Unit 4 SAC 1 Specific notes
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Safe Water
Refers to water that is not contaminated by human waste and disease causing pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses or chemicals such as lead and mercury.
People in low- and middle-countries are at greater risk of the effects of unsafe water as they are less likely to have the infrastructure to supply clean drinking water effectively, especially if they live in rural and remote areas
What are the implications of not having Safe Water?
Collecting water takes lots of time, takes away time from pursuing education/employment, therefore decreasing social and spiritual health.
Diarrhoea can be caused by drinking water contaminated by disease causing pathogens. The body dehydrates because of diarrhoea, which leads to a greater rate of morbidity. More unsafe water then needs to be consumed because of thirst. This causes more deadly bacteria to be consumed and can lead to other conditions such as an increased incidence in cholera which can lead to premature death, particularly in children, therefore, increasing Under 5 Mortality Rate.
Required for:
Food preparation and cooking
to remove harmful pathogens that could lead to illness and safe for human consumption. Prevent the spread of diarrahoea, cholera and hookworm.
Washing and hygiene
Agriculture and food production
Sanitation
If there is adequate sanitation this may mean there is sewerage disposal, so that human waste doesn’t flow into the streets. This reduces the risk of contracting an infectious disease such as diarrhoea from contaminated sewerage water, contributing to higher morbidity rates.
Poverty
Used to describe the lack of access to resources often as the result of a lack of access to money
Extreme poverty
People living on less than US$1.90 per day.
Relative poverty
Individuals living on less than 50% of the country's average income.
affect on BOD & health status
individuals in poverty are unable to afford essential resources such as food. This causes them to become malnourished which weakens immune system, causing them to be more susceptible to disease, thus increasing morbidity and yld’s By being susceptible to diseases such as cholera. individuals are more likely to contract this. contributing to increased mortality rates.
Can result in:
Low literacy rates:
Reduced access to education results in lower literacy rates. This reduces opportunities for employment, perpetuating the cycle of poverty and the associated impacts such as limited access to food, water and healthcare, which contributes to higher rates of morbidity and premature mortality.
High maternal & infant mortality
Malnutrition is often the result of an inability to afford nutritious foods. Malnutrition decreases immune function, which increases the risk of infection and premature death, especially among children. Pregnant women who cannot access nutritious foods are more likely to die as a result of their pregnancy and have babies who are more susceptible to premature mortality due to underdeveloped body systems.
Who classifies countries (World Bank)
World bank
$$ gross national income(GNI) per capita
what you earn before tax
whole amount a country can earn divided by the population size = avg.
Can only talk about GNI if asked to classify. characteristics can include e.g LE, access…
Low Income countries
GNI per capita = $1005 -
Average of less than $1025, based on GNI per capita\
e.g. Zimbabwe, Congo, Chad, Mozambique, Nepal
Lower Middle Income countries
GNI per capita = $1006 - $3955
Average from $1026-$4025, based on GNI per capita
e.g. Indonesia, Cambodia, India, Pakistan
Upper Middle Income countries
GNI per capita = $3956 - $12235
Average from $4026-$12475, based on GNI per capita
e.g. Mexico, South Africa, China, Turkey, Fiji, Cuba
High Income Countries
GNI per capita = $12236 +
Average more than $12476, based on GNI per capita
E.g. Australia (GNI per capita of 60,000), Canada, UK, Greece, Ireland, Japan
$ Economic Characteristics of countries
Industries
high income = wide range e.g. tourism, agriculture
Middle income = mixture
low income = limited, mainly farming to feed themselves
Global Trade opportunities !!
high income = many opp. e.g. animal trade, mining
middle income = emerging global trade
low income = not much trade - no desirable goods
Social Characteristics of countries
employment, ed. etc.
Gender Equality
high income = high levels
low income = low levels (women are controlled my men and get no protection)
High income countries often experience gender equality. In these countries, both males and females have opportunities and choices with regards to education, employment, community participation and recreation. In many low income countries, however, females do not have the same opportunities as males in society. Females may have limited opportunities for education and often work in fields tending crops and/or spend significant time collecting water and preparing meals.
Legal & social security(Centrelink, NDIS) systems !
high income = developed systems & vice versa
High levels of economic development and stable political systems increase the ability of governments in high-income countries to provide social security payments for those in need. Individuals who are unemployed, or unable to work due to illness or disability, are provided with financial support. Low- and middle-income countries often do not have the means to provide assistance to those who are unemployed or unable to work and they are driven further into poverty.
