Adaptive Immune System
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts of the adaptive immune system, including its components, mechanisms, and associated disorders.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
What takes over when the innate immune system fails to kill germs?
The adaptive immune system.
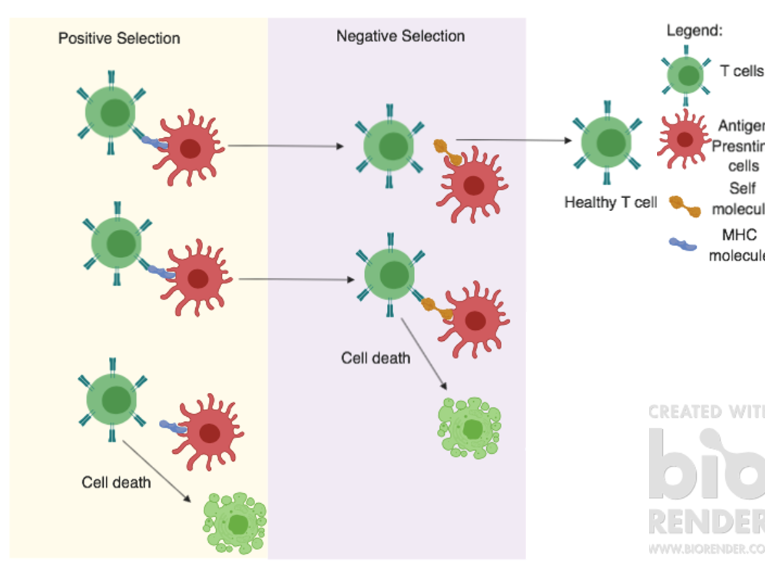
Draw a diagram of what happens after a dendritic cell presents an antigen to a T cell
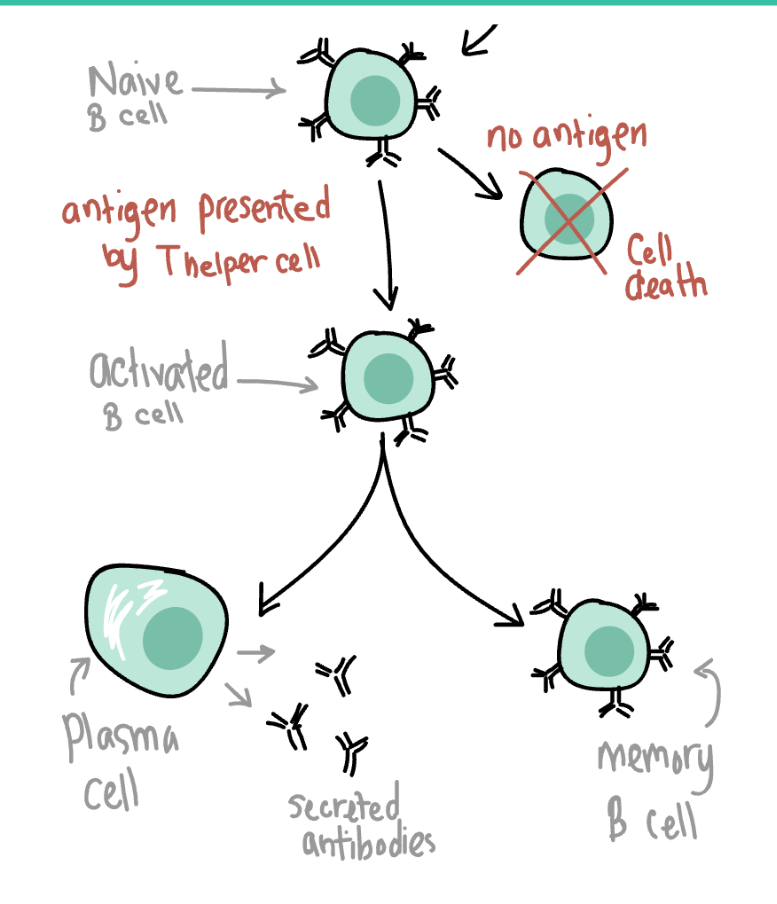
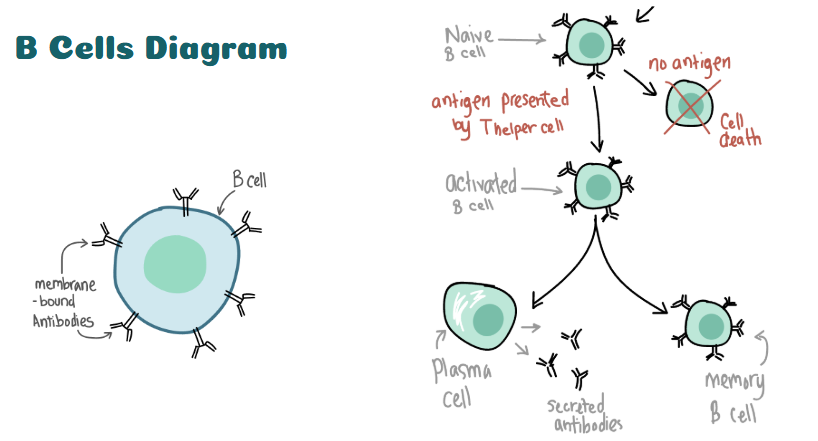
Draw a diagram of what happens after a T cell presents an antigen to a B cell
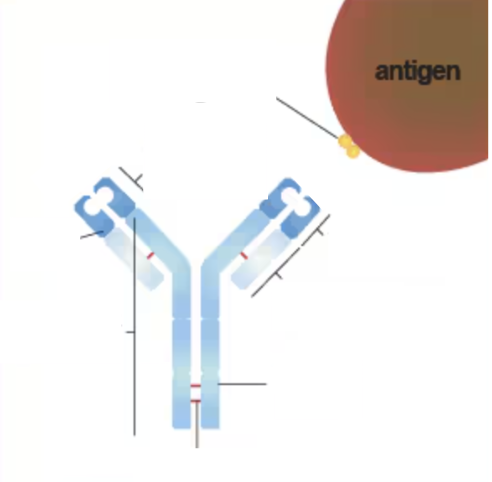
What are the functions of antibodies?
Makes antigen harmless
Attach to the cell surface of viruses/bacteria
Prevention of latching onto normal body cells
One antibody to one antigen
Analogy: lock and key
Activate other immune system cells
Activate proteins
How is tetanus treated?
In vaccinated patients, antibodies block the toxin from reaching cell receptors.
Antibodies can also mark the pathogens for phagocytosis.
What are the three main components of the adaptive immune system?
T cells, B cells, and Antibodies.
The adaptive immune system has the ability of remember germs
true
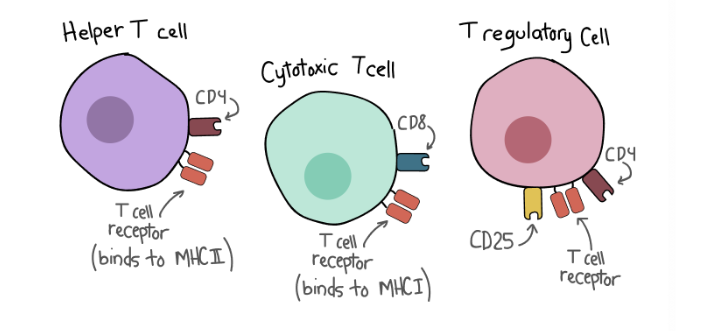
What is the role of T cells in the immune system?
Helper
Activate other cells of the immune system
Start of the immune system response
Done through chemical messengers
Cytotoxic
Detect the cells infected by the virus
Destroy the infected cells
Regulatory
Act as memory T cells after the infection has cleared
“Remember” how the infection/germ was fought off by the immune system
Regulate the immune response to make sure everything is okay
Where do T cells mature?
In the thymus.
