Animal Nutrition Exam 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:10 PM on 10/31/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
1
New cards
Acidosis
digestive upset characterized by decrease in rumen pH that kills off the good MCOs
caused by: rapid increase in grain in diet, rapid change from forage to concentrate, grazing residue crop, improper ration balancing/management
symptoms: decrease intake, abdominal pain, dehydration, laminitis
caused by: rapid increase in grain in diet, rapid change from forage to concentrate, grazing residue crop, improper ration balancing/management
symptoms: decrease intake, abdominal pain, dehydration, laminitis
2
New cards
Rumination
set of steps that reduce particle size of digesta for passage to lower tract
regurgitation, remastication, back into complex stomach
regurgitation, remastication, back into complex stomach
3
New cards
Eructation
Process of removing gas from the rumen
gas forced up esophagus
gases produced: H2, CO2, Ch4, H2S
gas forced up esophagus
gases produced: H2, CO2, Ch4, H2S
4
New cards
Bloat
Caused by the inability of the ruminant to eructate
Signs: froth or foam at mouth, distention of left side
primary cause: legumes (soluble protein)
Signs: froth or foam at mouth, distention of left side
primary cause: legumes (soluble protein)
5
New cards
Colic
Condition caused by compaction of food in the digestive tract of the horse
Symptoms: mild to severe abdominal pain and depression
Other causes: too much or too rapid grain consumption; stoppage of intestinal flow; parasites; gas production; improper husbandry
symptoms: pawing/kicking at belly, abnormal postures, rolling
Symptoms: mild to severe abdominal pain and depression
Other causes: too much or too rapid grain consumption; stoppage of intestinal flow; parasites; gas production; improper husbandry
symptoms: pawing/kicking at belly, abnormal postures, rolling
6
New cards
HCl
Parietal cells
7
New cards
Pepsin(ogen)
Chief cells
8
New cards
Amylase
pancreatic enzyme that breaks down starch
9
New cards
Bile
Liver
10
New cards
Lipase
Pancreas
11
New cards
Tripsin(ogen)
Pancreas
12
New cards
Maltase
Brush border of small intestine
13
New cards
(pro)Carboxypeptidase
pancreas
14
New cards
Sucrase
Brush border of small intestine
15
New cards
Chymotrypsin(ogen)
pancreas
16
New cards
Cellulase
Not produced by cell of GI tract
17
New cards
Lactase
brush border of small intestine
18
New cards
Enterokinase
Brush border of small intestine
19
New cards
Start of cellulose digestion in the pig
Cecum
20
New cards
Start of sucrose digestion in the horse
Small intestine
21
New cards
Start of cellulose digestion in the cow
rumen
22
New cards
Start of starch digestion in the sheep
rumen
23
New cards
Start of cellulose digestion in the horse
cecum
24
New cards
Start of starch digestion in the dog
Small intestine
25
New cards
Start of lactose digestion in the pig
small intestine
26
New cards
Enzyme that is high in concentration in the suckling calf?
Lactase
27
New cards
enzyme that starts starch digestion
amylase
28
New cards
Enzyme that is involved in fiber digestion
cellulase
29
New cards
Enzyme involved in amylopectin digestion but not amylase
Isomaltase
30
New cards
Enzyme that breaks down milk sugar
Lactase
31
New cards
Enzyme found only in the rumen and cecum
cellulase
32
New cards
end product of cellulose digestion in the rumen of the cow
VFA
33
New cards
end product of amylose digestion in the small intestine of the pig
glucose
34
New cards
end product of starch digestion in the cecum of a horse
VFA
35
New cards
end product of cellulose digestion in the small intestine of the sheep
no end product
36
New cards
end product cellulose digestion in the small intestine of a dog
no end product
37
New cards
end product of maltose digestion in the small intestine of the horse
glucose
38
New cards
end product of starch digestion in cecum of the pig
VFA
39
New cards
end product of protein digestion in the small intestine
amino acids
40
New cards
end product of protein digestion in the rumen
MCO protein
41
New cards
end product of protein digestion in the cecum
glucose
42
New cards
end product of cellulose digestion in the small intestine
no end product
43
New cards
end product of starch digestion in the small intestine
glucose
44
New cards
end product of amylose digestion in the rumen
VFA
45
New cards
end product of maltose digestion in the small intestine
glucose
46
New cards
end product of starch digestion in the cecum
amino acids
47
New cards
end product of starch digestion in the rumen
VFA
48
New cards
End product of cellulose digestion in the rumen
glucose
49
New cards
end product of cellulose digestion in the rumen
VFA
50
New cards
Cecum can be a site of
microbial fermentation
51
New cards
Jejunum is the main site of
nutrient absorption
52
New cards
Duodenum is the main site of
digestion
53
New cards
The Ileum is the last chance for
nutrient absorption
54
New cards
What CAN be produced by bacteria in the Cecum that can provide energy
VFAs
55
New cards
which is considered to be glandular?
