Chapter 8: Articulations and Movement
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/97
Last updated 2:38 AM on 11/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
1
New cards
Articulations/Joints are named by (3 things)
1. Bones/parts united (temporomandibular)
2. Only one bone (humeral)
3. Latin equivalent of common name (cubital)
2. Only one bone (humeral)
3. Latin equivalent of common name (cubital)
2
New cards
Classification of joints:
1. Structural: based on major connective tissue that binds
2. Functional: based on degree of motion
2. Functional: based on degree of motion
3
New cards
3 structural joints
1. Fibrous
2. Cartilaginous
3. Synovial
2. Cartilaginous
3. Synovial
4
New cards
3 functional joints
1. Synarthrosis (unmovable)
2. Amphiarthrosis (slightly moveable)
3. Diarthrosis (freely moveable)
2. Amphiarthrosis (slightly moveable)
3. Diarthrosis (freely moveable)
5
New cards
Characteristics of fibrous joints (3 things)
1. united by fibrous connective tissue
2. no joint cavity
3. move little or none
2. no joint cavity
3. move little or none
6
New cards
3 types of fibrous joints
1. Sutures
2. Syndesmoses
3. Gomphoses
2. Syndesmoses
3. Gomphoses
7
New cards
Characteristics of sutures (2 things)
1. Bones interdigitate
2. Continuous periosteum
2. Continuous periosteum
8
New cards
3 types of sutures
1. Sutural ligament: two periosteum + connective tissue
2. Synostosis: fully ossified suture
3. Fontanels: in suture between bones that allow change in shape of head
2. Synostosis: fully ossified suture
3. Fontanels: in suture between bones that allow change in shape of head
9
New cards
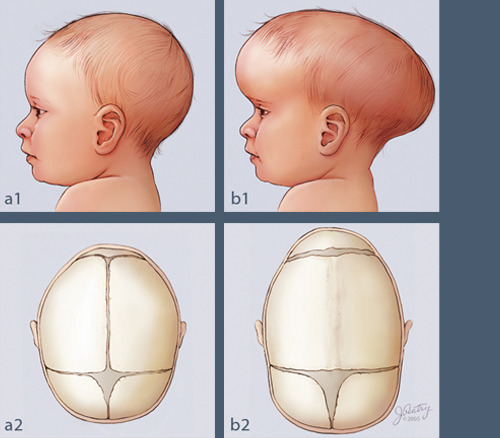
Craniosynostosis
the premature fusing of the sagittal suture
10
New cards
2 characteristics of syndesmoses
1. Bones farther apart than a suture, and joined by ligaments
2. Some movement (radioulnar or interosseous membrane)
2. Some movement (radioulnar or interosseous membrane)
11
New cards
3 characteristics of gomphoses
1. Specialized
2. Pegs fit into sockets
3. Periodontal ligaments (hold teeth in place)
2. Pegs fit into sockets
3. Periodontal ligaments (hold teeth in place)
12
New cards
Gingivitis
inflammation of the periodontal ligaments
13
New cards
4 Stages of Periodontal Disease
1. Healthy teeth and gums - 0mm pockets
2. Gingivitis - 2-3mm pockets
3. Gum recession & moderate periodontitis - 4-5mm pockets
4. Advanced periodontal disease & bone loss - 6-10mm pockets
2. Gingivitis - 2-3mm pockets
3. Gum recession & moderate periodontitis - 4-5mm pockets
4. Advanced periodontal disease & bone loss - 6-10mm pockets
14
New cards
What is a fibrous joint?
A. When two bones are united by fibrous connective tissue.
B. Two bones grow together across a joint and form a single bone.
C. When two bones are united by fibrocartilage.
D. Two bones grow together across a joint and form a synovial bone.
A. When two bones are united by fibrous connective tissue.
B. Two bones grow together across a joint and form a single bone.
C. When two bones are united by fibrocartilage.
D. Two bones grow together across a joint and form a synovial bone.
A. When two bones are united by fibrous connective tissue.
15
New cards
What is synostosis?
A. When two bones are united by fibrous C. T. (connective tissue).
B. Two bones grow together across a joint and form a single bone.
C. When two bones are united by fibrocartilage.
D. Two bones grow together across a joint and form a synovial bone.
A. When two bones are united by fibrous C. T. (connective tissue).
B. Two bones grow together across a joint and form a single bone.
C. When two bones are united by fibrocartilage.
D. Two bones grow together across a joint and form a synovial bone.
B. Two bones grow together across a joint and form a single bone.
16
New cards
What are the characteristics of a fibrous joint? Name three types and give an example of each.
