OB Study Guide
1/360
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
361 Terms
What is conception through the 8th week of gestation?
Embryo
What is the 9th week of gestation to delivery?
Fetus
What is Primigravida (Primip)?
First pregnancy
What is the Multigravida (Multip)?
2+ pregnancies
What is the fetal demise after 20 weeks gestation?
*early 20-27 wks, late 28-36 wks, term ≥37 wks
Stillbirth
What is a low birth weight?
≤ 2500 g (5 lb 8 oz)
What is a normal birth weight?
2500 - 4500 g
What is a high birth weight (fetal macrosomia)?
≥ 4500 g (8 lbs 13 oz)
What is considered an immature infant?
Completed weeks 20 - <28
What is considered a preterm infant?
Born before 37 weeks
(premature = completed weeks 28 - < 37)
What is considered a post mature infant (post dates)?
Completed 42 weeks
What is considered a full term (mature) infant?
37 - 42 weeks
When can a fetus survive outside of the womb?
22 weeks
What is the MCC of secondary amenorrhea?
Pregnancy
What is the first trimester?
Conception - 12 weeks & 6 days
What is the second trimester?
13 weeks - 27 weeks & 6 days
What is the third trimester?
28 weeks until full delivery
How long does normal human pregnancy last?
280 days / 40 weeks / 10 months
How is the estimated due date (EDD) from LMP calculated?
Nagele’s rule → take the 1st day of LMP, subtract 3 mos, add 7 days and add 1 year
How do you calculate GA from EDD?
[280 - (EDD - reference date)] / 7
What is gravida?
Number of times pregnant, carried to term or not
How many gravidas & paras do twins / multituplets count as?
1
What is Para?
Number of births that occurred after 20 weeks, viable or nonviable
What are the subcategories of Para?
Full term: ≥ 37 wks
Premature birth: 20-36 wks & 6 days
Abortion/miscarriages: < 20 wks
Living children
What is the GPA classification?
Gravida, para, abortus
How are fundal heights calculated?
Measure the distance from the superior edge of the pubic symphysis to the palpable fundus of the uterus (cm w/ soft tape measure)
*heights roughly correlate w/ gestational dates
What is the fundal height from 20 weeks to 36 weeks gestation?
Distance = weeks of gestation +/- 2
(ex: 24 weeks = 24 cm +/- 2cm)
What is the landmark to determine uterine size at 8 weeks?
Palpable at pubic symphysis
What is the landmark to determine uterine size at 12 weeks?
Becomes an abdominal organ
What is the landmark to determine uterine size at 16 weeks?
Midpoint between pubic symphysis and umbilicus
What is the landmark to determine uterine size at 20 weeks?
At umbilicus
What is the landmark to determine uterine size at 26-34 weeks?
Fundal height correlates with GA (± 2)
What is the landmark to determine uterine size at 36-40 weeks?
Decrease in fundal height
What is a normal FHT?
120-160 bpm
If in the 1st trimester, the US dating measures > 1 week difference GA than calculated by LMP, which do you go with?
US
If in the 2nd trimester, the US dating measures > 2 week difference GA than calculated by LMP, which do you go with?
US
If in the 3rd trimester, the US dating measures > 3 week difference GA than calculated by LMP, which do you go with?
US
In general, if there is no difference in GA calculations, should you stick with US or LMP?
LMP
What does a lecithin:sphingomyelin (L:S) ratio of 2:1 indicate?
Lung maturity
What does a L:S ratio of < 2:1 indicate?
Immature lungs → consider maternal steroid injection to decrease risk of of NRDS if in labor
What is one of the last fetal surfactants to develop (≥37 weeks), but is a less reliable indicator of lung maturity if the mother is diabetic or if amniotic fluid is contaminated?
Phosphatidylglycerol (PG) presence
When should the first obstetric US be done?
≥ 6 weeks→ earlier than this may be prior to cardiac development & can’t detect FHT or determine viability
*TV if < 6 wks, TA if > 6 wks
What is the first line RX for syphillis in pregnancy?
PCN
What is the first line RX for chlamydia in pregnancy?
Azithromycin
What is the first line RX for gonorrhea in pregnancy?
Ceftriaxone
What is the first line RX for HSV in pregnancy?
PO suppressive therapy at 35-36 wks; C section if active lesions
What is the first line RX for trichomoniasis in pregnancy?
Metronidazole (category B)
What is the first line RX for candidiasis in pregnancy?
Miconazole cream
What is the first line RX for BV in pregnancy?
Metronidazole (category B) after first trimester
What is used to assess fetal positioning in the 3rd trimester?
