Sampling Methods
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
bias
biased samples are more likely to produce some outcomes than others
convince
too easy to collect
volunteer response sample
self - elected sample of people who respond from general appeal
simple random sampling (SRS)
a sample of n subjects selected in a way that every possible sample of the same size n has the SAME CHANCE of being chosen
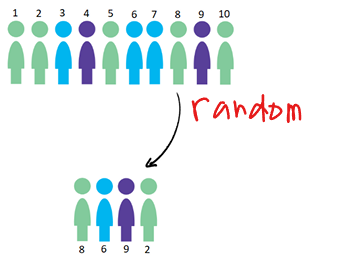
simple random sample
stratified sample
subdivide the population into at least two different subgroups (strata) so the subjects within the same subgroup share the same characteristics. Then draw a sample from each subgroup - proportionally with respect to the size of population
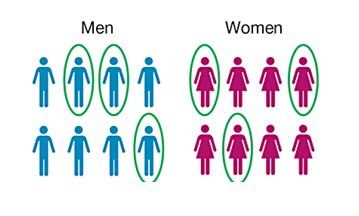
stratified sample
cluster sample
divide the population area into naturally occurring sections (clusters) then randomly select some of those clusters and choose ALL the members from the selected clusters
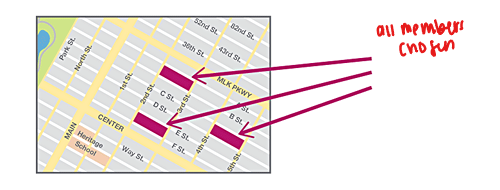
cluster sampling
systematic sampling
select a starting point and then select every kth element in the population
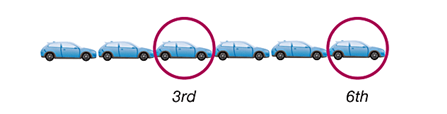
systematic
multistage sample
collection of data by using some combination of basic sampling methods
bad sampling frame
when attempting to list all members of a population, some subjects are missing
under coverage
the sampling frame is missing groups from the population or the groups have smaller representation in the sample than in the population
non-response bias
some part of the population chooses not to respond, or subjects were selected and not able to be contacted
response bias
responses given are not truthful
wording and order
the way a question or statement is worded may be misleading or influencing to give a particular response