AP Biology Unit 1- The Chemistry Of Life Review
Topic 1.1: Structure of water and hydrogen bonding
Properties of Water
Hydrogen Bonds + Polarity
Polar: Oxygen has a partial negative charge, hydrogen has a positive charge
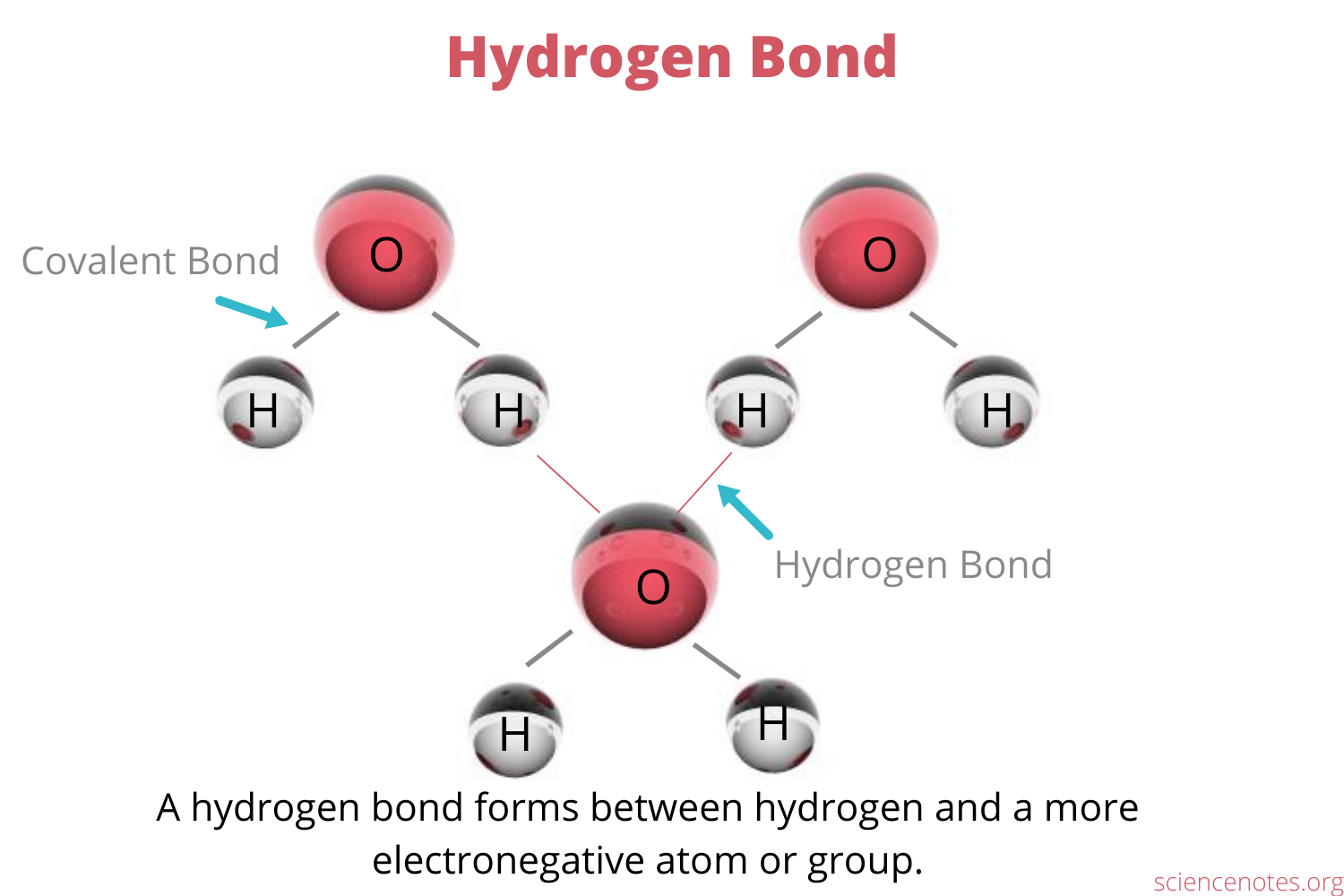
Hydrogen bond: Weak bond between hydrogen in a polar molecule and a small electronegative atom, forms due to the two atoms’ opposite charges
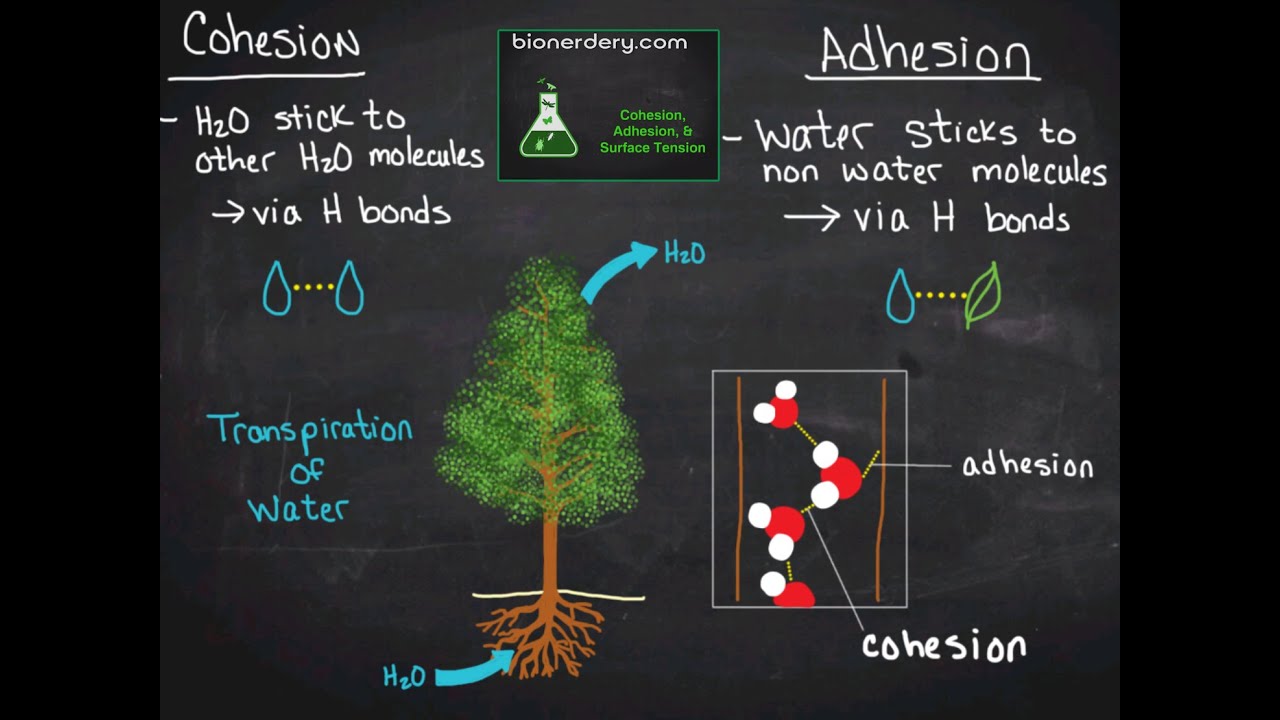
Cohesion: Hydrogen bonds hold a substance together
Adhesion: Clinging of one substance to another-- especially between water and another polar substance
Both adhesion and cohesion allow water to move against gravity
Surface temperature: How difficult it is to break or stretch the surface of a liquid, water has a high surface tension due to hydrogen bonds
Temperature Moderation
- High specific heat: Water is able to absorb/release a lot of heat without its own temperature changing much, water absorbs warm air and releases it to cooler air. Allows climate moderation
- High heat of vaporization: Water has to absorb a lot of heat to change from a liquid to a gas and water cools when its molecules evaporate. Allows evaporative cooling
Ice Floats
- Water expands (becomes less dense) in its solid form, so ice floats
Floating ice insulates water below it

Solvent
