biology topic 2 (triple content) year 10
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
what are root hair cells
enlarged epidermis cells with large surface : volume ratio = that absorb water and mineral ions
have transport proteins in cell membranes to allow mineral ions to be absorbed by active transport
exchange substances with soil
how is water absorbed by root hair cells
water is absorbed into the roots by osmosis = due to the high concentration of minerals in the root cell
water is drawn into the cell from a high water potential in the soil to a low water potential in the cell
the root hair cells are on the outer layer and help greatly increase the surface area for osmosis
why do stomata open and close
to allow water vapour and gas to pass in and out of the leaf
what happens when stomata are closed
they conserve water and prevent wilting
what happens when stomata are turgid = open
gas exchange occurs = CO2/O2/H2O
water loss
what happens when stomata are flaccid = closed
prevents wilting
photosynthesis and respiration take place
what is transpiration
the loss of water vapour by evaporation from the stomata
what is the transpiration stream = how water moves from the soil to the xylem vessel
water enters root hairs by osmosis
water passes up xylem to stem and leaves = due to transpiration
if leaf is photosynthesising then water is lost through stomata
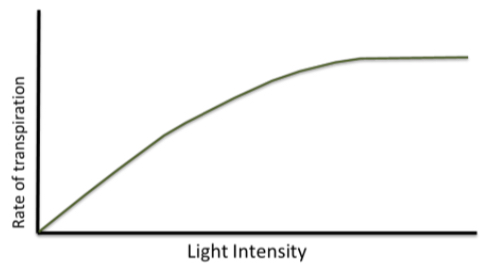
how is the rate of transpiration affected by light intensity
as light intensity increases = more stomata open = at the top of the leaf = for photosynthesis
so more transpiration occurs
eventually all stomata will open so any more increase of light intensity will not effect the rate of transpiration
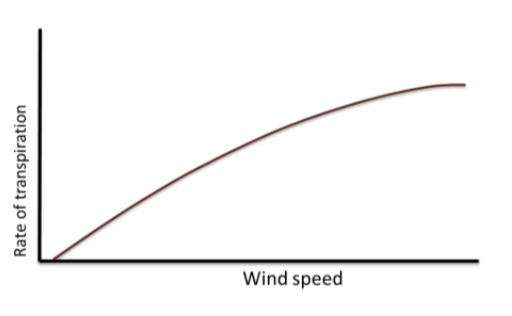
how is the rate of transpiration affected by wind speed
as wind speed increases it moves away the water particles surrounding the leaf