Leopold’s maneuvers
When is is nuchal translucency (NT) US screening completed to measure fetus’s nuchal fold thickness?
11-13 wks
> 3.33 mm = soft marker for down syndrome
What is non-invasive prenatal testing/screening (NIPT)?
*blood test- MaterniT21, integrated screening
Screening for chromosomal fetal abnormalities between 10-20 wks
*inaccurate before 10 wks d/t insufficient fetal fraction
What does MaterniT21 evaluate for?
Common trisomies, select microdeletions (22q, 15q), rare sex aneuploidies, & fetal sex
*does NOT evaluate for open neural tube deficits
What is integrated screening?
Combines maternal age risk, 1st trimester NT, & serum PAPP-A w/ 2nd trimester measurements of AFP, uE3, hCG, & DIA
*provides risk assessments for Down syndrome, open spina bifida, & trisomy 18
What has the highest detection rate and lowest false positive rate of detecting pregnancies with Down syndrome?
Integrated screening
When is the maternal serum alpha fetoprotein (AFP) level drawn?
15-21 wks (18 is most accurate)
What protein is produced by the fetal liver & yolk sac & is drawn during the second trimester to look for an increased risk of neural tube defects such as spina bifida?
AFP
In what conditions is the maternal serum AFP increased or decreased?
Elevated in spina bifida
Low in trisomy 18 & 21
When is the fetal anatomy screening by US completed to check fluid levels, growth, viability, & detect anatomic abnormalities suggestive of aneupolides and congenital defects?
18-21 wks (20 preferred)
When is the simple glucose challenge test (GCT) performed to screen for GDM?
24-28 weeks
How is the simple GCT test performed?
Nonfasting pt drinks 50g glucose soln & blood sugar is measured at 1 hr
*positive if > 140 → do a 3 hr GTT
What risks are associated with GDM?
Macrocosmic or LGA (> 9 lbs), birth comps, shoulder dystocia, preterm delivery, still birth, maternal risk of T2DM PP
What test performed at 15-20 wks (not routine) allows for the collection of amniotic fluid to provide a sample of fetal DNA to diagnose potential genetic defects?
*risk of clubfoot if performed before 15 wks
Amniocentesis
When is the US screening completed in the 3rd trimester to help determine final positioning of the fetus?
~ 36 weeks
When should a routine rectovaginal swab culture be performed to check for GBS?
35-37 wks
What is there an increased risk of if a pregnant woman has a GBS infection?
Preterm labor, amnionitis, endometritis, maternal wound infx, & transmission during delivery causing generalize sepsis of the newborn
What is the treatment for GBS in pregnancy?
1st line: PCN
Allergy: need a C&S to guide tx d/t resistance (macrolide)
When is a biophysical profile (BPP) completed in pregnancy?
32 weeks (sometimes earlier) in high risk pregnancy
After 40 wks in normal pregnancy
What does a biophysical profile (BPP) evaluate?
Fetal breathing, gross fetal tones, gross fetal movements, amniotic fluid levels, & NST (fetal HR monitoring w/o stress/contraction)
*each worth 2 pts; 10 pts total
What is a good or reassuring BPP score?
8-10
What BPP score may indicate early delivery and should be retested in 12-24 hours?
6-7
What BPP score is concerning & requires immediate management?
