Chapter 13: The Respiratory System
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Professor Frank @ UCF
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
The _____ is a thin membrane located between the pharyngeal pouch & the pharyngeal groove.
If this structure ruptures, the pharyngeal pouch & groove will be connected and water can exit the pharynx.
Branchial Plate
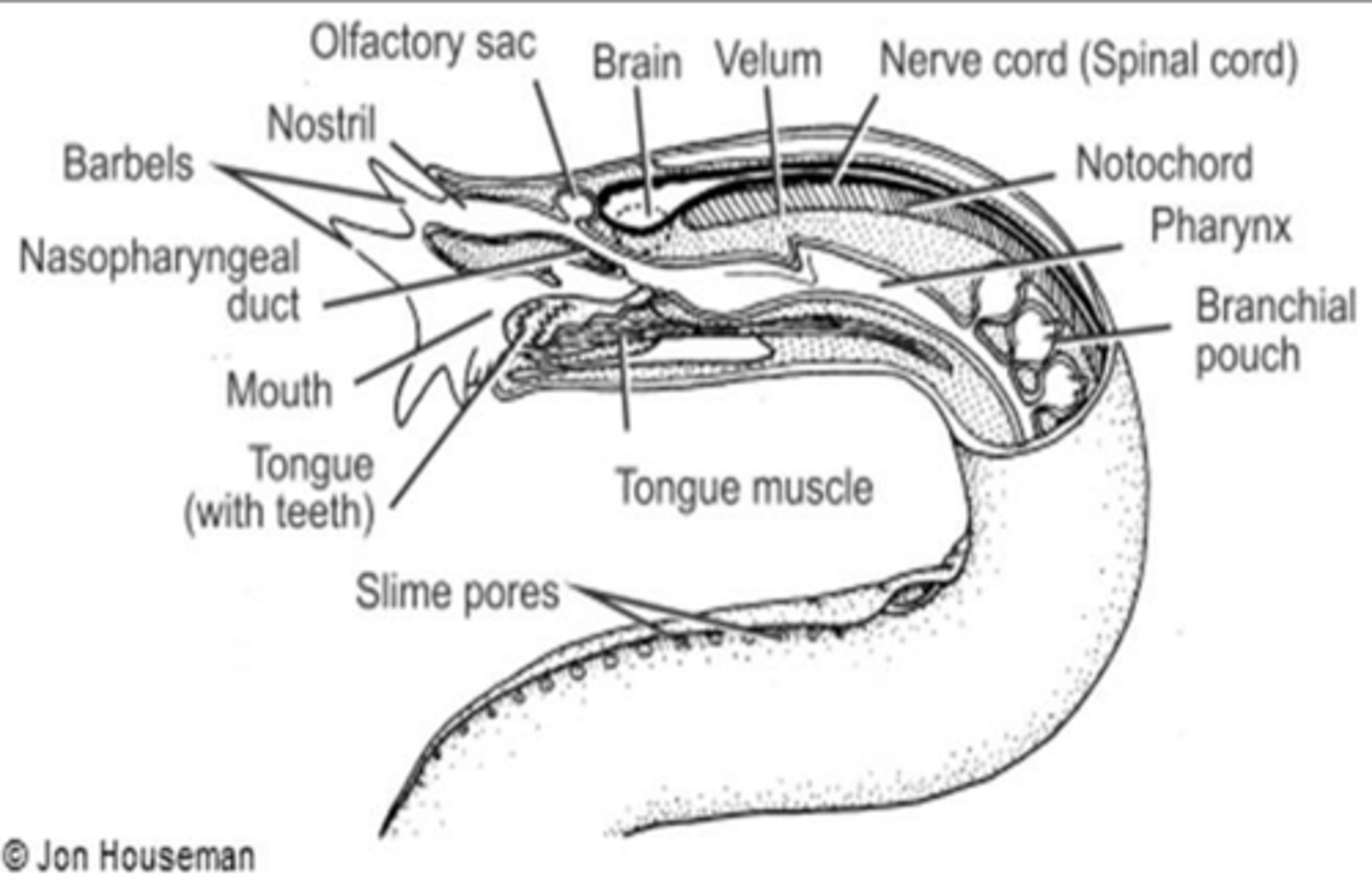
In hagfish, the number of pharyngeal pouches varies with the species.
____ conduct respiratory water from the pharynx into the pharyngeal pouches.
Afferent Branchial Ducts
In hagfish, the number of pharyngeal pouches varies with the species.
____ lead from the pharyngeal pouches to the external environment.
Efferent Branchial Ducts
A pulsating muscle, supported by cartilage, that pumps water from the velar chamber into the pharynx & into the gill pouches.
This causes the creation of vacuum pressure, which will draw more water from the naris & nasopharyngeal duct.
