DNA Mutations and Base Repair Mechanisms
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Mutations
changes in DNA base sequence
Loss-of-function mutation
Gain-of-function mutation
Germline mutation
Somatic mutation
Conditional mutation
Reverse mutation
Splice mutation
DNA Mutations (8)
Base substitutions
Base insertion and deletion
Gene Mutations (2)
Transition
Transversion
Base substitutions
Frameshift mutation
Base insertion and deletion
Transition
Base Substitutions
purine-purine substitution or pyrimidine-pyrimidine substitution
Transversion
Base Substitutions
purine-pyrimidine substitution or vice versa
Thymine-guanine wobble
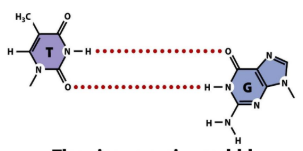
Cytosine-adenine protonated wobble

Base Substitutions
-Replication proceeds properly, resulting in one of the two new chromatids having the wrong base on both strands of its DNA
- During the next cell cycle, the strands with the mismatched bases serve as templates for DNA replication leading to incorporation of errors
strand slippage
Base Insertion and Deletion
Insertions and deletions may arise through _____________

Forward Mutation
Phenotypic Effects of Mutation
- wild-type to mutant
Reverse Mutation
Phenotypic Effects of Mutation
- mutant to wild-type
Missense
Phenotypic Effects of Mutation
- one Amino Acid to a different Amino Acid
Nonsense
Phenotypic Effects of Mutation
- Sense codon to a Nonsense (Stop) codon
Silent
Phenotypic Effects of Mutation
- Codon to a synonymous Codon (no change in Amino Acid)
Neutral
Phenotypic Effects of Mutation
- one Amino Acid to a new similar Amino Acid (no change in function)
Sickle cell anemia
Physical Example
– change in amino acid sequence causes the hemoglobin to crystalize at low O2 levels.
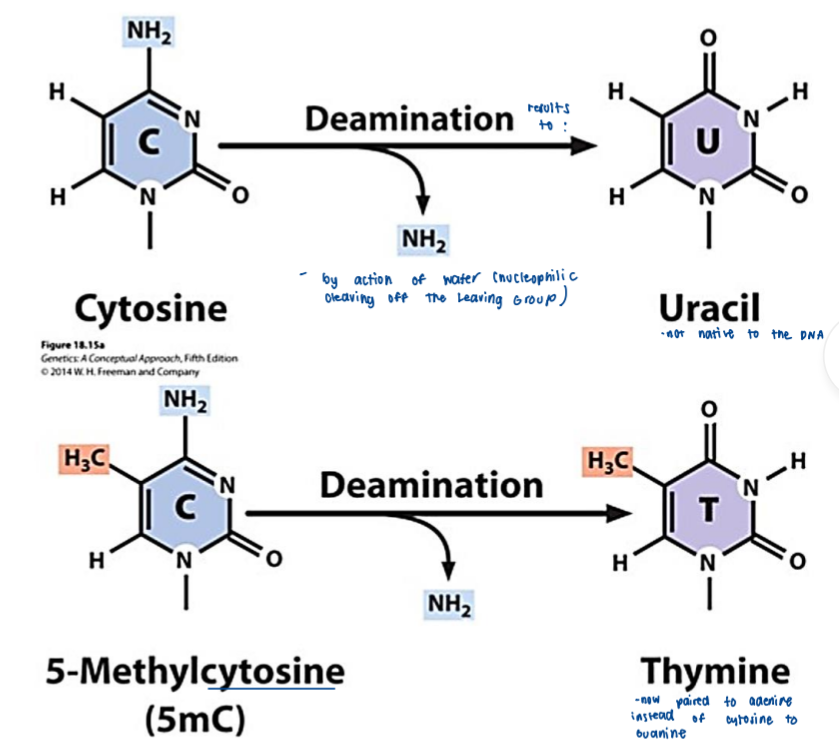
Spontaneous Modification
Base modifications caused by hydrolytic cleavage and other chemical reactions
Hydrolysis reactions
A
Spontaneous Modification
1. __________ remove purine (A and G) rings by cleaving the N-C glycosidic bond that holds them to the sugar
2. An _-containing nucleotide is usually incorporated across from the depurinated one during the next round of replication
Pyrimidines
__________ can be deaminated by hydrolysis of the NH2 group without requiring an enzyme
Mutagens
Base analogs
Induced Mutations
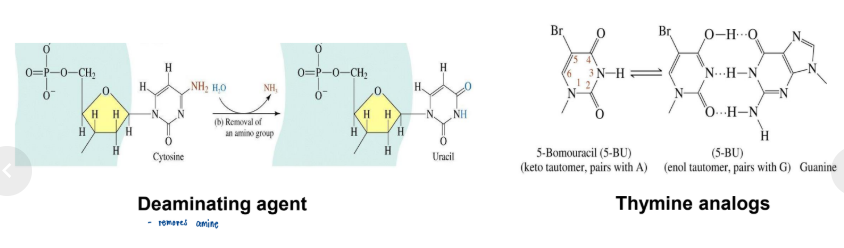
Mutagens
physical or chemical agents that causes mutation
Base analogs
chemical that can substitute for a normal base in the DNA.
5-bromouracil
Base analogs
- ____________ in the enol form pairs with G. G → C a transition mutation
Alkylating agents
Deaminating agents
Hydroxylaminating agents
Mutagens
- _________________, _____________, _____________ chemically change functional groups on the DNA bases
Alkylating agents
Deaminating agents
Hydroxylaminating agents
Intercalators
Reactive-oxygen species
UV light radiation
Mutagens
Intercalators
flat hydrophobic, usually aromatic molecules that insert between stacked base pairs in DNA
Reactive-oxygen species
free radicals
UV light radiation
brings the two neighboring nucleotides closer together, leaving the bases unable to bond with the bases from the other DNA strand
Repair Mechanisms
• DNA polymerase proofreads itself, but makes an error every approximately 10,000-100,000 nucleotides (104 – 105)
• After repair, the frequency of errant nucleotides is only approximately 1 in 1 billion (109) nucleotides
Base mismatch
Direct
Base excision
Nucleotide excision
Common repair mechanisms
Base mismatch repair
Mismatched bases and loops such as
those that lead to deletions and
duplications form bubbles in the DNA
double helix, which are recognized by
the repair systems

