Unit 2 - Understanding the Atom
The Historical Development of Atomic Theory
- Democritus - Early philosopher who proposed the existence of the atom
- Dalton’s Atomic Theory
- First scientific theory of the atom
- Based on Joseph Proust and other scientists’ research
- Proust’s research: each compound contains exact proportions
- Law of definite proportions
- Atoms are indivisible
- Elements are made of identical atoms unique to each element
- Compounds are made of 2+ atoms in fixed proportion
- A chemical reaction is the rearrangement of atoms
- Discovery of the Electron (Cathode Ray Experiment)
- By JJ Thompson
- Led to the Plum Pudding Model
- Oil Drop Experiment
- By Millikan
- Thompson found charge & mass of electron
- Discovery of Nucleus (Gold Foil Experiment)
- By Rutherford
- Most particles pass directly through the atom, some get deflected
- → Most of the atom is empty space, with a large particle at the center
- Quiz: https://quizizz.com/admin/quiz/5faee2a376564d001b6fb43a/the-historical-development-of-atomic-theory
Electromagnetic Waves
- Vocab
- Electric Field - The area surrounding a charged object in which it can act upon another charged object
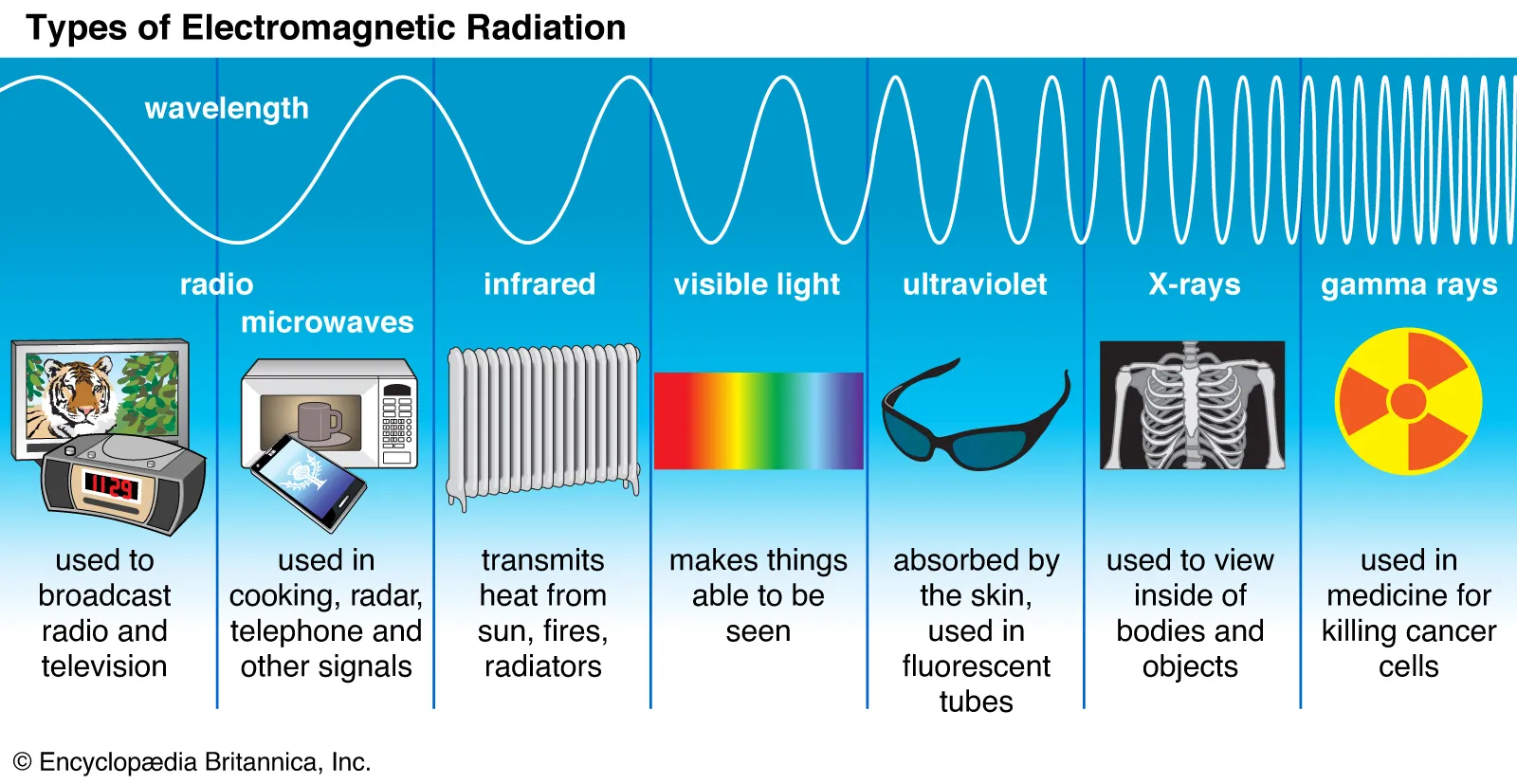
- Electromagnetic Spectrum
- The frequency spectrum containing all electromagnetic waves
- Electromagnetic Wave
- A combination of electric & magnetic fields radiating from a source @ the speed of light.