Characteristics:
- united by a fibrous connective tissue
- no joint cavity
- don't move or move very little
Types - Example:
1. Sutures - a synostosis, like the coronal suture in your skull
2. Syndesmoses - the radioulnar membrane
3. Gomphoses - periodontal ligaments that keep teeth in place
- united by a fibrous connective tissue
- no joint cavity
- don't move or move very little
Types - Example:
1. Sutures - a synostosis, like the coronal suture in your skull
2. Syndesmoses - the radioulnar membrane
3. Gomphoses - periodontal ligaments that keep teeth in place
17
New cards
2 types of cartilaginous joints
1. Synchondroses (hyaline cartilage)
2. Symphyses (fibrocartilage)
2. Symphyses (fibrocartilage)
18
New cards
4 characteristics of synchondroses
1. Made of hyaline cartilage
2. Little or no movement
3. Most temporary (they turn into synostoses - ex: epiphyseal plate -> epiphyseal line)
4. Some permanent (1st costochondral joint)
2. Little or no movement
3. Most temporary (they turn into synostoses - ex: epiphyseal plate -> epiphyseal line)
4. Some permanent (1st costochondral joint)
19
New cards
2 characteristics of symphyses
1. Made of fibrocartilage
2. Slightly movable (ex: symphysis pubis, manubriosternal symphysis, intervertebral disks)
2. Slightly movable (ex: symphysis pubis, manubriosternal symphysis, intervertebral disks)
20
New cards
What changes in the symphysis occur during pregnancy?
Estrogen, progesterone, and relaxin cause the symphysis to become more stretchable. The joint can relax some, then after delivery it goes back to original condition.
21
New cards
Define cartilaginous joints, describe two different types and give an example of each.
Cartilaginous joints are joints held by hyaline or fibrocartilage. Synchondroses are made of hyaline, don't move, and usually turn into synostoses, while symphyses are made of fibrocartilage and are slightly movable. An example of a synchondrosis is the epiphyseal plate. An example of a symphysis is the manubriosternal joint.
22
New cards
6 characteristics of synovial joints
1. Contains synovial fluid in joint cavity
2. Allows for considerable movement
3. Make up most joints of appendicular skeleton (to provide greater mobility)
4. Complex
5. Contain hyaline cartilage
6. No blood vessels or nerves in articular cartilage, the nerves are in the capsule
2. Allows for considerable movement
3. Make up most joints of appendicular skeleton (to provide greater mobility)
4. Complex
5. Contain hyaline cartilage
6. No blood vessels or nerves in articular cartilage, the nerves are in the capsule
23
New cards
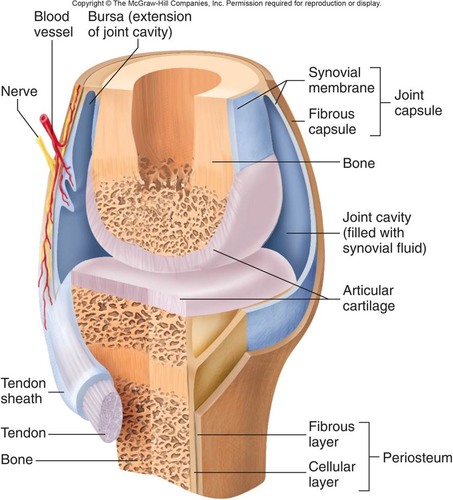
Joint cavity (of synovial joint)
encloses articular surfaces with synovial fluid
24
New cards
Joint capsule (of synovial joint)
fibrous capsule that is continuous with the bone periosteum and is lined on the inside with the synovial membrane
25
New cards
What does having the nerves in the joint capsule allow for?
proprioception
26
New cards
Would it be okay to have nerves or blood vessels grow in the articular cartilage?
No, because it would be between two bones and the blood flow/electrical signals would be obstructed. Plus, the nerves would be pinched and would cause pain.
27
New cards
Synovial fluid
thin, lubricating film that covers the surfaces of joints
28
New cards
What would happen if the synovial membrane covered the articular cartilage?