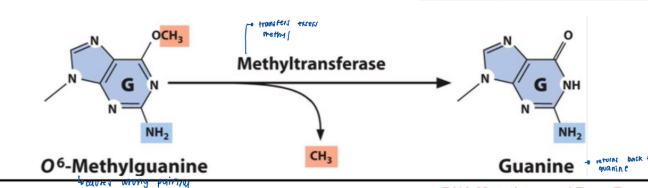
O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase
photolyase
• Alkylation can be reversed by_______________________
• In bacteria, _____breaks the bonds that
maintain pyrimidine dimers
• Thymine dimers can be repaired by photo-
reactivating enzymes
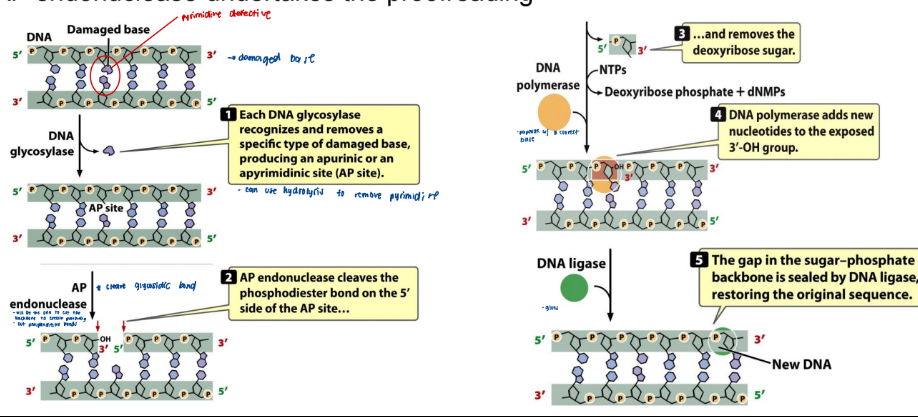
Base Excision Repair
• In eukaryotes, DNA poly B which has no proofreading ability, fills in the gap
• DNA poly B’s error rate is high enough to leave 10 new mutations uncorrected per day
• The AP endonuclease undertakes the proofreading
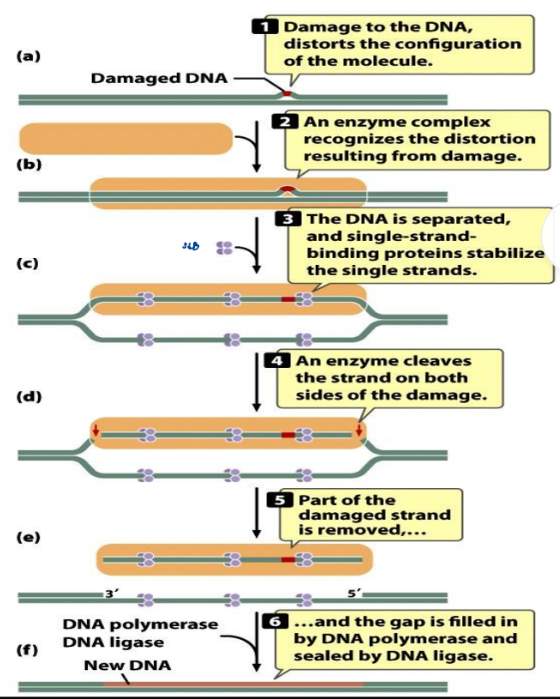
Nucleotide Excision Repair
Acts on pyrimidine dimers and large
distortions of the DNA helix
Antimutagens
decrease the frequency of mutations and inhibit the mutagenic effect of chemical or physical agents