Birth rates and pop. growth
high income = low births rates and pop growth
low income = high rates but higher infant mortality rate (no health lit, don’t know about STI’s and unprotected sex/birth control, hence fall pregnant easy. Also sex trade&work)
Environmental Characteristics of countries
Housing
high income = adequate
Compared to high-income countries, many people in low- and middle-income countries lack access to adequate housing. Low and middle income countries often live in substandard housing with poor ventilation, lack of heating and cooling, poor resistance to infestation of disease-carrying organisms such as insects, lack of cooking facilities and running water, and poor protection from the elements.
Food security
Refers to reliable access to sufficient quantity of affordable, nutritious, culturally appropriate food.
People in high-income countries generally have access to a quality food supply. Those in low-income countries, however, often lack food security. Natural disasters such as floods and droughts tend to have a more pronounced impact on the availability of food for those in low-income countries, as they lack the financial resources to purchase food in emergency situations.
Sim. & dif’s. in health status & BOD in low, mid & high income countries
LE:
Sim:
Globally, life expectancy has more than doubled since 1900
Overall, female life expectancy is 75.6 years and male life expectancy is 70.5 years.
Dif:
The lower the average income of a country, the lower the life expectancy and health-adjusted life expectancy.
Many African countries, for example, experienced a significant decrease in life expectancy in the 1990s due to the AIDS epidemic.
Mortality & morbidity:
The U5MR in low- and middle-income countries varies but is significantly higher than that in high-income countries like Australia.
Sim:
Since 1990, the global rate and number of child deaths have been reduced by more than half.
Dif:
Premature mortality among adults generally increases as average incomes decrease.
Maternal mortality significantly higher in low-income countries
Malnutrition is an underlying factor contributing to the high rates of mortality and morbidity experienced in low- and middle-income countries.
BOD:
sim:
The rate of YLD generally increases with life expectancy.
Dif:
the total YLL by non-communicable diseases is much higher in high-income countries than in low-income countries.
Economic Sustainability
Relates to the capacity of future generations to earn an income and the efficient use of resources to allow economic growth over time that’s inline with inflation and future living costs.
Impact of good Economic Sustainability
Employment allows individuals to earn an income and purchase health-promoting resources, giving them the means to prevent and treat conditions. This growth allows governments to provide infrastructure and services, such as clean water and sanitation, therefore increasing pride and sanitation and supporting spiritual & physical health and wellbeing.
High levels of employment and increasing incomes, ensures money is used to invest in infrastructure such as education and hospitals which enhances individual’s physical, mental,
social H&W
Greater opportunities in employment also allow people to be more connected to their community enhancing spiritual H&W
Developed industries
A diverse range of industries is required for a country to improve their economic situation and ensure economic sustainability. Many developing countries rely solely on the agriculture industry. This is unsustainable as with the impact of weather events such as drought, the economic growth of a country suffers.
Multiple industries allow for a range of opportunities to enhance a countries economic growth. If one industry faces difficulty, for example due to extreme weather conditions, the country is able to stay economically stable and people can retain jobs, increasing incomes and enhancing many health and wellbeing dimensions
Sustainable incomes
A country's income (GNI) must increase in line with inflation, to ensure its sustainability. This will see economic growth of a country and its people and allow for more money to be invested into services and infrastructure, education and hospitals.
Sustainable incomes of a country and it’s people ensure that essential resources remain affordable such as food, improving physical H&W and a country is able to achieve economic growth and therefore enable investment in long term sustainable projects.
Social Sustainability
Creating an equitable society that meets the needs of all citizens and can be maintained indefinitely.
Education systems
Ensuring equal access to education is a country’s greatest resource, educate a girl - educate a nation as the knowledge learnt at school will passed down to future generations. Educated girls also are more likely to have healthier children.
Physical H&W - educated individuals are able to understand health promotion messages, more likely to earn a higher income and therefore afford basic prerequisites for health such as food and shelter, thus reducing poverty globally.
Social H&W - builds effective communication, meaningful relationships, teamwork skills, allows greater participation in community
Social support systems
Social support systems are designed to assist the most vulnerable people in the community, such as unemployed, elderly, disabled and those who are unable to work due to illness.
Through provision of economic support to the most vulnerable they are able to afford access to essentials such as education, food, shelter, safe water and sanitation. This will reduce levels of ill health and malnutrition promoting physical H&W
There will also be lower levels of diseases and illness on a global scale. Through the provision of social support, stress and anxiety levels are decreased, improving mental H&W
Gender equality
Includes elimination of violence against women, equal opportunities to education, employment and community life and leadership opportunities.
Reduction in violence and discrimination against women and girls, improves overall physical H&W. This may lead to lower rates of child marriage globally and reduction in rates of maternal mortality.
Social health and wellbeing is enhanced as women and girls can be involved in the community and are valued members of society
Gender equality results in a decreased level of stress and anxiety as they are not living in fear from violence, this improves levels of mental H&W
Environmental Sustainability
Ensuring the natural environment is used in a way that will preserve resources into the future.
