summary of formed elements in blood
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
red blood cells (RBCs) or erythrocytes
4.8 million/μL in females
5.4 million/μL in males
red blood cells (RBCs) or erythrocytes
7-8 μm diameter
biconcave discs
without nuclei
live for about 120 days
red blood cells (RBCs) or erythrocytes
hemoglobin within RBCs transports most of the oxygen and part of the carbon dioxide in the blood
red blood cells (RBCs) or erythrocytes

neutrophils
eosinophils
basophils
lymphocytes (T cells, B cells, NK cells)
monocytes
5 types of white blood cells (WBCs) or leukocytes
neutrophils
eosinophils
basophils
3 granular leukocytes
lymphocyte (T cells, B cells, NK cells)
monocytes
2 kinds of agranular leukocytes
T cells
B cells
NK cells
3 kinds of lymphocytes
white blood cells (WBCs) or leukocytes
50,000-10,000 cells/µL
white blood cells (WBCs) or leukocytes
most live for a few hours to a few days
white blood cells (WBCs) or leukocytes
combat pathogens and other foreign substances that enter the body
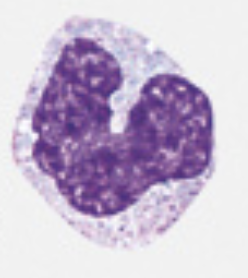
neutrophils
neutrophils
60-70% of all WBCs
neutrophils
10-12 µm in diameter
nucleus has 2-5 lobes connected by thin strands of chromatin
cytoplasm has very fine, pale lilac granules
neutrophils
phagocytosis
destruction of bacteria with lysozyme
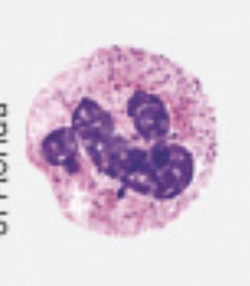
eosinophils
eosinophils
2-4% of all WBCs
eosinophils
10-12 µm diameter
nucleus usually has 2 lobes connected by a thick strand of chromatin
large, red-orange granules fill the cytoplasm
eosinophils
combat the effects of histamine in allergic reactions
phagocytize antigen-antibody complexes
destroy certain parasitic worms
basophils

basophils
0.5-1% of all WBCs
basophils
8-10 µm diameter
nucleus with 2 lobes
large cytoplasmic granules appear deep blue-purple
basophils
liberate heparin, histamine, and serotonin in allergic reactions that intensify the overall inflammatory response
lymphocytes (T cells, B cells, NK cells)
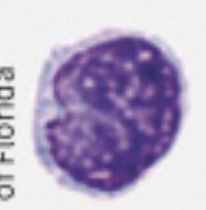
lymphocytes (T cells, B cells, NK cells)
20-25% of all WBCs
lymphocytes (T cells, B cells, NK cells)
small, 6-9 µm in diameter
large, 10-14 µm in diameter
round or slightly indented nucleus
cytoplasm forms a rim around the nucleus that looks sky blue
the larger the cell, the more cytoplasm is visible
lymphocytes (T cells, B cells, NK cells)
mediate immune responses, including antigen-antibody reactions
B cells
develop into plasmocytes, which secrete antibodies
T cells
attack invading viruses, cancer cells, and transplanted tissue cells
NK cells
attack a wide variety of infectious microbes and certain spontaneously arising tumor cells
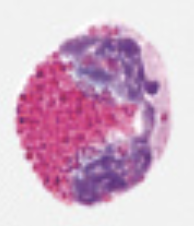
monocytes
monocytes
3-8% of all WBCs
monocytes
10-20 µm diameter
kidney-shaped or horseshoe shaped nucleus
blue-gray cytoplasm with foamy appearance
monocytes
phagocytosis (after transforming into fixed or wandering macrophages)
platelets (thrombocytes)

platelets (thrombocytes)
150,000-400,000/µL
platelets (thrombocytes)
2-4 µm diameter cell fragments that live for 5-9 days
contain many granules but no nucleus
platelets (thrombocytes)
form platelet plug in hemostasis
release chemicals that promote vascular spasm and blood clotting