Living Environment Regents Review
1/154
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
155 Terms
What are the steps to the scientific method?
Purpose/problem, research, hypothesis, experiment, analysis, conclusion
Independent variable
“If” part of hypothesis, what the scientist changes
Dependent variable
“then” part of hypothesis, depends on the independent variable
Nervous system
quick control, regulates all body processes
Endocrine system
hormones, works with nervous system for regulation
hormones
protein messengers
diabetes
body cannot properly synthesize insulin, causes high blood sugar levels
insulin
a protein that lowers blood sugar levels
circulatory system
transports nutrients and oxygen to cells and wastes away from them
respiratory system
function: gas exchange
Digestive system
breaks down food into smaller molecules so they can diffuse into cells
3 R GENTS
respiration, regulation, reproduction, growth, excretion, nutrition, transport, synthesis
metabolism
all chemical reactions that occur in an organism to make and use energy (3 R GENTS)
homeostasis
maintaining a constant internal condition, regardless of the external environment example: shivering or sweating
cellular respiration
produces ATP (energy) and occurs in the mitochondria
What are the three parts of the cell theory?
All organisms are composed of one or more cells.
The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms.
All cells come from pre-existing cells.
What are the exceptions to the cell theory?
Viruses are NOT living.
No one knows where the first cell came from.
Mitochondria and chloroplast have their own genetic material and can reproduce on their own but they are organelles not cells.
OCTOOSO (levels of organization)
organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
prokaryote
has no organelles example: bacteria cell
eukaryote
has organelles example: animal or plant cell
explain the function for all of these organelles
cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, ribosome, ER, golgi, vacuole, mitochondria, centriole, cell wall, chloroplast
how many um in one mm?
1mm = 1000um
passive transport (diffusion)
materials move through cell membrane from a region of high concentration to low concentration without energy (with the concentration gradient)
diffusion
movement of molecules from high to low concentration (passive transport)
dynamic equilibrium
is reached when molecules spread out evenly on either side of a membrane
osmosis
diffusion but just with water
synthesis/lysis
synthesis build things, lysis destroys
facilitated diffusion
carrier proteins form channels for diffusion of certain molecules, does not use energy, glucose needs to go through one of these protein channels
active transport
movement of molecules from a low concentration to a high concentration using energy (against the concentration gradient)
autotroph
makes its own food for energy
heterotroph
does not make its own food, needs to eat for energy
What does CHONP stand for?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorous
atom
the smallest unit of matter. they have a nucleus (containing neutrons and protons) with electrons surrounding it
What is a compound?
the result of atoms of elements bonding together, bonds are formed when electrons from nearby atoms interact
ionic bond
electrons from one atom transfer to another atom
covalent bond
electrons are shared between neighboring atoms
organic/inorganic compound
organic compounds contain both carbon and hydrogen. inorganic compounds lack carbon and/or hydrogen (cho cho chon chonp are all organic compounds)
carbohydrates (cho)
made of simple sugars/glucose, shaped like a hexagon, quick energy, ends in ose
lipids (cho)
made of fatty acids or glycerol, shaped like an E with branches off of it, slow energy
proteins (chon)
made of folded chains of amino acids, the shape determines its function
nucleic acids (chonp)
made of molecular bases (ATGC) shaped like a house a pool and a hot tub, genetic information DNA and RNA
hot tub=phosphate, house=sugar, pool=base
how many elements are known today?
118
what are the names for the quantity of simple sugars?
monosaccharides- 1 simple sugar
disaccharides- 2 simple sugars
polysaccharides- multiple simple sugars
dehydration synthesis
water is removed to create a bond
hydrolysis
water is added to break bonds (digestion)
what is another word for proteins?
polypeptides
what are the terms used to say the quantity of amino acids?
dipeptide- 2 amino acids
polypeptide- long chain of amino acids
enzyme
biological catalyst, a protein, names end in ase (more on this in following flashcards)
active site
the location on an enzyme where the substrate attaches
substrate
thing that goes into an enzyme
how does an enzyme work?
a substrate fits into the enzyme’s active site like a puzzle piece
enzymes make either two substrates come together or one substrate come apart
they might do more things idk but note that cell receptors also work like this in regards to fitting like a puzzle piece
denatured enzyme
when the shape of the enzyme changes. this can happen due to temperature or pH changes. when the shape of an enzyme changes, the substrate no longer fits into the active site and the enzyme can’t do its job.
acidic/neutral/basic (pH)
acidic- 0-6
neutral- 7
basic- 8-14
activation energy
the energy needed to make the reaction happen, enzymes lower activation energy of a reaction
formula for photosynthesis
CO2 + water = glucose + O2
“COWS GO”
note: the equal sign is an enzyme
formula for respiration
glucose + O2 = CO2 + water + ATP
“GO COWS”
note: the equal sign is an enzyme
where is energy stored?