≤ 5
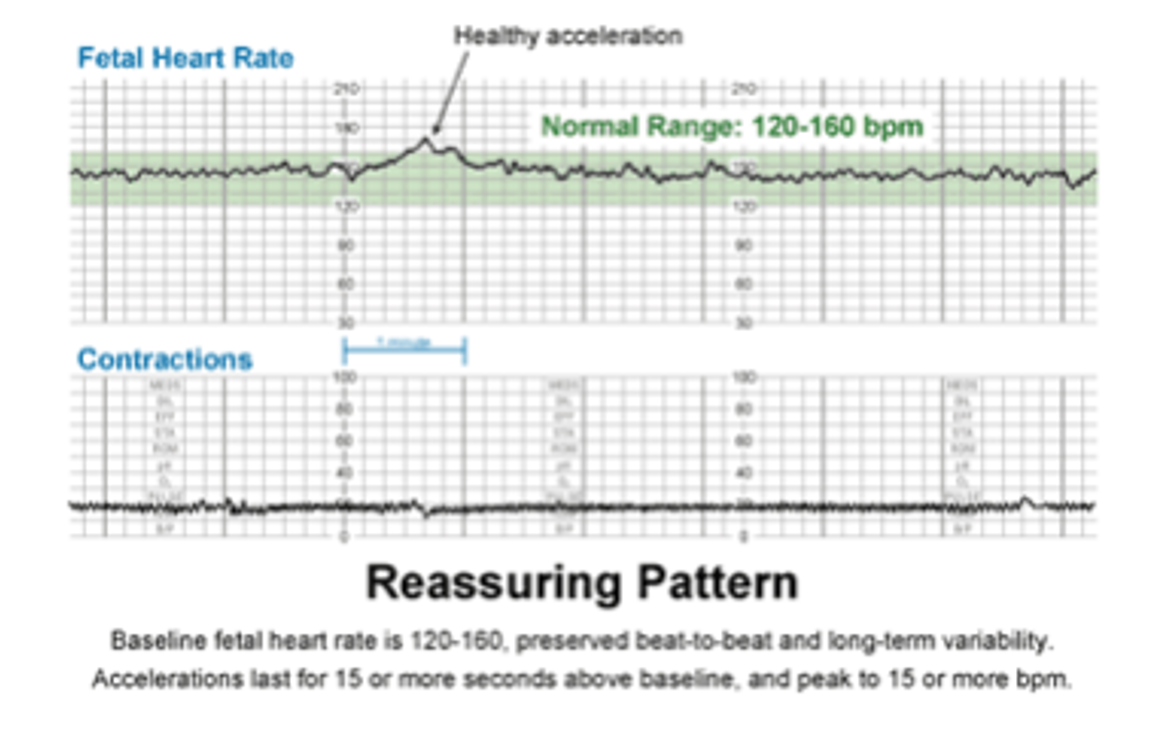
What test utilizes a fetal monitor to measure cardio accelerative response (FHR) in response to fetal movement, and is most reliable after 28-32 wks?
Non-stress test (NST)
What is the criteria for a reactive NST?
Baseline FHR 120-160 bpm
Presence of periodic accelerations (2 accelerations w/in 20 minutes) w/ increases of 15 bpm for 15s
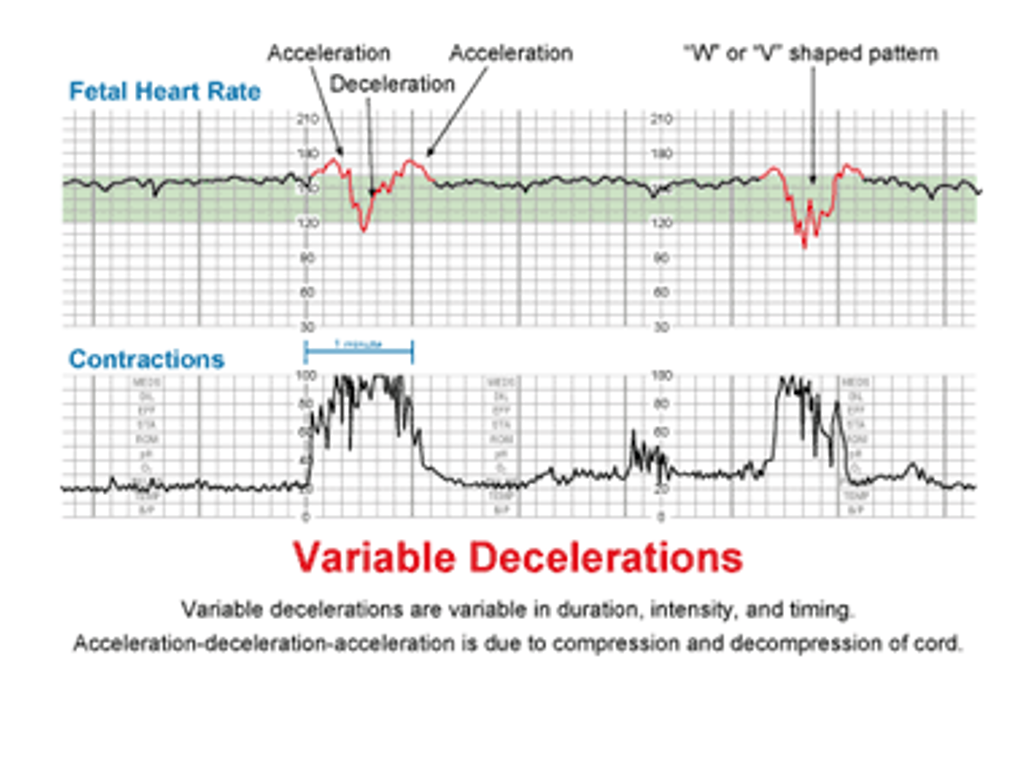
What is the criteria for an abnormal (non-reactive) NST?