Waste management/pollution control
Effective waste management ensures that waterways are not polluted and therefore reducing the risk of waterborne disease such as cholera improving physical H&W
Children can attend school and adults work when disease is controlled, enhancing other dimensions such as social, mental and spiritual health and wellbeing.
Respiratory conditions are also reduced when air pollution due to emissions are reduced, enhancing physical H&W
Sustainable agriculture practices
Crop diversification enhances soil quality, enabling farmer to yield both larger and more varied crops. The use of sustainable water systems, also ensures land conservation for future generations.
Practices such as crop rotation, allow for a variety of crops to be grown, reducing levels of malnutrition, especially in drought prone areas. Increased access to income for farmers, through increased trade options.
Factors affecting Inequality/Discrimination
Inequality is when people aren't given equal opportunities and rights. They are treated unfairly and experience discrimination.
Discrimination is the unfair treatment of someone because of their particular characteristics e.g. race, religion, gender etc.
QU. Outcome and affect on H&W & health status
discrimination and inequality based upon sex may cause women to be excluded or isolated from society. This makes it difficult to maintain relationships with others and have positive communication, therefore negatively impacting social health and wellbeing. The lack of relationships reduces and individuals support they are receiving which can contribute to the development of mental health conditions such as depression therefore increasing morbidity rates from this.
Factors affecting Global Distribution/Marketing
Due to tabacco:
High-income countries have high health literacy and lots of laws and regulations to prevent smoking.
This therefore decreases rates of smoking and therefore there is an increase of sales to Low-income countries; as they don’t have as much health promotion and warning around the effects of smoking; therefore increasing rates of cancer/CVD/respiratory conditions, therefore increasing double burden of disease.
Smoking H&W affects:
Physical – Reduced physical fitness, and poor functioning body systems due to illness and disease such as athersclerosis, CVD, lung cancer
increase yld, and the risk of premature death, thus mortality rates
Due to processed foods:
Increase in non-communicable diseases (e.g. type 2 diabetes, CVD, Cancer, obesity).
Due to rapid urbanization there has been an increase in the consumption of energy dense diets in low and middle income countries which are high in sugar, salt, sat. fat & low in carbs, fruit & veg.
H&W affect:
Physical – Reduced physical fitness due to overweight, obesity, and poor functioning body systems due to illness and disease such as diabetes 2 or CVD.
Burden of disease
A measure of the impact of diseases and injuries. Specifically it is the gap between current health status and an ideal situation where everyone lives to an old age free of disease and disability. Burden of disease is measured in a unit called Disability Adjusted Life Year (DALY)
Years of life lost (YLL) rates for most causes are higher in low- and middle-income countries than in high-income countries, including Australia.
Treatment options are often limited in low- and middle-income countries, which can increase the risk of premature death and result in a higher rate of YLL
Australia’s well-developed health system means that many conditions that can cause premature death are often effectively treated, and this can extend life expectancy and reduce the rate of YLL that otherwise might have occurred.
Double Burden of Disease
The coexistence of communicable and diet related non-communicable diseases.
Human Development
gives a more accurate picture of how well people are living within particular countries.
created though the untied nations
Definition:
Creating an environment in which people
can develop to their full potential and lead
productive, creative lives in accord with their needs and interests.
Aspects:
Human development is creating an enabling environment in which people can:
develop to their full Potential
a student can develop to their full potential but ensuring that they have access to education which can ensure future employment opportunities thus reach their full potential.
Participate in their community
lead Productive & creative lives
expand Choices & enhance Capabilities
have access to Knowledge and Health
educating a girl would build her skills to get meaningful employment to provide income, shelter and food. She can then participate in her community and improve her life.
enjoy a Decent standard of living
E.g. Explain how measles vaccination could enhance HD? 2mark
Measles vaccination mean people including children won’t become sick with measles. This means they can attend school to gain access to knowledge and enhance their capabilities
If children aren’t sick with measles, then parents don’t need to stay home to look after them, but rather can go to work and earn an income which then allows them to afford a decent standard of living and lead productive & creative lives.
It is an approach that is focused on people and their opportunities and choices.
People:
improving the lives people
lead rather than assuming that
economic growth will lead,
automatically, to greater
wellbeing for all.
Opportunities:
giving people more freedom to live
lives they value. In effect, this means developing people’s abilities
and giving them a chance to use them.
Choices:
providing people with opportunities, not insisting that they make use of
them. No one can guarantee human happiness, and the choices people make are their own concern.