increasing the water diffusion gradient between inside and outside the leaf
increasing the rate of transpiration
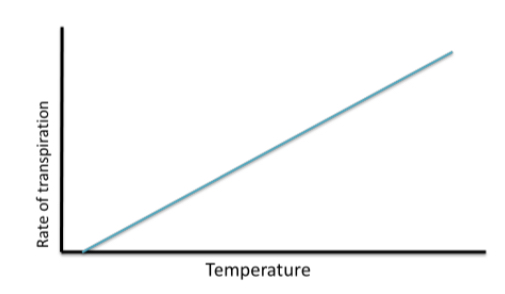
how is the rate of transpiration affected by temperature
the higher the temperature the more kinetic energy the water particles have = the faster they move
they will evporate and diffuse from the surface of the leaf faster
increasing the rate of transpiration
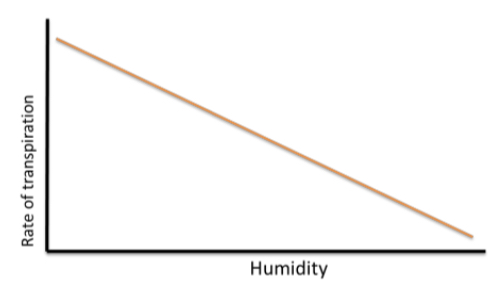
how is the rate of transpiration affected by humidity
the more humid the air the more water is in it
reducing the water concentration gradient between inside and outside the leaf
as humidity increases the rate of transpiration decreases
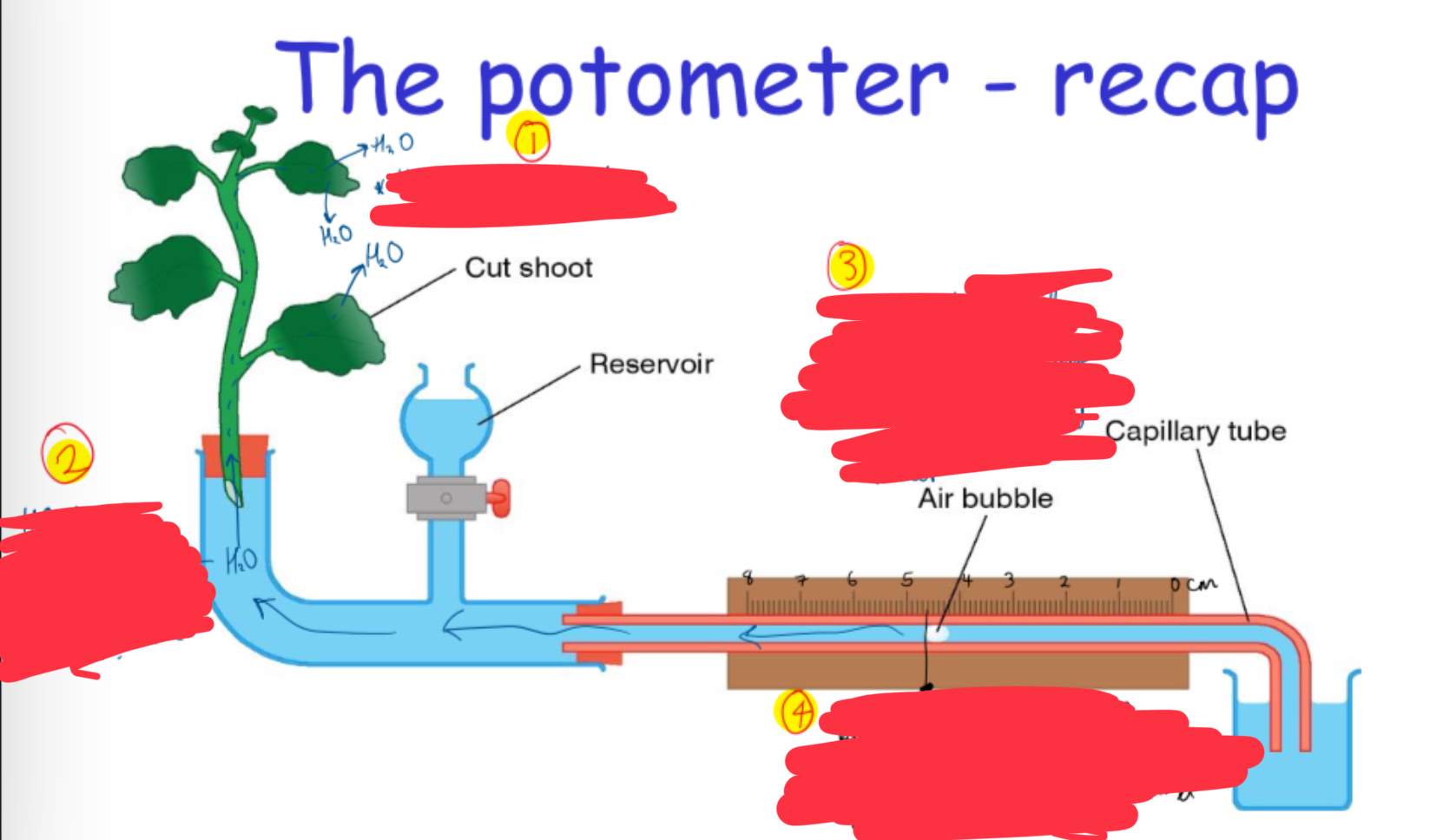
diagram of the potometer + what happens at each step
H2O exits the stomata via transpiration
H2O lost from the stomata is replaced by the cut stem = it draws more up from the potometer
the air bubble moves to the left as the stem draws more H2O from the potometer = the air bubble starts at 0mm on the ruler
measure the front of the bubble = see how far it has moved during the certain length of time
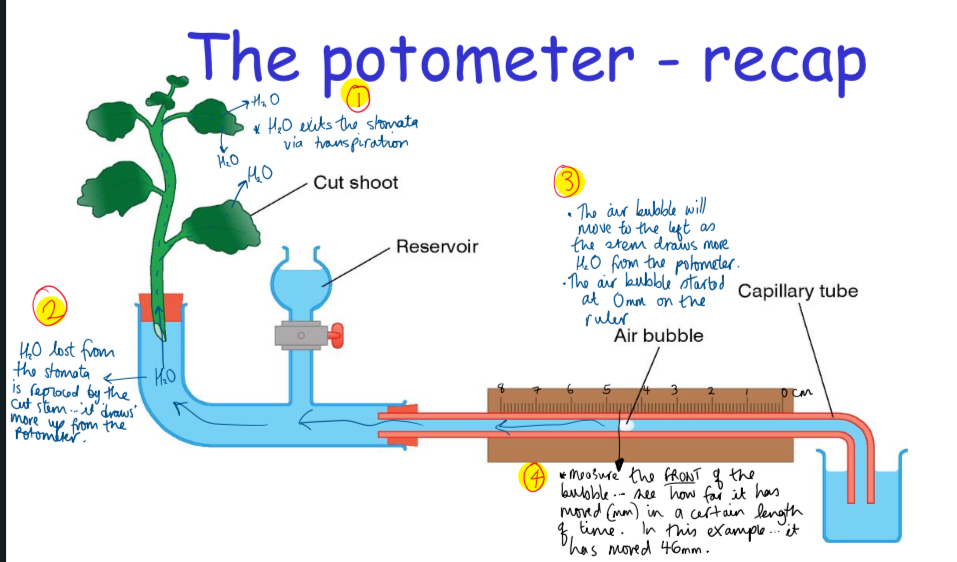
what can the pototmeter be used for
to measure the rate of transpiration = as it measures how far the bubble moves in a set time = in different conditions = with the further the bubble moves the faster the transpiration
method for the practical using the potometer to find the rate of transpiration in hot and cold air
choose time for how long you are going to measure for
set air as either hot or cold
measure how far the bubble moves as you remove the leaves one by one
then do the same with the other temperature
conclusion for the practical using the potometer to find the rate of transpiration in hot and cold air
the more leaves there are the more transpiring the plant does = due to the decrease in leaves mean less stomata
