Oxygenation (Class 15)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:59 PM on 3/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
1
New cards
True
True or False: If the heart fails, the lungs fail, and vice versa.
2
New cards
True
True or False: Respiration is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide during cellular metabolism.
3
New cards
True
True or False: The airways of the lungs transfer oxygen from the atmosphere to the alveoli, where the oxygen is exchanged for CO2.
4
New cards
True
True or False: The diaphragm and external intercostal muscles contract to create a negative pleural pressure increasing the size of the thorax for inspiration.
5
New cards
Ventilation
Process of moving gases into and out of the lungs with air flowing in and out during inspiration and expiration.
6
New cards
Perfusion
The ability of the cardiovascular system to pump oxygenated blood to the tissues and return deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
7
New cards
Diffusion
Responsible for moving the respiratory gases from one area to another by the concentration gradient
8
New cards
Inspiration
An active process, stimulated by chemical receptors which monitor pH, PaCO2, and PaO2 in the blood.
9
New cards
Expiration
A passive process that depends on the elastic recoil properties of the lungs, requiring little or no muscle work.
10
New cards
Compliance
The ability of the lungs to distend or expand in response to increased interalveolar pressure.
11
New cards
Atelectasis
Collapse of the alveoli that prevents normal exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
12
New cards
Surfactant
Chemical produced in the lungs to maintain the surface tension of the alveoli, keeps the lungs from collapsing.
13
New cards
Myocardial Pump
* Two atria
* Two ventricles
* As the myocardium stretches, the strength of the subsequent contraction increases (Starling’s Law)
* Two ventricles
* As the myocardium stretches, the strength of the subsequent contraction increases (Starling’s Law)
14
New cards
Myocardial Blood Flow
* Unidirectional flow through four valves.
* Ensures forward flow
* Ensures forward flow
15
New cards
Coronary Artery Circulation
* Supply the myocardium with nutrients
* Removes waste
* Removes waste
16
New cards
Systemic Circulation
* Arteries deliver nutrients and oxygen to tissues.
* Veins remove waste from tissues.
* Veins remove waste from tissues.
17
New cards
Blood Flow Regulation
* Cardiac output
* Stroke volume
* Preload
* Afterload
* Stroke volume
* Preload
* Afterload
18
New cards
Cardiac Conduction
* Transmits electrical impulses.
* Generates impulses needed to initiate the electrical chain of events for a normal heartbeat.
* Generates impulses needed to initiate the electrical chain of events for a normal heartbeat.
19
New cards
Factors that Influence Adequate Circulation, Etc.
1. Physiological Factors
2. Developmental Factors
3. Lifestyle Factors
4. Environmental Factors
20
New cards
Factors Affecting Chest Wall Movement
* Pregnancy
* Musculoskeletal abnormalities
* Influences of chronic lung disease
* Obesity
* Trauma
* Neuromuscular diseases
* CNS alterations
* Musculoskeletal abnormalities
* Influences of chronic lung disease
* Obesity
* Trauma
* Neuromuscular diseases
* CNS alterations
21
New cards
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Oxygenation
* Nutrition
* Hydration
* Exercise
* Smoking
* Substance abuse
* Stress
* Hydration
* Exercise
* Smoking
* Substance abuse
* Stress
22
New cards
Hypoventilation
Occurs when alveolar ventilation is inadequate t meet the oxygen demand of the body or to eliminate sufficient CO2. The body retains CO2.
23
New cards
Hyperventilation
A state of ventilation in which the lungs remove CO2 faster than it is produced by cellular metabolism.
24
New cards
Hypoxia
Inadequate tissue oxygenation at the cellular level, results from deficiency in oxygen delivery or oxygen use at the cellular level. Can lead to fatal dysrhythmias.
25
New cards
True
True or False: Restlessness and acrocyanosis are early warning signs of hypoxia.
26
New cards
Acrocyanosis
Peripheral cyanosis
27
New cards
Left Side Heart Failure
Decreased functioning of the left ventricle. Less blood is being ejected leading to decreased cardiac output and fluid backup in the lungs.
