Buddhism
Buddhism Basics
- Originated in India as an offshoot of Hinduism
- Believes that the human condition is sick and needs a cure
- Gautama Buddha “the enlightened one”
- Stories of Buddha’s life were recorded centuries after his death
- Born around 560 BCE, died around 480 BCE
- Warrior Class; Feudal Lord (very privileged)
- Parents made sure he never encountered any suffering
The Four Passing Sights
- Left home to see the world in his early 20’s
- Parents got rid of slums etc. to ensure that Buddha didn’t see anything that would distress him; didn’t work
Elderly
Disease
Death
Ascetic
- Someone who draws away from worldly/physical pleasures to develop spiritually
- At age 29, Buddha left the castle and everything he knew
- “The [Great] Going Forth”
- left to solve old age/disease/death
- Attempts to solve old age and death
- Solitude
- Extreme fasting
- Yoga
- Comes up with the Middle Way
The Middle Way
- Rejection both extremes of life (sensual indulgence and asceticism)
- Don’t live excessively or completely ignore your own needs
- Spiritual health and physical health are united
Enlightenment
- Sat in Lotus position under Bodhi Tree (Wisdom Tree)
- Battled Gods, Death, Discontent, Delight, Desire
- Each of these tempts him off the path of Enlightenment, so he has to overcome them
Stages of Enlightenment
- 1: Can see past lives through meditation
- 2: See death/rebirth of all things
- 3: The Four Noble Truths are revealed
Temptation
- Buddha was tempted to pass into Nirvana but resists
- Nirvana: The extinction/letting go of any desires and individual self-worth
- Buddha was compassionate and teaching
- Described self as “awake”
Buddhism in Practice
Buddha’s Followers
- 5 people followed him and became saints (arhats)
- Founded Sanga
3 Jewels of Buddhism
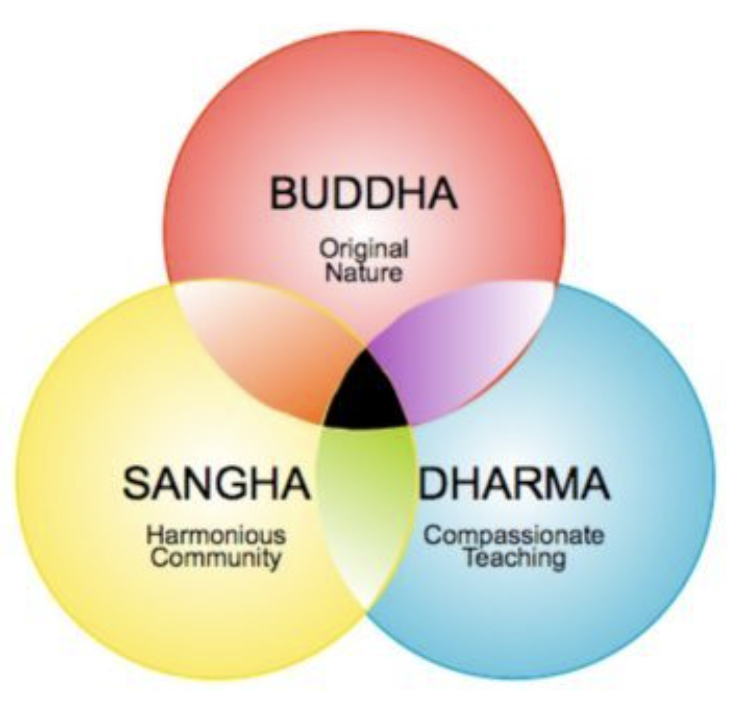
Buddha: Founded Buddhism
Dharma: Teachings of Buddha, how he lived his life
The universe is eternally created and destroyed (Hinduism)
- Were many Buddhas before and many will follow
- Samsara: The continuous cycle of birth and death
Rejects sacrificial system to the gods/goddesses
Rejects caste system and segmentation of society; allows women to have status
Rejects education (barrier to entry for religion; not accessible for everyone)
- Wrote in Pali: the ancient language of common Indians
Center of Dharma wheel = spiritual balance achieved through teachings
Sangha: The community and life of person themself
Destiny
- Discover inner realm of self to achieve Nirvana
- Everything within and outside of self is changing
- Accept that not everything about self is real
- Three Marks of Existence
- Anatta: There is no self
- Opposite of the Hinduism
