Body Fluid Analysis
1/335
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
336 Terms
Gives three-dimensional images, but high cost prevents use by most laboratories
Interference contrast
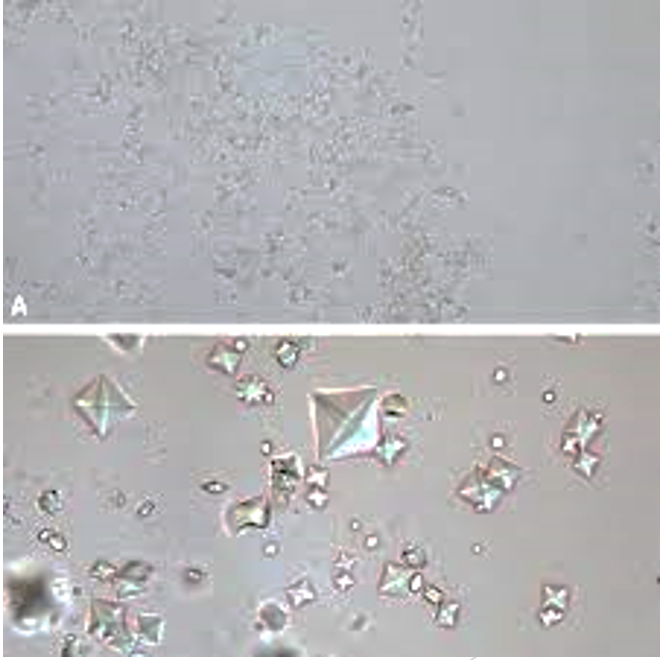
Confirms presence of cholesterol, which forms a Maltese cross pattern with polarized light; also used on crystals
polarizing
Ideal for urine sediments; allows more detailed visualization of translucent or low-refractile components and living cells
phase contrast
Most commonly used microscope
brightfield
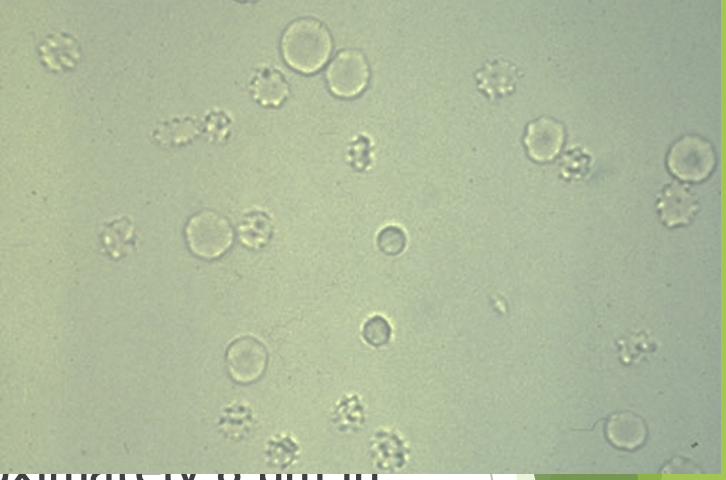
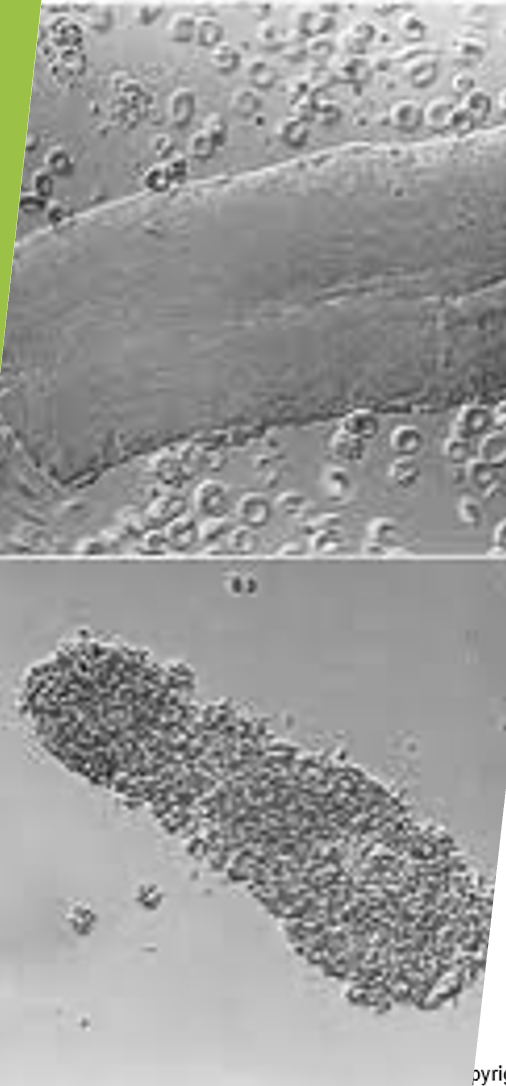
red blood cells
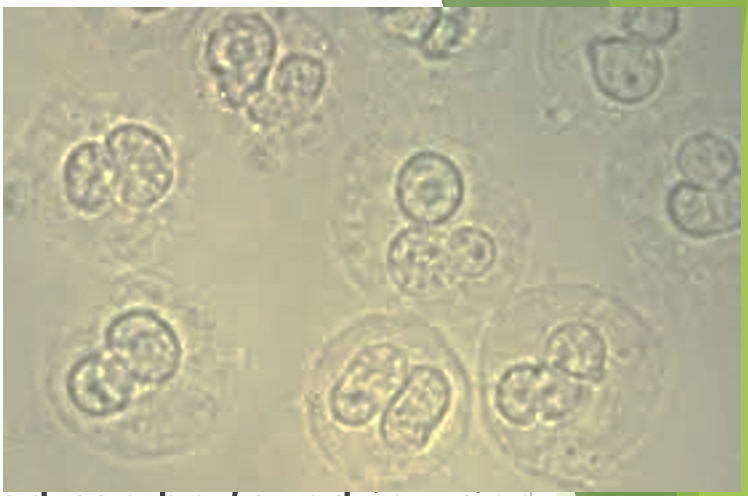
white blood cells
white blood cells
Protects fetus while enabling movement and produced by amnion and placenta initially
amniotic fluid
Transabdominally or vaginally with simultaneous ultrasound examination
Transabdominal most common
ambiocentasis
bilrubin is
light sensitive
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) has higher levels of what than does plasma
sodium, chloride, and magnesium
CSF has lower concentration of what then plasma
potassium and calcium
Brain and spinal cord surrounded by three membranes called
meninges
Increased numbers of capillary endothelial, mesangial, and epithelial cells in glomerular tuft
Cellular proliferation
Neutrophils and macrophages attracted by a local chemotactic response
leukocytic infiltration
Any process that results in enlargement of basement membrane (immune complexes and diabetes)
Glomerular basement thickening
Accumulation of homogeneous eosinophilic extracellular material
Hyalinization with sclerosis
Most often immune mediated
glomerular
Result from toxic or infectious substances
tubular
Result from toxic or infectious substances
interstitial
Caused by a reduction in renal perfusion that induces morphologic and functional changes in kidney
vascular
Systemic diseases that initially and principally involve other organs but also affect kidneys
secondary glomerular diseases
Specifically affect kidneys, often only organ involved
primary glomerular diseases
•Primary diseases consist of several different types of
glomerulonephritis
hematuria, proteinuria, oliguria, azotemia, edema, and hypertension are all clinical features of
glomerular diseases
blood in urine
hematuria
protein in urine
proteinuria
limited output, less than 400 mL/day