Velum
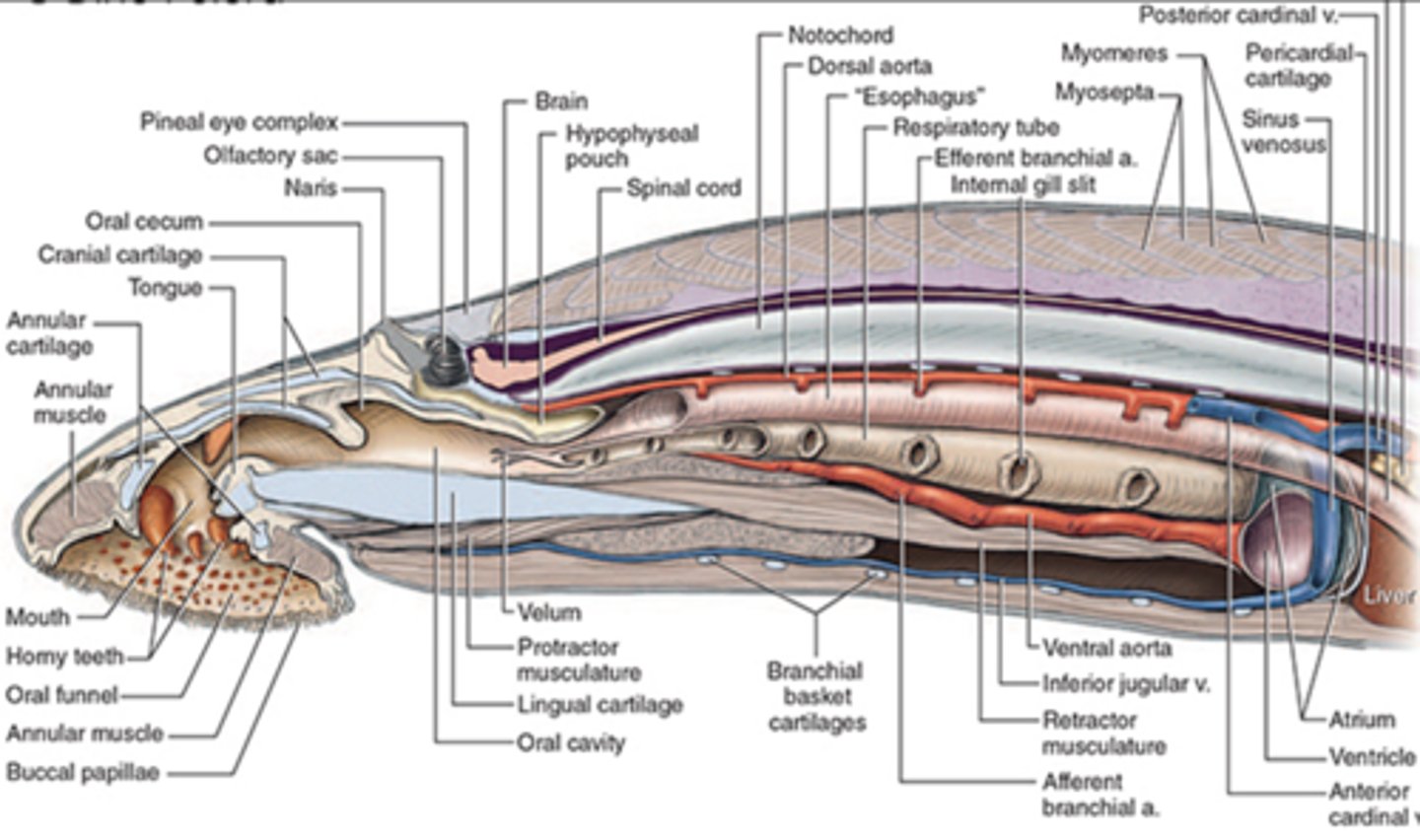
In lampreys, to allow for parasitic feeding & breathing to occur simultaneously, the pharynx is longitudinally divided into an esophagus and a blind-ending _____ located ventral to the esophagus.
Respiratory Tube
Most elasmobranchs are ____, having 5 pairs of gill
pouches. The only exceptions are the 6-gill & 7-gill sharks.
Pentanchid
True or False: The gill slits of elasmobranchs are said to be "naked" since they are not covered by a valve or an operculum.
TRUE
In elasmobranchs, each gill slit opens into a gill chamber. In the first 4 chambers, the anterior & posterior walls have a ____, a well-vascularized gill surface.
Demibranch
In elasmobranchs, each gill slit opens into a gill chamber. A ____ is composed of 2 demibranchs of a single gill arch (the posttrematic demibranch of the prior gill chamber & the pretrematic demibranch of the next gill chamber).
The typical shark has 4 of these.
