Intramolecular Forces V.S. Intermolecular Forces
Molecular Forces
Intramolecular Forces- Forces between atoms that hold molecules together and determine the chemical behavior or substances
- Ionic
- Covalent
Intermolecular Forces- Forces between molecules
Dipole-dipole interactions
Hydrogen Bonding
London Dispersion Forces
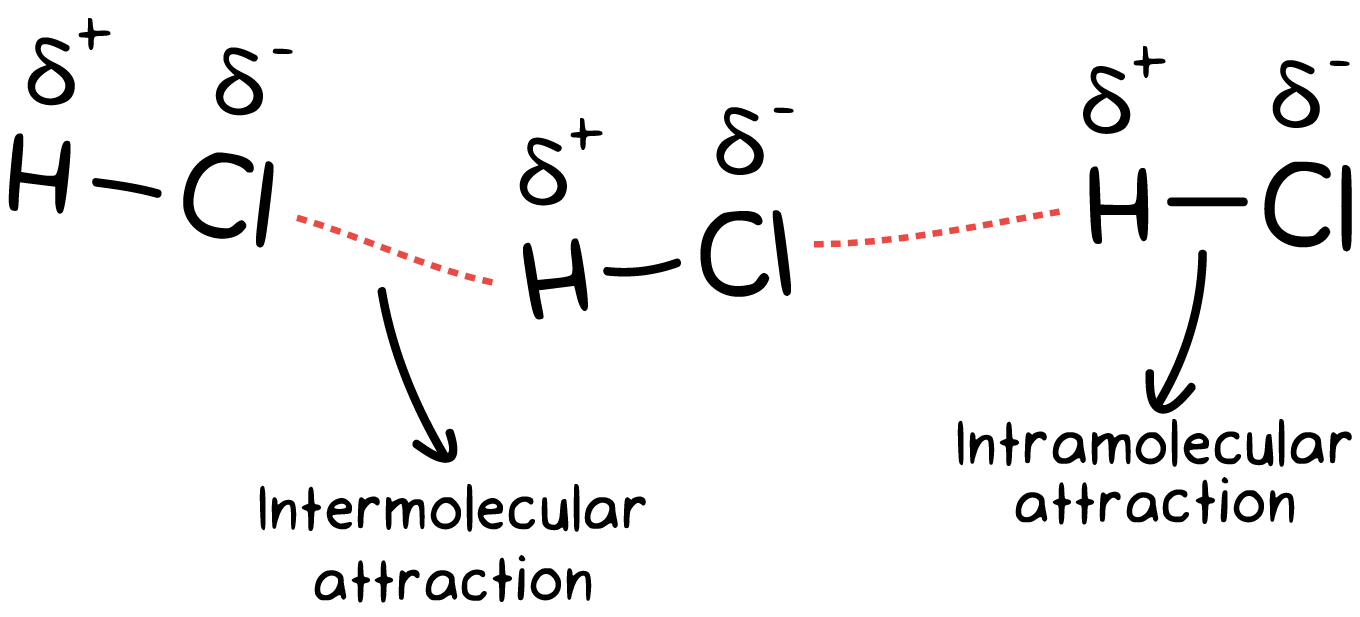
Intermolecular Forces
Much weaker than intramolecular bonds but they are important because they determine physical properties of the molecules :
-Melting Point
-Boiling Point
-Density
-Viscosity
-Volatility
There are three types of intermolecular forces
- Dipole-dipole interactions
- Hydrogen Bonding- Important in Water and DNA
- London Dispersion Forces
- More polarized bonds in a molecule results in greater intermolecular attractions
- Greater intermolecular attractions have higher melting and boiling points, greater viscosities, and lower volatiles than non-polar covalent compounds.
Examples: Honey and Syrup
Scenario: If I wanted to pour honey into a container, it would flow very slow. To quicken the process, I would need to heat up the honey to break/ weaken the intermolecular forces to make it flow quicker,
| Intermolecular Bonds | Intramolecular Forces | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Forces Between Molecules | Forces Between Atoms |
| Weaker or Stronger (Than Other Force | Weak | Strong |
| What Characteristics Do they Determine? | Physical (Heating up the substance can allow it to flow quicker, which changes its physical properties.) | Chemical (By breaking the intramolecular forces, it will split the atoms which will change the element that it is.) |
| Is it a Force or a Bond? | Force | Bond |
| Three Types | 1. Dipole-dipole Interactions \n 2. Hydrogen Bonding3. London Dispersion Forces | 1. Ionic2. Polar Covalent3. Non-Polar Covalent |
Strong V.S. Weak Intermolecular Bonds
| Lab Tests | Strong Intermolecular Forces | Weak Intermolecular Forces |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | High | Low |
| Melting Point | High | Low |
| Volatility (Evaporation) | Low | High |
| Example | Honey, Syrup | Water |
Strength of Intermolecular Forces
| Intermolecular Force | Occurs Between? | Relative Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Dipole-dipole | Polar Molecule | Medium |
| Hydrogen Bonding | H-F, H-O, H-N | Strong |
| London Dispersion | Between All Molecules | Weak |
Strength of Intramolecular Forces
| Intramolecular Force | How is it Formed? | Relative Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Ionic | Transfer of Electrons | Strong |
| Polar Covalent | Unequal sharing of electrons | Medium |
| Non-polar Covalent | Equal sharing of electrons | Weak |