oliguria
Elevated levels of urea and other nitrogen compounds in the blood
azotemia
greater than 3L/day, a lot of pee
polyuria
ADH decreased
Neurogenic diabetes insipidus
Lack of renal response to ADH
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
Used to differentiate causes of polyuria due to water diuresis
Fluid deprivation tests
heavy proteinuria, hypoprotenemia, hyperlipidemia, lipiduria, edema, mild hematuria and fatty, waxy, and renal tubular epithelial casts are all signs of what
nephrotic syndrome
immnoglobulin A (IgA) neuropathy and minimal change disease are all types of what
glomerulonephritis
Autoimmune disorder with immune complex deposits and complement activation
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Carbohydrate metabolism disorder leads to glomerular syndrome, hypertension, susceptibility to pyelonephritis
diabetes mellitus
Systemic disease involving many organs; characterized by deposits of amyloid, a pathologic protein substance
amyloidosis
amyloidosis leads to what
proteinuria and nephrotic syndrome
Seen in sepsis, shock, trauma
Ischemic ATN
From exogenous or endogenous nephrotoxins
Toxic ATN
Fanconi’s syndrome, Cystinosis and cystinuria, Renal glucosuria, Renal phosphaturia, and Renal tubular acidosis are all signs of what
tubular dysfunction
Urinary tract infections (UTIs), Acute pyelonephritis, Chronic pyelonephritis, Acute interstitial nephritis, and Yeast infections are examples of what
Tubulointerstitial disease/infections
-Sudden decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR), azotemia, and oliguria
-Functional abnormality; but no cellular changes
-Classified as prerenal, renal, and postrenal
Acute renal failure
-Progressive loss of renal function
-Due to hypertrophy of remaining healthy nephrons, not clinically recognizable until 80% to 85% function lost
Chronic renal failure
Azotemia, acid-base imbalance, abnormal calcium (Ca) and phosphate (PO4) metabolism is indicative of what
Chronic renal failure
Chronic renal failure causes what
abnormal calcium (Ca) and phosphate (PO4) metabolism
how much of renal calculi contain calcium
75%
what are the factors that influence calculi formati
-Supersaturation of chemical salts in urine
-Optimal urinary pH
-Urinary stasis
-Nucleation or original crystal formation
Renal Calculi is found primarily where