Holobranch
Elasmobranch gill arches also have ____. These are stubby, projecting structures radiating from the pharyngeal border to protect the gills from mechanical trauma.
Gill Rakers
One group of chondrichthyes, the ____, differ from elasmobranchs in having 4 pairs of gill pouches, lacking spiracles, & having a fleshy operculum that covers the gill slits.
Holocephalians
Each gill slit opens into a gill chamber, & the first 4 chambers will have anterior and posterior demibranchs. The demibranch on the anterior wall is called the ____.
Pretrematic Demibranch
Each gill slit opens into a gill chamber, & the first 4 chambers will have anterior and posterior demibranchs. The demibranch on the posterior wall is called the _____.
Posttrematic Demibranch
Each gill slit opens into a gill chamber, & the first 4 chambers will have anterior and posterior demibranchs. Between the posttrematic demibranch of one gill slit & the pretrematic demibranch of the next gill slit is a partition called the ____.
Interbranchial Septum
Between the posttrematic demibranch of one gill slit & the pretrematic demibranch of the next gill slit is the interbranchial septum. The interbranchial septum is supported by long, tapering, & sometimes branching cartilaginous ____ that radiate from the gill cartilages.
Gill Rays
The typical shark has 4 holobranchs. Anterior to the first holobranch is the pretrematic demibranch of the first gill chamber called the ____.
First Demibranch
The ____ in bony fishes is a bony flap that covers the gill slits. It originates on the hyoid arch & extends caudally to cover the gill chambers.
Operculum
Extending from the ventral edge of each operculum is the ____.
Branchiostegal Membrane
The right & left branchiostegal membrane are joined
midventrally to enclose the ____. This structure receives water that has passed through the gills & is about to exit the body through a cleft at the caudal margin of the operculum.
Opercular Chamber
In fishes, the nostrils (or external nares) end in a blind ____ for scent detection. The nostrils are NOT used for breathing.
Olfactory Sac
In lobe-finned fishes, the nostril had an extra opening, an opening into the oropharyngeal cavity, called the ____.
Internal Nares
Fishes only have a(n) ____ that is associated primarily with respiration but does allow for the passage of food into the esophagus.
Oropharynx / Oropharyngeal Cavity
Mammals have 3 subdivisions to the pharynx. The ____ extends from the internal nares to the level of the soft palate. It has the openings of the eustachian tubes and the pharyngeal tonsils.
Nasopharynx
Mammals have 3 subdivisions to the pharynx. The ____ extends from the soft palate to the hyoid.
Oropharynx
Mammals have 3 subdivisions to the pharynx. The ____ extends from the hyoid to the glottis.
Laryngopharynx
The ____ is a short passageway between the glottis & trachea. Its walls are supported by cartilage to withstand air pressure.
Larynx
The opening into the glottis is surrounded by the ____, which are folds of mucus membrane. They are sometimes called "vocal cords" but they are not true
vocal cords.
Vocal Folds
A singular tube that carries air from the larynx to the
lungs. Due to the vacuum pressure of air during inhalation, it is reinforced by cartilaginous or bony plates.
Trachea
Birds have a specialized structure called the ____ that serves as their larynx, & is located at the carina.
Syrinx
There are 3 types of syrinxes found in birds. All 3 serve as resonance chambers for sound. The ____ is located in the trachea & primary bronchi.
Bronchotracheal Syrinx
There are 3 types of syrinxes found in birds. All 3 serve as resonance chambers for sound. The ____ is located only in the trachea.
Tracheal Syrinx
There are 3 types of syrinxes found in birds. All 3 serve as resonance chambers for sound. The ____ is located only in the primary bronchi.
Bronchial Syrinx
The ____ are branching structures that serve to conduct air into the various subsegments of the lungs. They are structurally similar to the trachea, & they branch into primary, secondary, & tertiary segments.
Bronchi
The tertiary bronchi branch into even smaller branches called ____. Typically, these smaller branches lack cartilage plates. They will carry air into the respiratory portion of the lungs.
Bronchioles
____ are typically paired, sac like structures that serve as the site of external respiration.
Lungs
Internally the lungs have a ____. This structure of the lungs is thin (to increase diffusion), moist, well-vascularized, & has a good deal of surface area all to
increase the efficiency of external respiration.
Respiratory Membrane
Some reptilian lungs have extensions, called ____, that can be used to inflate the body as a scare tactic against predators (ex; puff adders).
Air Sacs

Crocodilians & a few squamates have the lungs separated from the rest of the pleuroperitoneal cavity by tendinous extensions called the ____.
Oblique Septum
In mammalians, within the thoracic cavity, each lung resides in its own chamber called the ____.
Pleural Cavity
The smallest bronchioles terminate in _____, which are sac-like structures that serve as the site of external respiration in mammals. To aid in this, these are very thin walled & closely associated with numerous capillaries.