29
New cards
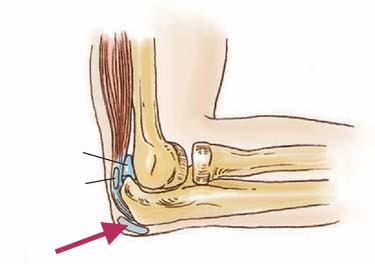
Bursae
pockets of synovial membrane that contains synovial fluid and provides a cushion between structures
30
New cards
Bursitis
inflammation of a bursa
31
New cards
Articular disks
additional fibrocartilage that provides extra strength and support to articulation surfaces (like the TMJ, sternoclavicular and acromioclavicular joints)
32
New cards
Meniscus
a fibrocartilaginous pad (i.e. knee)
33
New cards
Tendon sheaths
synovial tissue forming bursae that surround tendons for some distance
34
New cards
Synovial joint characteristics include all the following except?
A. Synovial fluid.
B. Considerable movement.
C. Most joints of appendicular skeleton.
D. No joint capsule.
A. Synovial fluid.
B. Considerable movement.
C. Most joints of appendicular skeleton.
D. No joint capsule.
D. No joint capsule.
35
New cards
Labelled synovial joint
36
New cards
Housemaid's Knee
prepatellar bursitis - the prepatellar bursa (closer to the surface than the patella bone) becomes inflamed
37
New cards
Which of these is not associated with synovial joints?
A. Nerves in the capsule around the joint.
B. Synovial membrane lining the capsule.
C. Synovial fluid contained within the capsule.
D. Nerves on the surface of articular cartilage.
A. Nerves in the capsule around the joint.
B. Synovial membrane lining the capsule.
C. Synovial fluid contained within the capsule.
D. Nerves on the surface of articular cartilage.
D. Nerves on the surface of articular cartilage.
38
New cards
Uniaxial
a joint with one axis
39
New cards
Biaxial
a joint with two axes at right angles to each other
40
New cards
Multiaxial
a joint with several axes
41
New cards
Plane (gliding) joints
uniaxial, where some rotation is possible but limited (Ex: intervertebral)
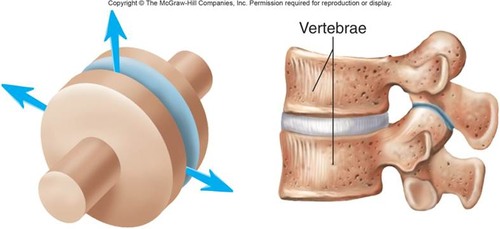
42
New cards
Saddle joints
biaxial (Ex: thumb - carpometacarpal pollicis)
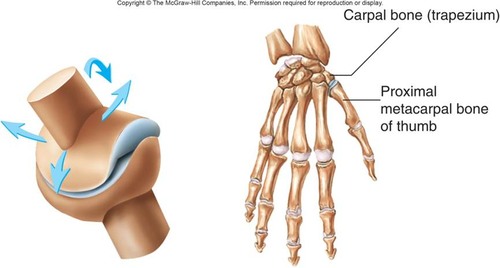
43
New cards
Hinge joint
uniaxial, with a convex cylinder in one bone and a concavity in the other (Ex: elbow, knee, ankle, interphalangeal)
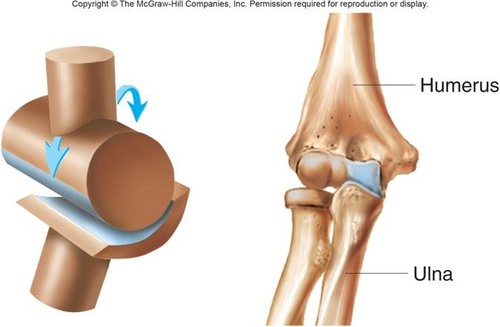
44
New cards
Pivot joints
uniaxial, usually with a cylindrical bony process rotating around a single axis within a circle of bone and ligament (Ex: atlantoaxial, proximal radioulnar)
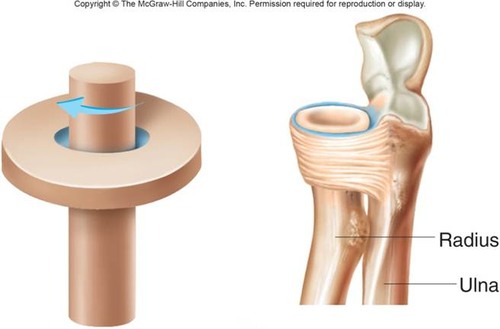
45
New cards
Ball-and-socket joints
multiaxial (Ex: shoulder and hip joints)
46
New cards
Ellipsoid (Condyloid) joints
biaxial, modified ball-and-socket joints with articular surfaces like an ellipse (Ex: atlantooccipital)
47
New cards
Which of these Joints is correctly matched with the type of joint?
