EXAM 1 continued - NURS198 - Ryno - Fun size
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Physiological changes in aging?
1) sensory loss and changing the perception
-vision, hearing touch
2) decline of central nervous system and cognitive functions
3) decline of muscular and skeletal system
4) reduced ability to adapt to temperature changes
5) disease: arthritis, heart disease, alzheimer's
6) mobility problem: reliance on walkers/wheelchairs
7) thinner skin, bruise easy, dry skin
8) Slower HR
9) kidneys are slower = more toxicity build up
10) slower metabolism
If an older person comes in what do we want to assess and check first?
1) there medicaitons they are on - to see if that is causing confusion.
2) Get a urinalysis to check for a UTI
3) Want to rule out that it is dementia
Ageism
Discrimination based on age
Delirium vs Dementia
1. Delirium- Acute, dramatic onset, common causes= illness, toxin, withdrawal, usually reversible. Poor attention and fluctating arousal level. (sepsis, stroke, UTI) - affects consciousness
2. Dementia: Chronic, insidious onset, usually not reversible, attention usually unaffected and normal arousal level. - Doesnt affect consciousness
Role as a nurse with abuse
Report it no matter what.
Patients with cognitive issue are most at risk
What is polypharmacy?
the simultaneous use of multiple drugs to treat a single ailment or condition (5+ drugs)
Interventions for polypharmacy?
1. medical reconciliation - make sure they arent taking any duplicates.
2. BEERS crtieria ( which ones can older people take)
3. Have a daily planner and reminders
What is a chronic illness?
1) Anything longer than 6 months
2) Effects the whole family
3) Continuous help for illness
4) Persistance and adhere to the treatment plan
5) nonpharm treatements
Non-pharm treatment
- exercise, light therapy, music therapy, reminiscence therapy, relaxation techniques, massage, ice and heat therapy
Management for chronic illness
1) learn to live with it
2) able to grief the life you had is normal
3) financial - how are they going to afford this
4) Are there resources to help them
5) lifestyle changes
nursing process
Assessment
Diagnosis
Planning
Implementation
Evaluation
Hypovolemia
LOSS OF WATER AND ELECTROLYTES
DUE TO: Vomiting, diarrhea, burns, sweating, dehydration, organ dysfunction
SYMP: weight loss, decreased skin turgor, concentrated urine, less urine
hypovolemia treatment
replace water and electrolytes with balanced IV solutions
ISOTONIC SOLUTION: normal saline
monitor daily weight
Hypervolemia
EXCESSIVE FLUIDS IN BODY
DUE TO: Kidney Injury, CHF
SYM: EDEMA, increased urine output, HTN
treatment for hypervolemia
- diuretics
- monitor weight
Hypocalcemia
deficient calcium in the blood
DUE TO: too little calcium usually from hypoparathyroidism, malabsorption, pancreatitis, alkalosis, deficiency in VIT D
SYM: numb/tingling in toes and fingers
hyperactive deep tendon reflex
chvostek sign/trousseaus sign
Nurse intervention with hypocalcemia
Give calcium/vit D
nutrition education
Hypercalcemia
excessive calcium in the blood
Due to: too much calcium due to hypoparathyroidism
, malignant neoplastic disease ( turmors), immobilzation, vit d increase, diuretic use
SYMP: hypoactive deep tendon reflex
nurse intervention for hypercalcemia
1) diuretics
2) movement
3) calcitonin
4) find the underlying issue
Hyponatremia
deficient sodium in the blood
DUE to: too little sodium from diuretics, loss of gi fluids, renal disease, head trauma.