in the bonds
how do water and minerals enter plants?
through the roots
xylem and phloem
transport water and food through the plant
i think xylem transports the water and phloem transports the food but thats from google not the notes so im not completely sure
stomates
pores under a leaf which let gases in and out (gas exchange)
guard cells
specialized cells can open and close to regulate water loss
each guard cell contains a large vacuole which can fill with water to open the stomata. this same vacuole can empty its water, thus closing the stomata
how is energy released?
when chemical bonds are broken
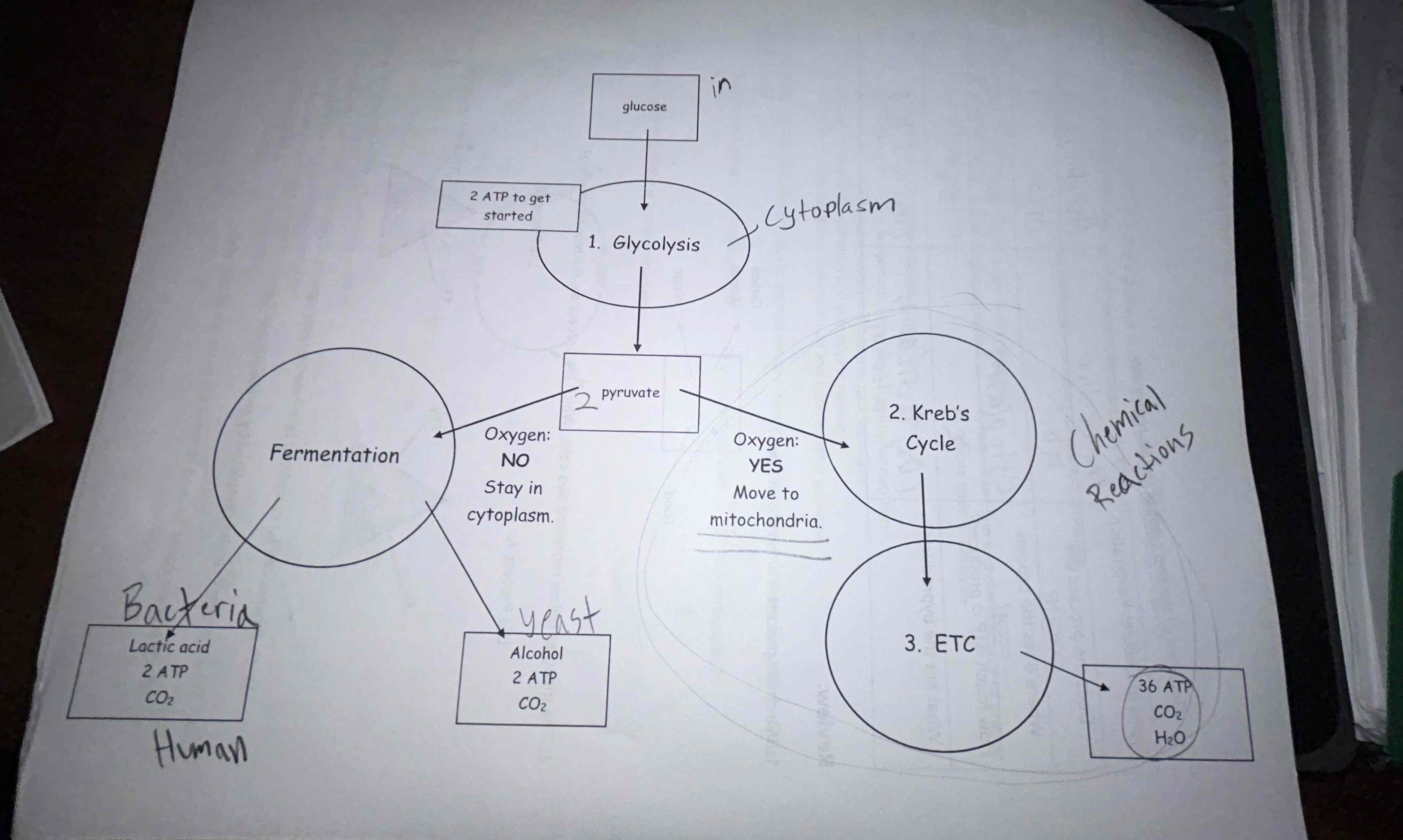
what is the difference between aerobic and anerobic respiration?
aerobic respiration requires oxygen while anerobic does not (aerobic is just the classic “go cows” and produces much more ATP than anerobic, hence running out of breath)
how much ATP can be produced in aerobic respiration?
38
how much ATP can be produced in anerobic respiration?