A. Atlas to occipital condyle - pivot
B. Scapula to humerus - saddle
C. Femur to coxal bone - ellipsoid
D. Tibia to talus - hinge
A. Atlas to occipital condyle - pivot
B. Scapula to humerus - saddle
C. Femur to coxal bone - ellipsoid
D. Tibia to talus - hinge
D. Tibia to talus - hinge
48
New cards
An example of a pivot joint is:
A. Atlantoaxial
B. Femerocoxal
C. Cubital
A. Atlantoaxial
B. Femerocoxal
C. Cubital
A. Atlantoaxial
49
New cards
3 types of movement
1. Gliding: in plane joints; slight movement
2. Angular
3. Circular
2. Angular
3. Circular
50
New cards
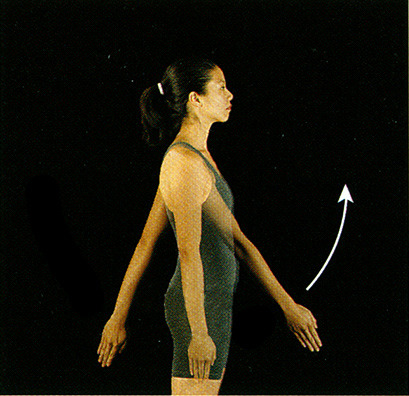
Flexion
- angular movement
- moves anterior to the coronal plane
- moves anterior to the coronal plane
51
New cards
Extension
- angular movement
- moves posterior to the coronal plane
- moves posterior to the coronal plane

52
New cards
Hyperextension
- angular movement
- extension beyond anatomical position
- extension beyond anatomical position
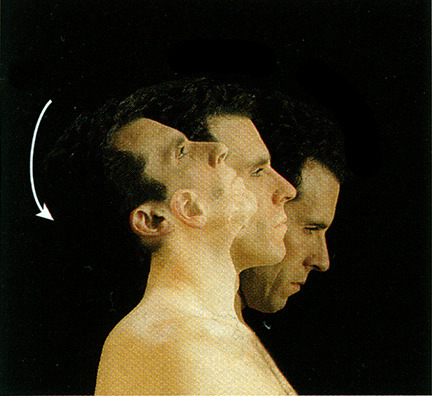
53
New cards
Plantar flexion
- angular movement
- move foot toward plantar surface (standing on tip toes)
- move foot toward plantar surface (standing on tip toes)
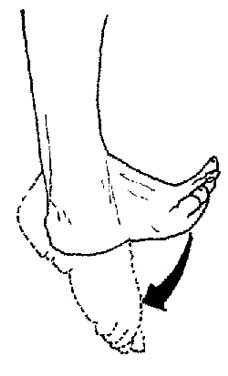
54
New cards
Dorsiflexion
- angular movement
- foot lifted toward shin
- foot lifted toward shin
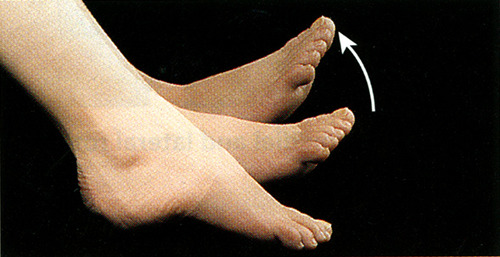
55
New cards
Abduction
- angular movement
- take away from the midline (abducting means taking something away)
- take away from the midline (abducting means taking something away)
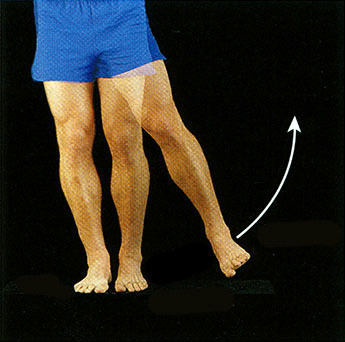
56
New cards
Adduction
- angular movement
- bring toward the midline ("add" something back)
- bring toward the midline ("add" something back)

57
New cards
Rotation
- circular movement
- turning of a structure on its long axis (medial - toward the midline, and lateral - away from the midline)
- Ex: rotation of the head, humerus, or body
- turning of a structure on its long axis (medial - toward the midline, and lateral - away from the midline)
- Ex: rotation of the head, humerus, or body
58
New cards
Pronation
- circular movement
- palm faces posteriorly
- palm faces posteriorly
59
New cards
Supination
- circular movement
- palm faces anteriorly (like you're holding soup)
- palm faces anteriorly (like you're holding soup)
60
New cards
Circumduction
- circular movement
- includes: flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction
- includes: flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction
61
New cards
Spreading the fingers apart is___.
