Chapter 4: Histology - Part 2
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Connective tissues
connect all other tissues to one another
Connective tissue cells types
resident cells, wandering or migrant cells
Resident (muscle) cells
cells that are permanently located in that tissue
Wandering or migrant (muscle) cell
cells that move around to different areas of the body in response to various needs
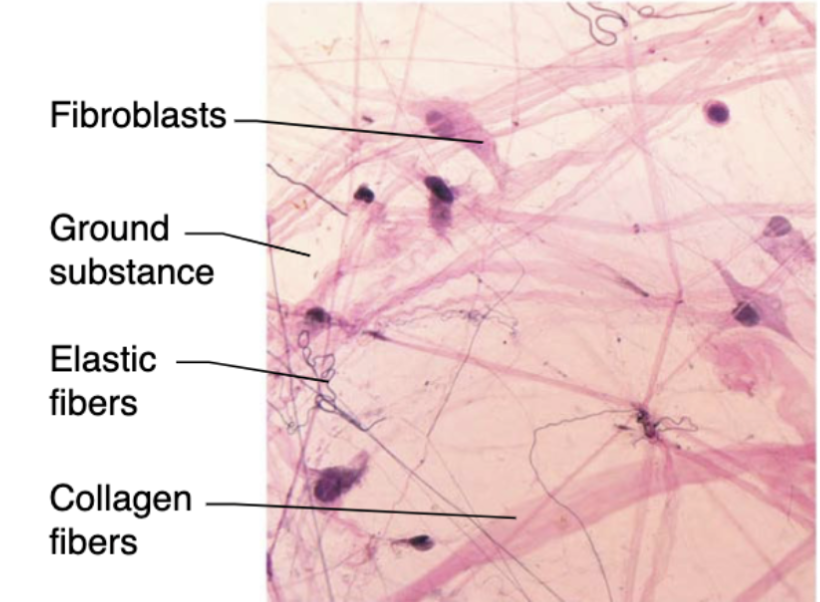
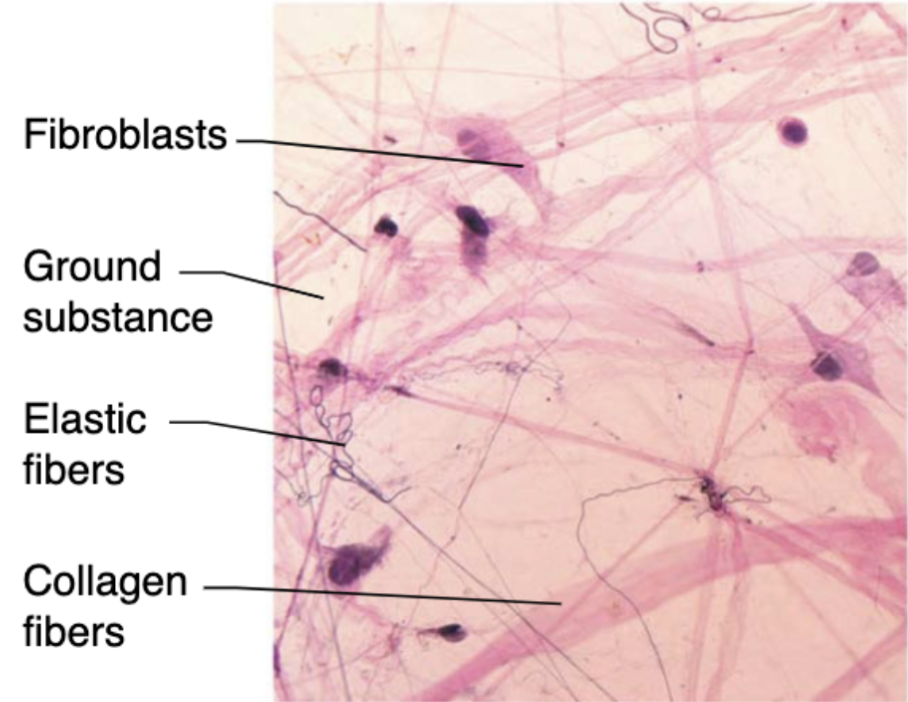
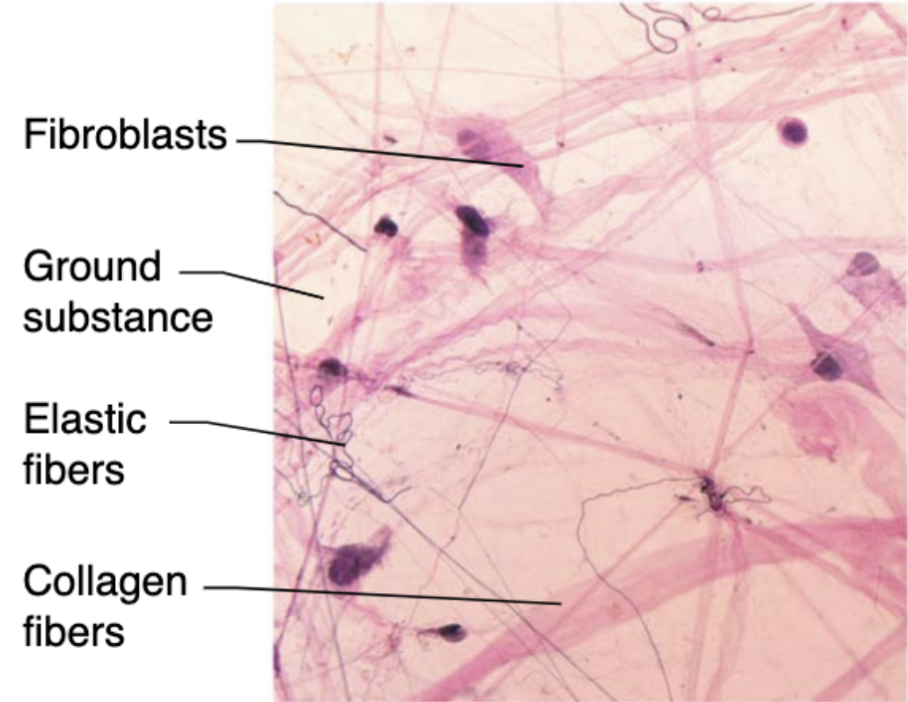
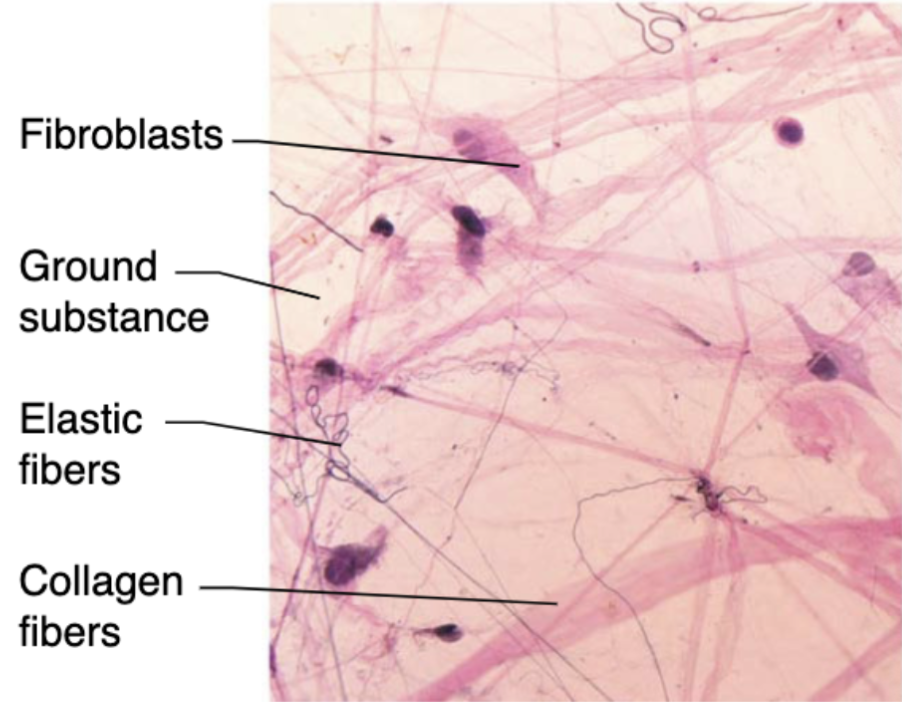
Fibroblast
most common resident cells that make protein fibers and ground substance
Connective tissue proper
“general” connective tissue that is found all throughout the body, connecting organs and tissues to one another
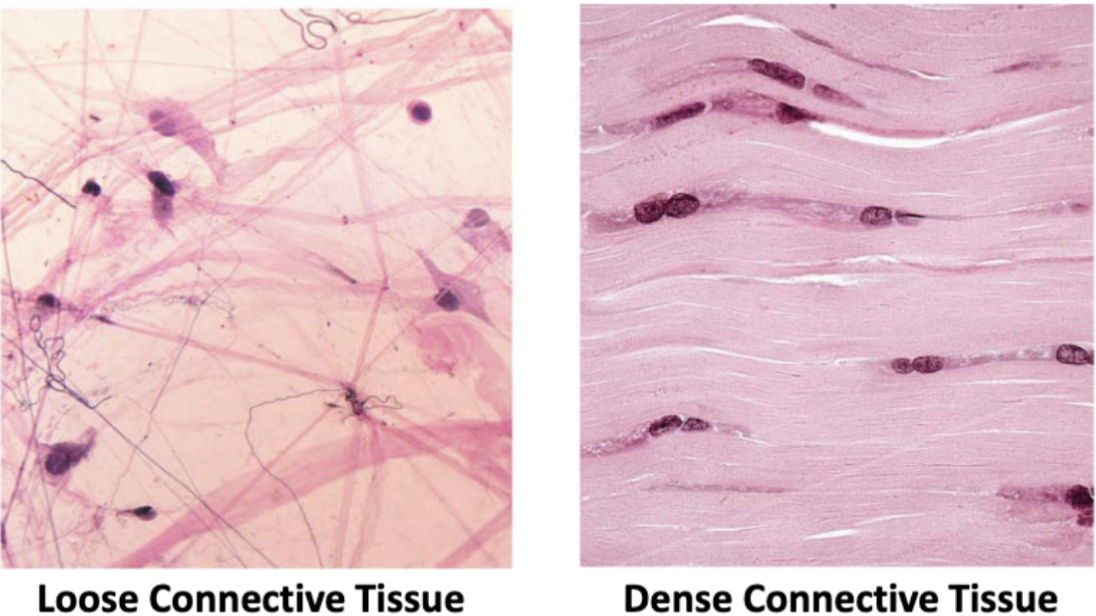
Types of connective tissues proper
loose or dense (how closely packed together the protein fibers are)
Areolar connective tissue (description)
loose network of collagen and elastic fibers embedded in a gel-like ground substance (containing fibroblasts, macrophages, and mast cells)
Areolar connective tissue (function)