* Fatigue
* Dizziness
* Breathlessness
* Confusion
* Crackles over the lung bases
* Fatigue
* Dizziness
* Breathlessness
* Confusion
* Crackles over the lung bases
28
New cards
Right Side Heart Failure
Impaired function of the right ventricle. Usually results from pulmonary disease and long-term left-side failure. (A systemic backup)
29
New cards
Impaired Valvular Function
Congenital disorder of the cardiac valves of hardening or impaired closure of the valves.
30
New cards
Myocardial Ischemia
Supply of blood to the myocardium is insufficient to meet demands leading to angina or myocardial infarction.
31
New cards
Angina
Transient imbalance between myocardium oxygen supply and demand. Results in chest pain and tingling.
32
New cards
Assessment Questions
1. Describe the breathing problems you’re having.
2. Does chest pain occur while coughing?
3. How has your breathing changed?
4. How do your symptoms affect your daily activities, appetite, sleeping, etc.?
5. Describe the problem that you’re having with your heart.
33
New cards
Inspection Cues
* Thorax
* Breathing effort
* Skin color extremities
* Level of consciousness
* Breathing patterns
* Chest wall movements
* General appearance
* Circulation
* Skin color
* Extremities
* Chest wall movement
* Breathing effort
* Skin color extremities
* Level of consciousness
* Breathing patterns
* Chest wall movements
* General appearance
* Circulation
* Skin color
* Extremities
* Chest wall movement
34
New cards
Palpation Locations
* Chest
* Feet
* Legs
* Pulse
* Feet
* Legs
* Pulse
35
New cards
Percussion
* Prescence of abnormal fluid or air
* Diaphragmatic excursion
* Diaphragmatic excursion
36
New cards
Auscultation
Normal and abnormal heart/lung sounds
37
New cards
Orthopnea
Patient cannot lie flat, they can’t breathe.
38
New cards
Hemoptysis
Bloody sputum
39
New cards
Common Diagnostic Tests
* Arterial blood gases (ABGs)
* Complete blood count (CBC)
* Cardiac enzymes (CK-MB)
* Cardiac troponin
* Pulmonary function test (PFT)
* Peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR)
* Bronchoscopy
* Lung scan
* Complete blood count (CBC)
* Cardiac enzymes (CK-MB)
* Cardiac troponin
* Pulmonary function test (PFT)
* Peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR)
* Bronchoscopy
* Lung scan
40
New cards
Arterial Blood Gases (ABGs)
Provides important info for assessment of patient’s respiratory and metabolic acid/base balance and adequacy of oxygenation.
Values:
* pH: 7.35-7.45
* PCO2: 35-45 mmHg
* PO2: 80-100 mmHg
* HCO3: 21-28 mEq/L
* SaO2 Sat: 95-100%
Values:
* pH: 7.35-7.45
* PCO2: 35-45 mmHg
* PO2: 80-100 mmHg
* HCO3: 21-28 mEq/L
* SaO2 Sat: 95-100%
41
New cards
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Determines the number and type of red and white blood cells per cubic millimeters of blood. WBCs= Infection. RBCs= Anemia
42
New cards
Cardiac Enzymes (CK-MB)
Providers use cardiac enzymes, along with troponin, to diagnose acute myocardial infarctions. Greater than 4-6% is highly indicative of a myocardial infarction.
43
New cards
Cardiac Troponin
Plasma cardiac troponin T< 0.1 ng/mL- Value often remains elevated 10-14 days.
Plasma cardiac T< 0.03 ng/mL- Value elevates as early as three hours after myocardial injury.
Plasma cardiac T< 0.03 ng/mL- Value elevates as early as three hours after myocardial injury.
44
New cards
Pulmonary Function Test (PFT)
Basic ventilation studies. Determines ability of the lungs to efficiently exchange oxygen and CO2. Used to differentiate pulmonary obstructive from restrictive disease.
45
New cards
Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR)
Reflects changes in large airway sizes; an excellent predictor of overall airway resistance in a patient with asthma. Daily measurement for early detection of asthma exacerbations. The point of highest flow during maximal expiration.
