BTEC Applied Science - Unit 1 - Physics
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
periodic time
the time taken (in seconds) for one complete cycle of a wave, vibration, or oscillation
T = 1/f
time period, T (in seconds) and frequency, f (in hertz)
wave speed
the distance in metres (m) travelled by a wave in one second (s)
wavelength
the distance (in metres) between two nearest corresponding points on a wave, e.g. the distance between two peaks (crests)
frequency
the number of waves produced in one second or the number of waves that pass a point each second
amplitude
the maximum displacement of a wave from its undisturbed position
oscillation
a regular repetitive motion, e.g. a weight on a spring bouncing up and down, or a pendulum swinging backwards and forwards
transverse
a wave in which the direction of oscillations is perpendicular (at right angles) to the direction of the wave
longitudinal
a wave in which the direction of oscillations is parallel to the direction of the wave
displacement
the oscillating distance of a point on a wave from its undisturbed position
coherence
two or more sources of waves that have the same frequency and are in phase or have a constant phase difference
path difference
the difference between the distances that two waves have travelled when they meet at a point (usually measured as a multiple of wavelengths)
phase difference
the amount by which one wave leads or lags (falls behind) another wave (usually measured in degrees, where 360⁰ corresponds to one full wave cycle)
in phase
when two waves have zero phase difference
antiphase (completely out of phase)
when two waves have a phase difference of 180⁰ (half a wave cycle)
superposition
when two or more waves combine; their displacements are added together (displacements can cancel each other out)
constructive interference
when the superposition of two waves cause the displacement to increase (greater amplitude)
destructive interference
when the superposition of two waves cause the displacement to decrease (smaller amplitude, even zero)
diffraction grating
an optical device that has a periodic structure of many slits which splits and diffracts light into several beams. Different frequencies (wavelengths) of light diffract by different amounts
(atomic) emission spectra
the range of frequencies of light emitted by an element because of electrons moving between energy levels within atoms
identifying gases
each element has a unique emission spectra and so by analysing the light given off all the elements can be identified
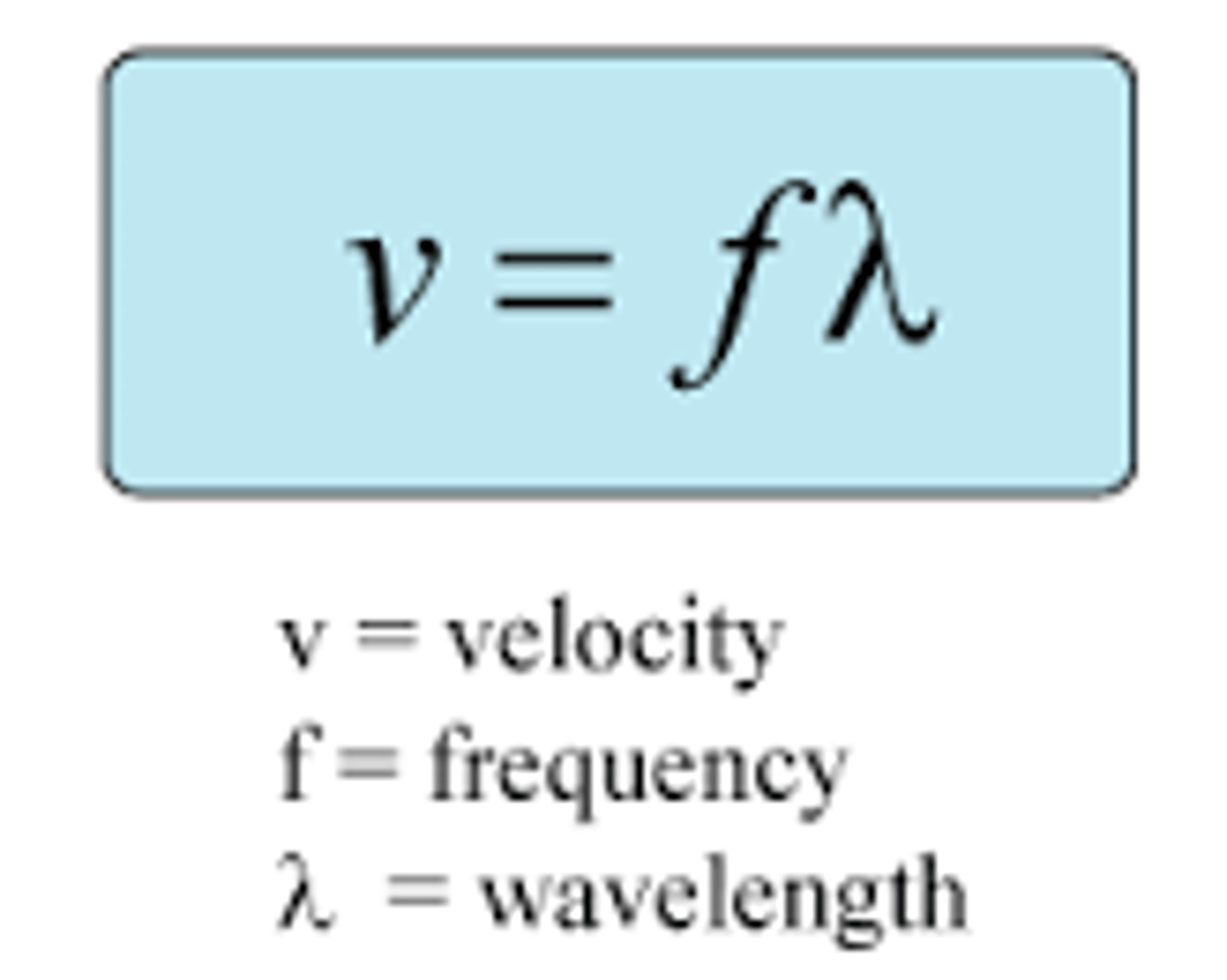
wave equation
v is the wave speed (velocity) in metres per second (m/s), f is frequency in hertz (Hz), and λ is wavelength in metres (m)