SYM: confusion, headache, muscle cramps, seizure, twitching, low BP, coma
Intervention for hyponatremia
1) fall and seizure precaution
2) mild = salt tablets
3) severe = hypertonic solution 3% solution
4) daily weight
5) intake and outtake
6) LR
7) Fluid restriction
Hypernatremia
high sodium
DUE TO: too much sodium
SYMP: thirst, sticky dry mouth and tongue, hallucinations, restless, irritable, seizure, twitching, high BP, death
Intervention Hypernatremia
1) fall and seizure precaution
2) hypotonic solution %0.45 normal solution
3) neuro check
Hypokalemia
deficient potassium in the blood
DUE TO: too little potassium due to diarrhea, vomiting, gastric suction
SYMP: constipated and ECG changes (FLAT T WAVES)
Nurse intervention for hypokalemia
1) give pottasium SLOW
2) cardiac telemetry
3) EKG
can give magnesium
Hyperkalemia
excessive potassium in the blood
DUE TO: too much pottasium from metabolic acidosis, renal insufficienses, NSAIDS
SYMP: TALL peaked t waves
Nurse interventions for hyperkalemia
1) telemetry
2) EKG
3) IV calcium gluconate
4) IV regular insulin/glucose(pulls in cell)
Diarrhea - make them poop!
Dialysis
Hypomagnesium
too little magnesium
Symp: insomnia, heart changes, increased tendon reflexes
Nurse intervention: give magnesium and seizure precaution
hypermagnesium
too much magnesium
symp: flushing, drowsy, low RR, cardiac arrest
Nurse intervention: vital signs, telemetry, give loop diuretic
which two electrolytes go together?
Potassium and magnesium
What is isotonic solution used for? %0.9 saline
blood loss
dehydration
fluid maintenance
What is hypotonic %0.45 normal saline used for?
used for someone with a lot of sodium and use slowly
Hypertonic solution %0.3 normal saline used for?
used for severe hyponatremia, use slow
What is insensible fluid loss?
The amount of fluid loss on a daily basis from the lungs, skin, respiratory tract, and water excreted in the feces. The exact amount cannot be measured.
Respiratory Alkalosis
Ph level rises above 7.45 carbon dioxide falls below 35
Caused by hyperventilation, pneumonia, ARDS
Symp: SOB, dizziness, chest pain, numbness in hands and feet
Respiratory Acidosis
Ph drops below 7.35 carbon dioxide level rises above 45
Cause by hypoventilation, pneumonia, COPD, asthma, benzos, opioids(overdose)
SYMP: confusion, lethargy, dyspnea, palm cyanotic skin
metabolic alkalosis
pH > 7.45 ----- HCO3 > 26
Caused by antacid(tums) overdose, loss of body acid = vomiting and ng suction
SYMP: tachycardia, dysrhythmias, muscle weakness, and lethargy, n/v, tingling in toes and fingers, lightheaded
metabolic acidosis
pH < 7.35 ------- HCO3 < 22
Caused by DKA, kidney failure, shock, starvation, diarrhea, and dehydration, will kill your organs
SYM: headache, confusion, drowsy, high RR and depth, nausea, vomiting, low BP, cold and clammy skin
IN COPD which ABG abnormality?
RESP acidosis
What is the role of the scrub nurse?
extra set of hands for the surgeon, remain in the sterile field- gowned & gloved
What is the role of the circulator nurse?
Grab supplies, fluid intake, sterile and sponge count. DONT WAnt anything left in the body. Documentation
Side effects of benzos with pre op meds?
They are anti-anxiety and make you sleepy. You want to monitor their RR and BP. You want them to stay in bed and not get up.
Pre-op nursing care
*explain the procedure
*explain the diagnosis
*explain ostomy care and the importance of turn/cough/deep breathing/IS
*Potential for Foley and other drains
*lessen patient anxiety
*make sure patient understands the care
+ baseline assessment and vitals
*informed consent
*meds needed?
*preparing site, cleaning/shaving skin
Pre op
Begins with the decision to have surgery and lasts until patient is transfered to the OR or procedure bed
Intra-op
Admission to surgical department goes til they are in recovery room
Intra-op nursing interventions
•Time outs
•Serve as Patient Advocate
•Monitoring
•Counts
•Documentation
•Allergic Monitoring (Latex)
•Prevent Complications (Pressure injury, etc)
•Maintain sterile / aseptic area
post-op
Admission to recovery room to complete recovery and last follow up visit with physician.