46
New cards
Bronchoscopy
Visual examination of the tracheobronchial tree through a narrow, flexible fiberoptic bronchoscope. Performed to obtain fluid, sputum, or biopsy samples; removes mucus plugs or foreign bodies. Normal= Normal airways without masses, foreign bodies, or pus.
47
New cards
Lung Scan
Nuclear scanning. Test used to identify abnormal masses, used in planning therapy and treatments. Also used to find a blood clot preventing normal perfusion or ventilation. Normal= Normal lung structure without masses.
48
New cards
Members of an Interdisciplinary Team For Oxygenation
* Family
* Physical therapists
* Nutritionists
* Community-based nurses
* Respiratory therapists
* Physical therapists
* Nutritionists
* Community-based nurses
* Respiratory therapists
49
New cards
Health Promotion’s Role in Oxygen Maintenance
Maintaining a patient’s optimal level of health reduces the number and/or severity of respiratory symptoms.
50
New cards
Vaccinations for Health Promotion
* Influenza
* Pneumococcal
* COVID-19
* Pneumococcal
* COVID-19
51
New cards
Clients that Should Receive the Flu Vaccine
* Patients with chronic illnesses
* Annually for people 6 months+
* Infants
* Older adults
* Pregnant women
* Healthcare workers
* Annually for people 6 months+
* Infants
* Older adults
* Pregnant women
* Healthcare workers
52
New cards
Clients That Should Receive the Pneumococcal Vaccine
* Children
53
New cards
Eliminating Risk Factors
* High cholesterol
* Inactivity
* Smoking
* Alcohol
* Inadequate
* Stress
* Hydration
* Inactivity
* Smoking
* Alcohol
* Inadequate
* Stress
* Hydration
54
New cards
Eating Right
* DASH diet
55
New cards
Regular Exercise
* At least 150 minutes of moderate activity per week.
* At least 2 days a week of muscle strength training.
* At least 2 days a week of muscle strength training.
56
New cards
Health Promotion for Oxygenation
* Vaccinations
* Healthy Lifestyle
* Eliminating risk factors
* Eating right
* Regular exercise
* Environmental Pollutants
* Secondhand smoke
* Work chemicals
* Pollutants
* Healthy Lifestyle
* Eliminating risk factors
* Eating right
* Regular exercise
* Environmental Pollutants
* Secondhand smoke
* Work chemicals
* Pollutants
57
New cards
Nursing Interventions in the Acute Care Setting
* Airway management
* Mobilization of pulmonary secretions
* Hydration
* Humidification
* Nebulization
* Cough and deep breathing techniques
* Chest pathophysiology
* Mobilization of pulmonary secretions
* Hydration
* Humidification
* Nebulization
* Cough and deep breathing techniques
* Chest pathophysiology
58
New cards
Airway Management
Keeping the airway free from obstruction (Ex. Adequate Hydration) to prevent thick, tenacious secretions and proper coughing techniques.
59
New cards
Mobilization of Pulmonary Secretions
Repositioning and suctioning assist in achieving and maintaining a clear airway and help promote lung expansion/gas exchange.
60
New cards
Hydration
Keeps mucociliary clearance normal. Good fluid intake (unless contraindicated) is 1500-2500 mL per day.
61
New cards
Humidification
The process of adding water to gas to keep airways moist. Flows greater than 4L/min are needed for adults.
62
New cards
False
True or False: You can use clean water in humidification devices.
63
New cards
Nebulization
Adds moisture to inspired air by mixing particles of varying sizes with the air. Medications can be administered this way.
64
New cards
Cough and Depp Breathing Techniques
Deep inhalation increases the lung volume and airway diameter, allowing greater air movement. Different coughs can clear the airway.
65
New cards
Chest Physiotherapy
External chest wall manipulation using percussion, vibration, or high-frequency chest wall compression. Use in conjunction with postural drainage and can help mobilize pulmonary secretions in a select group of patients. Aggressive treatment.
66
New cards
Incentive Spirometer
* Promotes deep breathing to prevent or treat atelectasis.
* 5-10 breaths every hour during INHALATION while the patient is awake.