- Solvent: The substance that dissolves other molecules in a solution
- H2O is a versatile solvent due to its polarity
- Water can carry many chemicals, nutrients, and minerals throughout an ecosystem and the organisms within it
Topic 1.2-1.6: Macromolecules and the elements of life
Carbon
Carbon: Has 4 valence electrons so can form 4 covalent bonds, allowing it to be the backbone for many complex and diverse molecules
Organic compounds: Compounds containing carbon
Functional Groups (not required course content but definitely helpful to know)
- Functional groups change function by being directly involved in chemical reactions
- Hydroxyl (OH-): Alcohol, make substance more basic (raises pH)
- Carboxyl (-COOH): Acid, contributes H+ (lowers pH)
- Amino group (-NH2)
- Phosphate group: Add negative charge to a molecule
Polymers and Monomers
Polymer: A molecule made of similar building blocks
Monomer: One of the units making up a polymer
Dehydration reaction: Monomers connected and covalently bonded by removing a hydrogen from both molecules and an oxygen from one (making H2O)
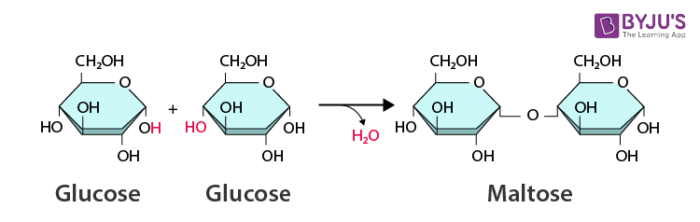
Hydrolysis: Bond between monomers of a polymer is broken by adding H2O
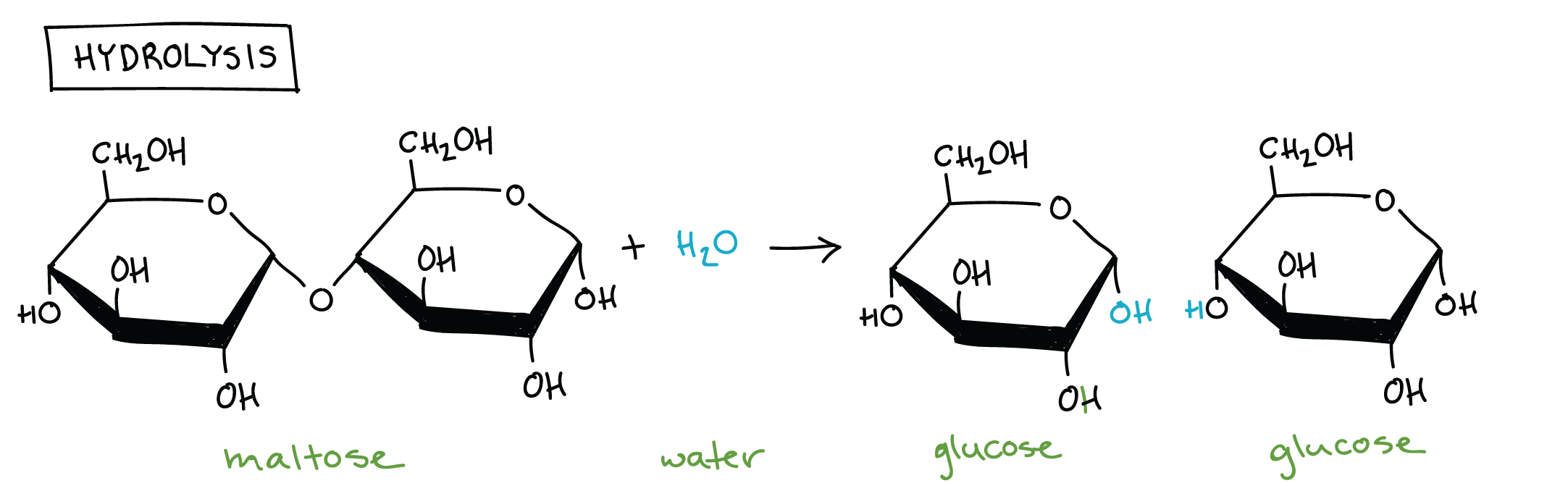
Carbohydrates
- Contain elements: Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