A. Rotation
B. Flexion
C. Abduction
D. Adduction
A. Rotation
B. Flexion
C. Abduction
D. Adduction
C. Abduction
62
New cards
For a ballet dancer to stand on her toes, her feet must
A. Abduct
B. Plantar flex
C. Dorsiflex
D. Invert
A. Abduct
B. Plantar flex
C. Dorsiflex
D. Invert
B. Plantar flex
63
New cards
Nursemaid's Elbow
Subluxation of the radial head
64
New cards
Fix to nursemaid's elbow
supinate the wrist and flex the elbow to 90 degrees
65
New cards
5 types of special movements
1. elevation and depression
2. protraction and retraction
3. excursion
4. opposition and reposition
5. inversion and eversion
2. protraction and retraction
3. excursion
4. opposition and reposition
5. inversion and eversion
66
New cards
Elevation/Depression
scapula and mandible moves
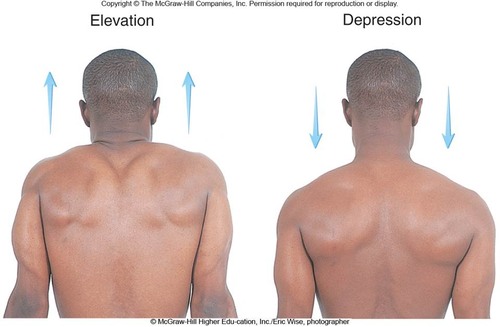
67
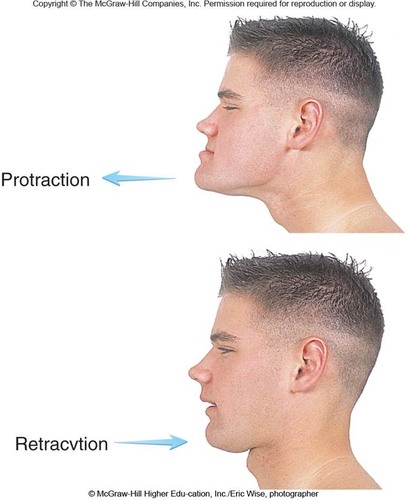
New cards
Protraction
mandible moves anterior
68
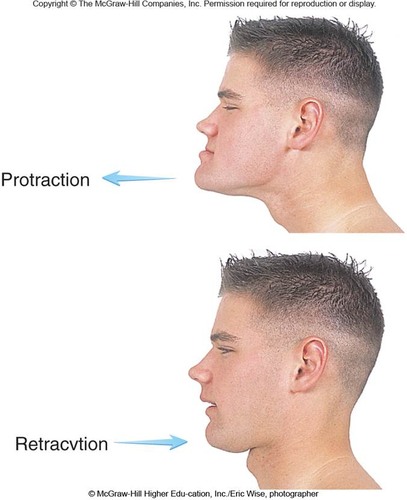
New cards
Retraction
mandible moves back into the correct anatomical position
69
New cards
Excursion
lateral - mandible moves either to the right or left of midline (the teeth grinding motion) and medial - mandible moves back into anatomical position
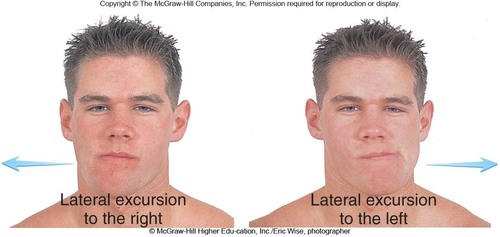
70
New cards
Opposition
movement of thumb and little finger towards each other
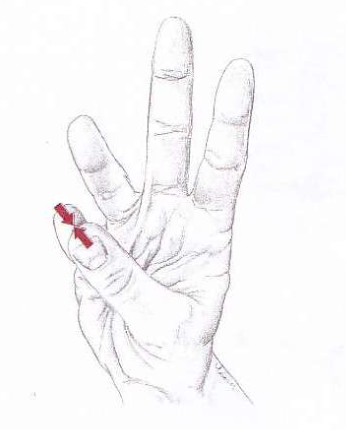
71
New cards
Reposition
the fingers return to anatomical position
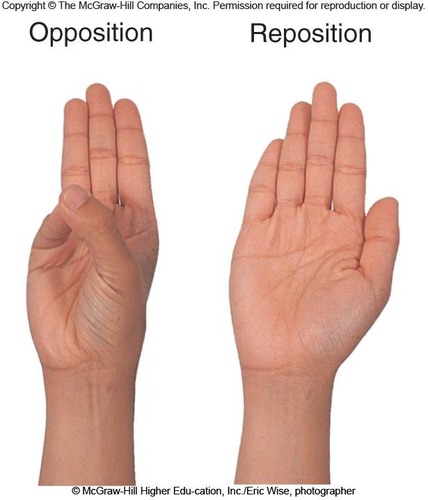
72
New cards
Inversion
foot moves so sole faces the opposite foot
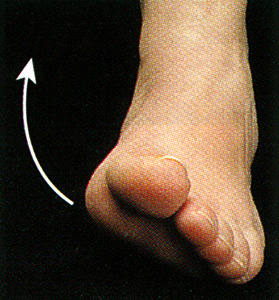
73
New cards
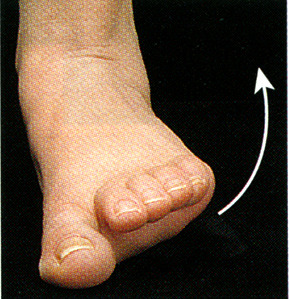
Eversion
foot moves so sole faces laterally
74
New cards
