McCance Chapter 18 Disorders of the CNS, PNS and NMJ
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Borrelia burgdorferi
Bacterial spirochete C—> Lyme d/z transmitted by ticks
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Degeneration U/L motor N. in cerebral cortex, brainstem, & spinal cord characterized by progressive muscle weakness leading to respiratory failure & death (2 to 5 years from symptom onset).
Person has normal intellectual & sensory function until death
Arteriovenous malformation
Arteries feed directly into veins through a vascular tangle of vessels
Autonomic hyperreflexia (dysreflexia)
afferent stimuli C→ intense sympathetic discharge in spinal cord above major splachnic outflow. symptoms:
hypertension, bradycardia, sweating of the forehead, severe headache, and piloerection on distention of the bladder and rectum.
Cavernous angiomas
Sinusoidal collections of blood vessels w/o interspersed brain tissue
Cerebellar astrocytoma
Brain tumor C→ symp. on the same side as the tumor including head tilt, limb ataxia, and nystagmus.
in R or L cerebellar hemisphere
Cerebral infarction
Area of the brain loses blood supply b/c of vascular occlusion
Chronic paroxysmal hemicrania
Cluster-type headache occurs w/
-high frequency (4 to 12/day)
-low duration (20-120 minutes)
Classic cerebral concussion
Diffuse brain injury w/ cerebral disconnection from the brainstem reticular activating system
phenomenon of physiologic, neurologic dysfunction w/o substantial anatomic disruption.
immd. loss of consciousness for less than 6 hours with retro/anterograde amnesia.
Cluster headache
Headache charact. by unilateral severe pain over the eye & forehead that lasts 30 minutes to 2 hours,
several attacks per day can occur over a period of days followed by long periods of remission
Contrecoup
Brain injury resulting from the brain hitting the inside of the skull on the side opposite the site of blunt force trauma.
Contusion
Bruise produced by bleeding into skin or underlying tissues from an insult that did NOT break the skin but did rupture blood vessels.
Coup
Brain injury that occurs on the same side of a blunt force to the head;
it results from the rapid acceleration and then deceleration of the brain as it hits the inside of the skull.
Injury directly b/w point of impact.
Diffuse brain injury
Brain injury C→ stretching & shearing forces of neuronal axons (injury)
(_____ axonal)
Embolic stroke
blockage of cerebral vessels C→ stroke
Encephalitis
Inflammation of the brain usually caused by a virus.
Ependymoma
Intracranial tumor commonly found in children
- typically arises from the inner lining of the 4th ventricle & spinal canal.
Extradural Hematoma
Hemorrhage usually from an artery a/w skull fracture post-head injury
Extramedullary tumors
Tumor originating from tissues outside the spinal cord including the meninges, epidura tissue or vertebral structures
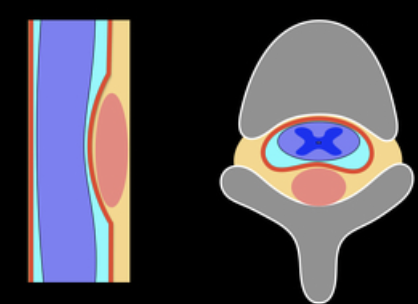
Fasciculation
Involuntary muscular twitching
Fusiform aneurysm (giant aneurysm)
Large aneurysm that stretches to affect the entire circumference of the arterial wall.
Guillain-Barré syndrome
bacterial/viral infection trig.→
Acute, inflam., autoim. →
demyelination of neurons resulting in atrophy & denervation (PNS) of muscle w/ numbness, pain, parasthesis or weakness
Hemorrhagic stroke (intracranial hemorrhage)
Hypertension or ruptured aneurysms C→
bleeding in brain, typically inc. intracranial pressure & may lead to death.
Intramedullary tumors
Tumor originating w/n neural tissue
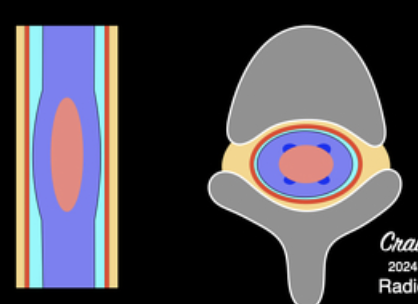
Lacunar stroke
occlusion (microinfarct) of a small branch of larger blood vessel a/w:
smoking, diabetes and hypertension
C→ stroke
Lyme d/z
Tick-borne spirochete bacterial (Borrelia burgdorferi) infection
lyme d/z
characterized by a rash in area of the bite, headache, neck stiffness, chills, fever, myalgia, arthralgia, malaise, fatigue, and possible development of arthritis in large joints.
Meningioma
A slow-growing, often encapsulated mass of cells derived from arachnoid tissue in the dural membrane that is usually benign but inc intracranial pressure.
Meningitis
Inflammation of the membranes covering the brain & spinal cord a/w bacteria/viruses/parasites infection or toxins
Metastasis
Spread of cancer to other parts of the body
Migraine
Headache that usually begins in the temporal region unilaterally after vascular changes of cranial arteries
C→irritability, nausea, vomiting, constipation or diarrhea, and photophobia.
Mild concussion
Tempr. axonal disturbances w/o the loss of consciousness in response to a violent blow, jarring, shaking, or other closed head injury.
Multiple sclerosis
Chronic, autoimmune, demyelinating disease of the CNS that C→ inflammation, axonal degeneration & scarring of myelin sheaths.