abomassum
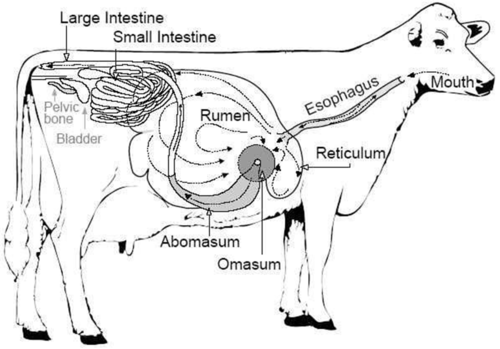
56
New cards
The first place milk goes in a calf
abomassum
57
New cards
The compartment of the ruminant's stomach is considered the pacemaker
reticulum
58
New cards
The compartment of the ruminant's stomach regulates the flow to the abomassum
omassum
59
New cards
Steps of rumination:
regurgitation, remastication, resalivation, reglutition
60
New cards
which organ of the forestomach of ruminants is characterized as many plies?
omassum
61
New cards
which organ of the fore stomach of ruminants is known as the honeycomb?
reticulum
62
New cards
for the cecum, what enzyme results in the breakdown of starch?
microbial amylase
63
New cards
protein digestion starts where in the gastrointestinal tract
stomach
64
New cards
Where would the absorption of glucose occur?
jejunum
65
New cards
Where does fat digestion occur?
duodenum
66
New cards
what is the classification of the horse?
monogastric herbivore
67
New cards
why is microbial digestion in the hind-gut less efficient compared to the ruminant?
passage rate is too fast and occurs past the primary site of absorption
68
New cards
For the rumen, what products of microbial digestion may benefit the ruminant?
VFA, Microbial Protein, and Heat
69
New cards
What would increase of an ionophore was included in the diet?
propionate
70
New cards
What can be used by microorganisms to synthesize microbial protein?
feed protein, amino acids, and C skeletons NH3
71
New cards
Fermentation is more efficient in the ruminant animal because it occurs before the primary site of absorption
true
72
New cards
feeding more concentrate (grain) and adding ionophores to the diet of ruminants will increase efficiency
true
73
New cards
starch digestion starts in the rumen of the ruminant and in the small intestine of the horse
true
74
New cards
horses should be fed in small meals because of their digestive system
true
75
New cards
Function of the rumen
storage, microbial fermentation, absorption of VFA
76
New cards
Which enzyme produced by the abomasum initiates protein digestion
pepsin
77
New cards
What makes the rumen a favorable environment for microbial growth?
pH is buffered, temperature is maintained at 101-103, anaerobic, end-products removed
78
New cards
Which is the primary end product of microbial fermentation from cellulose digestion?
VFA
79
New cards
which is the primary end product of microbial fermentation from starch digestion?
VFA
80
New cards
which is the primary end product of microbial fermentation from protein digestion?
microbial protein
81
New cards
which can be used by microorganisms to synthesize microbial protein?
feed protein, amino acids, urea
82
New cards
which VFA is the most efficient?
propionate
83
New cards
Changing an animal's diet from forage to concentrate would ____ the amount of propionate.
increase
84
New cards
What are sources of protein entering the stomach of the cow?
feed protein, microbial protein, bypass protein
85
New cards
Which of the following enzymes would NOT be produced by the pancreas of the ruminant?
aminopeptidase
86
New cards
process of removing gas from the rumen
eructation
87
New cards
condition caused by compaction of food in the digestive tract of the horse
colic
88
New cards
In the cecum of the horse, what enzyme results in the breakdown of starch?
microbial amylase
89
New cards
Protein digestion starts where in the gastrointestinal tract of the horse?
stomach
90
New cards
Where would the absorption of glucose occur in the gastrointestinal tract of the horse?
jejunum
91
New cards
Where does fat digestion occur in the gastrointestinal tract of the horse?
duodenum
92
New cards
What is the classification of the gastrointestinal tract of the horse?
Monogastric herbivore
93
New cards
What product(s) of microbial digestion can benefit the horse during first pass?
VFA
94
New cards
What is caused by the inability to digest milk sugar?
lactose intolerance
95
New cards
Bloat is characterized by what?
lack of ability to remove gas from rumen
96
New cards
Where does primary absorbance of nutrients occur?
small intestine (duodenum)
97
New cards
Where would microbial digestion occur?
cecum
98
New cards
Where does the start of starch digestion occur in ruminants?
rumen
99
New cards
What enzyme is only found in the rumen and cecum?
cellulose
100
New cards
What is considered the pacemaker for rumen contractions?
Reticulum