CT that contains and support blood vessels vital to avascular epithelial tissues and house immune system cells
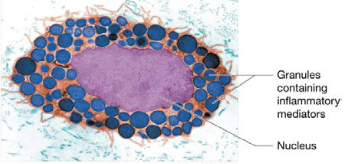
Mast cells
immune cells that release mediators (degranulate) when stimulated, cause inflammation through histamine
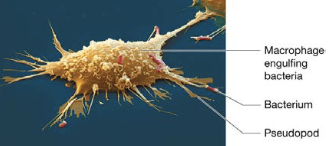
Phagocytes
immune cells that ingest foreign substances, microorganisms, and dead or damaged cells by phagocytosis, include macrophages or neutrophils
Areolar connective tissue (location)
CT located beneath many types of epithelium
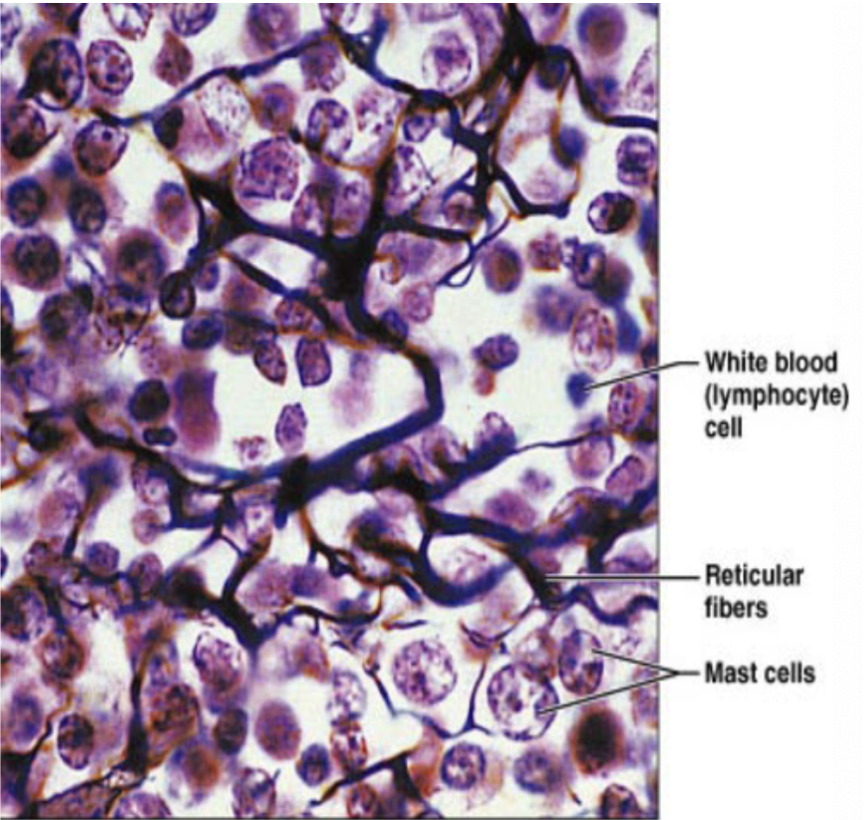
Reticular CT (description)
network of reticular fibers in a lose ground substance with reticular cells
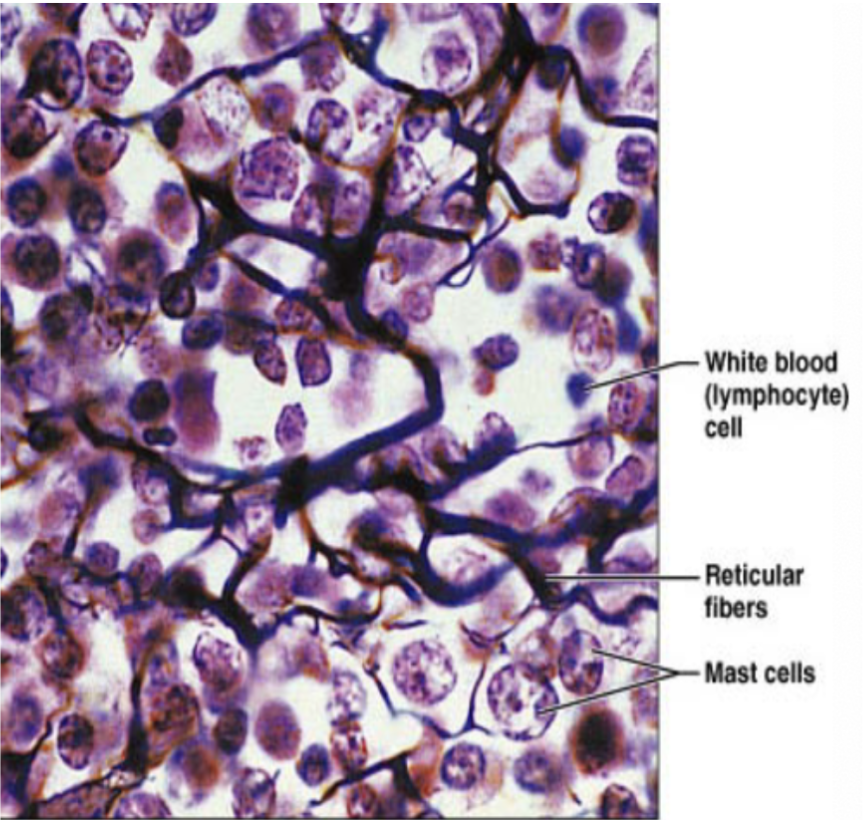
Reticular CT (function)
fibers form soft internal skeleton that support other cell types (WBC, mast cells, macrophages)
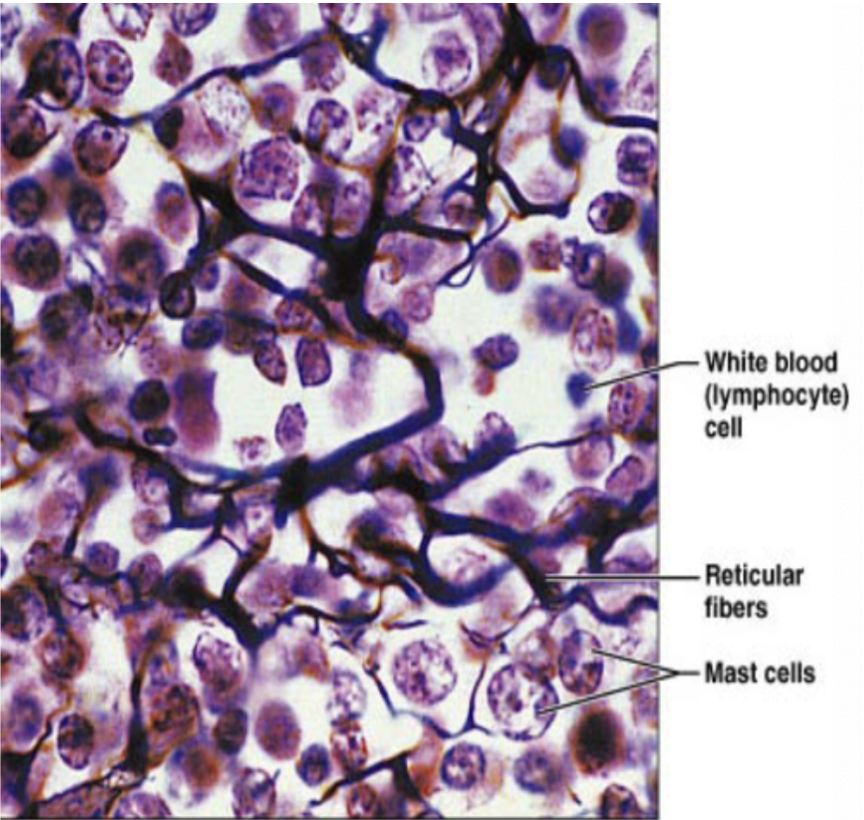
Reticular CT (location)
lymphoid organs
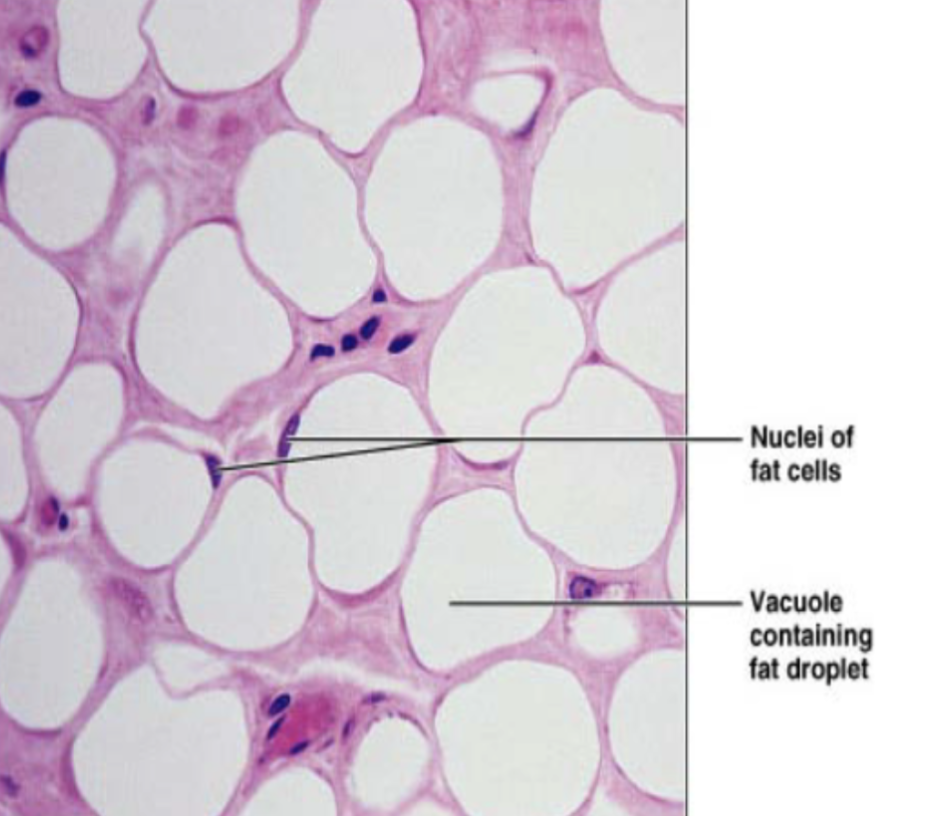
Adipose tissue (description)
matrix same as areolar, but sparse,, closely packed adipocytes have nucleus pushed to the side by huge fat droplet
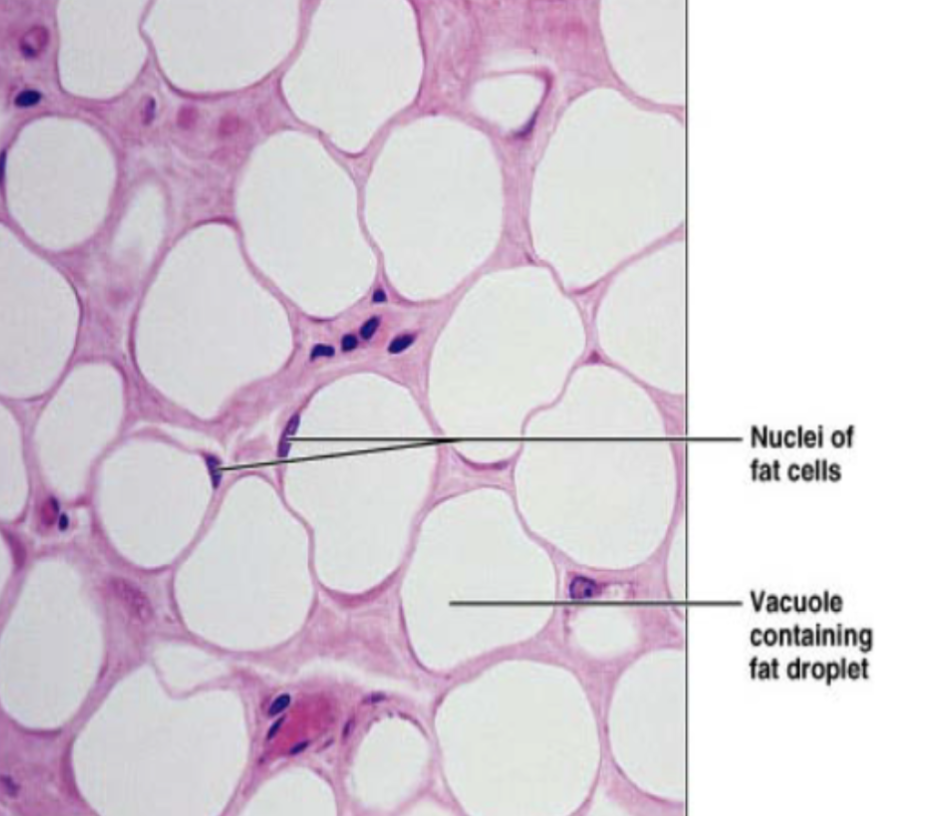
Adipose tissue (function)
store nutrients, highly vascularized (needs to be able to mobilize nutrients during metabolism of fat), insulation, protection