Myasthenia gravis
autoimmune response in which antibodies to acetylcholine receptors impair neuromuscular transmission.
Neuromuscular disorder caused by an
Mycotic aneurysm
Aneurysm that is caused by bacterial or fungal growth in the vessel wall or infection of a arteriosclerotic aneurysm.
Myelopathy
Degeneration of the spinal cord
Neurofibroma or schwannoma
Benign nerve sheath tumor in the PNS
Neurogenic shock
Sudden loss of the SNS signals to smooth muscle in vessel walls, c→
vasodilation, hypotension, bradycardia and hypothermia
Neuropathy
Degeneration of nervous system
Capillary telangiectasis
Dilated capillaries with interspersed brain tissue deep in the brain
Oligodendroglioma
Benign nerve sheath tumor in the CNS
Radiculitis
Inflam. of spinal nerve root
Saccular aneurysm (berry aneurysm)
congenital anomalies or degeneration C→ slowly progressing aneurysm that affects only a portion of circumference of arterial wall
Spinal shock
A complete loss of reflex f/x in skeletal muscles, bladder, bowel, sexual function & autonomic control b/w the level of lesion
Stenosis
Narrowing or stricture of a passage or vessel
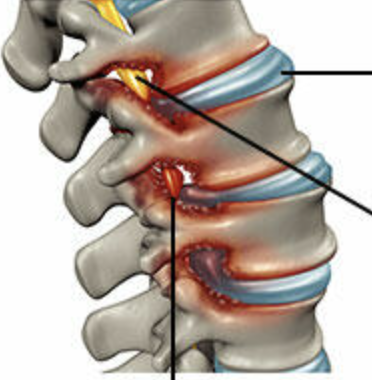
Spondylolisthesis
Stress factor allowing the vertebra to slide forward in relation to the vertebra b/w
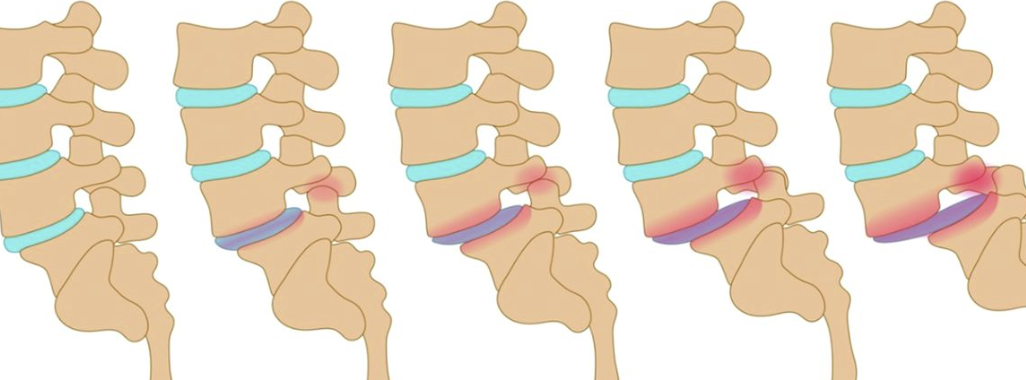
Spondylolysis
Degenerative process of the vertebral column & a/w soft tissue
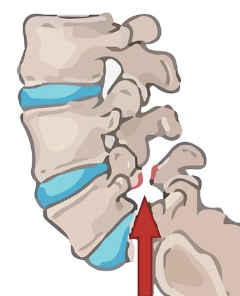
Subdural hematoma
rupture of veins → Collection of blood b/w the inner surface of the dura mater & surface of the brain
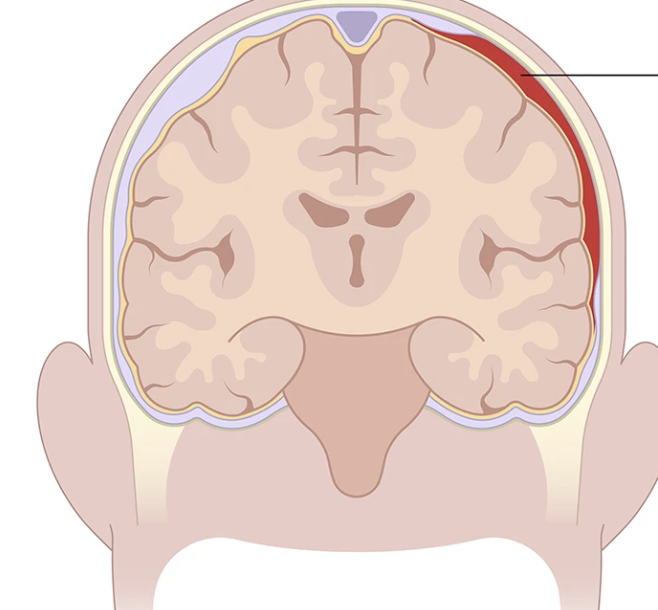
Tension headache
emotional strain or overwork focuses occipital region and can be continuous for months C→ headache
Thrombotic stroke (cerebral thrombosis)
Arterial occlusions in vessels supplying the brain or intracranial vessels caused by atherosclerosis or inflammation.
Transient ischemic attack
Tempr. neurologic dysfunction, symptoms last less than 1 hr,
no evidence of infarction
Venous angioma
Primitive embryologic veins in a radial pattern feedng a central vein