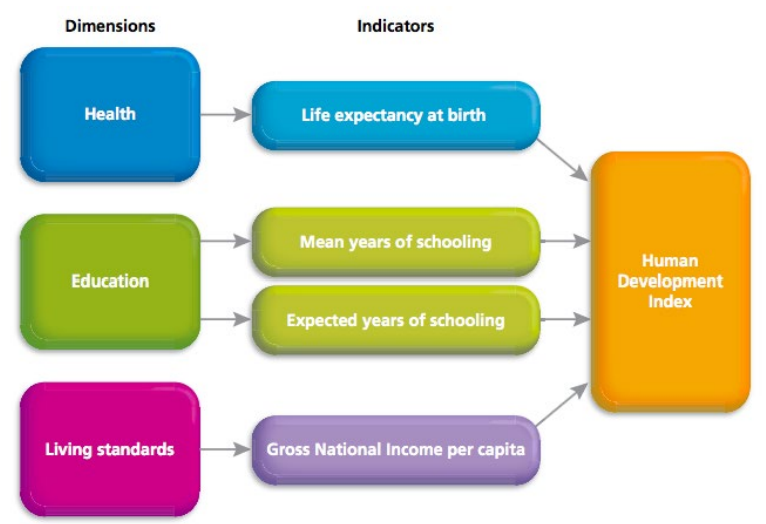
Human Development Index
Tool developed by the United Nations that measures and ranks the level of social and economic development experienced by a country.
It provides a single statistic between 0-1 based on three dimensions (2 social, 1 economic):
a long and healthy life (healthcare)
knowledge (education)
a decent standard of living (economy)
and four indicators
life expectancy at birth.
Expected years of schooling &
mean years of schooling
Gross Net Income
Divides countries by:
very high human development
e.g. Australia
high
e.g. China
medium
e.g. India
low
e.g. Uganda
Advantages:
The statistic between 0-1 makes it easy to compare and evaluate between countries.
Takes into account more than just economic measures, therefore providing a more comprehensive representative representation of human development levels.
Limitations:
Some low-income countries lack the resources to adequately measure and collect required data for this index, making some of the data unreliable and difficult to confirm.
This index is based on averages, and therefore does not indicate inequalities that exist within countries. E.g. Mumbai
Mean years of schooling vs Expected years of schooling
Mean years of schooling
Average number of years achieved by those aged 25 and over.
Expected years of schooling
Number of years of education expected for a child of school entrance age.
Global trend of Climate Change
refers to the increase in the earth's average surface temperature.
Aspects
Rising sea levels:
Increased atmospheric temperatures have led to polar ice caps melting at an increased rate, and
as a result we are seeing sea levels increase
Changing weather patterns & Extreme weather conditions:
Atmospheric warming as a result of climate change has been shown to be responsible for more frequent and more severe extreme weather events such as flooding, drought and extreme heat.
Impact on health:
Physical:
Reduced access to sufficient food sources impact nutritional intake thus reducing the efficient functioning of the body.
Increased risk of injury and death as a result of extreme heat and flooding events thus increasing morbidity and the risk of premature death.
Loss of infrastructure such as hospitals during extreme weather events may impact ability to access healthcare which can lead to illnesses and injuries not being treated thus increasing yld’s
Mental:
Loss of shelter due rising seal levels that cause floods can lead to increased feelings of helplessness and stress thus decreasing mental H&W
Social:
Rising sea levels and increased frequency of
extreme weather events may require individuals to leave their homes and communities, resulting in loss of community interaction and participation.
Spiritual:
If extreme weather events and rising sea levels cause people to leave their homes and communities, resulting in loss of community interaction may lead to people feeling disconnected and thus lack a sense of belonging.
Global trend of Conflict & Mass Migration
Movement of large groups of people from one geographical location to another.
Conflict results in violence and war.
Impact on health:
Physical:
A pregnant women that has been displaced due to conflict may not be able to access prenatal care. This can increase the risk of complications, thus leading the baby to be born with health issues. This can increase the risk of premature death, thus increasing infant mortality.
Malnutrition and increased risk of communicable disease, cholera, diarrhoea, and hypothermia.
Social& spiritual:
ability to attend school and work decreases, therefore reduces social and spiritual health and wellbeing
Sense of belonging is lost, as people move from their home and lose contact with familiar people.
Mental:
People that have been displaced as a result of conflict may live their lives in fear of harm or insufficient access to safe food and water., thus leading to them suffering extreme stress and anxiety.
Define Globalization
Refers to the process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide.
Define Sustainable Development/ sustainability
Refers to meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Differences in global health
High income countries health status and BOD are often related to lifestyle factors that can be said to be in the individuals control, such as diet and exercise.
In many low and middle income countries, however, resources that are often taken for granted in high income countries, such as safe water supply, are not readily available or totally absent. Therefore, outside an individual’s control.
Health status is also affected by political situations such as discrimination based on race, religion, gender identity, poverty, poor access to sanitation and unequal treatment of women.