Absence of accelerations or presence of sporadic repeated decelerations of FHR
What vaccinations should be AVOIDED in pregnancy?
Live virus or bacterial → MMR, yellow fever, BCG, varicella, oral polio
What vaccines are okay to give in pregnancy?
Tdap (27-36 wks if no UTD), Hep A, Hep B, flu & pneumovax
*use caution w/ inactivated or assembled vaccines
How often should Tdap vaccinations be updated?
Mom: once each pregnancy no matter when the last one was (~ 27-36 wks no UTD)
Anyone of age that will be around the baby after delivery: every 10 yrs
What prenatal vitamins are recommended for pregnancy?
*important for fetal neuro development
400-800 mcg Folate (1 mg if prescription), 40 mg elemental iron, & DHA omega 3
What kind of twin?
2 separate chorions & amniotic sacs
MC w/ fraternal twins
lowest mortality risk (but still higher than singletons)
form when spitting takes place by the 3rd day after fertilization
Dichorionic-Diamiotic (DiDi)
What kind of twins?
share the same placenta, have 2 amniotic sacs
MC w/ identical twins
occurs on days 4-8
Monochorionic Diamniotic (MoDi)
What is an increase in saliva production secondary to a placental hormone?
*tx: mints, gum, small frequent meals & sips of water, Nexium
Ptyalism
What condition is characterized by severe/refractory N/V that can lead to dehydration, hypovolemia, electrolyte imbalances, ketosis, weight loss & erosion of enamel?
Hyperemesis Gravidarum
What is the treatment for mild-moderate Hyperemesis Gravidarum (HG)?
PO fluids w/ elytes, ginger, unisom/B6, magnesium (PO/TD), antiemetics - zofran, reglan, promethazine rectal suppository
What is the treatment for moderate-severe HG?
Reglan, promethazine, IV zofran pump & IVFs at home (w/ home nurse)
Hospitalization & IV fluid transfusion if refractory
Low dose prednisolone if severe & not responding to antiemetics
What is the pathophysiology of gallbladder dysfunction associated with pregnancy?
Inc estrogen → inc cholesterol & lecithin → cholesterol supersat & crystallization → Cholelithiasis
Progesteron & relaxin → relaxes SM → less GB contraction → Cholestasis
*both inc risk of cholecystitis & choledocholithiasis
What condition?
3rd trimester; d/t increased estrogen & other hormones that reduce bile transport through the liver
lack of bile salts → dec fat digestion & absorption of fat soluble vitamins
bile back up in blood → hyperbilirubinemia & maternal & fetal comps
dx:
CMP: elevated LFTs, ALP, total & direct bili
Bile acids: increased
PTT: prolonged d/t poor vit K absorption
GGT: normal
Intrahepatic cholestasis
What sx are associated with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy?
Generalize pruritus worst on palms/soles & at night, secondary insomnia, RUQ pain, N, dec appetite, steatorrhea, encepahlopathy (severe)
What is the treatment for intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy?
Ursodeoxycholic acid until delivery; resolves w/ delivery of child
What causes hypercoagulability in pregnancy?
Inc in estrogen, factor VII, fibrinogen, thrombin
Dec in protein S (an anticoagulant)
*inc risk of VT: 2x during pregnancy, 5.5x puerperium
What is peripartum cardiomyopathy?
Specific type of dilated cardiomyopathy when other causes outside of pregnancy can’t be found; MC in mothers > 30 y/o
*may be d/t inc BV, pre-load, & HR
What may be an issue for asthmatics during pregnancy?
Mucosal hyperemia secondary to inc blood volume & overall vasodilation → congestion & inc secretions
How is renal function affected in pregnancy?
Increase: renal plasma flow, GFR, plasma renin, angiotensin, CrCl
Decrease: serum cr, uric acid, & BUN
What does increased GFR in pregnancy cause?
Inc load of glucose in renal tubules → inc glucose excretion
What effect does progesterone have on the bladder during pregnancy?
Dec bladder tone → inc residual volume → dilation of collecting system → increased risk of urinary stasis → increased risk of UTI & pyelonephritis in pts w/ asx bacteriuria
What does the increased amount estrogen and glucose in the urine during pregnancy increase the risk of?
Bacteria overgrowth & UTIs
What bone changes are seen in pregnancy?
Increase: PTH, bone turnover, ALP, (no change in bone density)
Decrease: serum Ca (hemodilution)
In what trimester are headaches common and often due to caffeine withdrawal?
First trimester
Headaches starting in which trimester can be a sign of pre-eclampsia?
Second trimester
What is Chadwicks sign?
Blue discoloration of vulva, vagina, and/or vaginal portion of cervix