* Splint and pain medication before use helps those with abdominal or chest pain.
* 5-10 breaths every hour during INHALATION while the patient is awake.
* Splint and pain medication before use helps those with abdominal or chest pain.
67
New cards
Positive Expiratory Pressure (PEP)
* On EXHALATION sends resistance and vibrations to the chest
* Loosens mucus making a cough more productive
* Acapella and Flutter are common brands
* Loosens mucus making a cough more productive
* Acapella and Flutter are common brands
68
New cards
Artificial Airway
For patients with decreased level of consciousness or airway obstruction who need prolonged ventilatory support and aids in removal of tracheobronchial secretions and maintaining a patient’s airway.
69
New cards
Oral Airway
Used for patients with a decreased level of consciousness, airway obstruction, or who need prolonged ventilatory support. Does not go past they larynx.
70
New cards
Endotracheal and Tracheal Airways
Short-term use to ventilate, relieve upper airway obstruction, protect against aspiration, and clear secretions.
71
New cards
Tracheostomy
Long-term assistance, placed surgically directly into the trachea.
72
New cards
Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation Options
* Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
* Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP)
* Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP)
73
New cards
CPAP and BiPAP
* Purpose is to maintain a positive airway pressure and improve alveolar ventilation without the need for an artificial airway.
* Goal: Improve gas exchange, improves sleep, enhances quality of life, reduction of morbidity, and improves physical function.
* Goal: Improve gas exchange, improves sleep, enhances quality of life, reduction of morbidity, and improves physical function.