- Monomer: Monosaccharide
- Polymer: Polysaccharides (chain of monosaccharides linked by covalent bonds called glycosidic linkages)
- Functions: Provide and store energy, provide structural support
Important polysaccharides (all are glucose polymers)
- Starch: Stores glucose in plants
- Glycogen: Glucose storage in animals
- Chitin: Structural polysaccharide in fungi cell wells and arthropod exoskeletons
- Cellulose: Cell wall component for plant cells
Lipids
Elements: Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen (sometimes N or P)
No true monomers of lipids
Have little to no affinity for water (hydrophobic)
Function: Energy storage and structure
Saturated: No double bonds between carbon atoms, atoms tightly packed
Unsaturated: Double bonds between some carbons creating a kink in the chain

Trigylcerol: 3 fatty acids attached to one glycerol, energy storage
Phospholipid: Form phospholipid bilayer, have a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
Cholesterol: Steroid that contributes to cell membrane integrity

Nucleic Acids
Elements: Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus
Monomers: Nucleotides, consist of a 5 carbon sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base
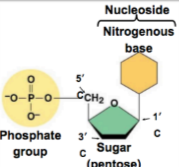
Polymers: Nucelic acids, linear sequences of nucleotides
Nitrogenous base pairs: Adenine pairs with thymine (or uracil in RNA), and cytosine pairs with guanine
Purines: Have a 2 ring structure (A and G)
Pyrmidines: Have a 1 ring structure ( C and T/U)
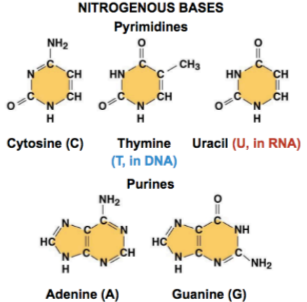
C and G are joined by 3 bonds, A and T are joined by 2
Directionality: Determined by orientation of sugars (hydroxyl = 3´ and phosphate = 5´)
Base pairs are joined by hydrogen bonds, nucleotides joined by covalent bonds
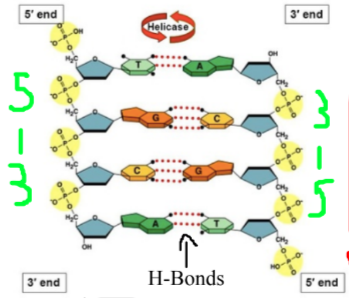
DNA: Antiparallel double helix (2 strands running in opposite directions), has deoxyribose
RNA: Single stranded, has ribose
Proteins
Elements: Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur
Monomers: Amino acids, consist of carboxyl group + amino group + R group
Different amino acids have different R groups
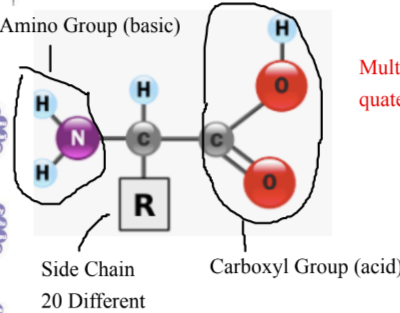
Polymer: Polypeptide
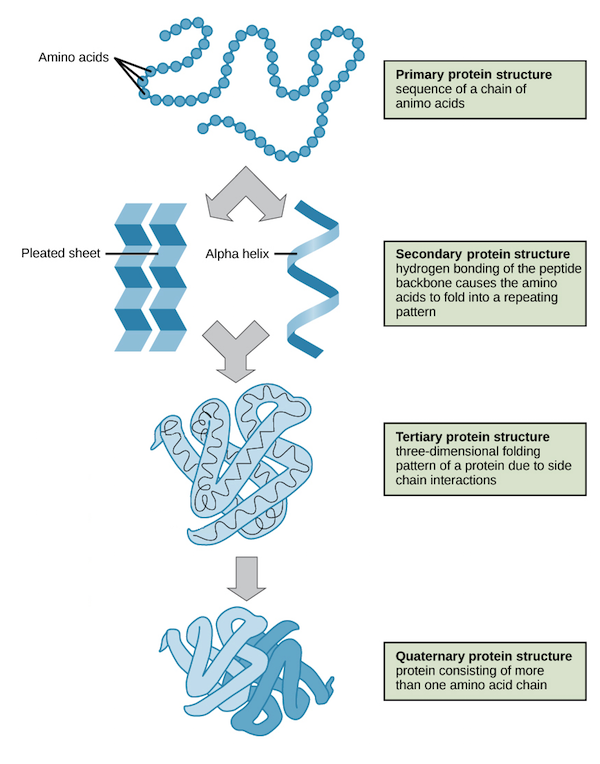
STRUCTURE
Primary: Linear sequence of covalently bonded amino acids
Secondary: Structure formed by interactions between polypeptide´s ¨Backbone¨ ( carboxyl and amino groups)
Tertiary: 3d structure formed by interactions ( hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bridge, hydrophobic, etc.) between R groups
Quaternary: More than one polypeptide chain joined together