Alveoli
True or False: In amphibians, each nostril is divided into an Incurrent Aperture where water enters & an Excurrent Aperture where water exits.
FALSE
In FISHES, each nostril is divided into an Incurrent Aperture where water enters & an Excurrent Aperture where water exits.
The openings associated with the pharynx include the _____, which is the opening into the trachea.
Glottis
In mammals, the glottis (trachea opening) is guarded by a laryngeal cartilage, the ____. In other tetrapods, it is guarded by fleshy folds.
Epiglottis
The openings associated with the pharynx include the _____, which are modified spiracles that connect the pharynx to the middle ear to equalize air pressure in the head.
Eustachian Tubes
The openings associated with the pharynx include the _____, which is the opening between the pharynx and the mouth.
Fauces
The openings associated with the pharynx include the _____, which are the openings between the pharynx and nasal cavity in tetrapods possessing a secondary palate.
Internal Nares
The fauces between the oropharynx and oral cavity is guarded by the ____ & ____.
A. Epiglottis & Uvula
B. Uvula & Pillars of the Fauces
C. Epiglottis & Pillars of the Fauces
D. Cricoids & Uvula
E. Epiglottis & Cricoids
B. Uvula & Pillars of the Fauces
Crocodilians & a few squamates have the lungs separated from the rest of the pleuroperitoneal cavity by the oblique septum. The resulting paired subchambers are termed ____.
Pleural Cavities
True or False: Avian lungs, like crocodilian lungs, occupy paired pleural cavities separated from the rest of the pleuroperitoneal cavity by the oblique septum.
TRUE
Birds have 5 or 6 pairs of air sacs. ____ are found dorsal to the furcula. They may fuse together.
A. Interclavicular Sacs
B. Axillary Sacs
C. Anterior Thoracic Sacs
D. Posterior Thoracic Sacs
E. Abdominal Sacs
A. Interclavicular Sacs
Birds have 5 or 6 pairs of air sacs. ____
Birds have 5 or 6 pairs of air sacs. ____ are found within the oblique septum.
A. Interclavicular Sacs
B. Axillary Sacs
C. Anterior Thoracic Sacs
D. Posterior Thoracic Sacs
E. Abdominal Sacs
D. Posterior Thoracic Sacs
Birds have 5 or 6 pairs of air sacs. ____ are found among the abdominal viscera.
A. Interclavicular Sacs
B. Axillary Sacs
C. Anterior Thoracic Sacs
D. Posterior Thoracic Sacs
E. Abdominal Sacs
E. Abdominal Sacs
Birds have 5 or 6 pairs of air sacs. ____ are found in axillas between the supracoracoideus & the pectoralis major.
A. Interclavicular Sacs
B. Axillary Sacs
C. Anterior Thoracic Sacs
D. Posterior Thoracic Sacs
E. Abdominal Sacs
B. Axillary Sacs
Diverticuli from the air sacs in avians will extend into most of the bones of the skeleton via _____. This gives birds their "hollow bones".
Pneumatic Foramina
Alveolar cells that are very thin, squamous cells that serve as the site of external respiration.
Type 1 Cells
Alveolar cells that are low cuboidal epithelial cells that secrete surfactant to keep open the alveoli.
Type 2 Cells
Alveolar cells that are phagocytic transient cells that clear the alveoli of particulate matter & pathogens.
Alveolar Macrophages / Dust Cells
In mammalians, the ____ is composed of type 1 cells, basal laminae, & the endothelial cells of the capillary
wall. It has been modified to increase diffusion.
Alveolar-Capillary Membrane
Gills are used in respiration by fishes & aquatic/aquatic-stage amphibians. The internal gills of fishes arise in the walls of the ____. These are paired evaginations of the embryonic pharynx.
pharyngeal pouches
The internal gills of fishes arise in the walls of the pharyngeal pouches. External to the pharyngeal pouches are the ____, which are invaginations of the surface ectoderm.
pharyngeal grooves
In teleosts, the branchiostegal membrane extends from the ventral edge of each operculum. It is supported by the ____.
Branchiostegal Rays
Along with facilitating respiration, gills also play a role in excretion. In marine species, the gills have _____.
salt-excreting glands
Most nonmammalian tetrapods have 2 pairs of laryngeal cartilages. What are they called?
Cricoids & Arytenoids
Mammals have a greater variety to the structure of the larynx since they use the greatest range of vocalizations. Most mammals have the arytenoids & cricoid cartilages, and also a 3rd pair called the _____.
Thyroids
In tetrapods other than urodeles, the trachea ends when it branches into the _____, which will enter into the right & left lung respectively.