Priority assessment with POst op?
AIRWAY, breathing, circulation
post op teaching
- Manage nausea and vomiting
- Monitoring for gas passing and bm
- deep breathing/coughing
- isometric leg exercises to prevent DVT
- repositioning/turning
- wound care
- infection prevention
- time lines for activities
- meds- when to take and not take
- keep up with doc visits
Types of Anesthesia
general: put to sleep
regional: epidural/ spinal block
local: wounds, burns
conscious sedation: short term and minimally invasive
Malignant hyperthermia
A hereditary condition of uncontrolled heat production that occurs when susceptible people receive certain anesthetic drugs. Causing body temp to sky rocket
treatment: dantrolene
What is medication tolerance?
more medication is required to achieve the same therapeutic effect
OLDCART
O- onset
L- location
D- duration
C- characteristics
A- aggravating factors
R- relieving factors
T- treatment
Different pain scales
Numeric scale, face scale (wong baker) , non verbals, FLACC (infants)
What meds are used for low- moderate pain?
1) NSAID
2) acetaminophen
3) aspirin
What meds are used for mild-severe pain?
OPIOIDS
Major side effects of opioids?
respiratory depression, constipation, sedation
HOw do you administer strong opioids?
SLOWLY
What is an opioid antagonist?
Naloxone (Narcan) - this is given to help with an overdose it blocks opioid activity
what is an opioid agonist?
Opioids that activate and bind receptors - morphine
What is dumping syndrome?
This is when the stomach empties quickly after eating and the client experiences uncomfortable to severe side effects. Usually secondary to gastric bypass, gastrectomy or gall bladder disease.
What does dumping syndrome cause?
Malabsorption due to diahrrea and diaphoresis
What interventions do you want to do to prevent dumping syndrome?
1. eat slow
2. drink fluids between meals not with them
3. room temp food
4. sit/rest after eating
5. EAT protein with every meal
6. sit in low fowlers (30 degrees)
Atopic Dermatitis
Eczema
How to treat: Topical treatment (antihistamine)
steroid cream
cold compress
Avoid what causes exacerbations: chlorine in the pool, avoid long baths,
Herpes Zoster
Shingles
-remains dormant in body- reactivated through stress, illness, immunosuppression
-occur along dermatome(rely on nerve connections to spine) and face
-Painful, when its on one side of body, it will not be on the other.
-Its contagious in the weeping stage
-can cause blindness
-Med they will be on: Acyclovir
Psoriasis
-Chronic autoimmune skin disease that causes skin cells to grow faster than usual, resulting in dry, scaly patches, commonly on the front of knees, posterior elbows plus trunk and scalp.
-Psoriasis frequently causes an inflammatory arthritis of joints and pitting of the nails
-Treatment: immunosuppressant, creams, ointments, oral medications, and injectable medications
KELOID SCAR FORMATION
• Benign overgrowth of scar tissue
• Can occur wherever there is a skin injury but usually forms on earlobes, shoulders, cheeks or the chest
• Risk factors include Brown or Black skin and younger age (20-30 years)
• Compression of wounds may help prevent keloids
• Treatment options include corticosteroid creams, laser therapy, or surgical removal
SEBORRHEIC KERATOSIS
• Common benign skin growth
• Tends to occur with aging
• No treatment required
• Slightly raised, brown or tan lesions that look waxy or scaly (May resemble a wart or a piece of gum)
• Only removed if irritating or the client uncomfortable with appearance
PRECANCEROUS & CANCEROUS SKIN LESIONS
• Most common type of cancer
• Frequently related to sun exposure
• Prevention: Use of sunscreen and avoiding sun exposure
• Skin inspection for non-healing lesions or abnormal dark lesions
• Prevention of all types of skin cancer involves protection from excessive sun exposure
ACTINIC KERATOSIS (PRECANCEROUS)
• Chronic sun damage to exposed areas like face, scalp, ears, nose and hands
• Scaly flaky lesions that feel like sandpaper when rubbed
• Precancerous lesions that may develop into a squamous cell carcinoma
• Risk of actinic keratosis is minimized by reducing sun exposure and protecting skin from ultraviolet (UV) ray damage.