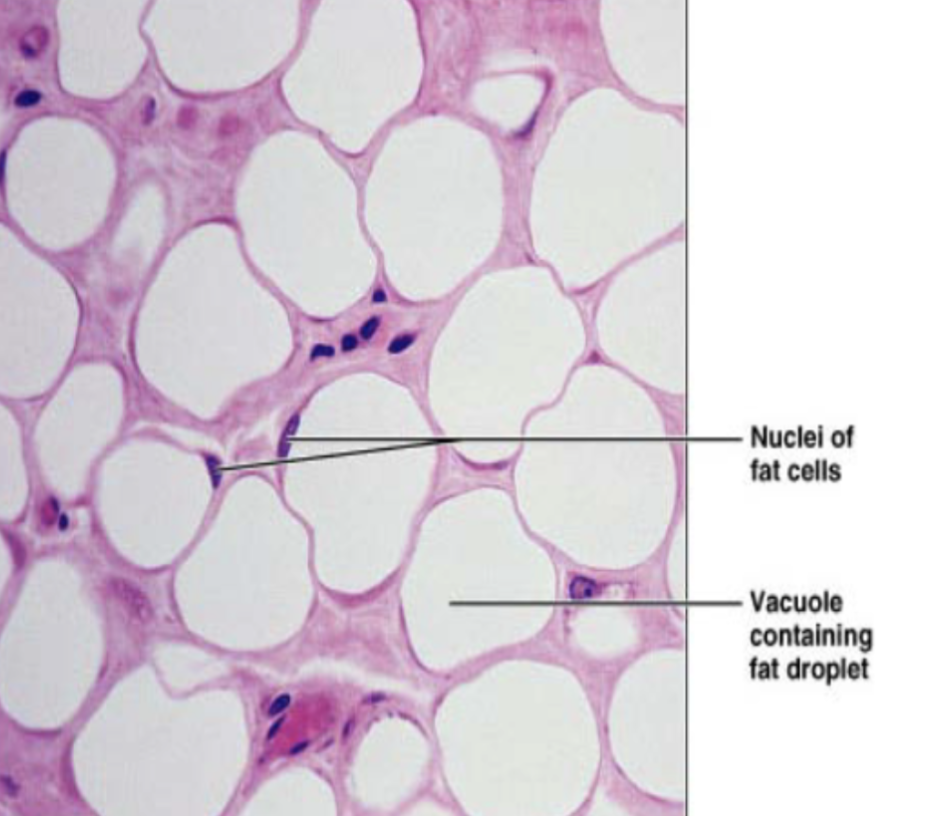
Adipose tissue (location)
mostly found in hypodermis (under skin), also around heart, lymph nodes, eyes, some muscles, abdomen, breasts
Dense connective tissue types
regular, irregular, or elastic
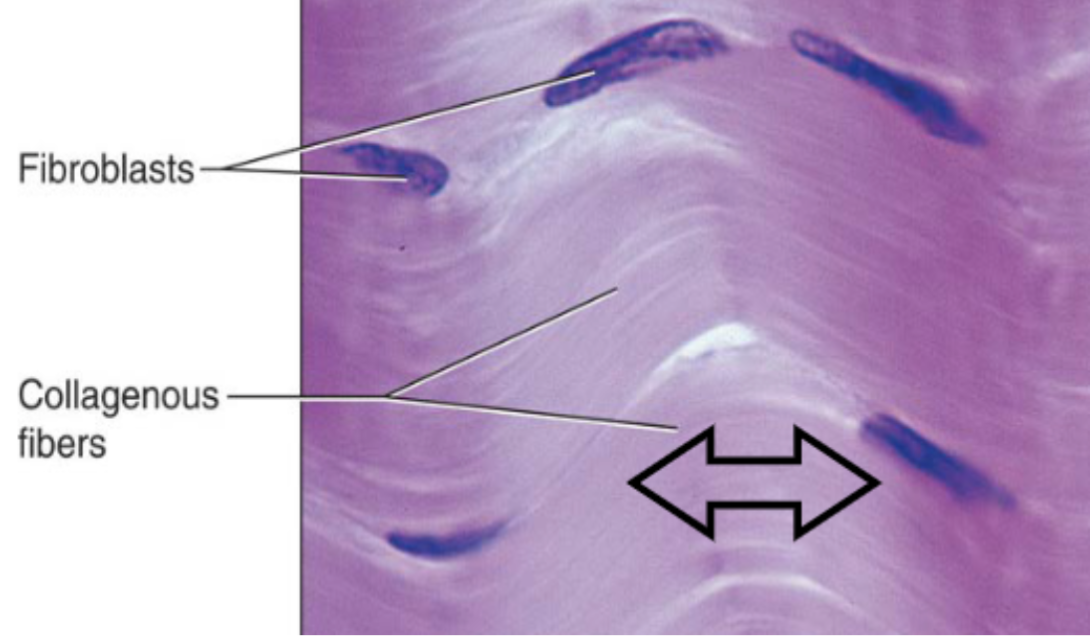
Dense regular CT (description)
primarily parallel collagen fibers w/ few elastic fibers
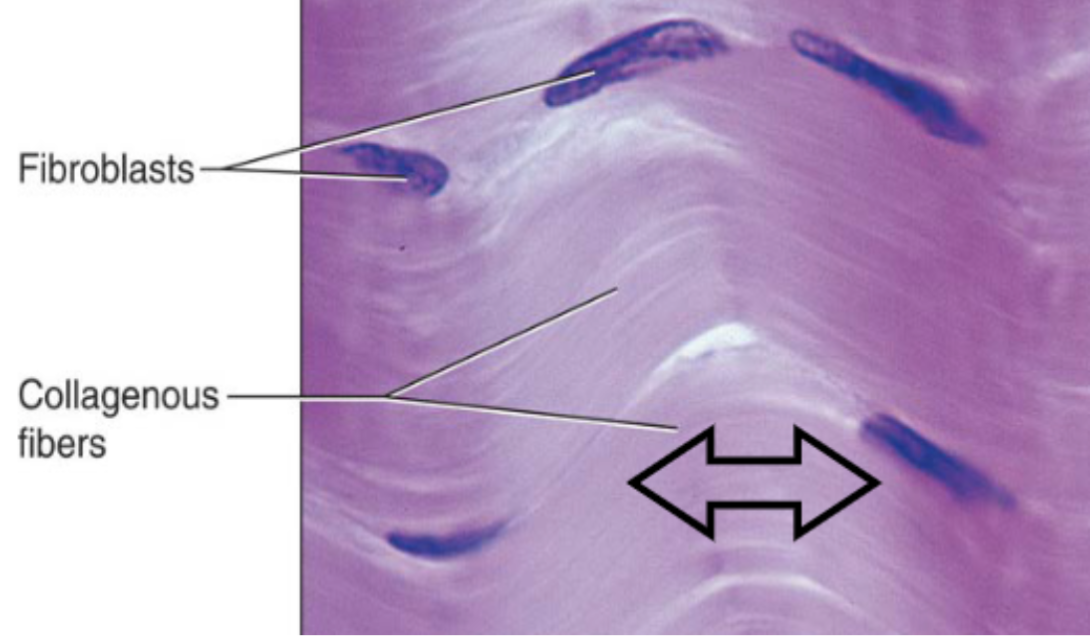
Dense regular CT (function)
attaches muscles and bones to other muscles or bones and can withstand great tensile stress in two opposing directions
Dense regular CT (location)
tendons, ligaments
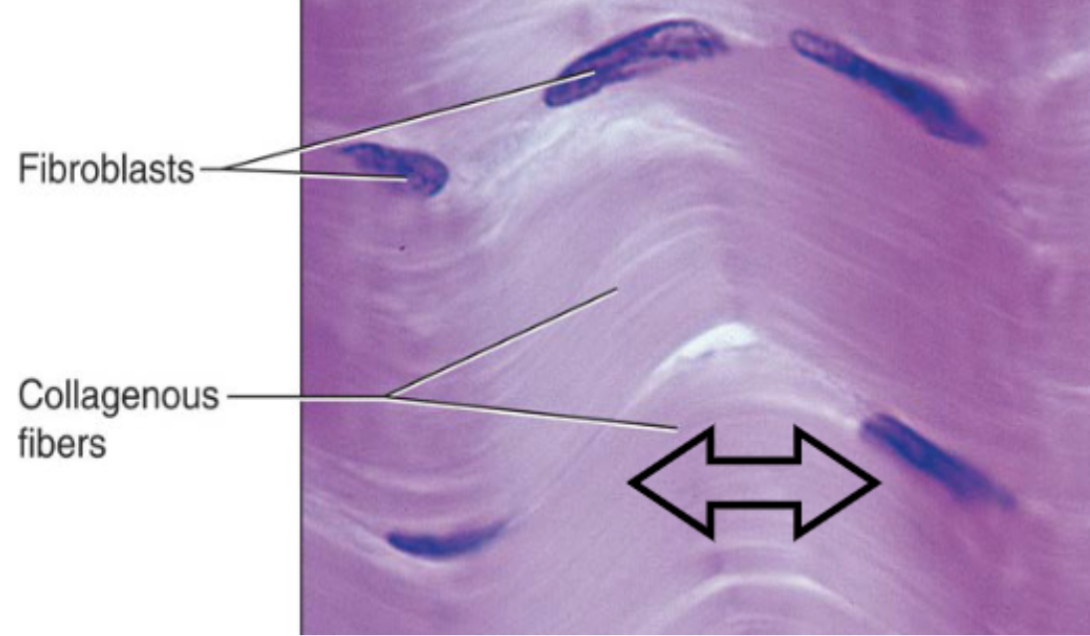
Dense irregular CT (description)
irregularly arranges collagen fibers with some elastic fibers
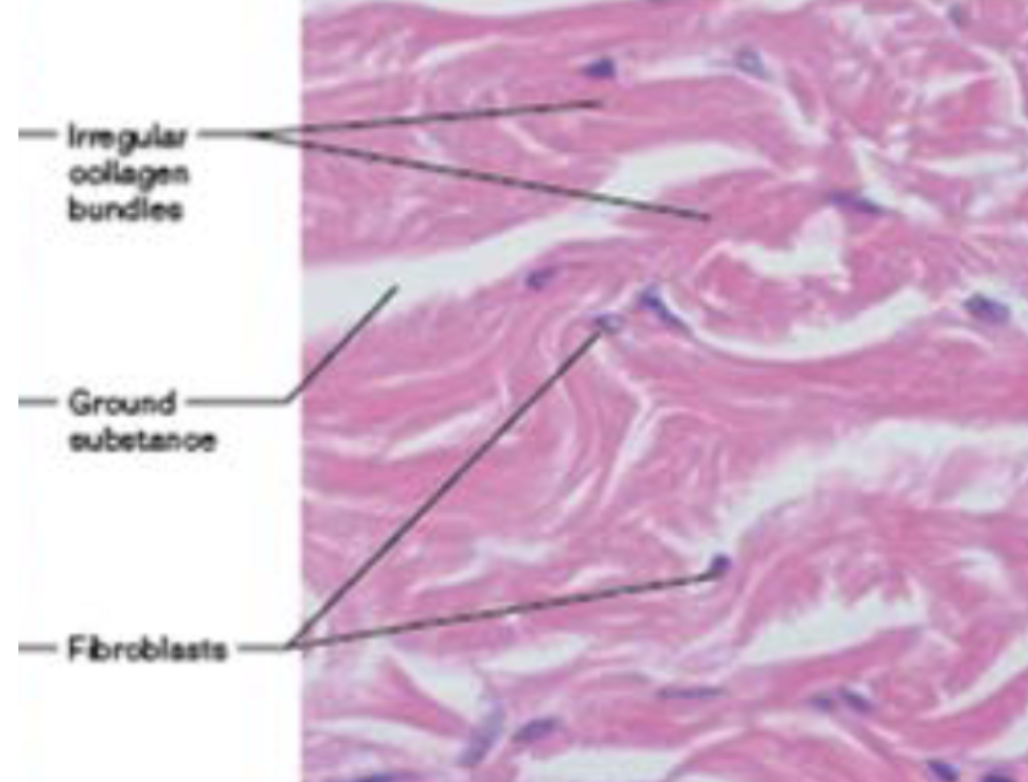
Dense irregular CT (function)
able to withstand tension exerted in many direction, structural strength
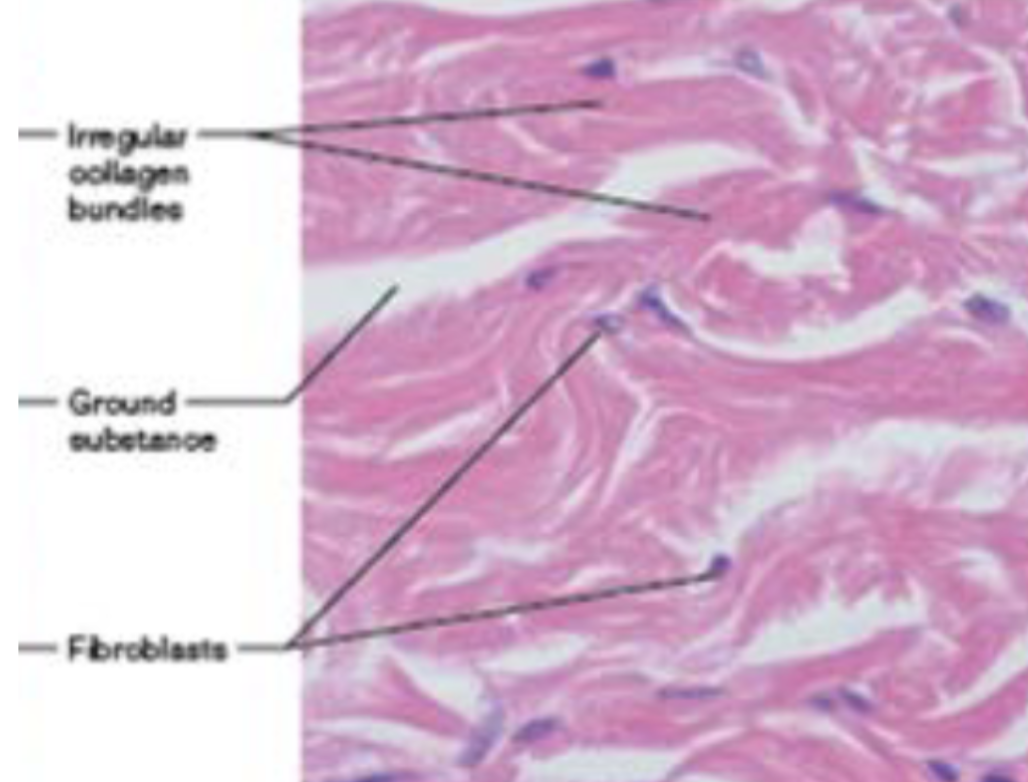
Dense irregular CT (location)
fibrous capsules of organs/joints, dermis of skin, submucosa of digestive tract
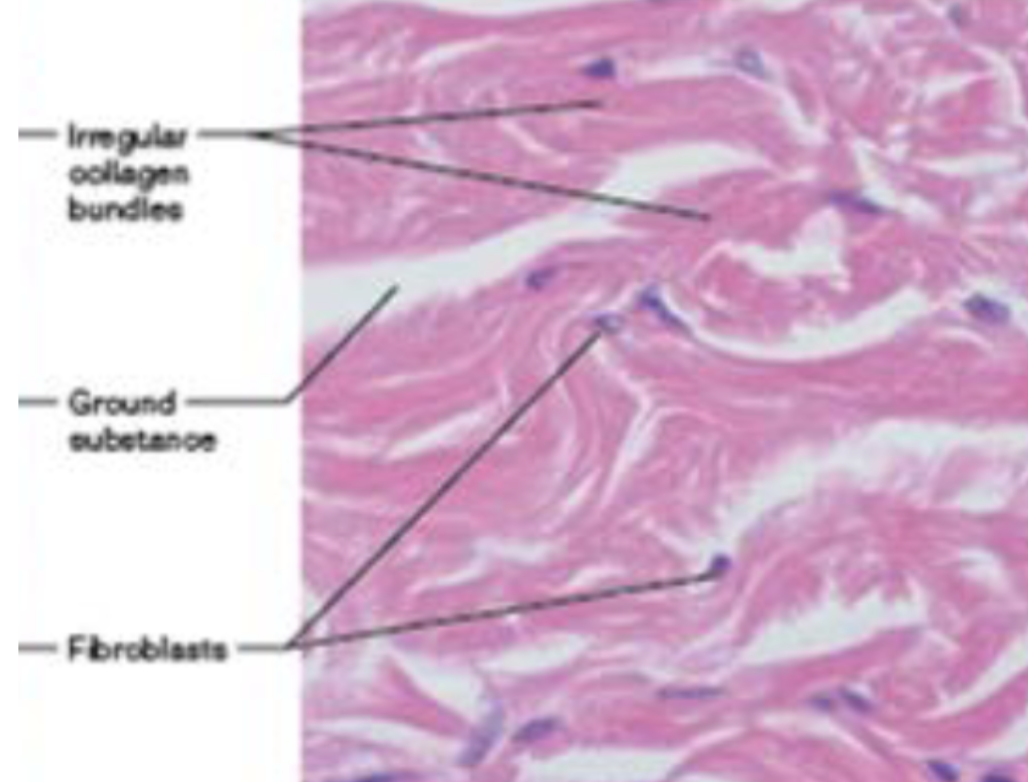
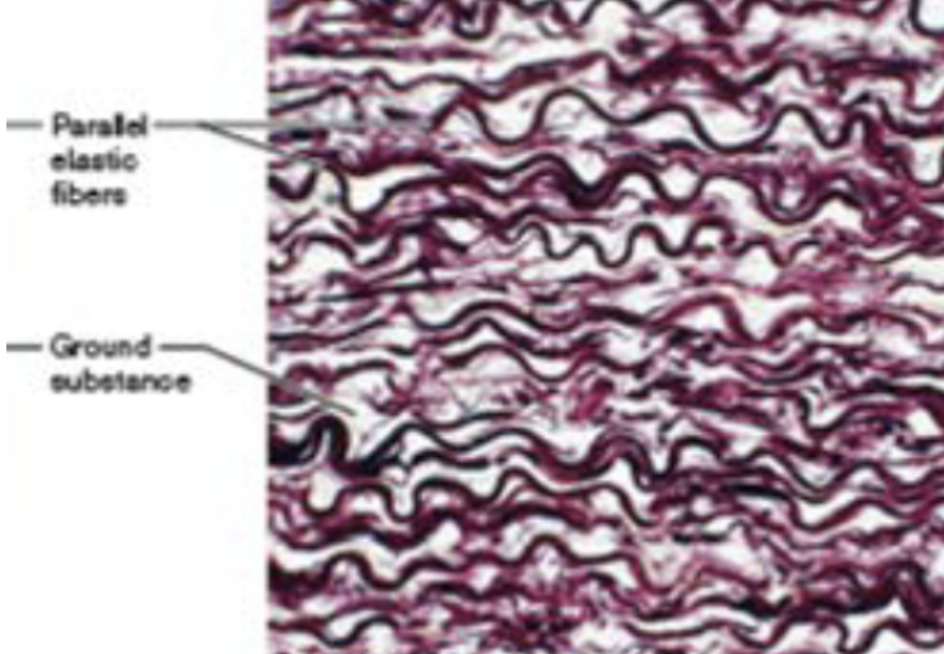
Dense elastic CT (description)