Right & Left Primary Bronchi
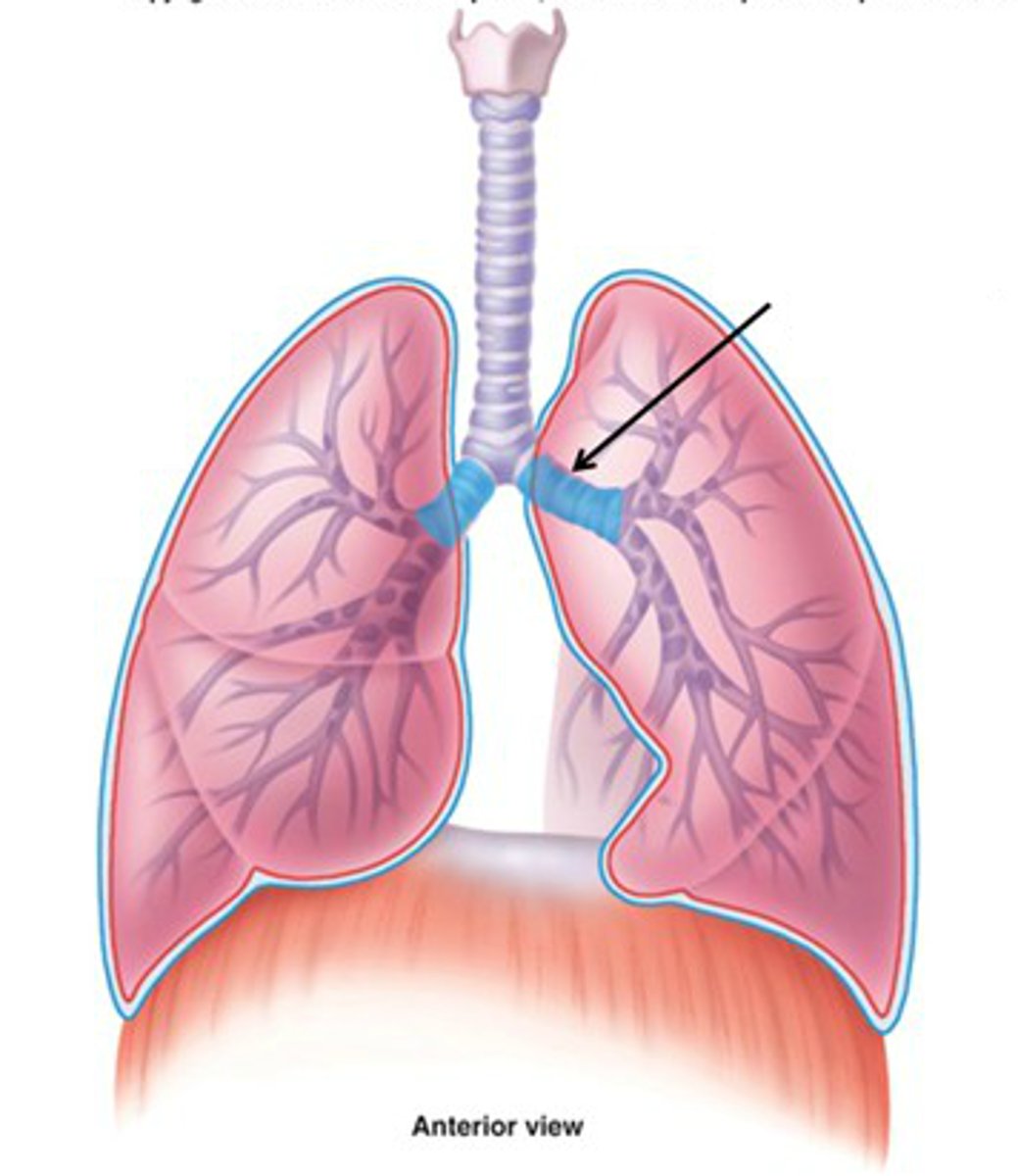
As in amphibians, reptilian lungs are located in the ____ along with the other viscera.
Pleuroperitoneal Cavity
Birds have 5 or 6 pairs of air sacs. ____ are found in their own chambers located lateral to the heart.
A. Interclavicular Sacs
B. Axillary Sacs
C. Anterior Thoracic Sacs
D. Posterior Thoracic Sacs
E. Abdominal Sacs
C. Anterior Thoracic Sacs
Although they use the ribs to a slight extent for ventilation, crocodilians primarily use skeletal muscle fibers derived from the hypaxial musculature for inspiration.
These skeletal muscle fibers make up the ____, which are paired structures extending from the pelvis to the fibrous investment of the liver.