hot air increases transpiration = due to it making the plant hot = creating less moisture in the air = forcing the plant to transpire
what are antibodies
proteins that recognise and bind to antigens
what are antigens
a protein on a foreign object that stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies
what are antitoxin
white blood cells produce them
what are antibiotics
this substance is used to kill bacteria
what are painkillers
this substance relieves only symptoms of a disease
what is the role of a antigen
when a new pathogen enters the body
it introduces a new antigen
for every new antigen, our lymphocytes build a specific antibody
this will have a complementry shape to the antigen so the antigen will bind to the pathogen and destroy it
what is a vaccine + its role
the administration of a weak or dead pathogen = provide long term immunity and help control the spread of disease
role =
harmless pathogen is given which has antigens on the surface
antigens trigger an immune response
lymphocytes produce antibodies to kill the pathogen and release antibodies which bind to antigens to destroy the pathogens by either 1. killing them directly 2. labelling them so phagocytes engulf them 3. neutralise their toxins 4. cause them to burst
some lymphocytes remain in the blood as memory cells which help give long term immunity by killing future pathogens by releasing antibodies when required
should the pathogen be encountered again the body responds by rapidly releasing thousands of antibodies = this should help with long term immunity + controlling the spread of disease
what 3 things does the MMR vaccine protect children against
measles
mumps
rubella
what are the two things platelets help prevent in the clotting process
pathogen entry into the blood
blood loss
what do platelets use to convert the soluble protein fibrinogen into the insoluble protein fibrin which forms the clot (scab)
platelets use calcium