dense, regular connective tissue with high elastic fiber content
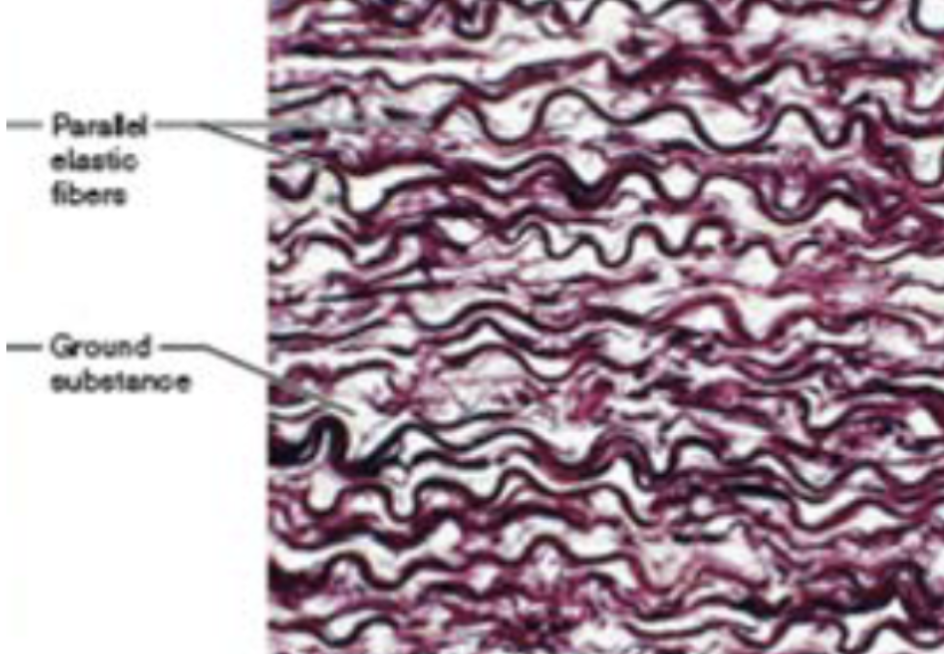
Dense elastic CT (function)
allows recoil of tissue following stretching
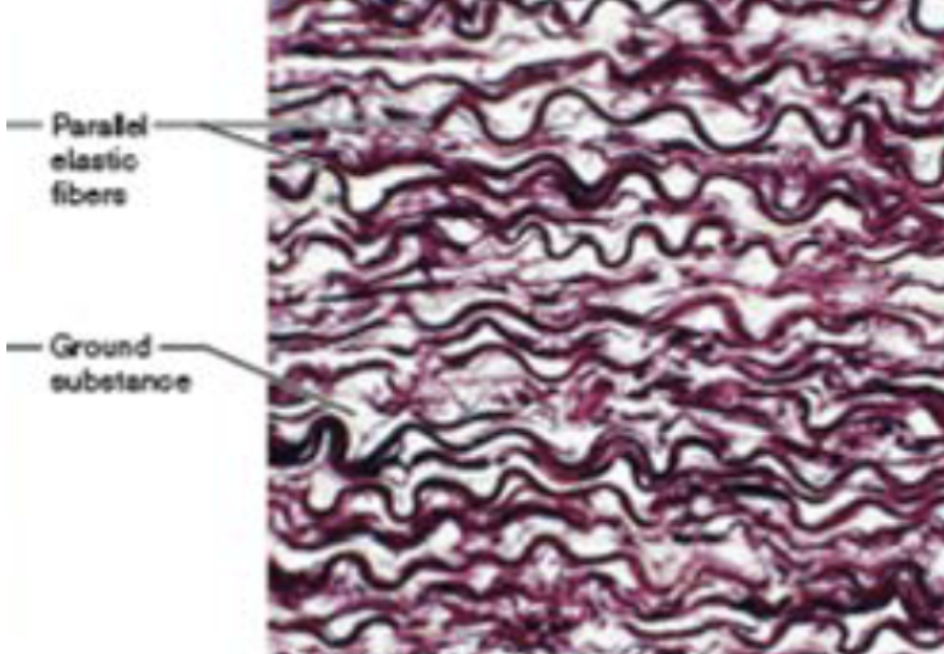
Dense elastic CT (location)
blood vessels, bronchial tubes of lungs
Specialized connective tissues
connective tissues with more specific functions (cartilage, bone, blood)
Cartilage (location)
CT in joints, ear, nose, and segments of respiratory tract
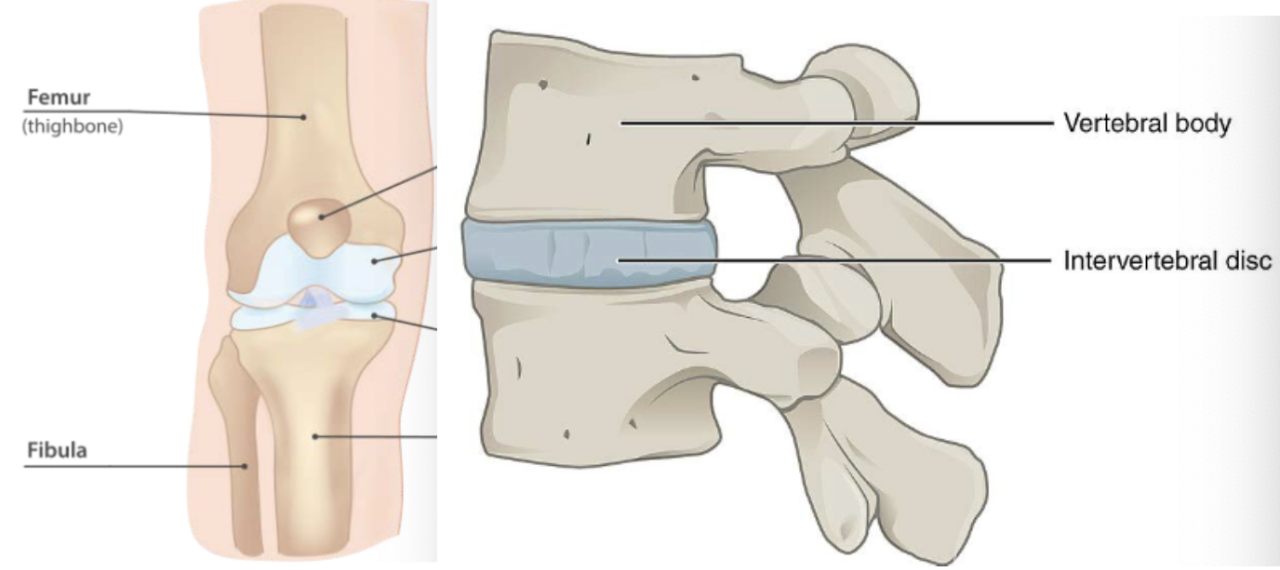
Cartilage (function)
CT that absorbs shock and resists tension, compression, and shearing forces
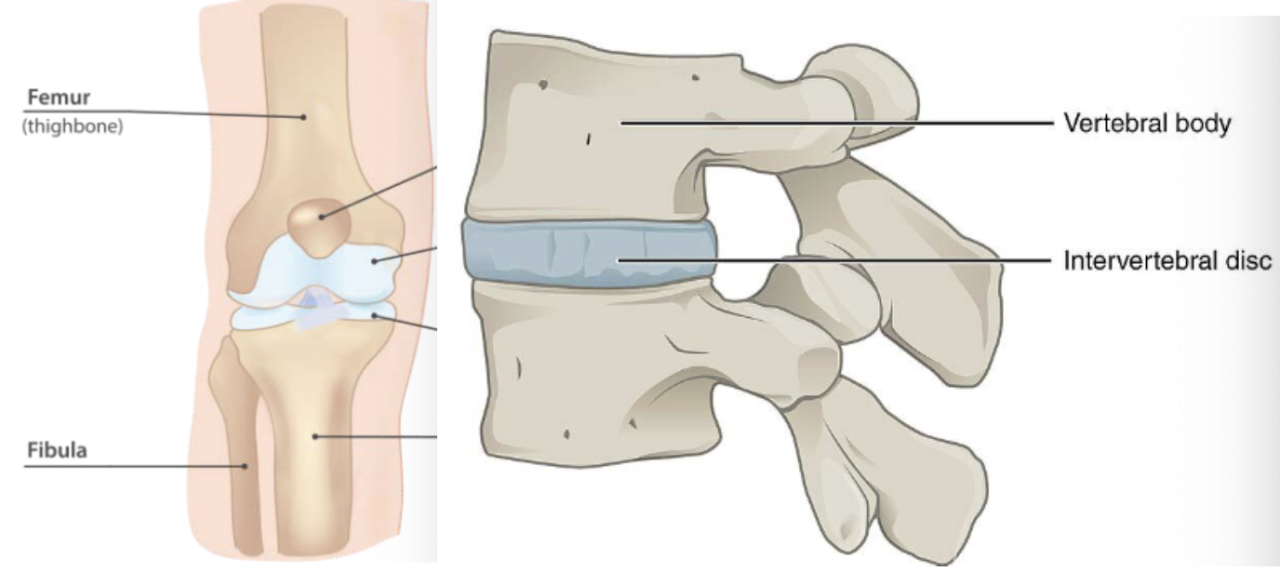
Cartilage (description)
tough, flexible CT that doesn’t have blood vessels or nerve supply
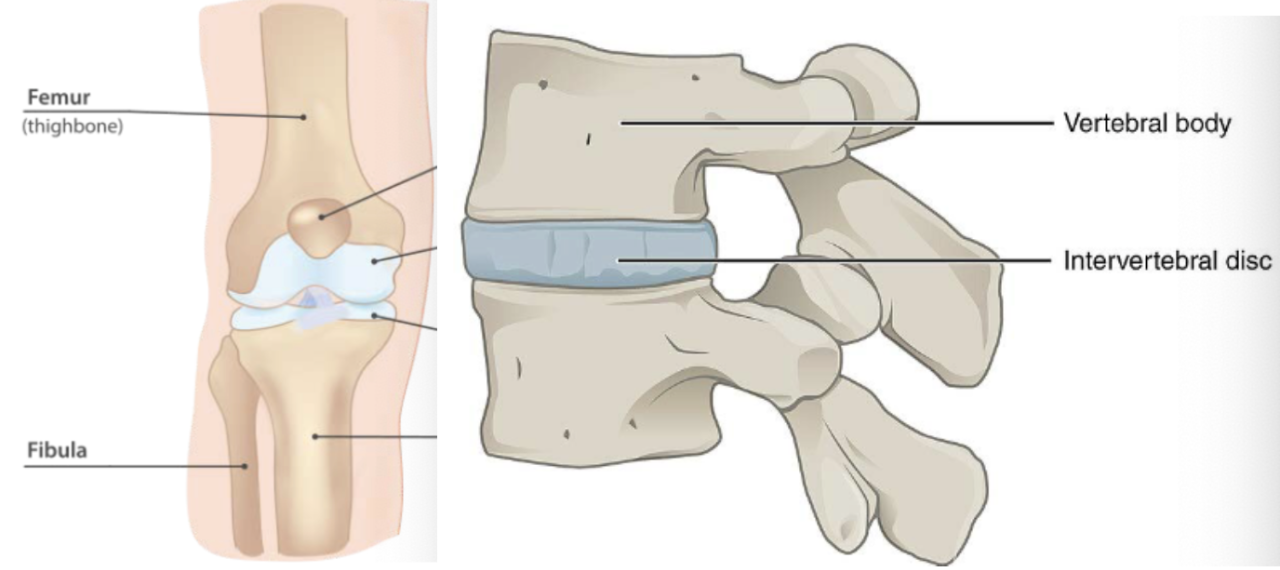
Chondroblasts
immature cells that divide by mitosis and make most of ECM, populates cartilage
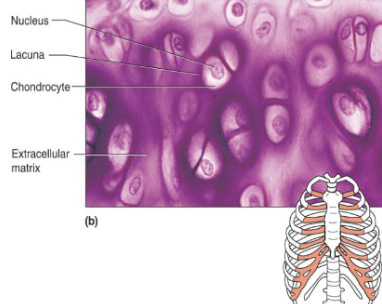
Chondrocytes
chondroblasts that mature and are largely inactive, located in small cavities called lacunae
Types of cartilage
hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage, elastic cartilage
Hyaline cartilage (description)