Diaphragmatic Muscles
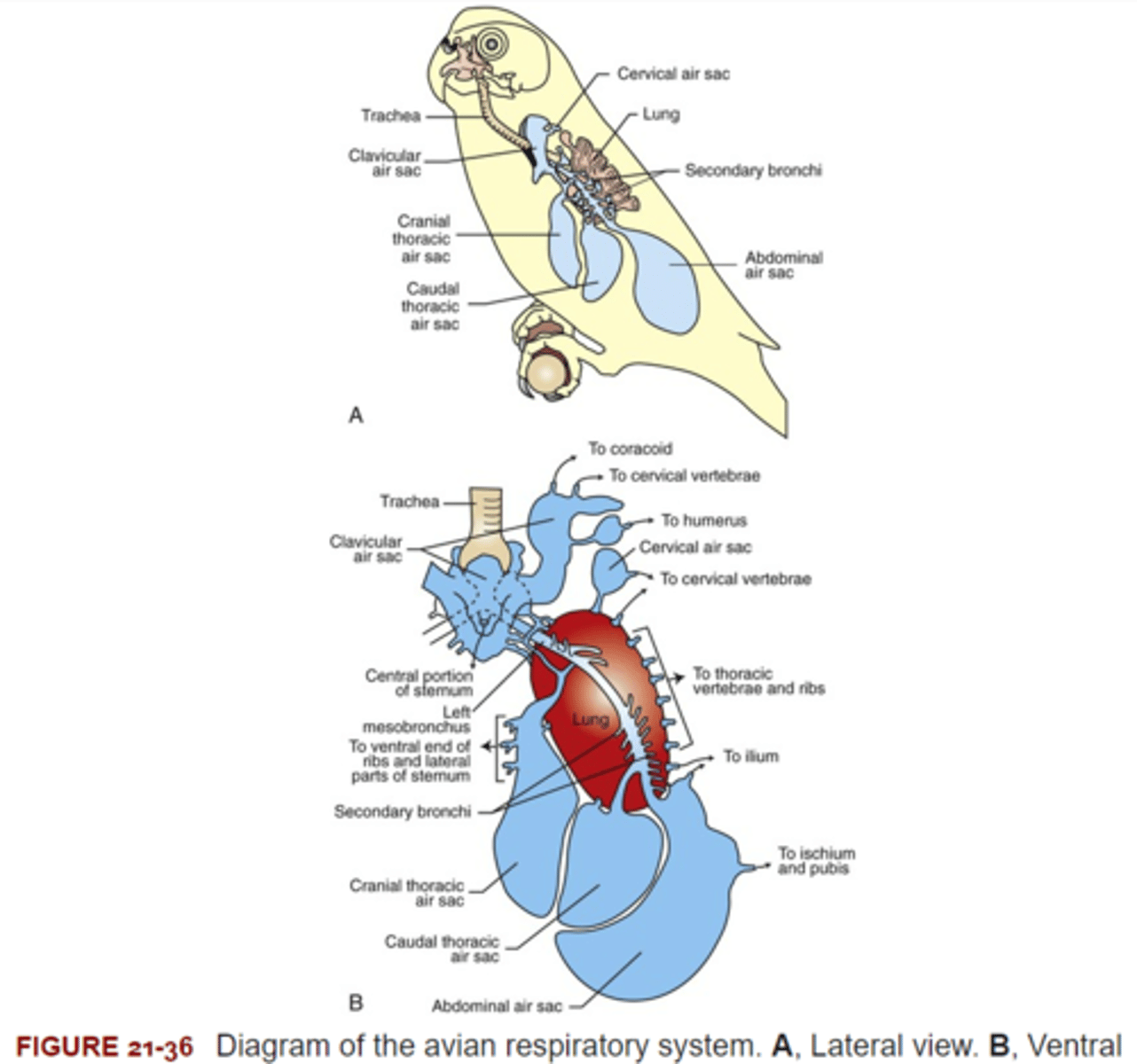
Avian lungs are unique in their structure and function. Inspired air enters each lung by way of the primary bronchus & travels through the lung without stopping to the air sacs. The air travels through the lungs to the air sacs by the _____.