What is the primary function of B cells?
producers of antibodies, which are proteins that specifically bind to and neutralize pathogens
can produce cytokines, signaling molecules that influence the activity of other immune cells and help regulate the immune response.
memory B cells, which can quickly produce antibodies upon subsequent exposure to the same antigen, providing long-term immunity.
What are antibodies?
Y-shaped proteins that recognize and neutralize pathogens.
What is the lymphatic system responsible for?
Managing fluids in the body
drains fluids from the bloodstream to tissues
helping transport immune cells.
What is the main function of helper T cells?
They activate other immune cells.
What type of cell is responsible for producing large amounts of antibodies?
Plasma cells.
What does MHC stand for in the context of T cells?
Major Histocompatibility Complex.
What happens during positive selection of T cells?
T cells must successfully bind to self-MHC molecules.
What occurs during negative selection of T cells?
T cells that bind too strongly to self-antigens are eliminated.
What type of T cell helps regulate the immune response?
Regulatory T cells.
What autoimmune disorder affects 1 in 4 adults in America?
Rheumatoid Arthritis.
What is the mechanism rheumatoid arthritis?
The immune system attacks the synovium around joints.
The synovium is the tissue lining around the joint.
Synovium swells and interferes with joints.
Rheumatoid Arthitis is considered a genetic condition
True
What is a common symptom of rheumatoid arthritis?
Swollen and tender joints.
What are some possible triggers of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
Infections and genetic factors
What genetic mutation is associated with RA?