chondroblasts produce the matrix and lie in lacunae when mature (chondrocytes)
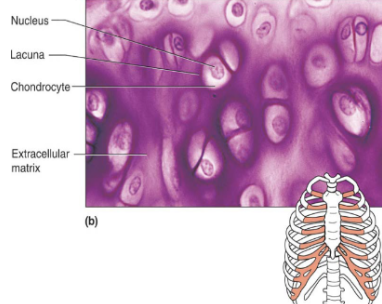
Hyaline cartilage (function)
cartilage that supports and reinforce due to resilient cushioning properties, resists compressive stress
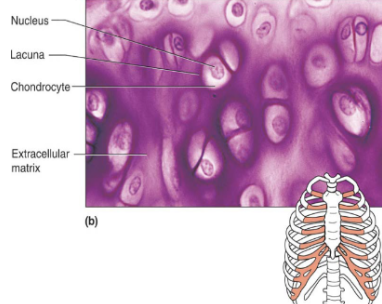
Hyaline cartilage (location)
embryonic skeleton, ends of long bone, costal cartilage of ribs, cartilages of nose, trachea, larynx
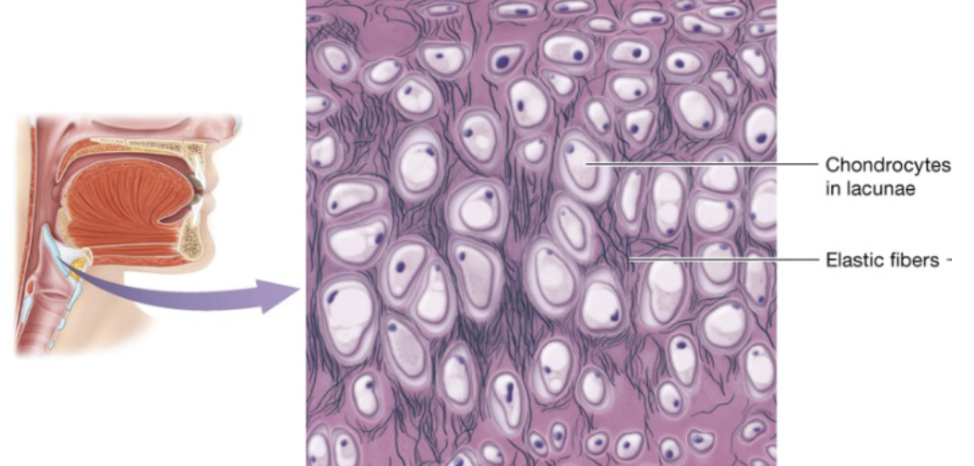
Elastic cartilage (description)
similar to hyaline, but more elastic fibers
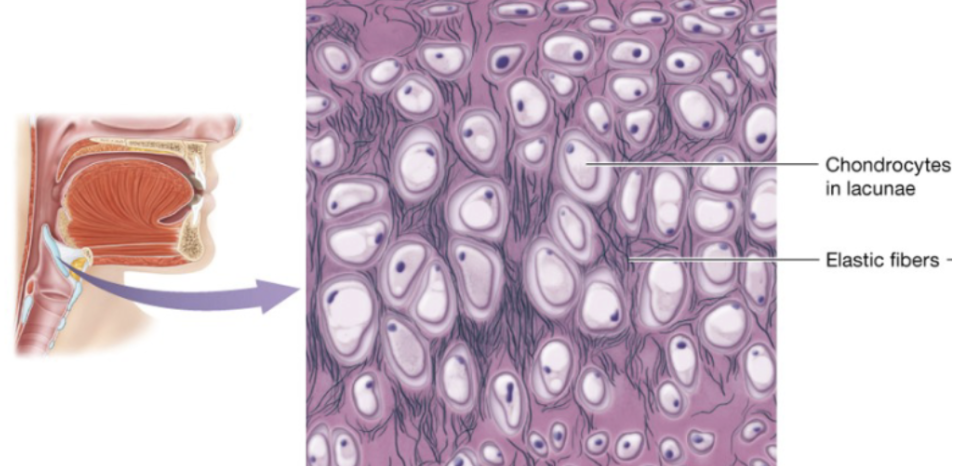
Elastic cartilage (function)
cartilage that maintains shape while allowing great flexibility
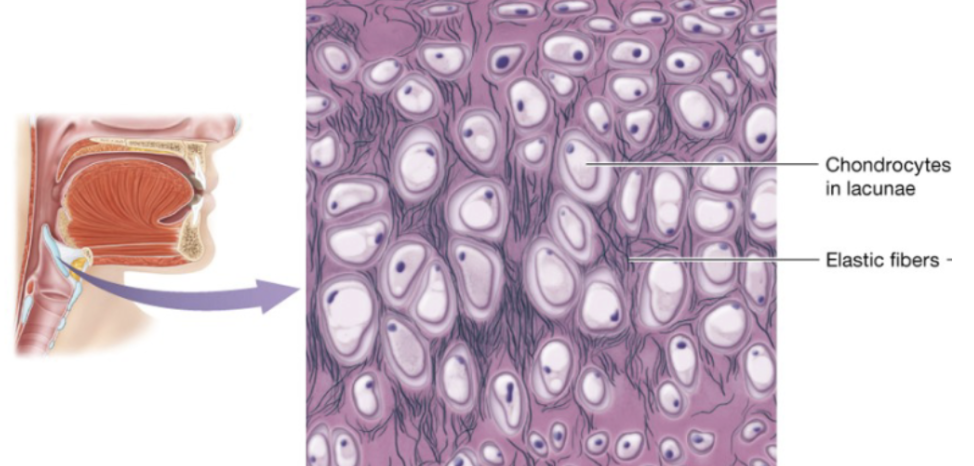
Elastic cartilage (location)
external ear, epiglottis
Fibrocartilage (description)
similar to hyaline but with thick collagen fiber
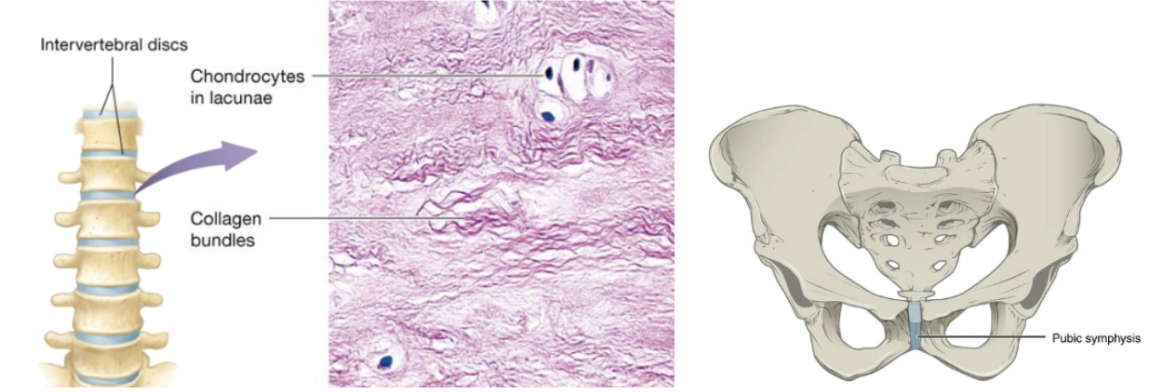
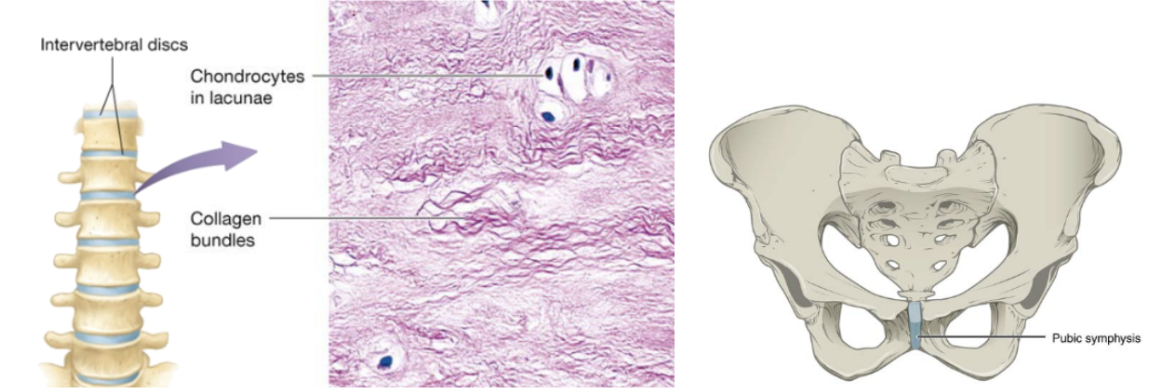
Fibrocartilage (function)
cartilage with tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock
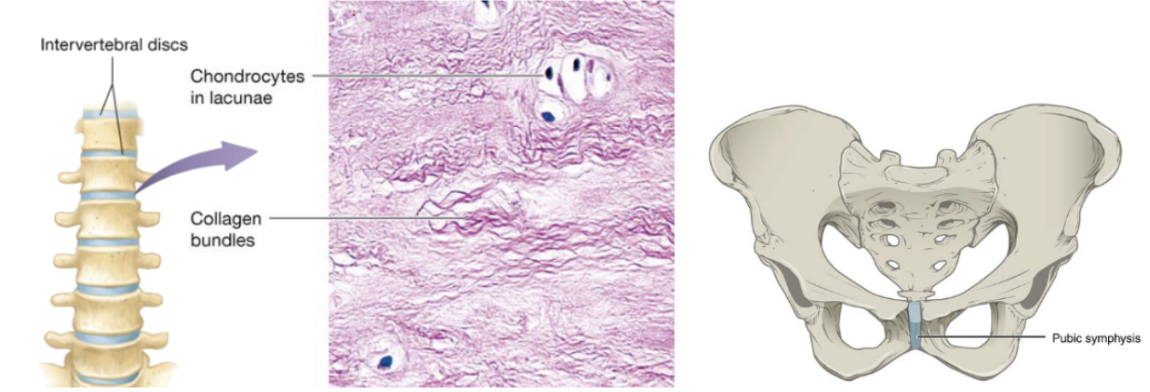
Fibrocartilage (location)
intervertebral discs, public symphysis, discs of knee joints, ends of long bones
Bones cell types
osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts
Osteoblasts
“bone-builders” on outer surface of bones that also synthesize (deposition from tension) and secrete ECM
Bone deposition
new bone formation that occurs as part of bone remodeling
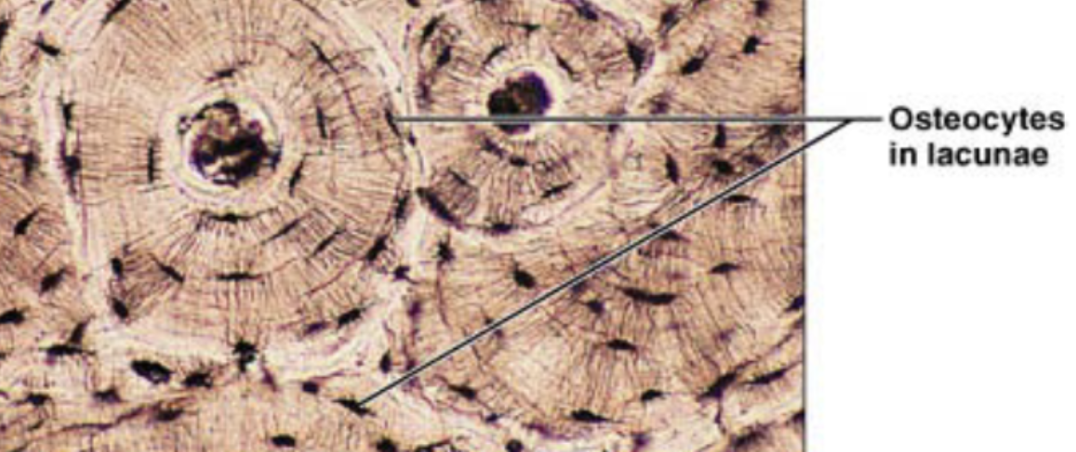
Osteocytes
mature and inactive osteoblasts that surrounded themselves with ECM in lacunae, continue to make and secrete substances important for bone maintenance
Osteoclasts
large, multinucleated bone destroyers, carry out bone resorption (from compression)
Bone resorption
secrete hydrogen ions and enzymes that break down ECM
Bone (description)
hard calcified matrix with collagen fibers, osteocytes (bone cells) lie in lacunae, well vascularized
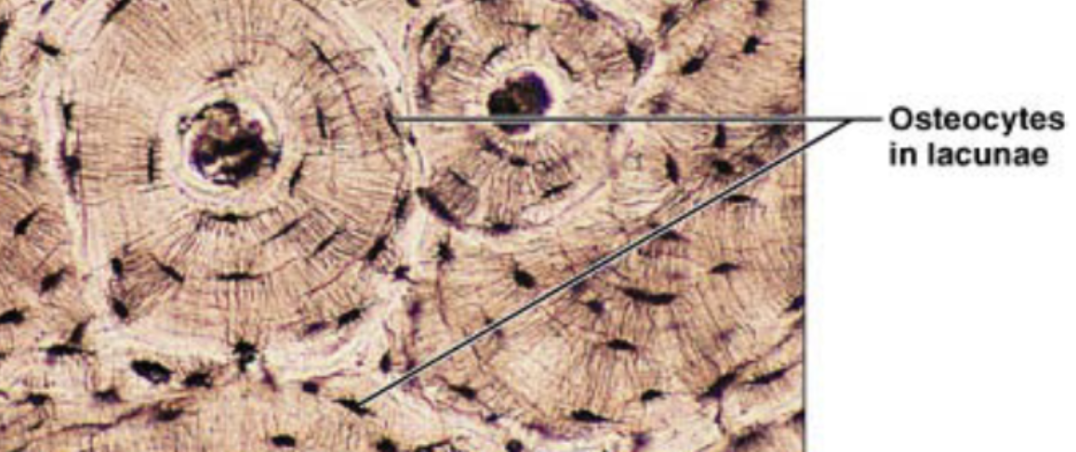
Bone (function)
bone support and protects
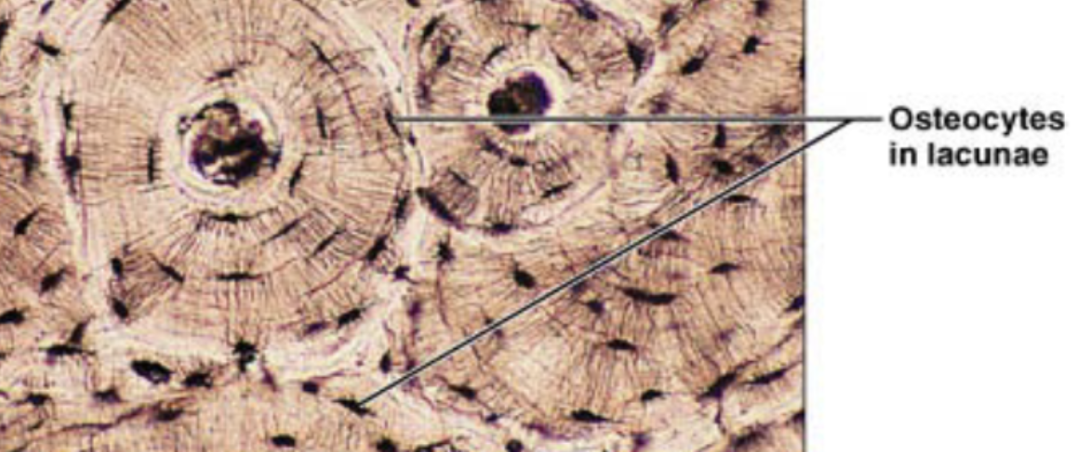
Bone (location)
bones
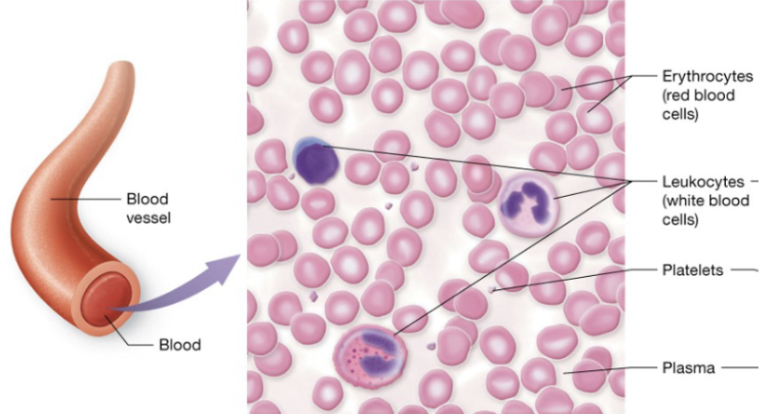
Blood cell types
erythrocytes (RBC), leukocytes (WBC), platelets (clotting fragments)
Blood ECM
plasma
Blood (description)
red and white blood cells in a fluid matrix
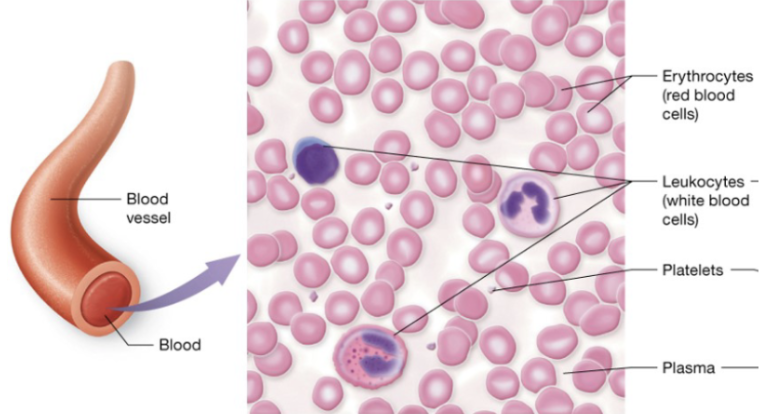
Blood (function)
transport of gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances
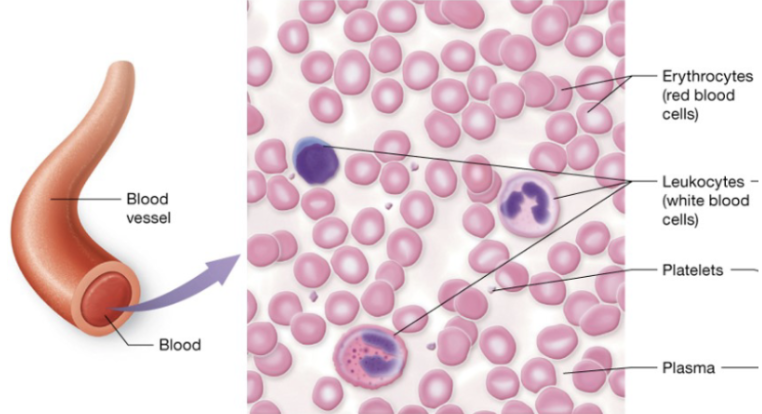
Blood (location)
within blood vessels
Muscle tissues
generate force by contracting, composed of myocytes (muscle cells)
Muscle cell types
skeletal, cardiac, smooth (not striated)
Striated
myofilaments arranged in alternating light and dark regions, appears striped (striated) under microscope
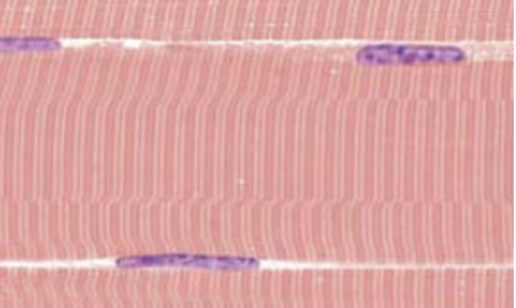
Smooth
myofilaments arranged in irregular bundles instead of repeating light and dark regions
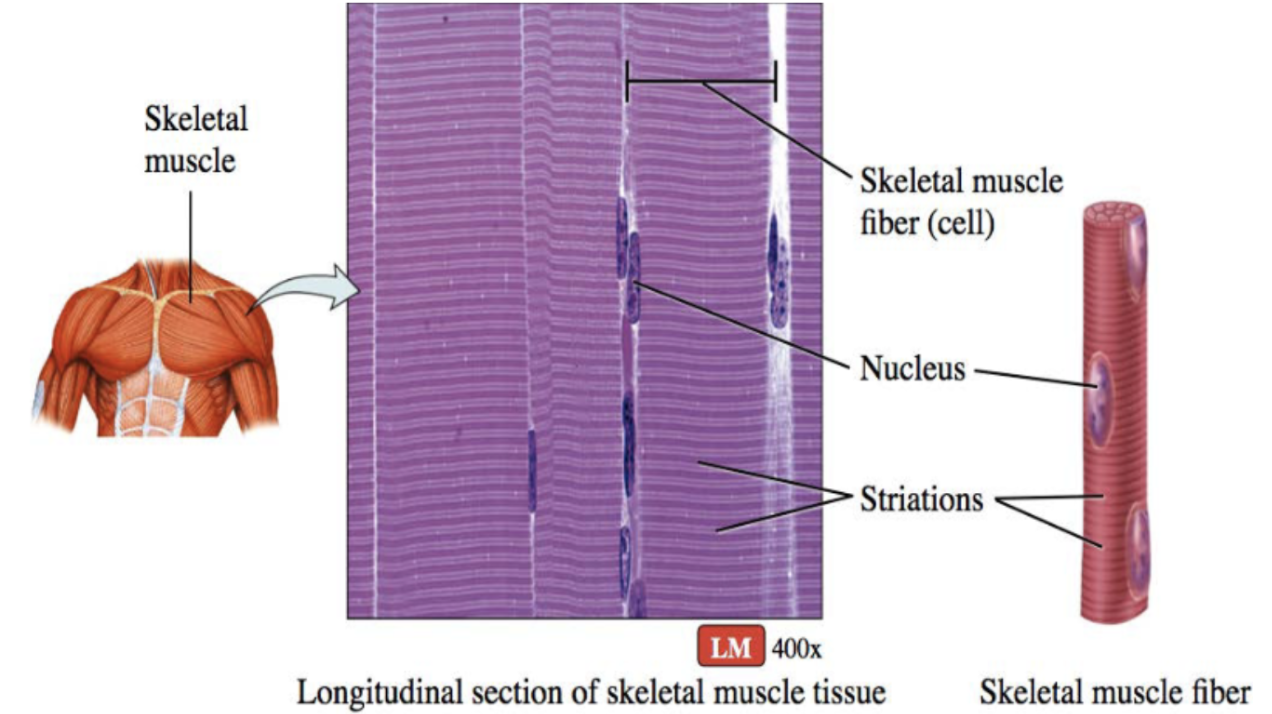
Skeletal muscle (description)
long and cylindrical cells, striated fibers, vary in length (3-40cm), multinucleated
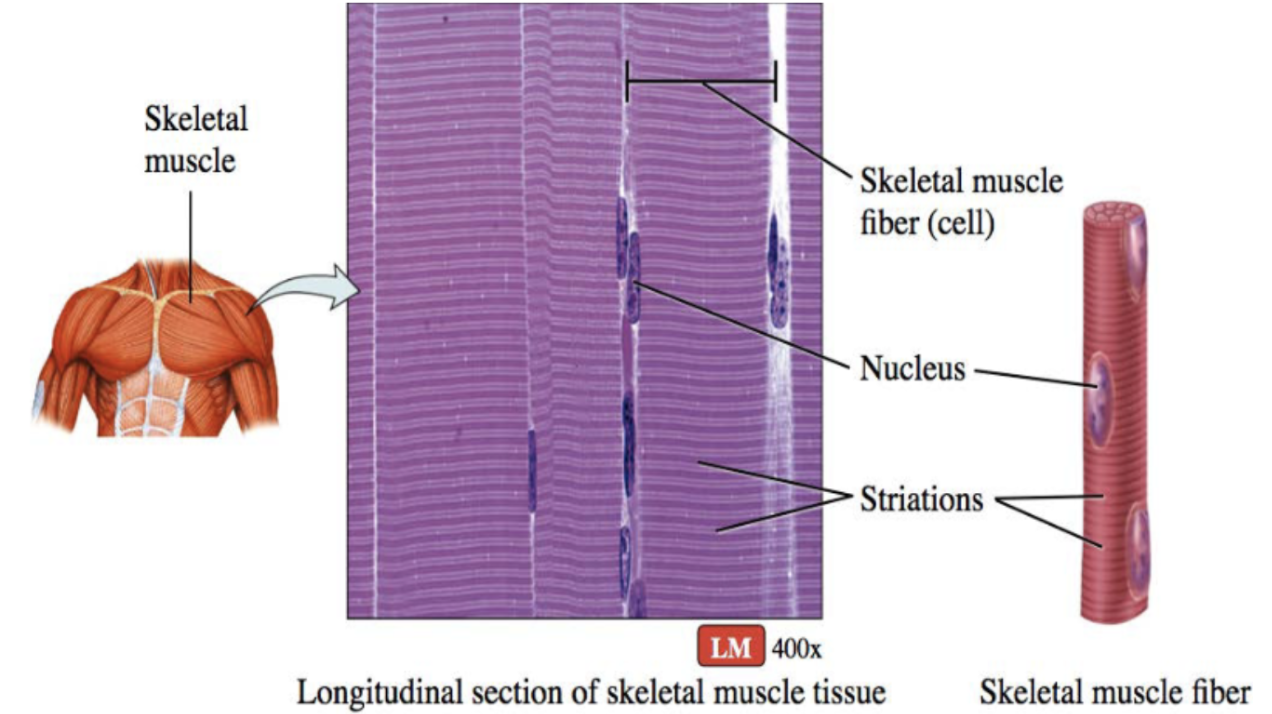
Skeletal muscle (function)
voluntary movement controlled by nerve cells
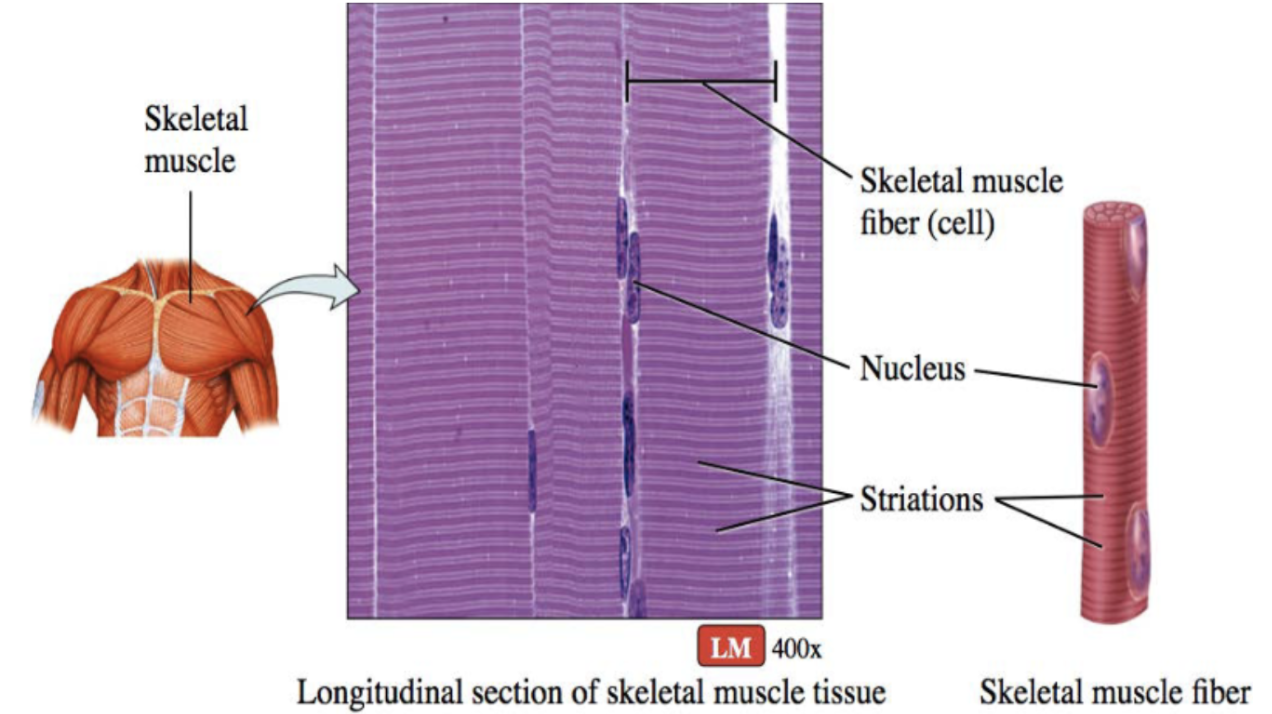
Skeletal muscle (location)
attaches to bones, tendons, skin
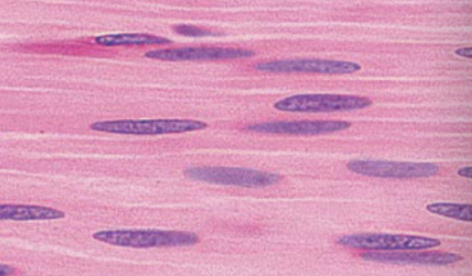
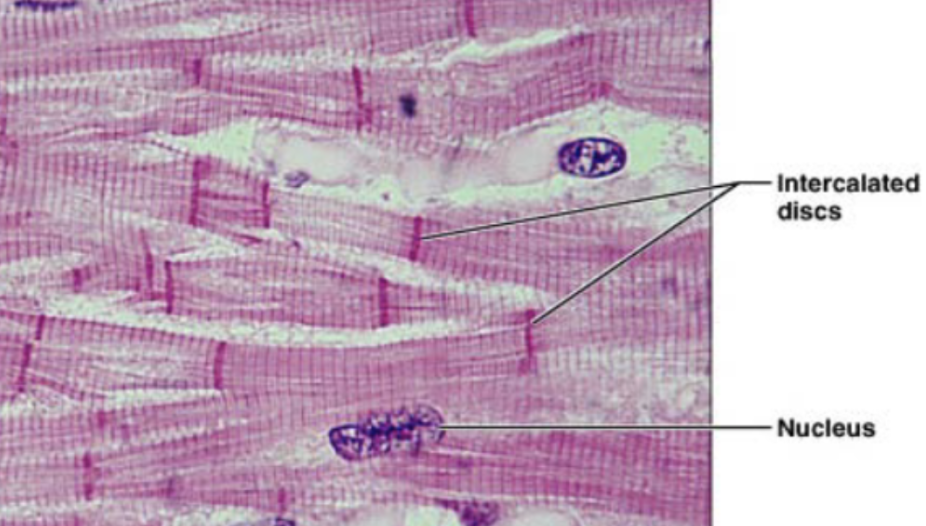
Cardiac muscle (description)
striated fibers, cells are short and branched, usually 1-2 nuclei per cell, intercalated disc, gap junction to allow contraction as unit
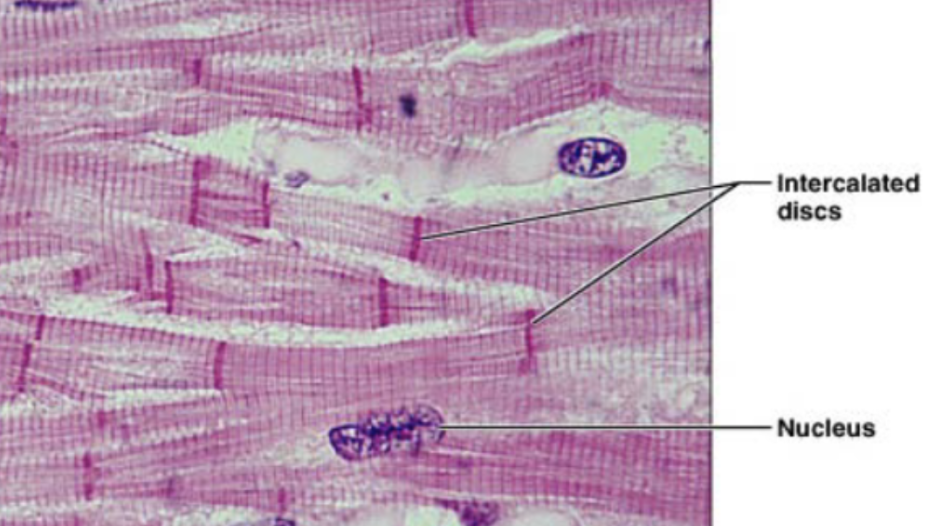
Intercalated disc
dark link separated individual cardiac muscle cells