Mesobronchi
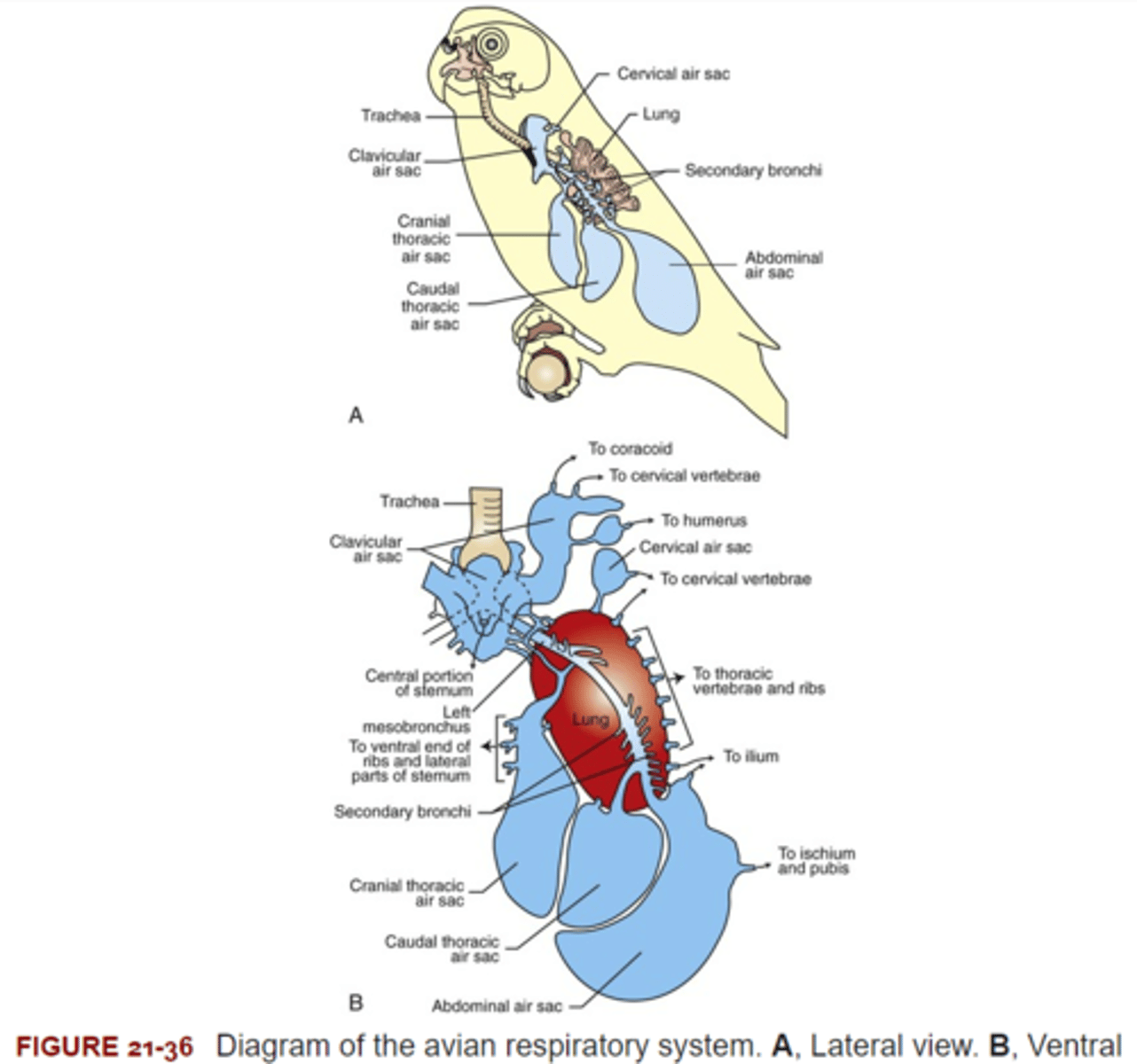
Avian lungs are unique in their structure and function. Inspired air enters each lung by way of the primary bronchus & travels through the lung without stopping to the air sacs. The air exits the lungs from the air sacs by the ____.
Excurrent Bronchi
Mammalian lungs are paired structures located in the ____, which is separated from the abdominopelvic cavities by the diaphragm.
Thoracic Cavity
In mammals, the lungs reside individually in their own pleural cavities. The 2 pleural cavities are separated by the _____ & _____.
mediastinum & pericardial cavity
The lining of the upper respiratory tract is a pseudostratified, ciliated, columnar epithelium with goblet cells resting on a well-vascularized areolar connective tissue. The underlying areolar connective tissue is called ____, & will have a high number of lymphoid cells.
Lamina Propria
The spiracle evolved into the mammalian ____.
eustachian tube
True or False: The gill apparatus in cartilaginous fishes & bony fishes have the same basic pattern.
TRUE
Both are a series of pharyngeal arches supporting holobranchs & a stream of respiratory water flows over the demibranchs as it travels from the pharyngeal cavity to the external environment.
The gill apparatus in cartilaginous fishes & bony fishes have the same basic pattern. The main difference is that bony fishes have?
They have an Operculum, Opercular Chamber, & the interbranchial septa are relatively shorter.
In ancient fishes, such as gars, ____ support the branchiostegal membrane.
Gular Plates
The ____ is the primary muscle driving mammalian inspiration. It will be assisted to some degree by the intercostals.
Diaphragm
For mammalian respiration, the diaphragm flattens & the
intercostals pull the rib cage up/out during (1)____. During (2)____, the diaphragm & intercostals relax, the pleural space becomes smaller, and intrapleural pressure increases.