renal calyces, renal pelvis, ureters, or bladder
Cystinosis and cystinuria, Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD), Phenylketonuria (PKU), Alkaptonuria, Tyrosinuria, and Melanuria are examples of what
Amino Acid Metabolism Disorders
Problems with glucose metabolism
Diabetes mellitus
what is a long term effect of Diabetes mellitus
glomerular damage and chronic renal failure
Decreased antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or nephrons are resistant to ADH
Diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus results in
polyuria
Hereditary defects of heme synthesis pathway. Increased porphyrins and porphyrin precursors in blood and urine
porphyrias
the analytical detection method used to screen for the substances produced in the many metabolic disorders
Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS)
used to screen for inherited metabolic disorders
Heel stick blood samples from neonates
outer layer next to bone
dura mater
middle layer resembling a spiderweb
Arachnoid mater
innermost layer adhering to surface of neural tissues
Pia mater
flows in subarachnoid space between arachnoid mater and pia mater, where it bathes and protects brain and spinal cord
CSF
Interface between blood and CSF called
blood-brain barrier
CSF forms, circulates, and is reabsorbed into ______, dynamically turning over ______ each hour
blood, 20 mL
If reabsorption process is blocked, CSF does what
builds up causing hydrocephalus
Collected by aseptic lumbar puncture in third or fourth lumbar interspace with local anesthesia
CSF collection
for csf testing what are the labeled tubes
chemistry, microbiology, cell counts
Normal what is clear and colorless with viscosity like water
CSF
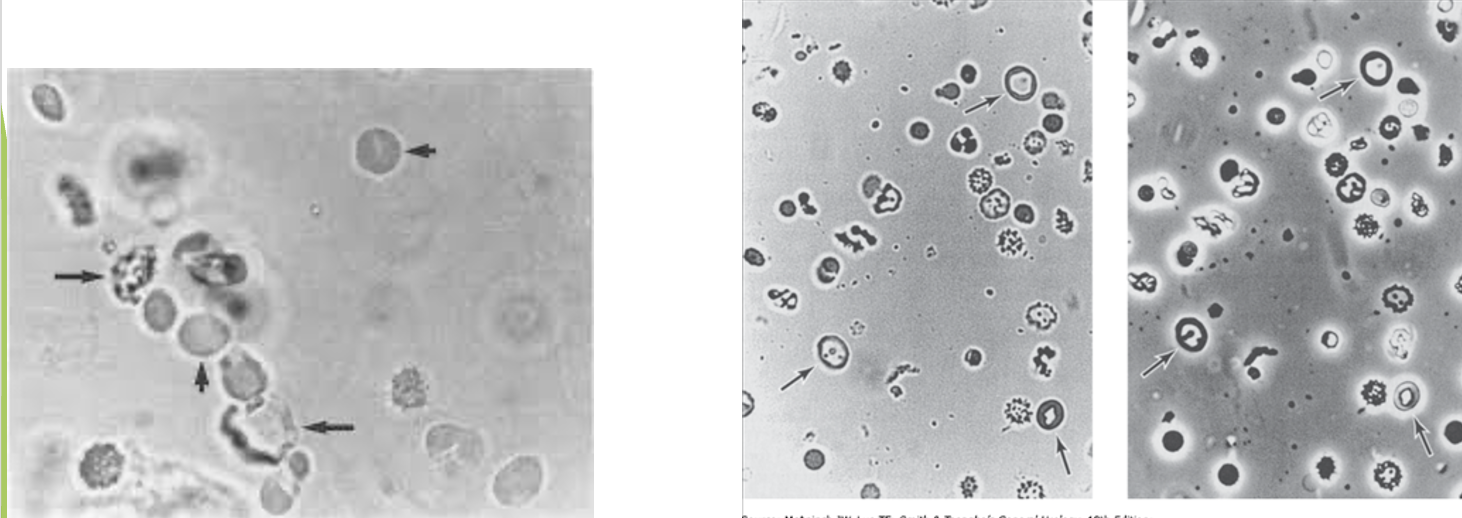
increased number of cells in CSF
Pleocytosis
Cloudy CSF associated with white blood cells (WBCs)
greater than 200 cells/mL
Cloudy CSF associated with red blood cells (RBCs)
greater than 400 cells/mL
Microorganisms or increased protein can cause
cloudy CSF
abnormal color of CSF, usually yellow, orange, or pink due to various conditions
Xanthochromia
in Traumatic tap what has the greatest amount of blood and the least
tube 1, tube 3
After centrifugation what is the traumatic tap’s supernatant
colorless supernatant
After centrifugation what is the hemorrrhage supernatant
xanthochromic supernatant
ØConsistent amount of blood in all three tubes