- The electric & magnetic fields oscillate perpendicular of each other
- Caused by disturbing charged particles, which then oscillate and produce oscillating fields
- Source produces an magnetic field, the magnetic field then produces an electric field, the electric field the produces another magnetic field, repeat forever
- Magnetic Field - The area surrounding a magnetic object in which it can act upon an object
- Polarization
- Types of Waves
- Mechanical - Waves that use matter to carry energy
- Electromagnetic - Waves that do not use/need matter to carry energy
- Are all transverse waves
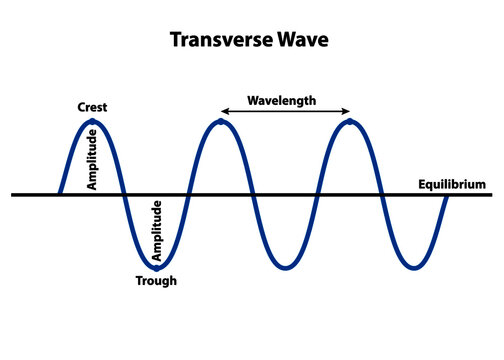
- Parts of a Transverse Wave
- Crest - Midline → Top
- Trough - Midline → Bottom
- Amplitude - Top → Midline or Midline → Bottom
- Wavelength - Crest 1 → Crest 2
- Frequency - Oscillations per second
- Electromagnetic Waves
- Each type is contained on a different part of the electromagnetic spectrum
- High frequency/low wavelength → low frequency/high wavelength:
- Gamma Rays → X-Rays → Ultraviolet → Visible Light → Infrared → Microwaves → Radio waves
- Energy transferred
- Energy = plank’s constant * frequency
- Plank’s constant ~ 6.63 * 10^-34
- Frequency, Wavelength, & Speed
- Speed of light = frequency(hertz) * wavelength(meters)
- Slower = Smaller wavelength
- Uses
- Gamma Rays - Used to destroy cancer cells
- Ultraviolet Rays - Disrupts DNA production in bacteria & viruses
- X-Rays - Used for medical imaging
- Infrared - Heat lamps, remote controls
- Microwaves - Warm food
- Radio waves - Long distance transmission of information
- Polarization - Modifying light by forcing it to only vibrate in a singular plane
The Modern Atomic Theory
- Theories of Light
- Newton - Corpuscular theory; light is made of particles
- Thomas Young - Diffraction double slit experiment; light behaves like waves
- Heinrich Hertz - Photoelectric effect observed; also acts like a particle
- Photoelectric Effect
- Electrons are emitted when electromagnetic waves hit a material
- Shows particle like behavior
- Einstein proposes light is a stream of particles called photons
- Energy = Plank’s constant * frequency
- Emission Spectrum
- Visible light spectrum where emitted light produce colored bands
- Some metals showed up as discrete lines
- Bohr Model
- Electrons orbit nucleus made of protons & neutrons
- Electron Cloud Model
- Electrons have probable locations
- Each cloud has different energy levels
The Structure of the Atom
- Atom - Smallest particle of a substance
- Made of a nucleus surrounded by orbitals
- Consists of 3 types of particals
- Protons - Positively charged
- Neutrons - Particle w/o charge
- Electron - Negatively charged electron
- Charge of proton = negative charged of electron
- If charge of atom = 0, then the atoms has == number of protons & electrons
- Locations
- Nucleus - Contains all the protons & neutrons
- Orbitals - Contains the electrons
- Atomic mass unit
- 1/12 of a C12 atom
- ~ 1.660538921 * 10^-24 g
- Proton - 1 amu
- Neutron - 1 amu
- Electron - 0.0006 amu
- Atomic Number
- \
# of Protons in an atom
- Ions
- Charged atoms
- Changed number of electrons
- Atomic Mass / Mass Number
- \
# of Protons + # of Neutrons
- Isotopes