2
another word for anerobic respiration
fermentation
buildup of lactic acid
causes muscle fatigue and anerobic respiration
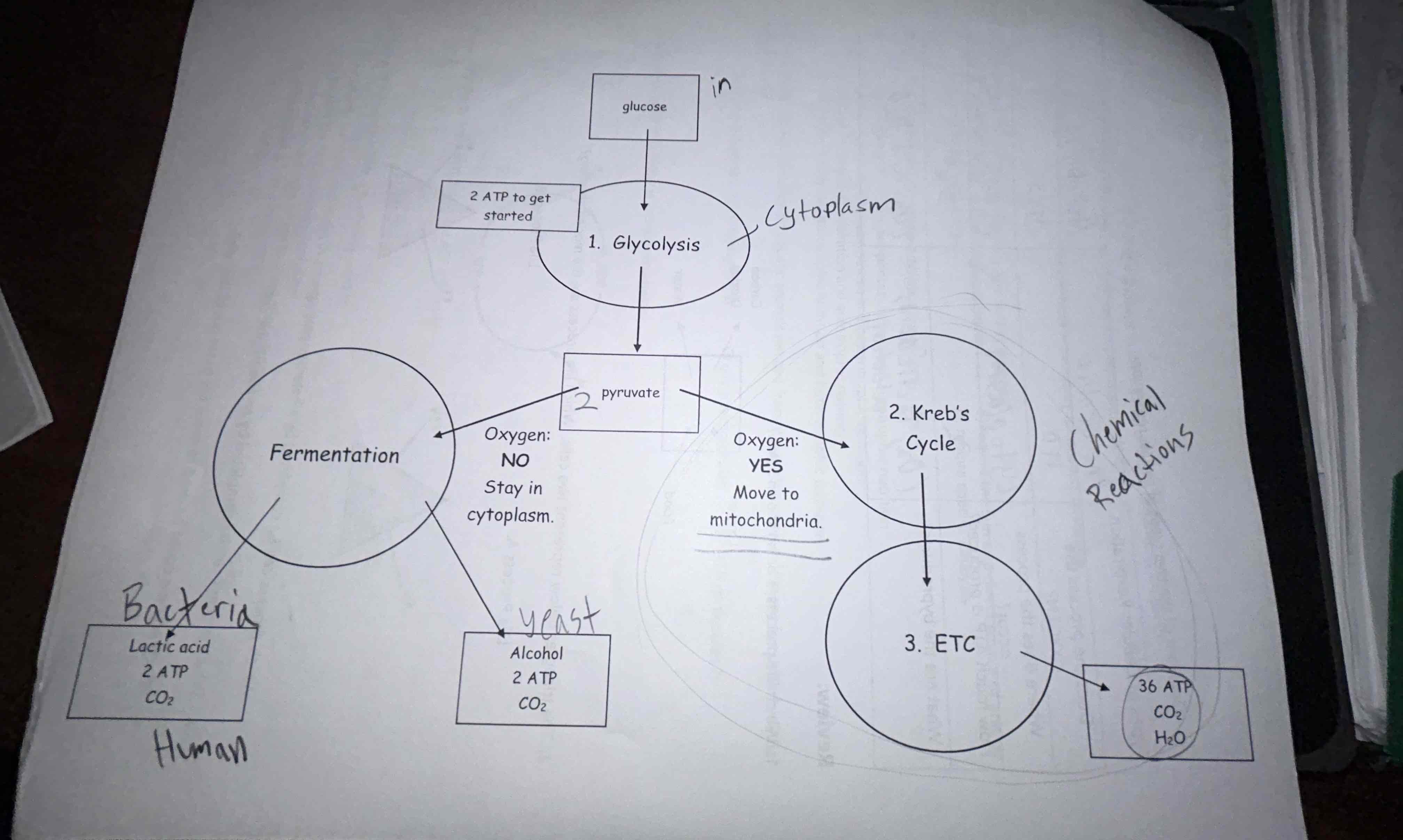
image that shows anerobic and aerobic processes
Image
feedback mechanisms
the process by which a certain function is regulated by the amount of substance or stimulus
ecology
the study of interactions between organisms and how they relate to the physical environment
species
individual group, which can mate and produce fertile offspring
population
all the members of a species inhabiting a given location
community
all the interacting populations in a given area
ecosystem
the living and non living things in an environment; needs a source of energy; stable
competition
occurs when different species living in the same habitat use the same limited resources such as food, space, water, etc. and they have to compete for it
niche
a job or a role in the environment; the role an organism plays in a community
abiotic/biotic factors
abiotic= non living
biotic= living
symbiotic relationships
include different organisms living together in a close association
commensalism
species A: receives benefit
species B: not affected
mutualism
species A and B both receive benefit
parasitism
