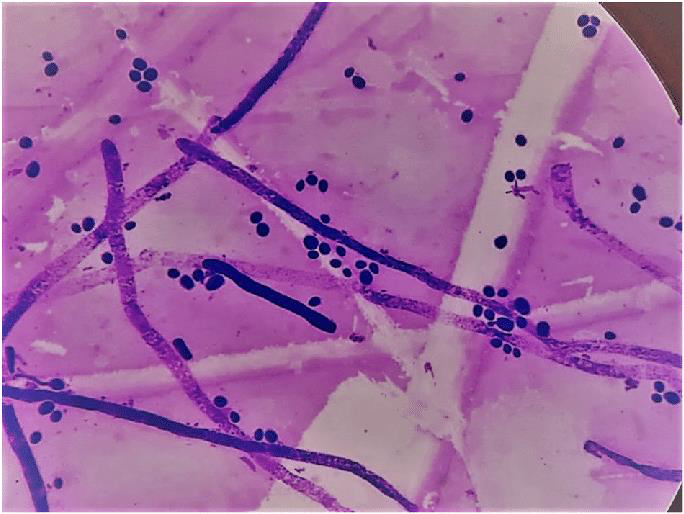
Gram Staining
Purpose: Differentiates partially acid-fast organisms like Nocardia spp. from other filamentous bacteria and fungi.
Acid-Fast Stain
Acid-Fast Stain Modified by Kinyoun stain is called
Cold method for partially acid-fast organisms.
A fluorescent technique that enhances detection sensitivity.
Auramine-rhodamine stain:
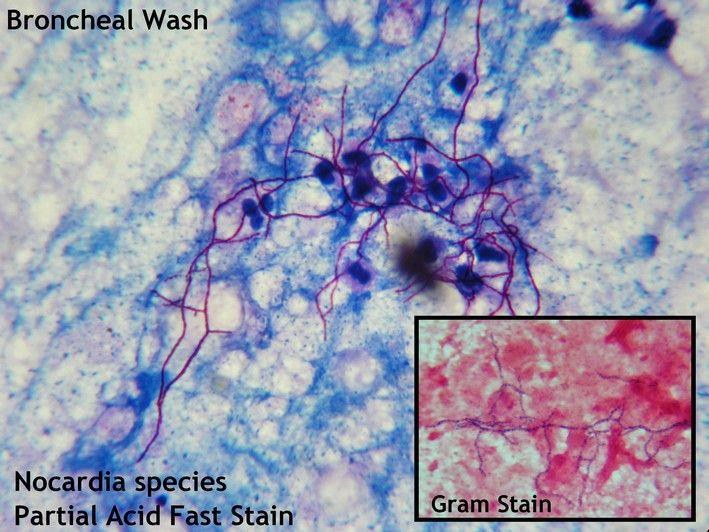
Acid fast stain
Purpose: Demonstrates the polysaccharide capsule of Cryptococcus neoformans in CSF
India Ink (Negative Stain)
India Ink (Negative Stain) is largely replaced by
lateral flow antigen tests due to higher sensitivity.
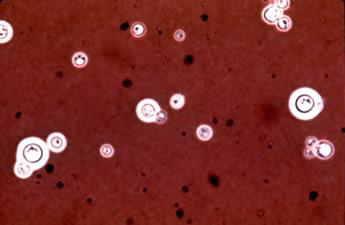
India Ink
Purpose: Stains polysaccharides in fungal cell walls magenta.
Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) Stain
Application: Useful in tissue sections for invasive mycoses
Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) Stain
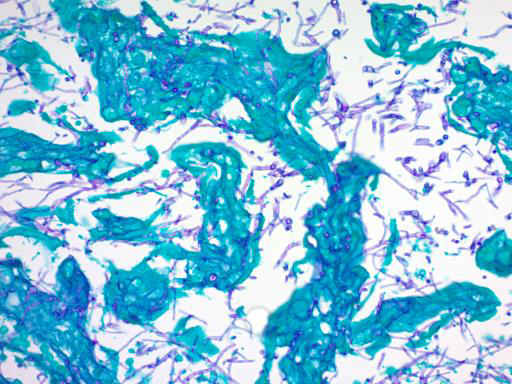
PAS
Purpose: Fluorescent dye that binds to cellulose and chitin in fungal cell walls
Calcofluor White Stain
In Calcofluor White Stain it is enhanced by
KOH
Higher than KOH or Gram stain for detecting fungal elements.
Calcofluor White Stain
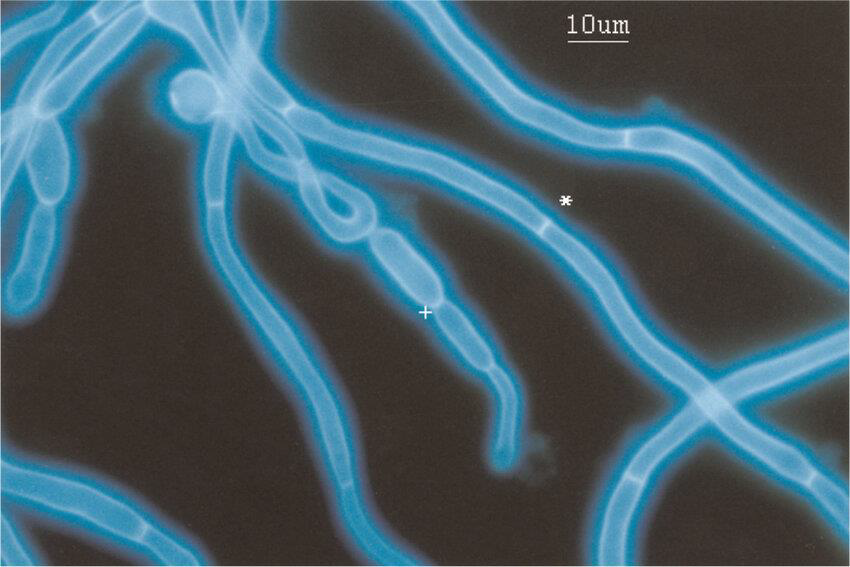
Calcofluor White Stain