1) inspiration; 2) expiration
True or False: For mammalian respiration, there is a decrease in intrapleural pressure, which sets up a vacuum pressure to push air out of the lungs (expiration).
FALSE
For mammalian respiration, there is a decrease in intrapleural pressure, which sets up a vacuum pressure to PULL AIR INTO the lungs (INSPIRATION).
"Respiratory water enters by a singular naris & passes through the nasopharyngeal duct into the velar chamber at the proximal end of the pharynx. Oxygen is picked up from water & carbon dioxide is dumped into
water in the gill pouches/pharyngeal pouches. Water then exits by a singular external gill aperture on each side."
This occurs in which aquatic vertebrates?
Hagfish
Along with the gill pouches, elasmobranchs also have _____, which are one-way intake valves. They are used in rays & skates on sediment to bring in water.
Spiracles
True or False: The modern tetrapod lung evolved from the swim bladder.
TRUE
The opening into the glottis is surrounded by vocal folds. Some vertebrates (primarily mammals) have an extra pair of mucus membrane folds that will contain muscle. The muscle allows these vocal folds to alter the stream of air passing through.
Mammals that have this extra pair are said to have _____.
False & True Vocal Cords
Due to its lower position, the larynx has an ____ which guards the opening into the glottis.
Epiglottis
True or False: Squamates can not use their ribs to aid in respiration, & instead use movements of the pectoral girdle to produce negative pressure for inspiration.
FALSE
TURTLES can not use their ribs (since they are fused to the shell), & instead use movements of the pectoral girdle to produce negative pressure for inspiration.
Expiration is caused by contraction of the _____, which causes an increase in intrapleural pressure.
Transversus Abdominis
Regardless of whether a bird is at rest or in flight, the excurrent air is still rich in oxygen. The bronchial tree conducts the air to the respiratory membrane for external respiration.
The main excurrent bronchi are the ______.
Dorsal & Ventral Bronchi
Regardless of whether a bird is at rest or in flight, the excurrent air is still rich in oxygen. The bronchial tree conducts the air to the respiratory membrane for external respiration.
The dorsal & ventral bronchi are connected by _____. These are thin-walled structures surrounded by copious, anastomizing capillary beds. They serve as the site of external respiration in birds.
Parabronchi
True or False: Unlike the muscular mammalian diaphragm, the oblique septum does not play a role in inspiration.
TRUE
The mechanism of ventilation varies among the reptiles. ____ use the intercostal muscles to move the ribs to increase & decrease intrapleural pressure to allow for exhalation & inhalation.
A. Squamates
B. Turtles
C. Crocodilians
D. Sphenodonts
E. A & C
A. Squamates
Which of the following groups of vertebrates does NOT use negative pressure to draw air into the lungs?
A. Birds
B. Amphibians
C. Reptiles
D. Mammals
E. All of the above use negative pressure to draw air into the lungs
B. Amphibians
Which of the following is NOT true about amphibian lungs?
A. Lungs are elongated in urodeles & bulbous in anurans.
B. In amphibians that are primarily aquatic, lungs serve as hydrostatic organs.
C. In aquatic species lacking gills, respiration is handled by the pharyngoesophageal lining primarily & by the skin.
D. Terrestrial amphibians only utilize the lungs for respiration.
E. The internal lining may be smooth throughout or it may have outpocketings throughout.
D. Terrestrial amphibians only utilize the lungs for respiration.
True or False: Ventilation mechanisms are different in birds resting vs when birds are flying. When in flight, the intercostal muscles contract to increase the coelomic space, which causes negative pressure & inspiration. The opposite occurs when expiration occurs.
FALSE
Ventilation mechanisms are different in birds resting vs when birds are flying. WHEN AT REST, the intercostal muscles contract to increase the coelomic space, which causes negative pressure & inspiration. The opposite occurs when expiration occurs.
True or False: Ventilation mechanisms are different in birds resting vs when birds are flying. When in flight, appendicular muscles contracting will cause inspiration & expiration.
TRUE
True or False: Most elasmobranchs have 4 holobranchs & 5 gill chambers.
FALSE
Most BONY FISHES have 4 holobranchs & 5 gill chambers.
Which of the following is NOT true about the gills in lampreys?
A. The naris connects to the nasopharyngeal duct, as in hagfish.
B. They move respiratory water in & out of the external gill slits.
C. The external gill apertures are guarded by thin flaps of skin that serve as two-way valves.
D. Water enters & exits the pharyngeal pouches by pulsations of pouch musculature.
E. The nasopharyngeal duct terminates & connects to the pharyngeal pouches.
E. The nasopharyngeal duct terminates & connects to the pharyngeal pouches.