why is blood clotting important
prevents significant blood loss from wounds
scab formation seals the wound with an insoluble patch to prevent entry of microorganisms
remains in place till new skin is grown which seals the skin again
What are the 4 things that make up the urinary system
Kidneys
Ureters
Bladder
Uretha
What does the urethra contain + what that does
The urethra contains two ring shaped muscles = sphincter muscles
They can contract to close the urethra + to hold back the urine
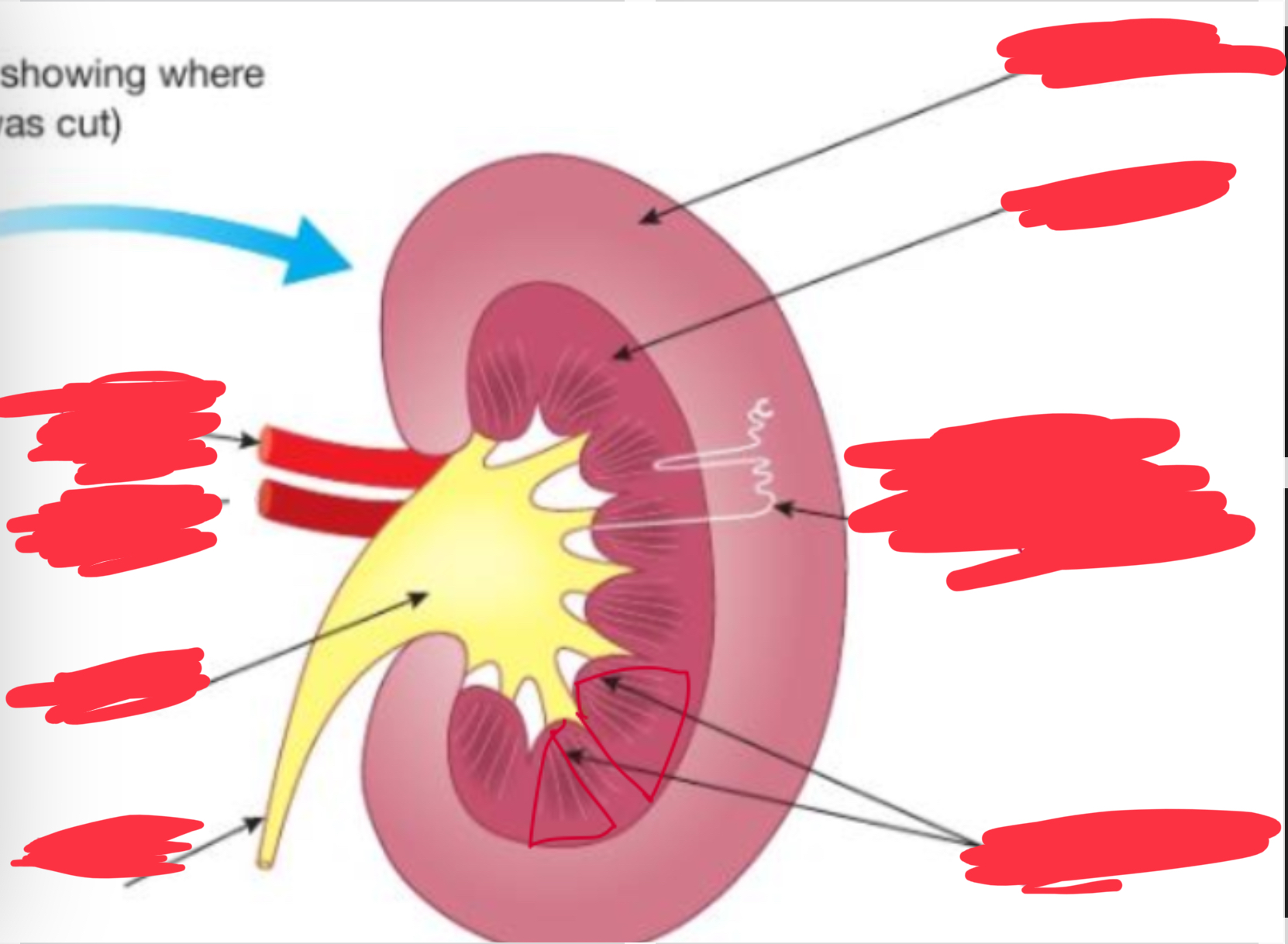
Label the parts of the kidney + what are the 6 parts of a kidney
Cortex
Medulla
Pelvis
Ureter
Renal vein
Renal artery
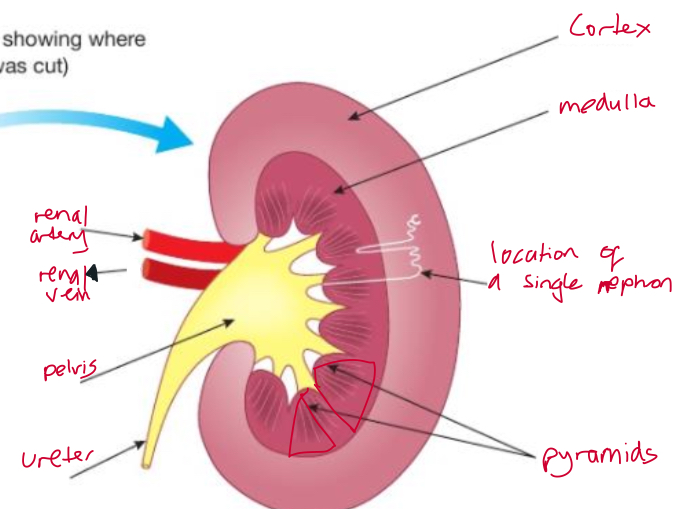
What is the function of the cortex
Where blood is filtered + contains nephrons
What is the function of the medulla
Where the concentration of urine is determined
What is the function of the nephron
Form the basic units of the kidney
What is the function of the ureter + what is it
Carries urine to the bladder + tube that leads kidneys to bladder
What is the function of the renal artery + renal vein
Empty urine into the pelvis from the pyramids
Label the nephron tube
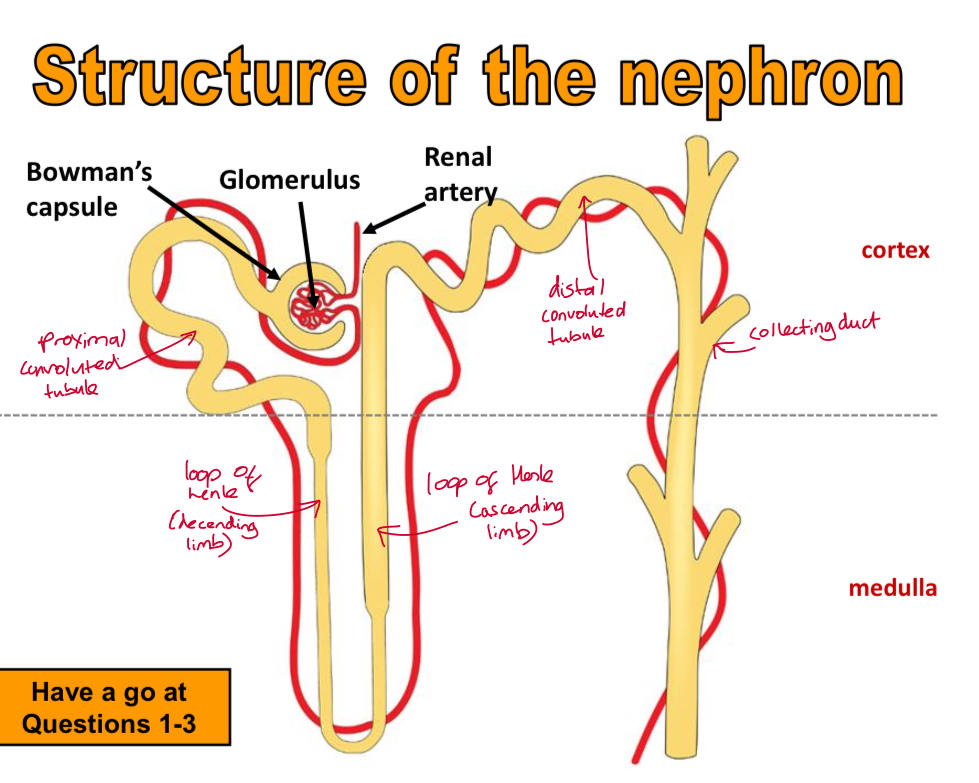
What happens in the bowman’s capsule
Ultrafiltration = tiny pores allow the glomerus filtrate to pass through + small substances are forced out of the blood + filtered by the bowman’s capsule into the nephron
What happens in the glomerulus
Blood from the renal artery = under high pressure = forces small substances (glucose, urea, ions, water) out into the glomerus that sits in the bowman’s capsule = as blood flows out of it fluid called = glometer filtrate = is forced out through pores into the bowman’s capsule
What are used in selective re absorption
PCT = proximal convoluted tubule
Loop of Henle
What happens in the PCT = proximal convoluted tubule
100% of glucose is reabsorbed into the blood via active transport