Mutations of the HLA gene.
What is the function of the HLA gene in the immune system?
It helps the immune system distinguish between foreign cells and the body’s own cells.
What are the two forms of Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome?
Classic Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome and X-linked thrombocytopenia (XLT). - passed down through X chromosome
What causes immunodeficiency in Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome?
Malfunctioning white blood cells.
What causes the blood disorder in Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome?
Platelets are produced in minimal amounts and are abnormally small.
What symptoms are associated with Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome?
Frequent bleeding
minimal immune response.
dermatitis
Vulnerability to live vaccines
What is the treatment for Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome?
Antibody immunoglobulin can be infused
Stem cell transplants are the closest thing to a cure
What does myelin do in the nervous system?
It serves as a protective sheath around axons.
What happens in multiple sclerosis?
The immune system attacks and degrades myelin.
What are symptoms of multiple sclerosis?
Muscle issues like tremors and weakness
Fatigue, confusion, and paralysis are more serious symptoms
What type of immune response is involved in Multiple Sclerosis (MS)?
An abnormal immune response.
What do T cells do in the central nervous system in MS?
They release cytokines, triggering an inflammatory response.
What effect does the inflammatory response have in MS?
It degrades myelin and signals other immune cells.
What role do cytotoxic T cells play in MS?
They invade the central nervous system and contribute to tissue damage.
What happens to T regulatory cells in MS?
dysfunctional
How do B cells contribute to MS?
They produce antibodies that damage nerve cells.
Is there a cure for Multiple Sclerosis (MS)?
no
How can physiotherapy help MS patients?
It can improve muscle strength.
What is the role of corticosteroids in MS treatment?
reduce nerve inflammation
What medications can help manage tremors in MS?
Anti-seizure and anti-spasm medications.
What is plasmapheresis and how does it help in MS?
It is a treatment that replaces affected plasma to remove harmful proteins produced by the immune system.
How is tetanus contracted?
Through open wounds or unvaccinated mothers during birth.
What can happen if tetanus is untreated?
Muscle spasms and lockjaw because the toxin blocks the passage of signals between the spinal cord and muscles.
How do vaccines work in the context of adaptive immunity?
They expose the immune system to specific pathogens.
What is the result of the immune response to the chickenpox virus?
Production of antibodies and activation of T cells.
Specifically, CD4+ T-helper and CD8+ T-lymphocyte cells are activated.
T cells connect to macrophages for a cell-mediated response.
What are the functions of antibodies?
To neutralize pathogens and activate immune response.
What type of immune response is triggered by the flu?
A cytokine storm.
What portion of an antibody binds to an antigen?
Fab fragment.
Which class of antibody is the most abundant in the blood?
IgG.
How many antigen binding sites does IgM have?
Ten.
What is the significance of the HLA gene in autoimmune diseases?
It helps the immune system differentiate between self and foreign cells.
What type of treatment might be necessary for severe rheumatoid arthritis?
Joint replacements.
What is characteristic of autoimmune disorders?
The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells.
What can trigger autoimmune disorders?
Multiple genetic mutations.
What happens to the adaptive immune system as one ages?
It experiences immunosenescence, leading to reduced function.
What condition results when T cells invade the central nervous system?
Multiple sclerosis.
What unique characteristic do memory B cells have?
They help the body respond faster to future infections.
What is the immune response against chickenpox viruses?
Activation of CD4+ T-helper and CD8+ T-lymphocytes.
What class of antibodies is involved in allergic reactions?
IgE.
What is the typical age range for the onset of multiple sclerosis symptoms?
Between 20 and 40 years old.
Which T cell co-receptor is found on cytotoxic T cells?
CD8.
What happens when the immune system misidentifies self-cells as foreign?
Autoimmunity occurs.
What is a significant risk factor for developing autoimmune disorders?
Genetic predisposition.
What is a common outcome of exposure to the tetanus bacterium?
The development of muscle spasms.
What is the purpose of plasmapheresis in treating MS?
To replace affected plasma and remove harmful proteins.
What do the symptoms of influenza usually include?
Fever, body aches, cough, and sore throats.
What class of antibodies is secreted into mucus, tears, and saliva?
IgA.
What can the dysfunction of regulatory T cells lead to?
Uncontrolled immune responses and autoimmunity.
What is the impact of childhood vaccinations on the immune system?
They help build immune memory for quicker future responses.
What is a therapy used to treat symptoms of MS?
Corticosteroids.
What cell type is responsible for the primary immune response?
B cells.
What virus causes chicken pox?
The varicella-zoster virus.
How does the varicella-zoster virus behave in the body?
it can replicate within the cell
What condition can the varicella-zoster virus cause later in life?
Shingles, when the virus is reactivated.