stationary (standing) wave
the superposition of a wave and its reflection to form a steady interference pattern of nodes and antinodes
node
points on a stationary wave with zero amplitude (two nodes are half a wavelength apart)
antinode
points on a stationary wave with maximum amplitude (two antinodes are half a wavelength apart)
resonance
when a system is periodically forced at a frequency that causes a massive increase in amplitude (e.g. when you push someone on a swing)
speed of wave on a string
v is the wave speed (velocity) in metres per second (m/s), T is the tension in the string in newtons (N), and 𝜇 is the mass per unit length of the string in kilograms per metre (kg/m)
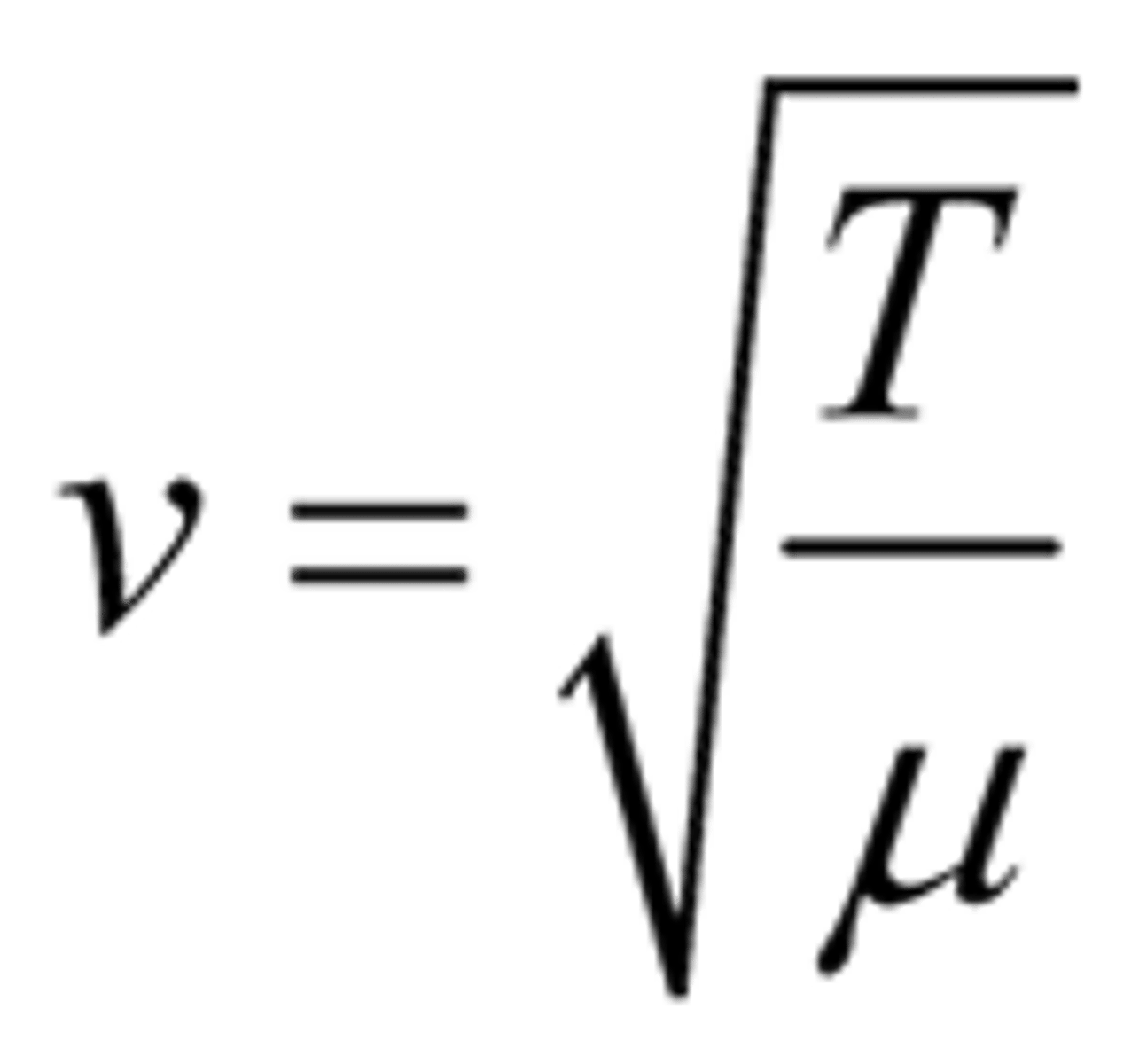
refraction
the change in direction of light (a wave) when there is a change of speed as it crosses a boundary between different media (e.g. passing from air into glass)
refractive index (of a medium)
the ratio of speed of light in a vacuum, c, to the speed of light in the medium, v. (c/v)
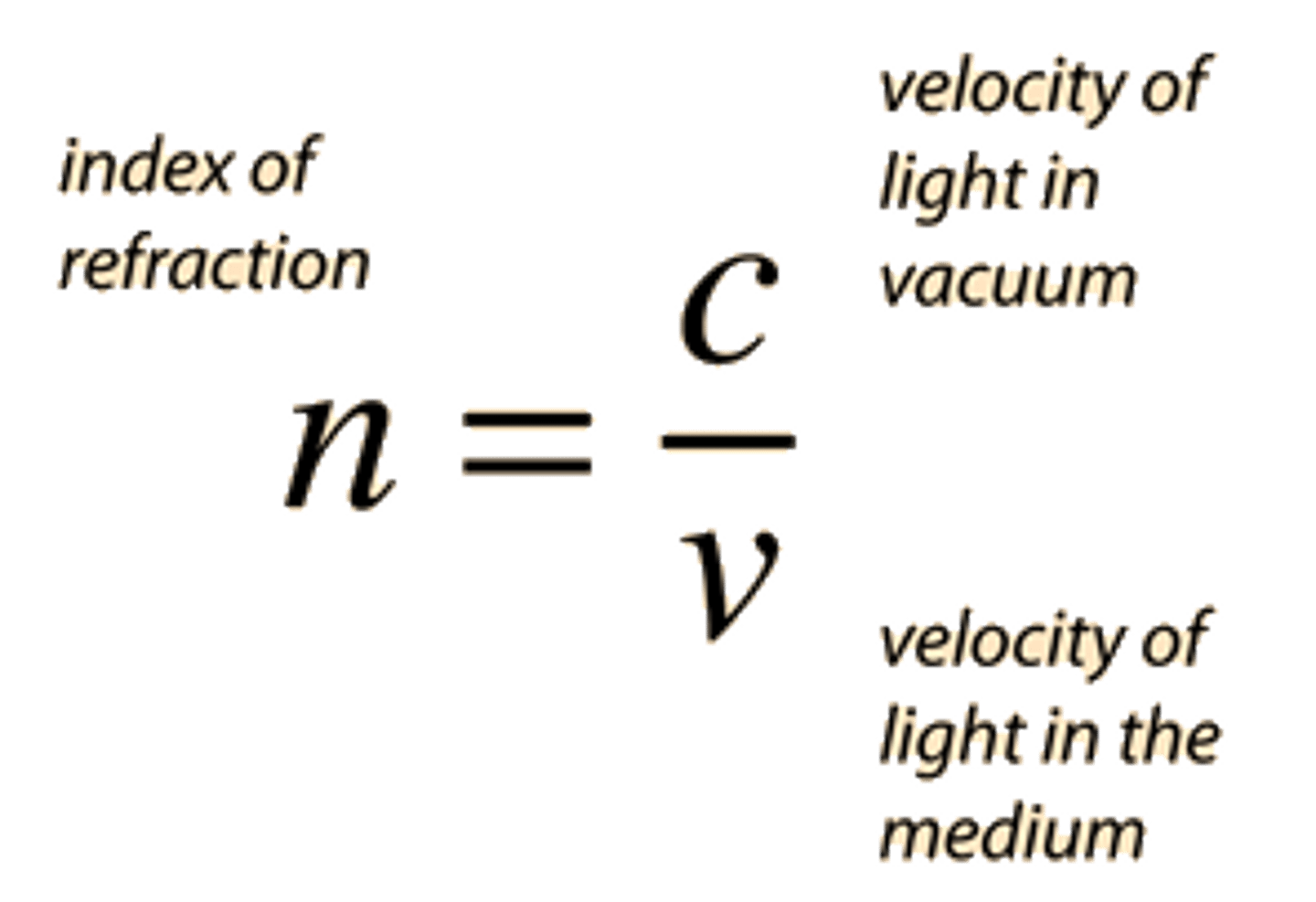
total internal reflection
when light reflects within a medium (of greater refractive index) instead of refracting across the boundary into another medium (of lower refractive index)
critical angle
the angle of incidence that causes an angle of refraction of 90⁰, total internal reflection occurs when the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle
optical fibre
thin fibre of glass that relies upon total internal reflection so light rays can pass down the length of it
endoscope
an optical device made of bundles of optical fibres. Light is sent into a hard to see place (usually the body) it then reflects and returns via a second bundle of fibres
analogue signal
a signal that continuously varies in both amplitude and frequency
digital signal
a signal that is made up of a stream of binary data in the form of zeros and ones
analogue-to-digital conversion
analogue signals are sampled (values taken) continuously at fixed intervals of time. The values are then converted into binary values (1s and 0s) so they can be sent as a digital signal
electromagnetic spectrum
there are seven types of electromagnetic waves, each with a range of frequencies, that make up a spectrum; radio-waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma rays
speed of light (in a vacuum)
all electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed of light in a vacuum, 3x10⁸ m/s
inverse square law
k is a constant (does not change) for a particular source of a wave, the intensity of a wave will reduce in line with the square of the distance, r. (E.g. if the distance doubles then the intensity will reduce by a factor of 4)
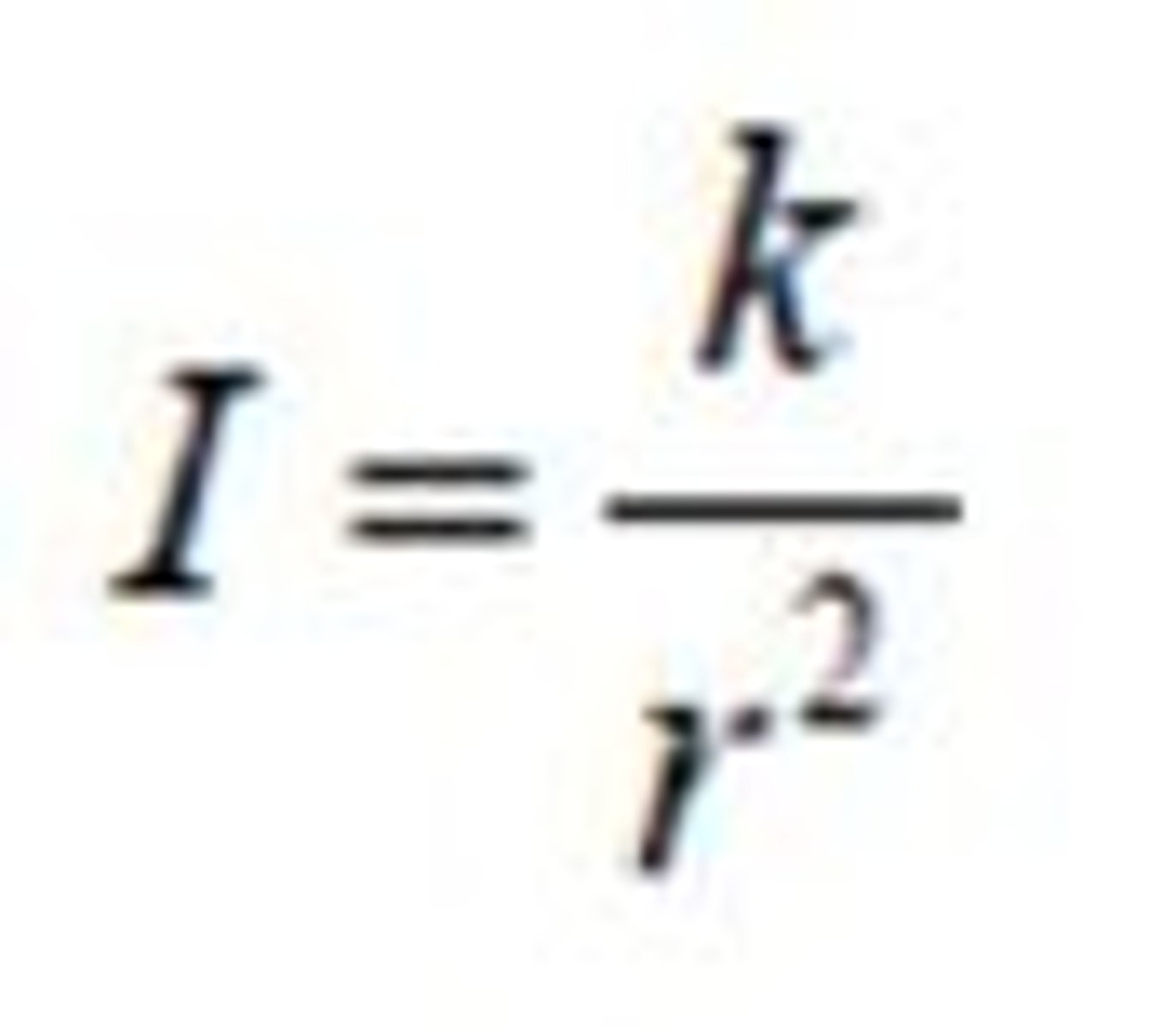
kilohertz (kHz)
1,000 Hz (kilo = 1,000)
megahertz (MHz)
1,000,000 Hz (mega = 1 million)
gigahertz (GHz)
1,000,000,000 Hz (giga = 1 billion)
terahertz (THz)
1,000,000,000,000 Hz (tera = 1 trillion)
satellite communication
high powered microwave and radio-wave signals are used to communicate long distances with satellites. Upload and download signals are transmitted at different frequencies. Radio-waves can be used for low orbit satellites. Microwaves are needed for high orbit satellites so that the signal can pass through the atmosphere
mobile phones
base stations transmit and receive signals over a limited range and allow phones to communicate across phone provider networks, which are allocated a band of frequencies in the radio/microwave region
Bluetooth
lower power devices communicate over a short range (about 10 m) directly with other devices e.g. mobile phone to ear buds. 'Frequency-hopping' is used to reduce interference with Wi-Fi signals that use similar frequencies of microwaves
Wi-Fi
computers and mobile devices can connect using a medium power signal to the internet via a router over a range of 100 m
infrared
low power devices like remote controls can send signals over a short range, but these signals require 'line-of-sight' and so are easily blocked and do not work well in bright sunlight