13: metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokenisis
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
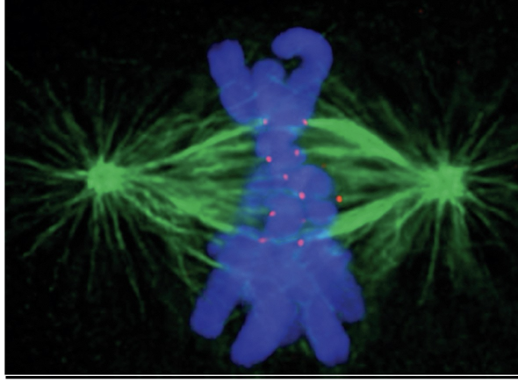
Kinetochores
large protein assemblies on chromosomes' centromeres
where spindle microtubules bind to chromosomes
ensure proper chromosome segregation
(image: red dots = kinetochores)
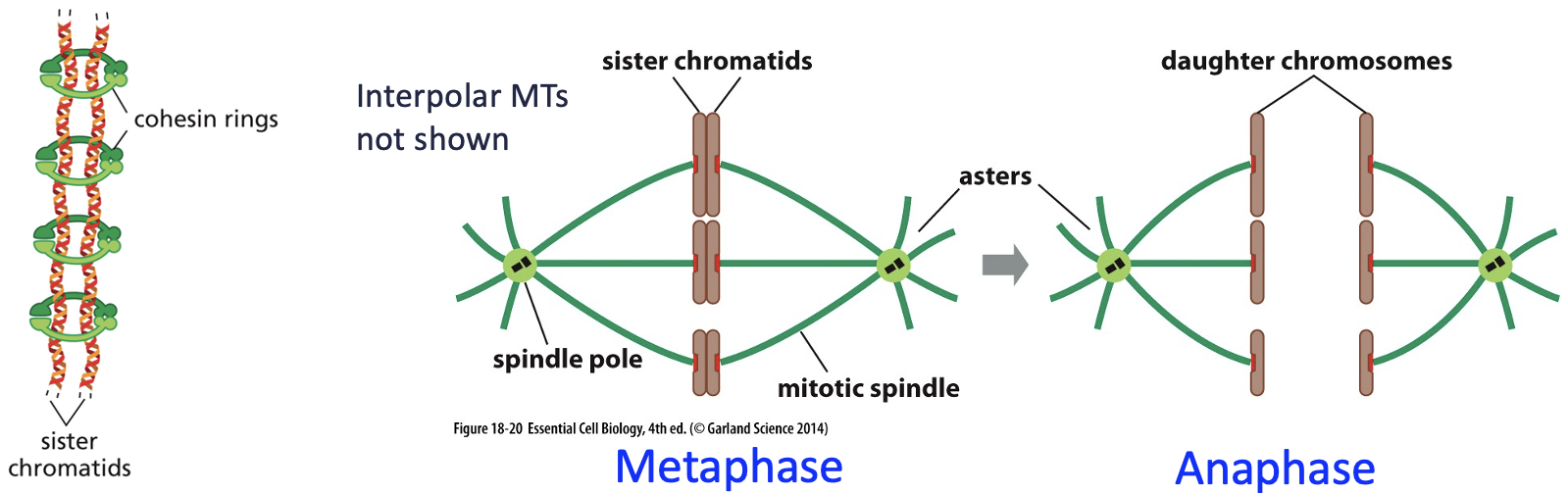
metaphase
• Chromosomes align in the middle of the spindle.
• Kinetochores attach to spindle microtubules, with one kinetochore attached to each pole.
