Concept 23.3: Natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow can alter allele frequencies in a population
1/6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
State at which a population is not evolving, given the required conditions of no mutations, random mating, no natural selection, large population size, and no gene flow
Most affected by:
Natural selection
Genetic drift
Gene flow
Natural selection
Process in nature based on differential success in survival and reproduction
Traits better suited to the environment produce more offspring than others, resulting in different proportions
Adaptive evolution
A process in which traits that enhance survival or reproduction increase in frequency over time as a result of natural selection
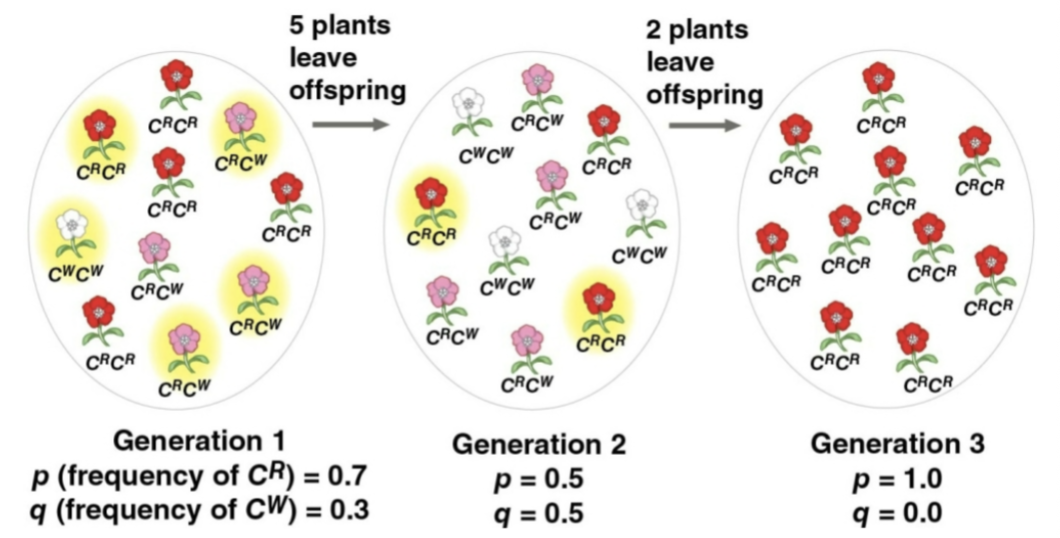
Genetic drift
A process in which chance events cause allele frequencies to fluctuate unpredictably from one generation to the next
Tends to reduce genetic variation through the random loss of alleles
More significant in small populations; can lead to the fixation of harmful alleles
Founder effect
Occurring when a few individuals become isolated from a larger population, allele frequencies in the smaller population are different from those in the parent population
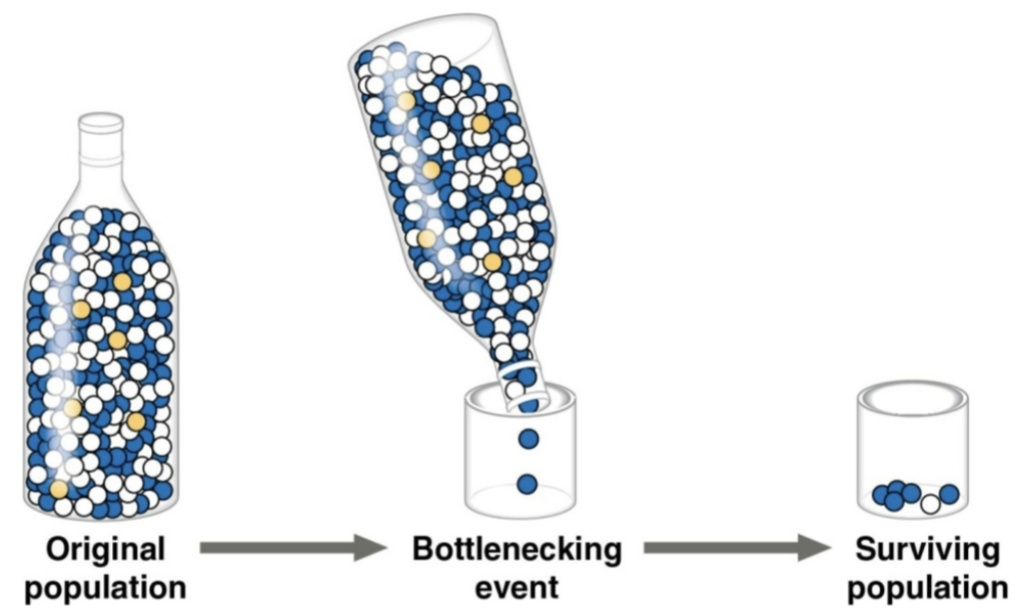
Bottleneck effect
Occurring when there is a drastic reduction in population size due to a sudden change in the environment, the resulting gene pool may no longer be reflective of the original population’s gene pool
Seen with the severe reduction of prairie chicken habitats in Illinois leading to low genetic variation and an increase in the frequency of harmful alleles; solved through the introduction of birds from other populations leading to better egg-hatching rates
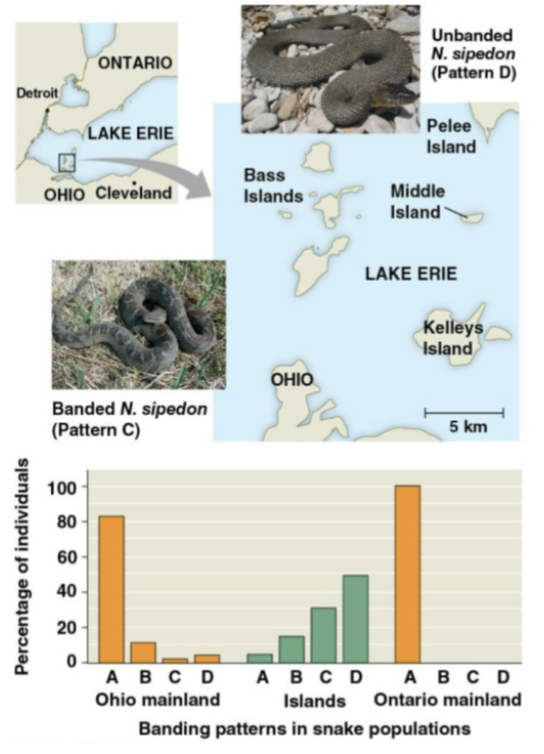
Gene flow
The movement of alleles among populations, transferred through the movement of fertile individuals or gametes
Tends to reduce variation among populations over time
Can affect adaptation to local environments or different threats in varying ways due to these new traits