AP 2: Cardiovascular Systems
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
4-5 Liters
Average blood volume in an adult female
5-6 liters
Average blood volume in adult male
Oxygenated Blood
Blood that is bright red in color
De-oxygenated Blood
Blood that is a dull brick red color
neutrophil
most numerous leukocyte in the blood stream, important for immune response, primarily responsible for attacking bacteria and fungi.
Granulocytes
type of white blood cell that has small granules, neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils.
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
what are the 3 types of granulocytes in the blood?
eosinophil, basophil, monocytes
Name the 3 phagocytic leukocytes
lymphocytes & monocytes
Name the 2 agranulocytes
Megakarocyte
precursor cell of platelets
Platelets
cell fragments
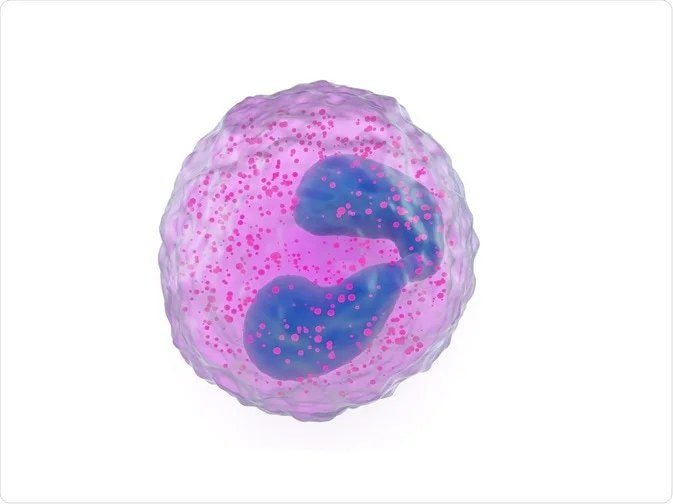
eosinophil
What cells are involved in destroying parasitic worms
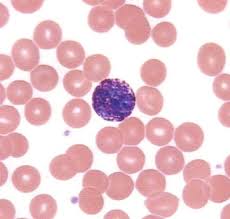
Basophils
What cells release histamines and promote inflammation
Lymphocytes
What cells produce antibodies?
Red Blood Cells
What cells transport oxygen
Plasma
primarily water, noncellular; the fluid matrix of blood
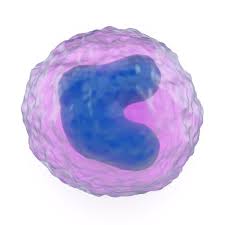
Monocyte
What cell exits a blood vessel to develop into a macrophage?
Formed Elements
The cells & cell fragments that make up blood; these include erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets
120 Days
What is the average life span of a red blood cell?
Anucleate
No nucleus, cell is unable to repair itself, therefore it must recycle or die after a certain time period
anemia
condition of too few RBC’s or of RBC”s with hemoglobin deficiencies
leukocytosis
abnormal increase in the number of WBC’s
Leukopenia
abnormal decrease in the number of WBC’s
polycythemia
abnormal increase in the number of RBC’s
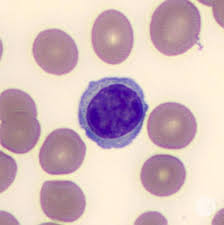
Lymphocyte
Monocyte
Basophil
Eosinophil
Transports gases, nutrients, and wastes
Regulation of PH & Ion Balances
Restriction of fluid loss (clotting)
Defense against toxins and pathogens
Maintaining body temperature
Name the 5 functions of blood
Kidneys: excreted through urine
Hemolysis: cell death
Liver: broken down & sent out through feces, iron recycled
What are the 3 places red blood cells go after their life cycle?
Decreased hematocrit
Blood clots (thrombus)
Pooling of blood in legs (varicose veins)
What are 3 age related changes of blood?
Less elastic arteries
Calcium deposits on vessel walls (blockages causing infarction or stroke)
Thrombi can form (plaques)
What are 3 age-related changes of blood vessels?
Right ventricle, pulmonary trunk, arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins, left atrium
What is the order of the pulmonary circuit?
Left ventricle, aorta, arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins, vena cava, right atrium
What is the order for the systemic circuit?
Venoconstriction
contraction of smooth muscle in vein
Arteries have the heart as their pump
Why are there valves in veins and not arteries?