• Treatment is usually with liquid nitrogen or 5-fluorouracil cream (chemo cream)
BASAL CELL CARCINOMA
• Most prevalent, rarely spreads or causes death
• Appears on sun exposed hands, face, neck, scalp
• Small waxy nodule with a central ulcer
• Rarely metastasizes, spreads locally
• Reoccurrence is common to other skin areas
SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA
• Also arises from sun-damaged skin
• Often occurs from actinic keratosis
• Less aggressive than melanoma, but can occasionally spread deeper
• Rarely, may metastasize by blood or lymph
• Rough, thickened, scaly tumor
• May be asymptomatic or may
TREATMENT FOR BCC AND SCC
-Prevention with sunscreens all year and minimize sun exposure
-Protective clothing, avoid tanning beds, broad brim hats
-Surgical removal
-Alternatives: radiation, topical chemotherapeutic creams (5-FU
ABCDE's of Melanoma
Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, Evolving
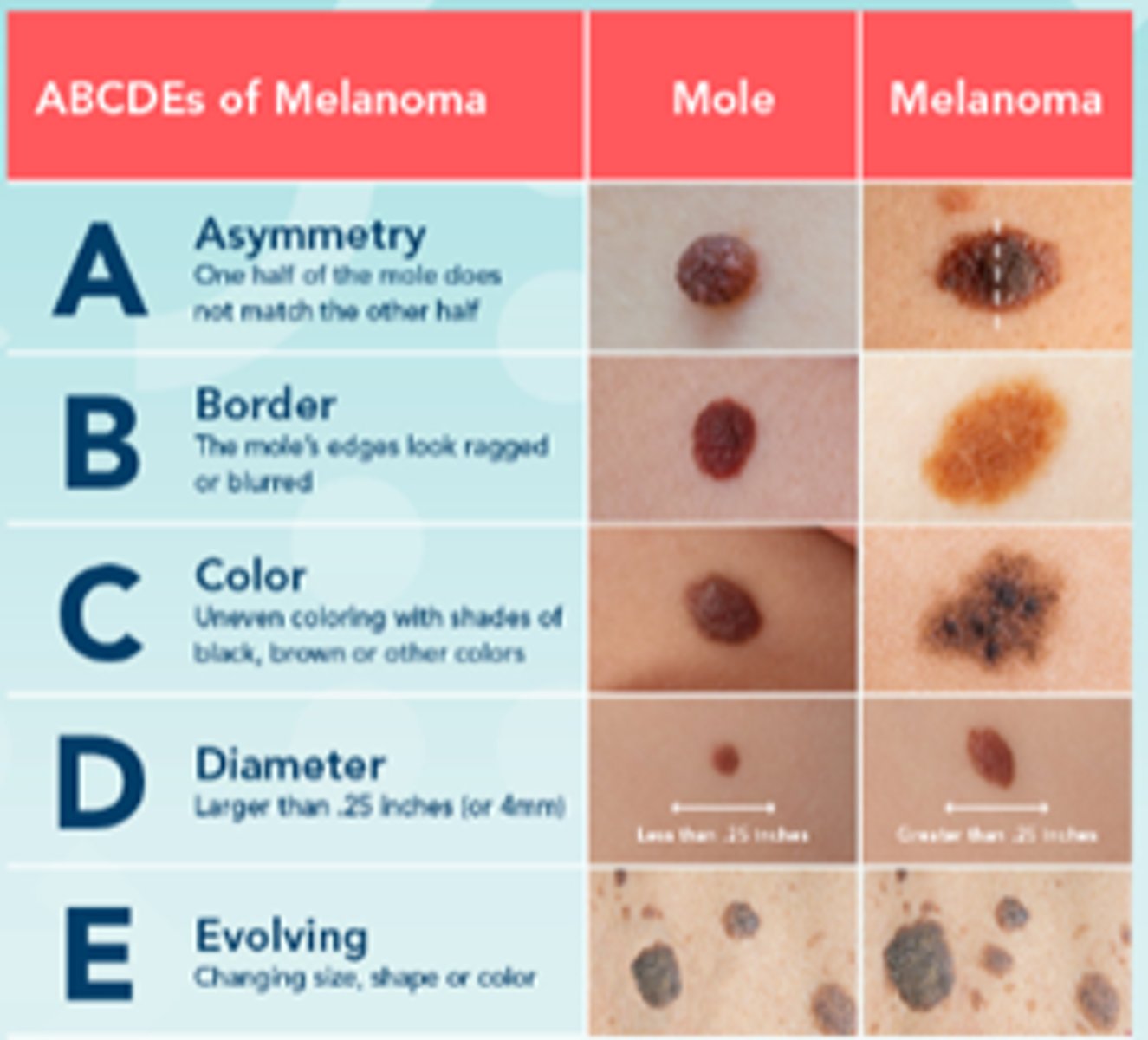
MALIGNANT MELANOMA
-Cancerous neoplasm present in dermis and epidermis
-Manifests as a change in nevus or a new growth on the skin
-Color is dark, red, blue colored or a mix, irregular shape
-Itching, rapid growth, ulceration, bleeding, metastasizes
-Treatment: Surgical excision, chemotherapy
• Malignant skin cancer
• Highly curable if caught early
• 5-year survival = 94%
Bariatric Surgery
•Results in weight loss of 10% to 35% body weight within 2 to 3 years
•Improvement in comorbid conditions
•Selection by multidisciplinary team
•Selection criteria has changed to include BMI of 30 for clients with comorbid conditions(diabetes, htn, etc)
18-65
Bariatric Surgery types
-Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB)
-Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG)
-Adjustable Gastric Banding (AGB)
-Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS)