Active mobility
muscle contraction results in motion
75
New cards
Passive mobility
outside force results in motion
76
New cards
What 5 things influence range of motion/amount of mobility? (the S.S. FLU)
1. Shape of articular surfaces/cartilage
2. Strength/location of ligaments and tendons
3. Location of muscles associated with joint
4. Fluid or pain in and around joint
5. Use/disuse of joint
2. Strength/location of ligaments and tendons
3. Location of muscles associated with joint
4. Fluid or pain in and around joint
5. Use/disuse of joint
77
New cards
What terms are used for turning the foot medially?
A. reversion
B. conversion
C. eversion
D. inversion
A. reversion
B. conversion
C. eversion
D. inversion
D. inversion
78
New cards
Define range of motion (ROM) and contrast active and passive.
ROM = amount of mobility. Active - by muscle contraction. Passive - outside force moves joint.
79
New cards
Touching the thumb with the little finger is called:
A. abduction.
B. adduction.
C. flexion.
D. opposition.
E. reposition.
A. abduction.
B. adduction.
C. flexion.
D. opposition.
E. reposition.
D. opposition.
80
New cards
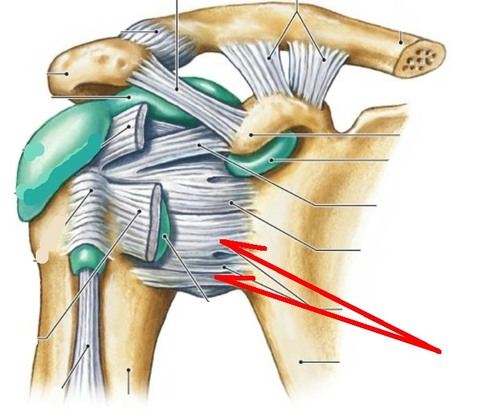
Shoulder (Glenohumeral) Joint
It's a ball-and-socket joint that is less stable (but more mobile) than the hip and can do circumduction.
81
New cards
Glenoid labrum
a rim of fibrocartilage around the glenoid cavity (a part of the glenohumeral joint)
82
New cards
What bursae are associated with the glenohumeral joint?
subacromial and subscapular bursae
83
New cards
Rotator cuff
four muscles that contribute to the stability of the glenohumeral joint
84
New cards
Where does the tendon of the biceps brachii insert?
