DPT ~ Lecture Based Pec Region
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
axio-appendicular muscles
a muscle that is attatched to the axial skeleton and appendage which moves the extremity
surface anatomy
the study of internal structures as they relate to the overlying skin surface
bony and soft tissue landmarks are used in lab procedures for …
dissecting, palpating, mobilizing and documentation process
jugular notch
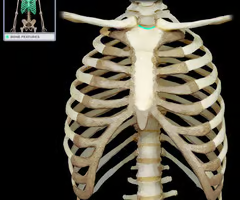
manubrium
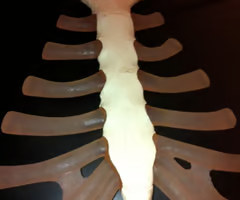
Sternal angle (manubriosternal joint)
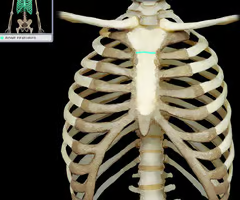
xiphoid process
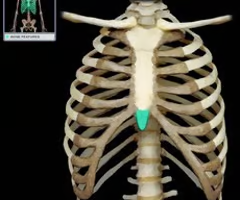
acromion

coracoid process

glenoid cavity

subscapular fossa

supraspinous fossa

suprascapular notch

spine of scapula
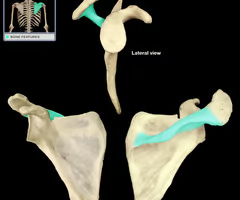
infraspinous fossa
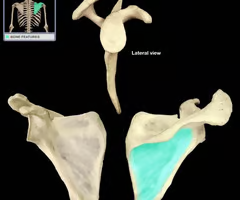
supraglenoid tubercle
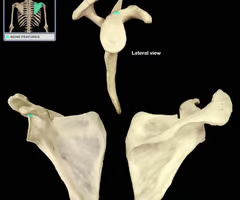
conoid tubercle
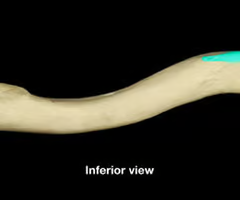
trapezoid line

subclavian groove
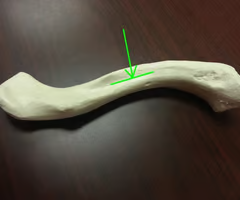
lesser tubercle
greater tubercle
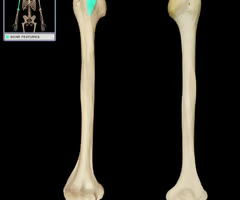
deltoid tuberosity
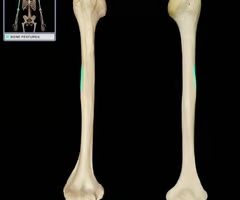
head of humerus

anatomical neck of humerus

Where does the clavicle typically fracture?
at the joint ot its middle and lateral third
How are clavicle fractures caused?
indirect force transmitted from an outstretched hand through the bones of the forearm and arm to the shoulder (foosh)
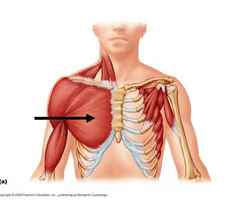
pectoralis major origin
Clavicular head: anterior surface of medial half of clavicle
Sternocostal head: anterior surface of sternum, superior six costal cartilages, aponeurosis of external oblique muscle
abdomial part: anterior layer of rectus sheath
pectoralis major insertion
lateral lip of intertubercular sulcus of humerus
pectoralis major innervation
lateral and medial pectoral nerves; clavicular head and sternocostal head
pectoralis major main action
Adducts and medially rotates humerus; draws scapula anteriorly and inferiorly
Acting alone, clavicular head flexes humerus and sternocostal head extends it from the flexed position
pec minor origin
3rd-5th ribs near their costal cartilage
pec minor insertion
medial border and superior surface of coracoid process of scapula
pec minor innervation
Medial pectoral nerve (C8, T1), Lat pectoral nerve
pec minor main action
Stabilizes scapula by drawing it inferiorly and anteriorly against thoracic wall
subclavius origin
junction of first rib and its costal cartilage
subclavius insertion
inferior surface of middle third of clavicle
subclavius innervation
Nerve to subclavius (C5, C6)
subclavius main action
anchors and depresses clavicle
serratus anterior origin
external surfaces of lateral parts of 1st and 8th ribs
serratus anterior insertion
anterior surface of medial border of scapula, including superior and inferior angles
serratus anterior innervation
Long thoracic nerve (C5, C6, C7)
serratus anterior main action
protracts scapula and holds it against thoracic wall; rotates scapula
motions of the shoulder
flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, internal rotation, external rotation, horizontal abduction, scaption
The first part of the axillary artery is located between the lateral border of the 1st rib and the medial border of the pec minor. It is has one branch the _________
superior thoracic artery
The second part of the axillary artery lies posterior to pec minor and has two branches the _________ and _________
thoracoacromial and lateral thoracic arteries
The third part of the axillary artery is from the lateral border of pec minor to the inferior border of teres major and gives of three branches: ________, ________, and ______
subscapular artery, anterior circumflex humeral and posterior circumflex humeral artery
nerves come from the brachial plexus
lateral pectoral (lateral cord of bp)
medial pectoral (medial cord of bp)
nerve to subclavius
anterior median line

midclavicular lines

anterior axillary line

1
midaxillary line
2
posterior axillary line
3
posterior median line

scapular lines

deltopectoral groove
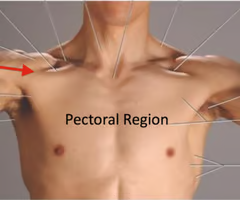
anterior axillary fold

posterior axillary fold
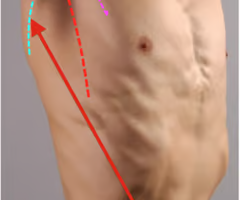
axillary fossa

sternocostal head of pectoralis major