species A: receives benefit
species B: harmed
food chain
displays a one way relationship of energy flow in an ecosystem
food web
shows the interrelationship between food chains

Review the energy pyramid in the image
Note that more energy is at the producer level and that primary consumers are herbivores
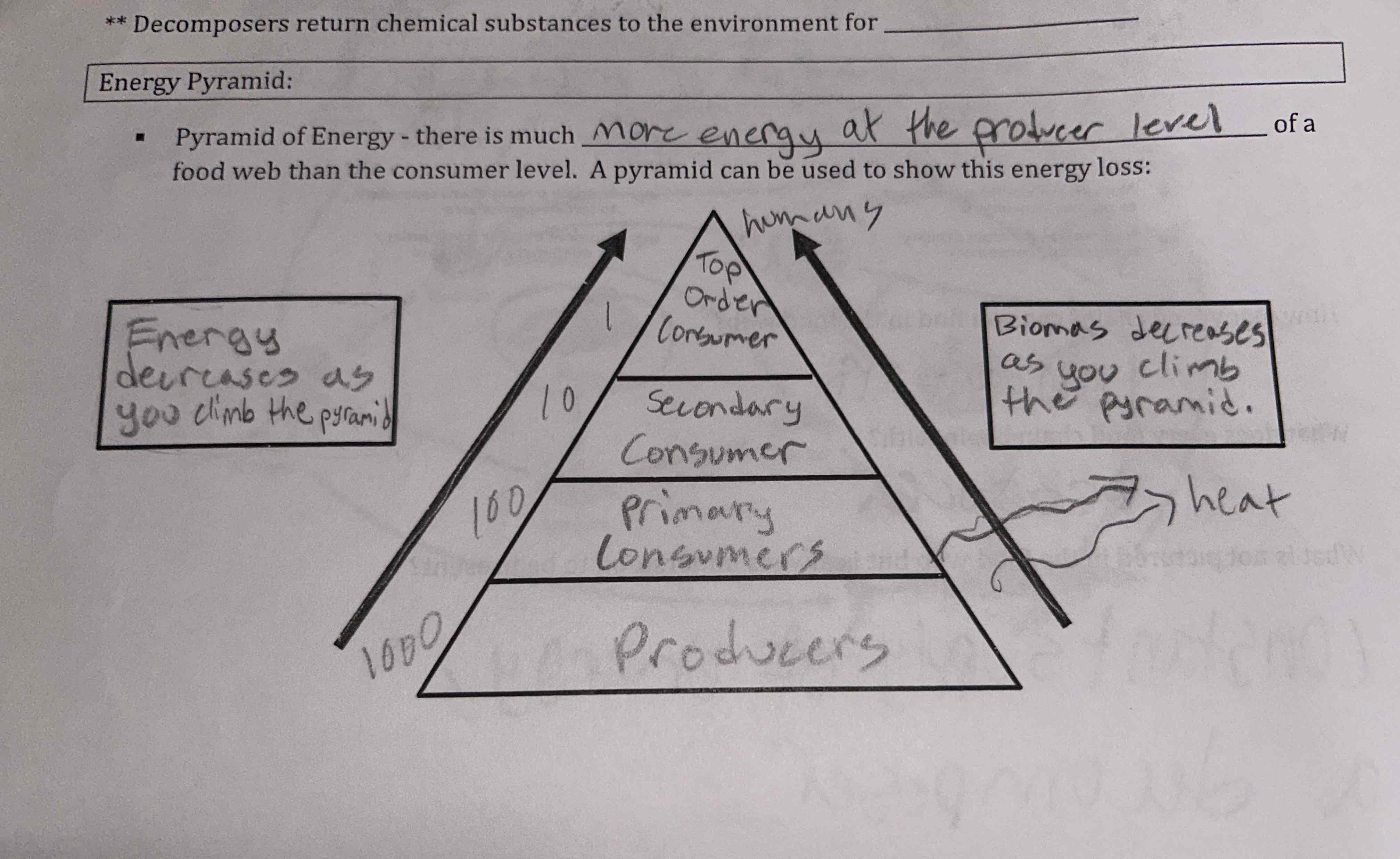
ecological succession
the replacement of one community by another until a stable climax community is reached
pioneer organism
organism that is first to inhabit an area
climax community
a stable ecological community in which little change occurs
limiting factor
any abiotic/biotic factor that limits the size of a population
carrying capacity
how many organisms an ecosystem can hold
biodiversity
the total of all different species living in a given area
biodiversity=stability
phenotype
trait displayed from a gene
genotype
gene composition
gamete
sex cell made from meiosis and is haploid (n)
sperm and egg
somatic cell
body cell made from mitosis that is diploid (2n)
allele
a variety of a gene
heterozygous
two different alleles
dominant
the expressed allele
recessive
the expressed allele when no dominant allele is present
mutation
a change in a gene or chromosome
transcription
DNA to RNA