• Tension at kinetochores ensures proper attachment
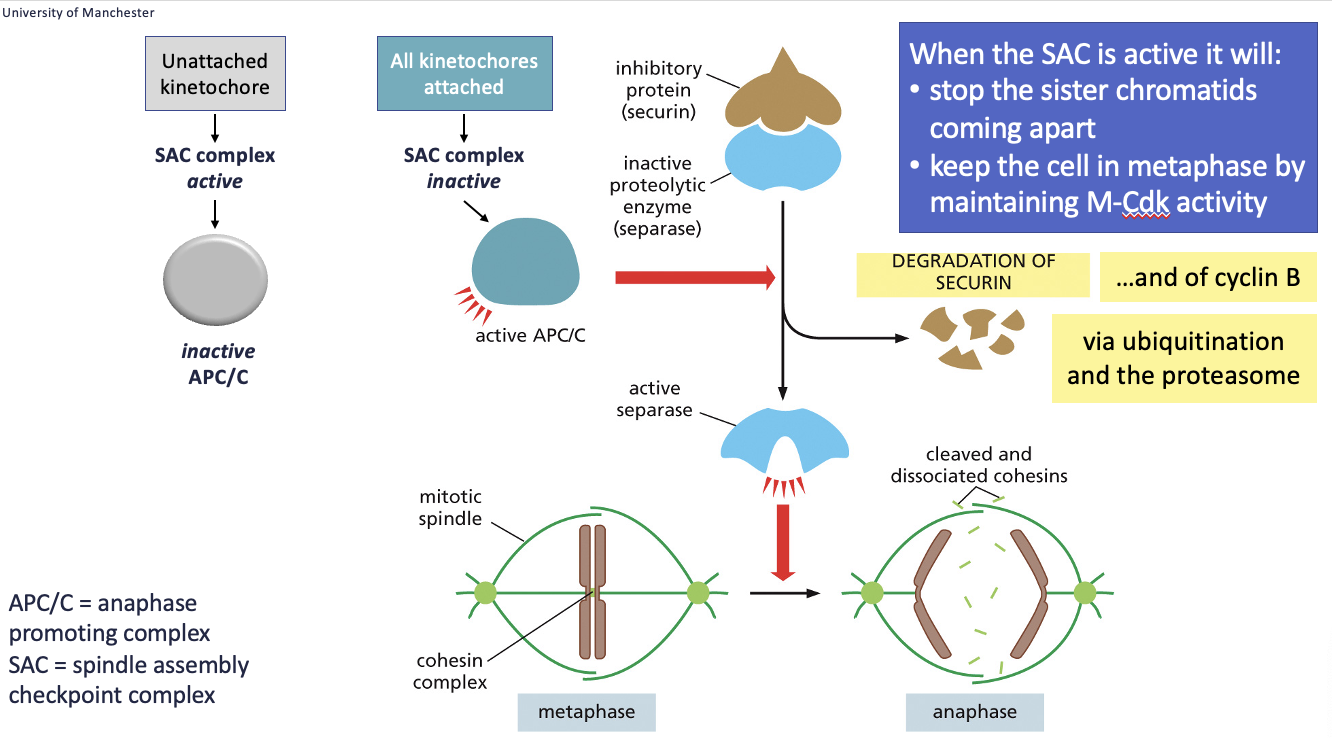
Spindle Assembly Checkpoint (SAC)
• Ensures proper chromosome alignment before anaphase.
• If microtubules are depolymerised (nocodazole) or stabilised (taxol), checkpoint blocks anaphase.
• Unattached kinetochores activate SAC, delaying anaphase.
• SAC proteins removed by cytoplasmic dynein once all kinetochores are attached => move on to anaphase
aneuploid daughters
daughter cells that have wrong number of chromosomes
Metaphase to Anaphase Transition: cohesins and separases
chromosomes are replicated in S-phase => 2 sister chromatids
sister chromatids stick together via cohesins
at anaphase, sister chromatids separate as cohesins are cleaved by separase enzymes
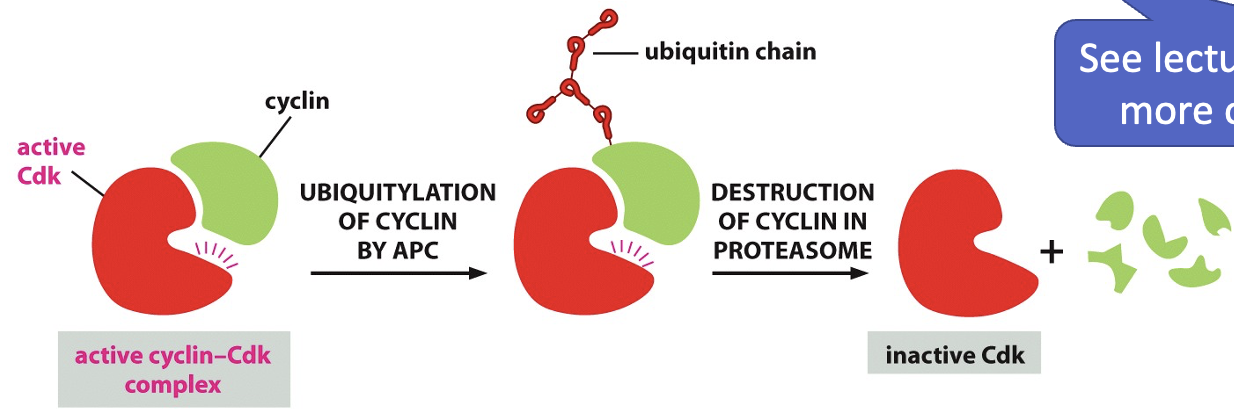
Metaphase to Anaphase Transition: anaphase promoting complex (APC/C)
APC/C triggers proteolysis of specific proteins by binding to them (like a tag):
covalently attaches ubiquitin (ubiquitylation)
this tagging directs proteins to the proteasome for degradation
What is M-Cdk and what does it do?
• M-Cdk (Mitosis Cyclin-Dependent Kinase) = Cyclin B + Cdk1.
• Function: Controls entry into mitosis (M phase) by triggering:
• Chromosome condensation.
• Spindle formation.
• Nuclear envelope breakdown.
• Regulation:
• Activated when Cyclin B binds to Cdk1.
• Inactivated when APC/C degrades Cyclin B, allowing the cell to exit mitosis.
metaphase to anaphase transition summary
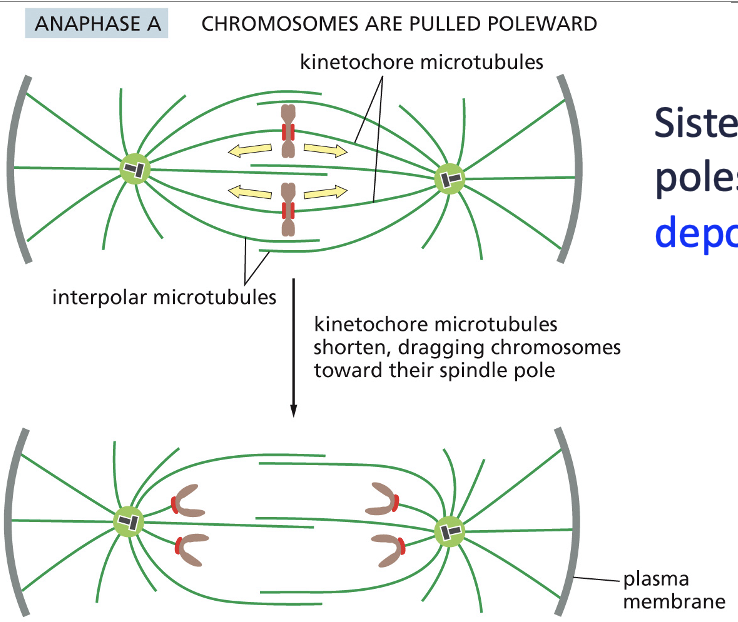
Anaphase A
• Anaphase A:
• Sister chromatids move towards spindle poles.
• Kinetochore microtubules depolymerise (shorten) at + ends, pulling chromatids apart.
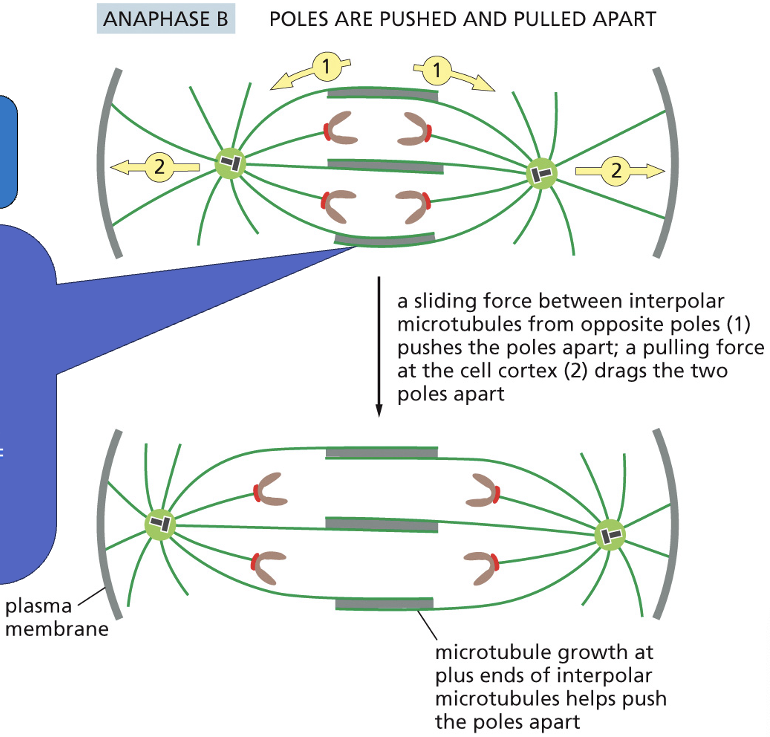
Anaphase B
• Spindle poles move apart.
• Eg5 kinesin pushes centrosomes apart.
• Dynein at the cortex pulls spindle poles apart.
anaphase a + b main difference
• Anaphase A = Chromosomes move toward poles.
• Anaphase B = Spindle poles move apart, stretching the cell.
telophase
• Nuclear envelope reassembles.
• Nuclear lamins reform (M-Cdk is inactive).
• Golgi apparatus reassembles
• secretion and endocytosis restart.
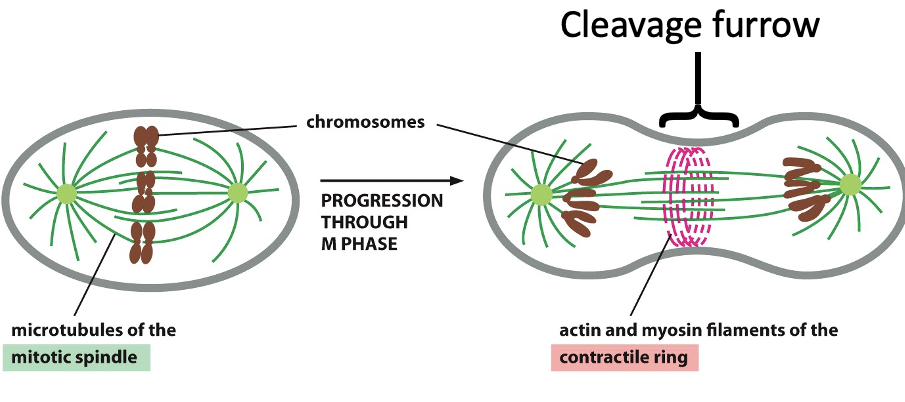
cytokinesis
• Contractile ring of actin and myosin II forms.
• The ring contracts to form a cleavage furrow, splitting the cell.
• Integrins are phosphorylated, weakening cell attachment to the surface.