Capillary bed
network of capillaries, supplied by more than 1 artery
valves
folds of tunica intima, ensures one way flow to the heart
Malfunctioning of valves
What causes pooling of blood in different locations?
varicose veins & hemmorids
Give 2 examples of valve malfunctioning:
Continuous capillary
type of capillary that prevents loss of blood cells & plasma proteins, in all tissues by epithelium & cartilage
Fenestrated capillary
type of capillary that contains windows or pores to penetrate endothelial lining
kidney filtration, absorption of interstitial tract, capillaries of hypothalamus & pituitary gland
Name locations where fenestrated capillaries can be found:
Sinusoids
type of fenestrated capillary, flattened & irregularly shaped, gaps between endothelial cells that permit water & other solutes; occurs in the liver, spleen, endocrine organs
Arterioles
smaller vessels that have poorly defined tunica externa and a small tunica media, smallest branches of arteries
venules
collect blood from the capillaries
Capillaries
these vessel walls allow change between blood & interstitial fluids, smallest blood vessel
8 micrometers
what is the average diameter of a capillary?
tunica intima, tunica media, tunica externa
What are the 3 structures of vessel walls?
tunica intima
structure of vessel wall with endothelium & internal elastic to increase size if needed
Tunica media
structure of vessel wall with a muscle layer and elastic
Tunica externa
structure of a vessel wall that is thick & strong, anchors vessels & collagen fibers
side by side
How do arteries & veins run?
Arteries have thicker walls for a higher blood pressure
Do veins or arteries have thicker walls?
artery lumen
lumen that is small & round
vein lumen
lumen that is large & flat
sickle cell anemia
red blood cells are oddly shaped, mainly affects the african american population
myleoid leukemia
disease stemming from having abnormal white blood cells
pulmonary circuit
carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs
systemic circuit
main path, carries oxygenated blood to lower & upper body
surface antigens
cell surface proteins, identify cells to the immune system
hemostasis: vascular spasm, constriction to slow blood loss
platelet phase: stick to edges to create a plug, stops blood loss
Coagulation: forms a mesh, traps RBCs & platelets, forms a clot
what are the 3 steps to site of injury?
release clotting chemicals
temporarily patch walls
reduce size of a break in a vessel wall
Name the 3 functions of platelets
Bicuspid & Tricuspid
Which valves are the AV Valves?
Aortic & pulmonary valves
What valves are the semilunar valves?
AV Valves
Open, blood pressure from contracting atria pushes cusps apart
Semilunar valves
closed, little pressure from ventricles, blood pressure from pulmonary & systemic circuit, keep both valves closed
Come from the sound of closing SV and semilunar valves closing with blooding hitting against them
Where do the sounds of the heart beats come from?
heart rate x stroke volume
What is the equation for cardiac output?
EKG
senses depolarization of the cardiac cells as they receive the signal to contract
SA Node
pacemaker, can be increased/decreased but no brain control, sends signal to AV valves across atrias
body temp/hormones, exercise, nervous system
what 3 factors affect the heart rate?
AV valves
the tricuspid and mitral valves are which type of valve
Semilunar valves
which types of valves are the pulmonary & aortic
systole
contraction
diastole
relaxation
Great cardiac vein
drains blood from the area of the anterior intraventricular artery into coronary sinus
anterior cardiac vein
empties into Right atrium
Posterior cardiac, middle & small cardiac veins
empty into great cardiac vein
Atria systole, ventricle diastole
Av valves open (blood into ventricles), atria diastole
Av valves close “lubb”, ventricle early systole
ventricles fully systole, semilunar valves open (blood goes out)
Semilunar valves close “dubb”, ventricles diastole, atria diastole
Explain the cardiac cycle
to produce cardiac output
What is the main function of blood?
It slows the heart rate
How does the parasympathetic system affect the heart rate?
It quickens the heart rate
How does the sympathetic system affect the heart rate?
Cardiac cycle
period between the start of 1 heartbeat and the beginning of the next
coronary sulcus
border between atria & ventricles
Left ventricle
Aorta
Coronary arteries (L & R)
Right Side:
right atrium, posterior ventricles, nodes
marginal arteries, Posterior interventricular artery
Left side:
Left atrium, anterior ventricles
Circumflex artery, anterior interventricular artery
Arterioles
Capillaries (02 & CO2)
Venules
Small cardiac vein
Medium cardiac vein
Anterior cardiac vein, right atrium
Great cardiac vein, coronary sinus, right atrium
Explain the steps of the coronary circuit: