physics first exam
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A disturbance that transfers energy from place to place.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Mechanical Wave |
A wave that requires a medium to travel through. |
Wavelength
The distance between two corresponding parts of a wave (e.g., crest to crest). |
Reflection
when a wave bounces off a surface
Diffraction
The spreading out of waves when they pass through an opening or around a barrier.
Freqeuncy unit
Hertz (Hz)
Period unit
Second(S)
Spring constant (K) unit
Newton/meters
Mass unit
usually Kg
Gravity Number and unit
9.8 m/s²
Length(L) unit
meters
amplitude(A) unit
m, cm
Wave
A disturbance that transfers energy from place to place.
Real image
𝑑𝑖 > 0,
period
The time it takes for periodic motion to complete one cycle
wavelength unit
m/cm
speed unit
m/s
wave number unit
K, rad/m
Angular frequency (omega) unit
W, rad/s
Phase shift unit
rad
Tension unit
N
Linear density unit
Kg/m
intensity unit
W/m²
index of infraction(n) unit
unitless
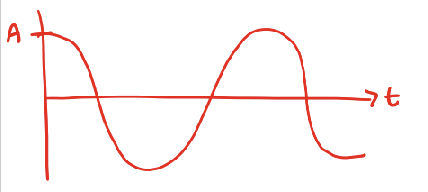
what is the phase shift?
0 or 360, 2pi rad
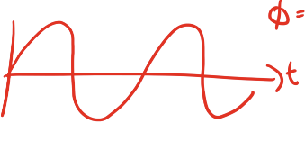
what is the phase shift
270 3pi/2
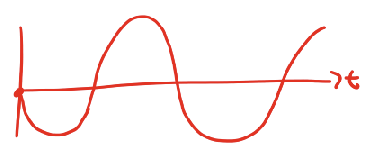
what is the phase shift
90, pi/2 rad
how can you rearrange f=1/T to get period?
T= 1/f
The wave speed in a stretched string depends on…
tension and linear density
Waves will travel slower through strings with lower mass density
False
Waves will travel slower through strings with lower tension
True
The energy in a wave depends on which factor(s)
amplitude and frequency
Resonance
the dramatic increase in a vibrating object’s amplitude when an external source forces it to vibrate at its natural frequency (pushing at the right time on a swing
Natural Frequency
characteristic frequency of vibration of an object
what is N in standing waves
number of anti nodes
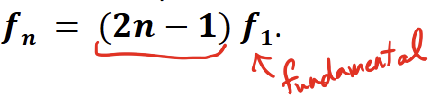
what does this formula give you
harmonic

what sign to use when approaching and departing
upper if approaching and lower if departing
If a light source approaches an observer, then the observed frequency is bigger than the source is called…
A blue shift
If a light source moves away from an observer, then the observed frequency is smaller than the source
A red shift
region of highly compressed air formed by constructive interference of sound waves when an object travels at the speed of sound
Sound Barrier
Does N2 have to be greater than N1 For TIR
Yes
moving in the +x direction means what sign?
means - sign
focal point is ± for diverging lenses
negative
power of a lens in always in
meters
When doing ray tracing with lenses, what is the minimum number of rays you need to find the image?
2
real image
Positive image distance
virtual image
Negative image distance
image height is _____ if inverted
negative
Magnification larger than 1
Enlarged image
positive magnification
upright image
Magnification less than 1
Reduced image
Negative magnification
Inverted image
Diverging lenses will always have……
virtual images that are upright and reduced.
for a converging lens and mirror
𝑓 > 0
for a diverging lens and mirror
𝑓 < 0
Flat mirrors produce images that are the same size as the object and …..
virtual
radius of curvature is negative for_____ mirrors
convex
Objects inside the focal length of a mirror produce images that are….
virtual, enlarged, and, upright
Images created by the eye are….
real reduced inverted
what is ideal vision
25 cm near point to infinity far point
1 over infinity equals…
0
Nearsightedness
Myopia, means can’t see far
Farsightedness
Hyperopia, means can’t see to close
To create an interference pattern that stays constant in time, the two wave sources must be…
coherent and monochromatic
what are bright spots labeled by
order (m)
if two wavelengths are 1, 2, 3, wavelengths apart, how do the waves interact?
constructive
if two wavelengths are 1.5, 2.5, 3.5, wavelengths apart, how do the waves interact?
Destructive