What happens in the loop of henle + what how much reabsorptionn depends on
Re absorption of salts and water = how much re absorption happens depends on hydration, diet and activity
What happens in the DCT = distial convuluted tubule and the collecting duct
Adjusts levels of water in the blood
Osmoreseptors in the brain detect high or low water levels in the blood
The pituitary glands (in the brain) responds by increasing or decreasing the release of ADH
ADH makes the DCT and the collecting duct more permeable to the water (causing reabsorbtion of more water in the blood) = osmoregulation
How does the levels of water affect ADH
High water = more ADH
Low water = less ADH
What is urine made out of
A solution of water, urea and ions
What is excretion
Removal of cellular / metabolic waste
What is osmoregulation
Regulating water levels of the blood
Why cant protein pass through the glomerculus but glucose can
Because protein is a large molecule and glucose is small nenough to pass through
How is water reabsorbed from the collecting duct + Why does selective re absorption of glucose happen in the proximal convultuted tubule
All glucose in the proximal convoluted tubule by active transport
As filtrate drips through the loop of henle = sufficient salts are reabsorbed back into the blood by diffusion and water follows by osmosis
Sufficient water is also reabsorbed from the collecting duct depending on how much the body needs
What is the effect of ADH + where it comes from + what it affects
Secretes many different hormones = from the pituitary gland + effects osmoregulation
What is the effect of LH + where it comes from + what it affects
Secretes many different hormones = from the pituitary gland + affects the ovulation and release of eggs
What is the effect of FSH + where it comes from + what it affects
Secretes many different hormones = from the pituitary gland + effects the growth of follicle