74
New cards
Oxygen Therapy Goal
Prevent or relieve hypoxia by delivering the lowest amount of oxygen possible to achieve adequate tissue oxygenation.
75
New cards
Nasal Cannula
* Delivers 1-6L/min at 24-44%
* Safe and simple
* Does not impede activities
* Safe and simple
* Does not impede activities
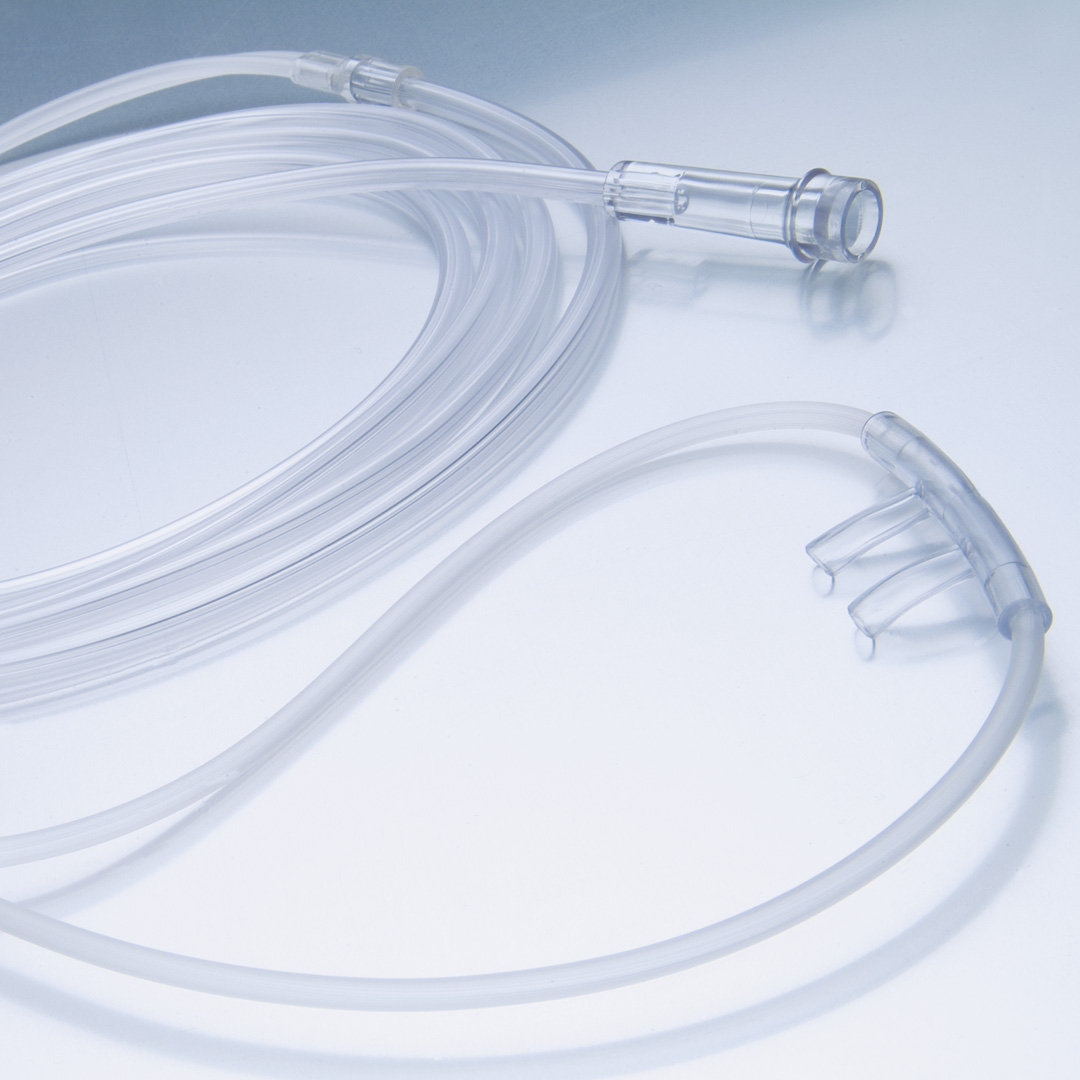
76
New cards
True
True or False: Humification must be apply to oxygen of 4L/min or more.
77
New cards
Simple Face Mask
* Delivers 6-12 L/min at 35-50%
* Used for short term oxygen therapy
* Used for short term oxygen therapy
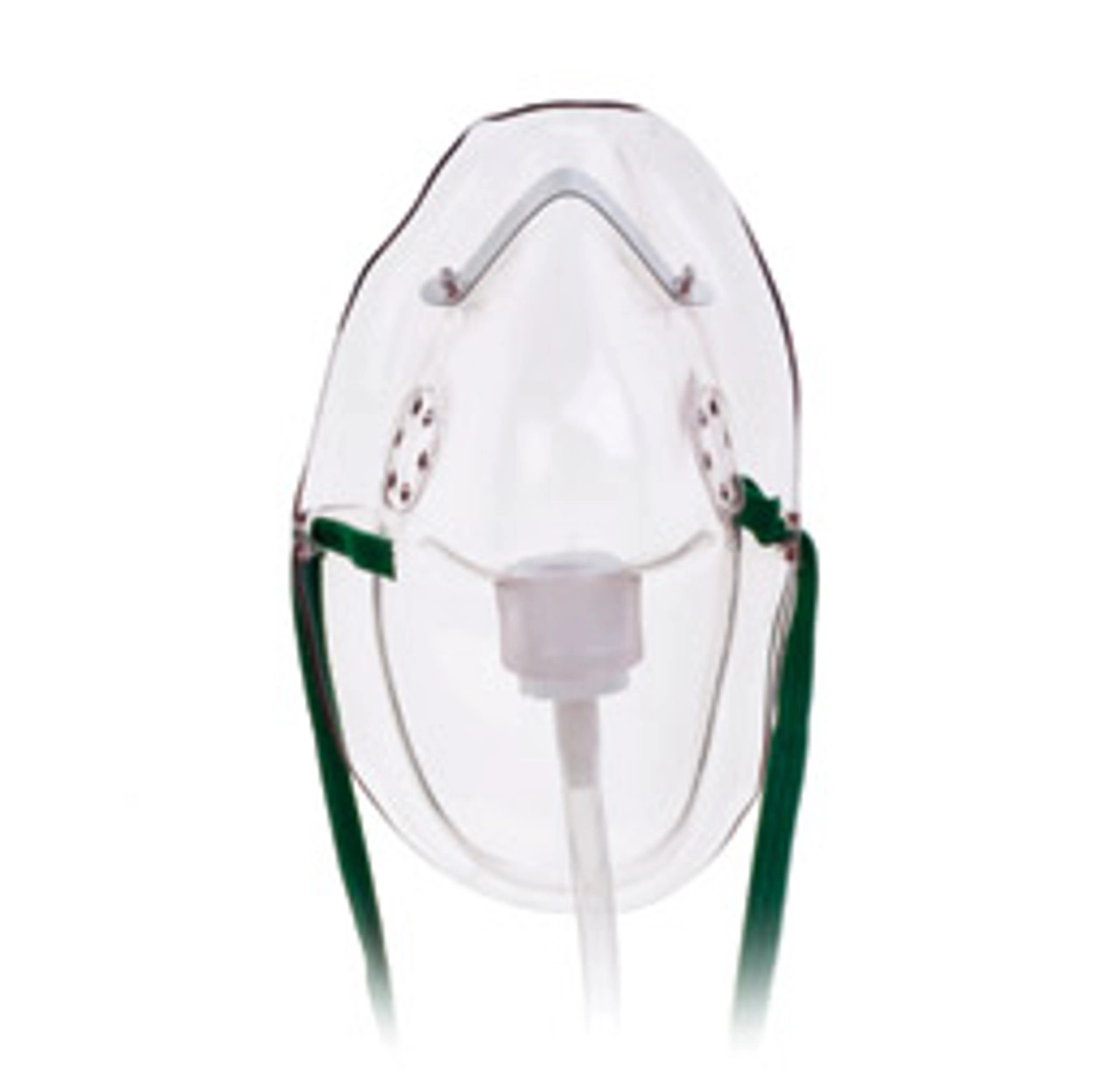
78
New cards
Partial and Nonrebreather Mask
* Most precise way to deliver oxygen
* 10-15 L/min at 60-90%.
* Has a reservoir bag that is capable of delivering high concentrations for a short time.
* 10-15 L/min at 60-90%.