hemorrage
Macrophages stain positive for _______ and may include _________
hemosiderin, hematoidin crystals
In adults, normal cell count is ______ white blood cells per microliter (WBCs/μL), specifically ______
0 to 5; lymphocytes and monocytes
Cell counts performed immediately to prevent lysing of WBCs; lysing slowed at
4 C
what is not normally present in microscopic examination
RBCs
If dilution needed, use
normal saline
Increased in diseases of central nervous system (CNS) and variety of other conditions
white blood cell counts
CSF diluted with _______ to lyse RBCs
2% acetic acid
In bacterial meningitis, up to 90% of WBCs can be
neutrophils
Increased in viral, TB, fungal, or syphilitic meningitis particularly in later stages
lymphocytes
Increased in viral, TB, fungal, or syphilitic meningitis particularly in later stages
neutrophils
Are abnormal when seen in multiple sclerosis and acute viral and chronic inflammatory conditions
plasma cells
May be increased in a mixed cell pattern such as TB or fungal meningitis, chronic bacterial meningitis, or rupture of cerebral abscess
monocytes
-10% or greater with parasitic, fungal, or allergic reactions
-Following injection of radiographic contrast media or medications
-Can also result from an allergic reaction to malfunctioning intracranial shunts
eosinophils
Often found after hemorrhage because of phagocytic ability
macrophages
Total Protein in Cerebrospinal Fluid is normall y
15 to 45 mg/dL
Increased in CSF from
-Contamination with blood during traumatic tap
-Change in blood-brain barrier
-Decreased reabsorption into venous blood
-Increased synthesis in CNS
Bacterial, viral, and other forms of meningitis, Cerebral infarction, Hemorrhage, Endocrine disorders, Multiple sclerosis, Obstruction of CSF flow, Trauma all results from
Increased protein seen in numerous disorders
-Increased reabsorption because of increased intracranial pressure
-Loss of fluid because of trauma or invasive procedures
decreased protein
Used to assess permeability of blood-brain barrier
Fluid (CSF)/Serum Albumin Index
Values greater than this range of Immunoglobulin G (IgG) index are associated with
increased intrathecal production of IgG
Values less than this range of Immunoglobulin G (IgG) index are associated with
indicate a compromised blood-brain barrier
indicate a compromised blood-brain barrier
.70