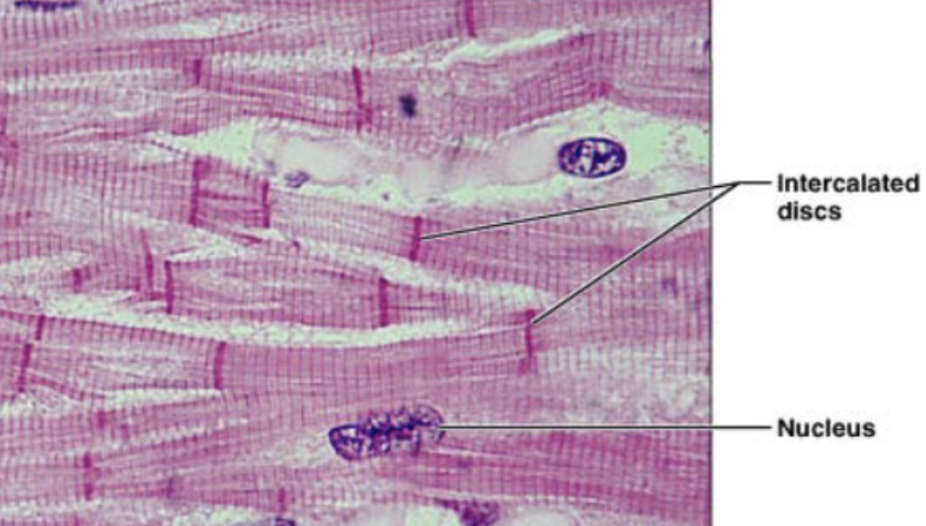
Cardiac muscle (function)
involuntary contraction
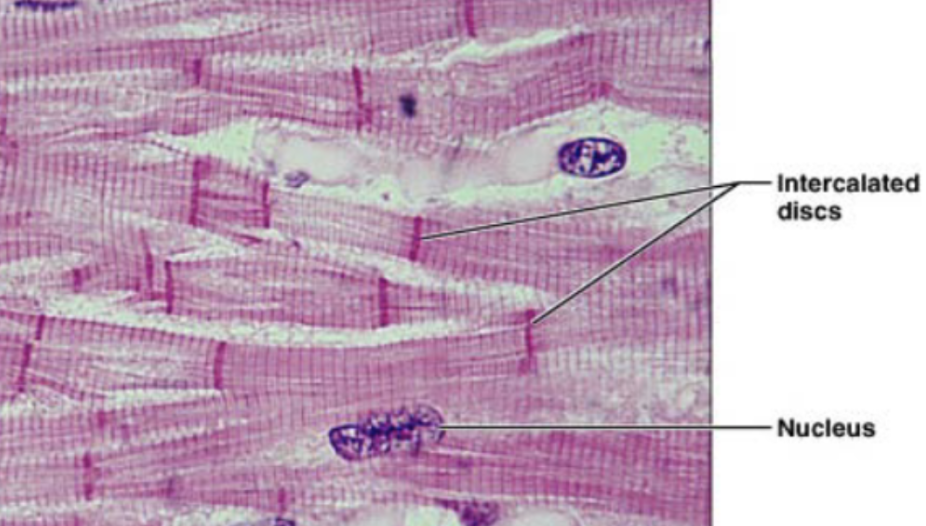
Cardiac muscle (location)
heart wall
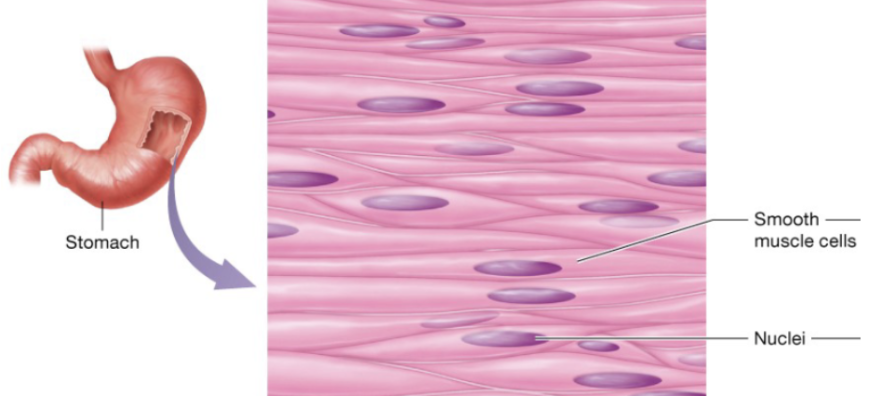
Smooth muscle (description)
flattened cells with one centrally located ovoid nucleus, gap junctions links neighboring cells
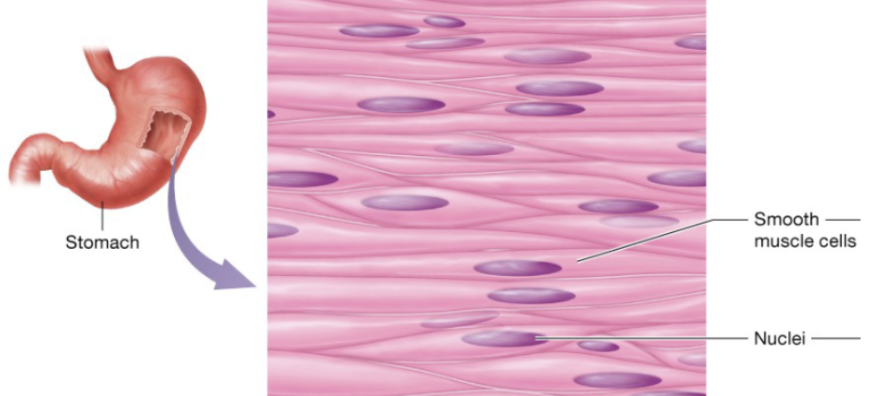
Smooth muscle (function)
involuntary movement
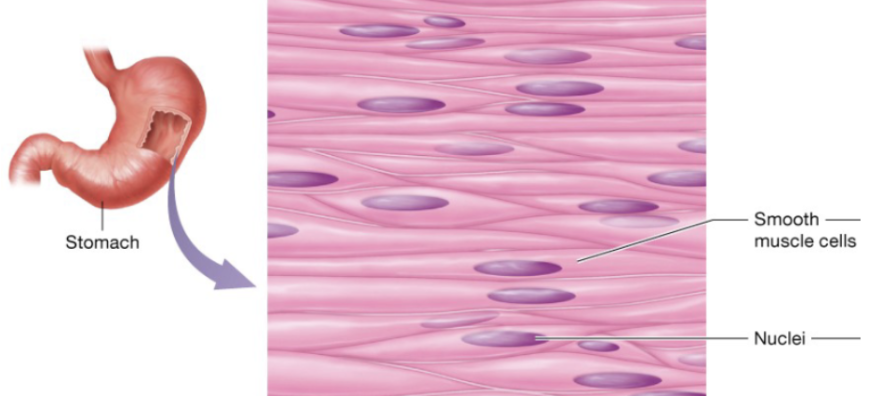
Smooth muscle (location)
in the walls of nearly every hollow organ (stomach, intestines, bladder, uterus), blood vessels, eyes, skins, and ducts of certain glands
Nervous tissues
generate, send, and receive message
Nervous cell types
neurons, glial cells
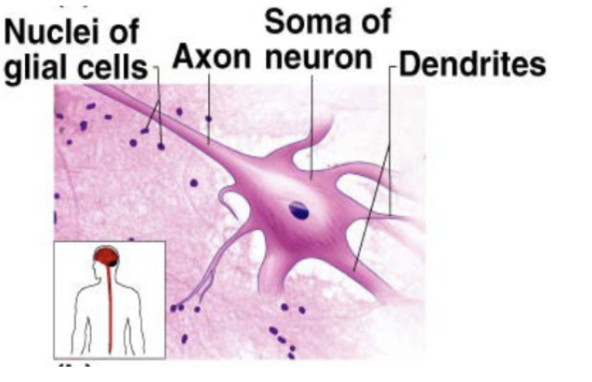
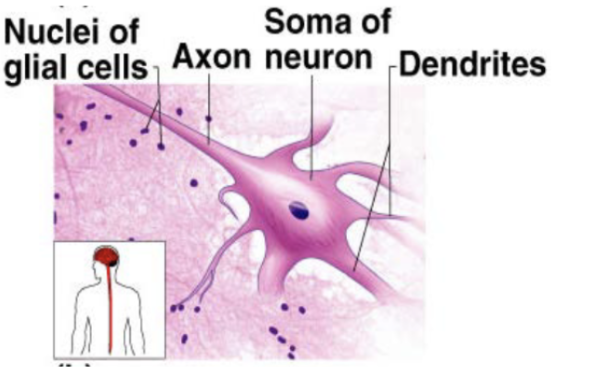
Neurons
nerve cells that are capable of initiation and conducting electrical activity throughout the body
Glial cells
cells that support and protect neurons
Neurons (description)
branching cells with long extensions
Neurons (function)
transmit electrical from sensory receptors and to effectors (muscles, glands, etc)
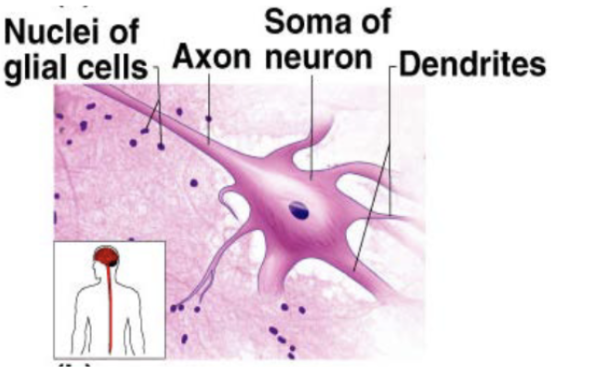
Neurons (location)
brain, spinal cord, nerves