* Has a reservoir bag that is capable of delivering high concentrations for a short time.
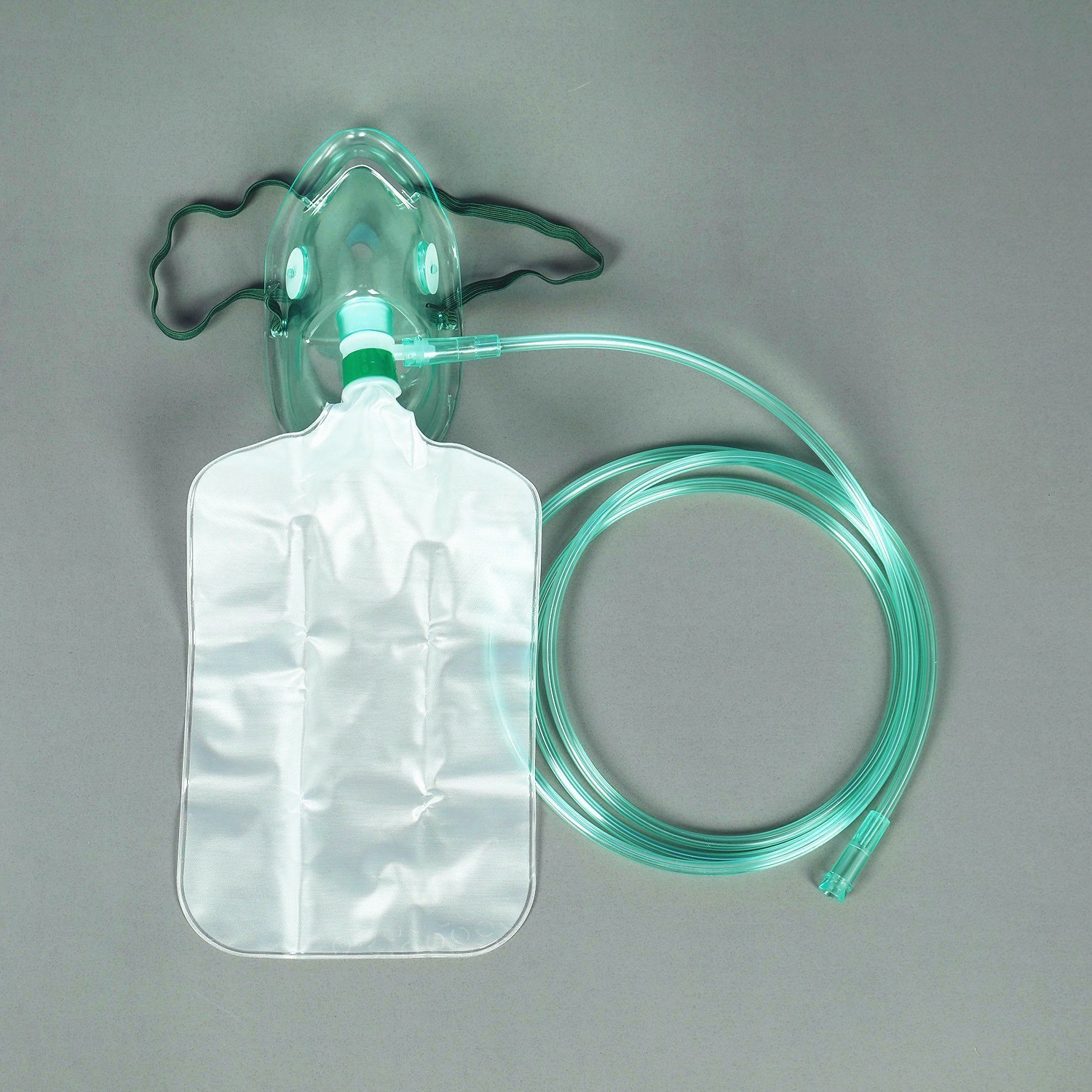
79
New cards
Venturi Mask
* 4-12 L/min at 24-50%
* Reserved for patients with CPOD who need low, constant oxygen concentration.
* Reserved for patients with CPOD who need low, constant oxygen concentration.
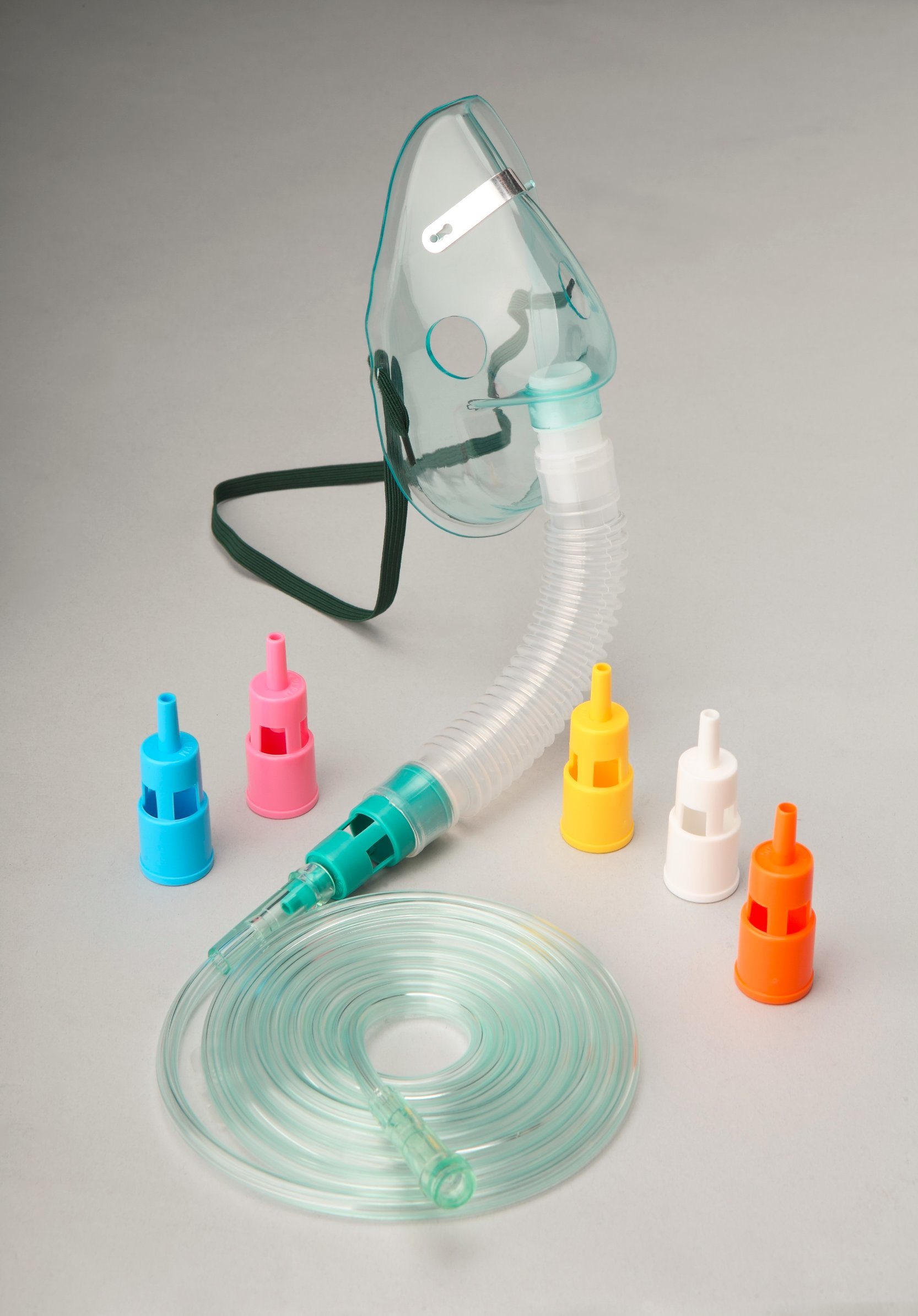
80
New cards
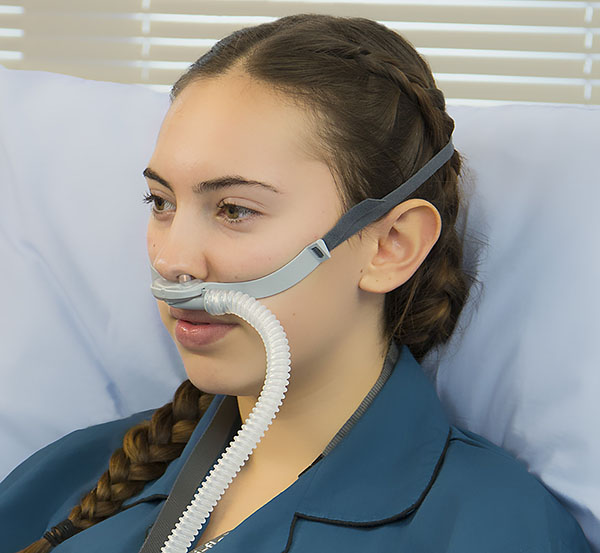
High Flow Nasal Cannula
* Up to 60 L/min at 21-100%

81
New cards
Safety Precautions for Oxygen Therapy at Home
* Notify the local fire department
* Check smoke detectors
* Do not adjust the gas yourself
* Keep oxygen 10 ft away from flames
* Store the canister upright and in a safe place (they can become projectiles if dropped)
* Make sure all electrical equipment works
* Check for adequate tubing and oxygen level before travel
* Post “no smoking signs” around property
* Check smoke detectors
* Do not adjust the gas yourself
* Keep oxygen 10 ft away from flames
* Store the canister upright and in a safe place (they can become projectiles if dropped)
* Make sure all electrical equipment works
* Check for adequate tubing and oxygen level before travel
* Post “no smoking signs” around property
82
New cards
FALSE
True or False: Oxygen is not flammable and patients can still smoke cigarettes around their oxygen therapy.
83
New cards
Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation
Helps patients achieve and maintain an optimal level of health through controlled physical exercise, nutritional counseling, relaxation, and stress/management techniques, prescribed medications, and oxygen.
84
New cards
True
True or False: As physical reconditioning occurs, a patient’s complaints of dyspnea, chest pain, fatigue, and activity intolerance decrease