- There is no Atman, Brahman, self, essence, ultimate reality
- We don’t have souls, there is only the now
- Anicca: Impermanence
- Existence is constantly changing
- Eg. nature of the river is flowing → you will never step in the same river twice
- Dukka: Suffering
- Result of other two marks
- Suffering exists because people can’t let go/go with the flow → creates suffering for self
- Must detach, see everything as loose and changing, don’t try to grasp
- Karma
- Same in Buddhism and Hinduism
- Basic Karma rules of Buddhism:
- What is wrong is the intention (why) of a moral act, not the outcome
Four Noble Truths
To live life is to experience dukka
- Discomfort, things are not as they should be
- The more attachment you have, the more you will suffer
- Circumstances in live (chance), stages of growth and development, sickness, old age, all will die, unfulfilled wishes
Suffering is caused by tanha
- Tanha: our personal thirsts and desires
- Self desire, personal fulfillment — increases dukka and tanha
- We are naturally selfish
Suffering can stop
Solution to suffering: the Eightfold Path
- The Eightfold Path: The basic practices of Buddhism that can lead you to Nirvana
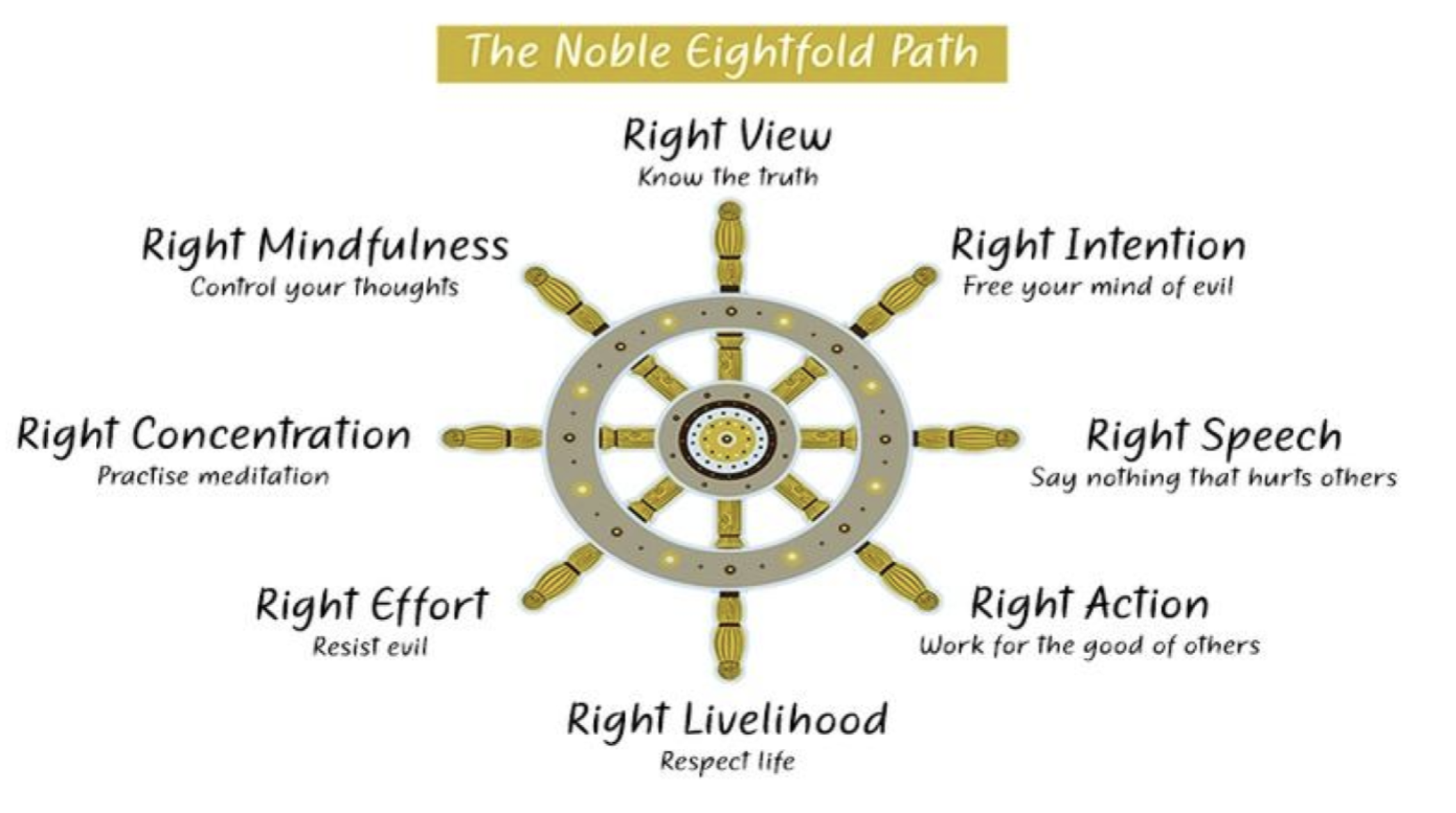
Enlightenment and Nirvana
- Final Nirvana happens at bodily death
- Arhat: one who is enlightened/awakened
- If you attain it, you see that there is no self, and you are free from tanha and dukka
- Buddhas do not need followers or models to attain Nirvana
- Nirvana is impossible to describe
Three Ways of Buddhism
- Theravada: The Way of the Elders
- There are no gods or goddesses to help you
- Buddha is the first to experience enlightenment
- The teachings of Buddha are the most important thing
- Nirvana is attainable by your own effort
- Mahayana: The Great Vehicle
- Largest sect of Buddhism
- See Buddha as a divine savior
- Primary teaching: foster compassion
- Didn’t enter Nirvana immediately
- Goal: become a bodhisatva
- Bodhisatva: a Buddha in the making
- Can enter Nirvana but stop short to help others
- Extend beyond the earthly realm
- Wait to enter Nirvana until the last blade of grass becomes enlightened
- Vajrayana
- Diamond sector teaching of Buddhism - harness
- Teachings are full of energy, strength, clarity
- Mandala: a pattern of icons/images that visually excite to enhance meditation
- Mudras: choreographed hand movements used in ritual
- Mantra: a sacred utterance (syllable, word, or verse) that is considered to possess mystical or spiritual efficacy
- Rituals are important
- Talk with gods/goddesses to achieve union with them and nirvana
- Dalai Lama
- Spiritual leader of Vajrayana Buddhism
- 14th reincarnation of bodhisattva