-Intragastric Balloon
-Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG)
Bariatric surgery pre op
includes months of education, counseling and evaluation. Know risk and benefits of surgery, complications, postsurgical outcomes, lifestyle changes, dietary changes, lifelong follow-up, lab testing.
Bariatric surgery intra op
Prep
anesthesia
procedure
PACU for monitoring
Bariatric expectations post op care
•Assess to ensure goals for recovery are met
•Assess for absence of complications
•Manage pain
•Nutritional status
•Fluid volume balance
•Decrease anxiety
•Body image changes
Bariatric surgery problems and potential complications
•Hemorrhage
•Venous thromboembolism
•Bile reflux
•Dumping syndrome (early and late)
•Dysphagia
•Bowel or gastric outlet obstruction
Sodium Functions
Nervous System
Fluid Balance
Hyponatremia symptoms
confusion
muscle cramps/weakness
seizures
Hypernatremia symptoms
irritability
muscle twitching
seizures
Potassium function
cardiovascular system
muscular system
Hypokalemia symptoms
ECG changes- PVCs, flat T wave, prominent U wave, prolonged P wave
constipation
muscle cramps
Hyperkalemia symptoms
ECG changes- peaked T waves, wide QRS, absent P wave
diarrhea
muscle weakness/paralysis
Calcium function
Neuromuscular system
Bones
hypocalcemia symptoms
Hyperactive reflexes
numbness/tingling to face and extremities
Chvostek and Trousseau sign
Hypercalcemia symptoms
Hyperactive reflexes
confusion/psychosis
bone pain/fractures
kidney stones
Magnesium function
cardiovascular system
neuromuscular system
hypomagnesemia symptoms
hyperactive reflexes
muscle cramps
hypermagnesemia symptoms
hypoactive reflexes
muscle weakness
respiratory distress
reduced LOC
pH range
7.35-7.45
PaCO2 range
35-45 mmHg
HCO3 range
22-26 mEq/L
what does PaCO2 indicate
respiratory
what does HCO3 indicate
metabolic