through the glenohumeral joint capsule
85
New cards
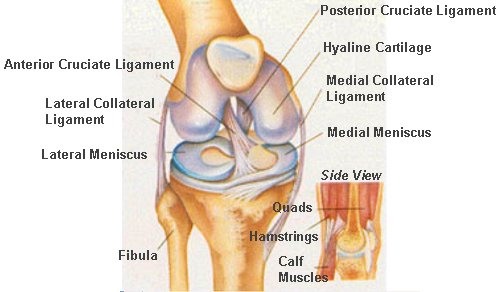
Knee Joint
traditionally considered a modified hinge joint but is actually a complex ellipsoid joint
86
New cards
Parts of the knee joint (3)
1. Menisci
2. Cruciate ligaments (anterior and posterior)
3. Collateral ligaments
2. Cruciate ligaments (anterior and posterior)
3. Collateral ligaments
87
New cards
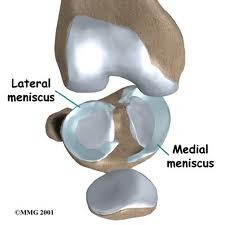
Menisci of the knee joint
fibrocartilage articular disks that build up margins of the tibia and deepen articular surface
88
New cards
Cruciate ligaments of the knee joint
ligaments that cross each other, forming an X between the notch in the femoral condyles (they also connect to the femur)
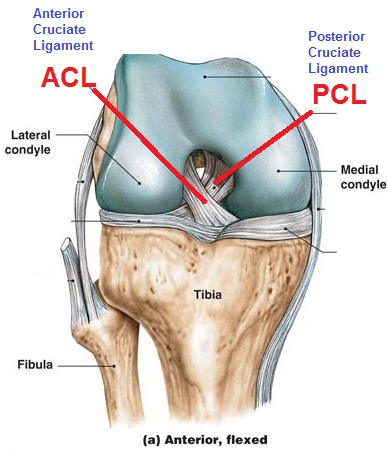
89
New cards
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
prevents anterior displacement of tibia
90
New cards
Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
Prevents posterior displacement of tibia
91
New cards
Collateral ligaments
help strengthen knee joint
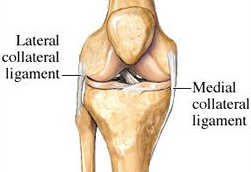
92
New cards
Knee injuries and disorders (4 things)
1. Football injuries: torn tibial collateral ligament, ACL, and medial meniscus
2. Bursitis
3. Chondromalacia: cartilage of patella is soft
4. Hemarthrosis: blood in joint
2. Bursitis
3. Chondromalacia: cartilage of patella is soft
4. Hemarthrosis: blood in joint
93
New cards
The fibrocartilage articular disks in this joint are referred to as menisci.
A. ankle
B. hip
C. knee
D. shoulder
E. temporomandibular
A. ankle
B. hip
C. knee
D. shoulder
E. temporomandibular
C. knee
94
New cards
7 effects of aging on joints
1. Tissue repair slows
2. Rate of new blood vessel development decreases
3. Articular cartilages wear down
4. Matrix becomes more rigid
5. Production of synovial fluid declines
6. Ligaments and tendons become shorter + decreased activity, both resulting in less flexibility and a decrease in range of motion (ROM)
7. Muscles around joints weaken
2. Rate of new blood vessel development decreases
3. Articular cartilages wear down
4. Matrix becomes more rigid
5. Production of synovial fluid declines
6. Ligaments and tendons become shorter + decreased activity, both resulting in less flexibility and a decrease in range of motion (ROM)
7. Muscles around joints weaken
95
New cards
Joint disorders (3 things)
1. Arthritis
2. Osteoarthritis
3. Rheumatoid arthritis
2. Osteoarthritis
3. Rheumatoid arthritis
96
New cards
Arthritis
inflammation of any joint (14% of people have it, there are more than 100 types, and swimming/walking is best for sufferers of it)
97
New cards
Osteoarthritis (OA)
wear and tear inflammation (most common, 10% of people in the USA have it)
98
New cards
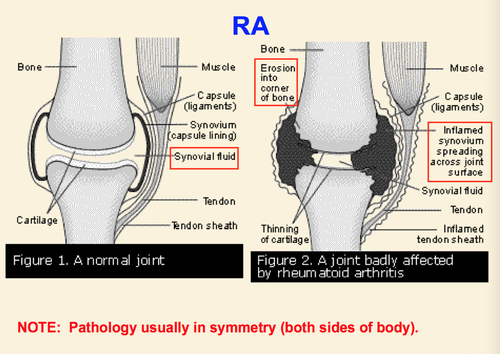
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the joints (the ratio of women to men who have it is 3:1, can cause ulnar drift)