Planet Earth
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What creates the Earth’s magnetic field
Circulating liquid metal in outer core generates electrical currents
Magentosphere
Formed by the magnetic field; shields Earth from solar wind (stream of
electrically charged particles emitted by Sun).
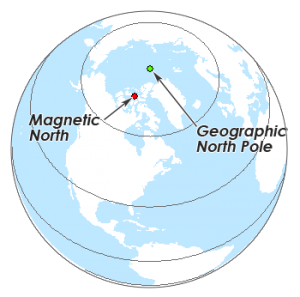
Magnetic North Pole
Found where the magnetic field enters the plane
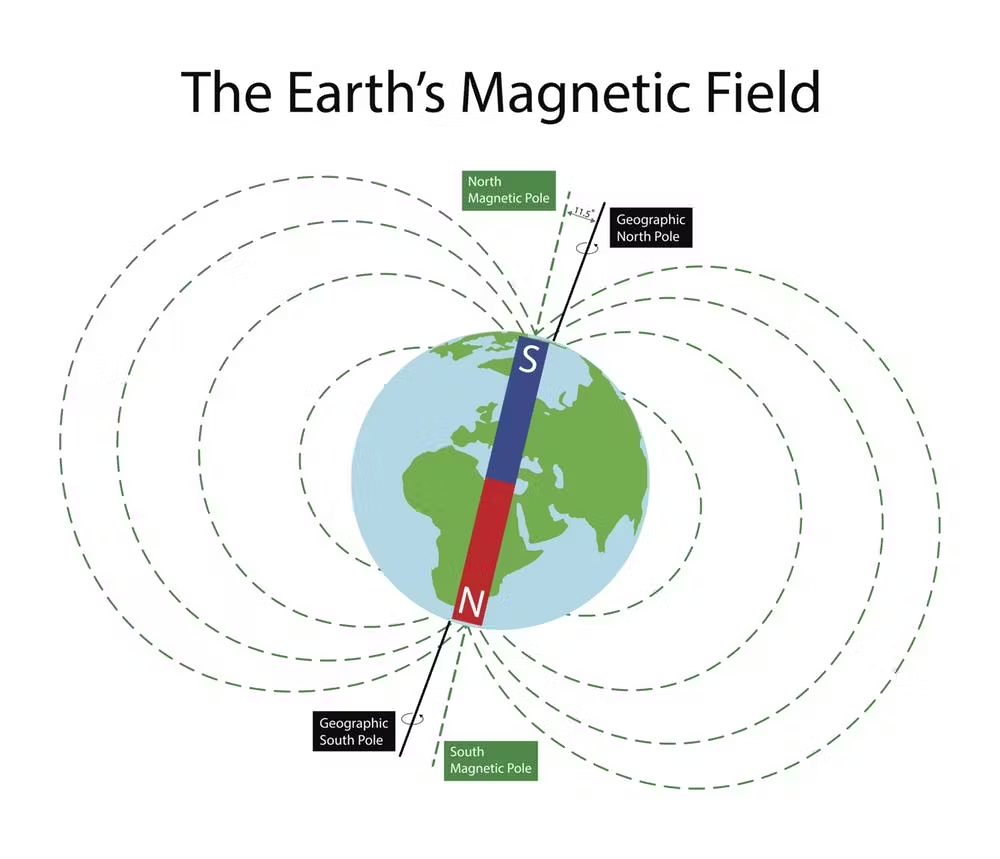
Geographic North Pole (true north)
Found at Earth’s axis of rotation
Aurora (aka Northern Lights)
When the sun’s plasmatic wind finds a gap in the planet’s magnetic
field and collides with the atmosphere.
Tropic of Cancer
The most northerly place on Earth
Receives direct sunlight during the Northern Hemisphere’s summer
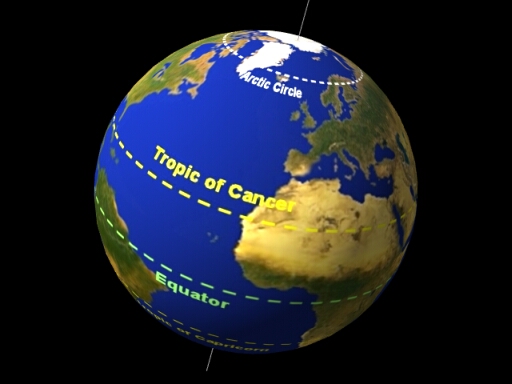
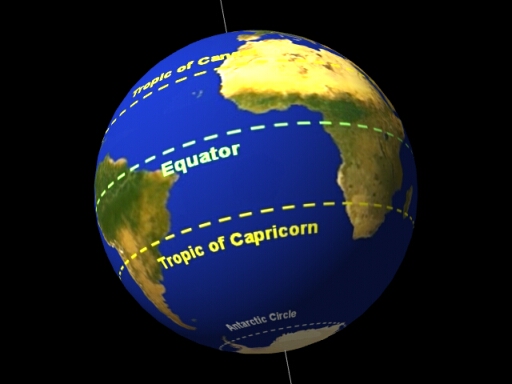
Tropic of Capricorn
The most southerly location on Earth
Receiving direct sunlight during the Southern Hemisphere’s summer
James Hutton (1726-1797)
Helped conceptualize uniformitarianism - Earth has always changed in uniform ways; the present is the key to the past
Catastrophism
Earth’s features, like mountains, were formed by catastrophes
Charles Darwin (1809-1882)
Funder of evolutionary biology; looked at uniformitarianism as support for his theory of how new species emerge.
Inner Core (1/6)
solid iron & nickel
center to 3,200 mi below
Outer Core (2/6)
liquid iron & nickel
3200 mi to 1800 mi below
Lower Mantle (3/6)
deforming solid rock
1800 mi to 125 mi below
below the crust
Asthenosphere (4/6)
softer than the lower mantle
64 and 124 mi below
Crust (5/6)
rigid outermost portion of Earth
stress from the asthenosphere forms lithospheric plates
Lithosphere (6/6)
Crust and the lithospheric mantle beneath it
Moho (Mohorovičić discontinuity):
Boundary that separates crust from lithospheric mantle
62 mi beneath
Magma
Melted rock below the crust’s surface; hardens into granite
Lava
Magma spilled onto the surface of the crust; hardens into basalt
Alfred Wegener (1880-1930)
Proposed the Theory of Coninental Drift (Earth's continents were once joined as a single supercontinent); wrote The Origins of the Continents and Oceans (1915)
Why does magma rise?
It is less dense and more buoyant than lithospheric mantle
Extrusive Igneous Rock (volcanic rock)
Rock that cooled from lava on crust’s surface
Intrusive Igneous Rock (magmatic rock)
Rock that cooled from magma deep underground
Sedimentary Rock
Sediments are compressed and cemented together (lithified)
Form only in depositional environments
Endogenic
Internal processes such as volcanic and tectonic activity
Exogenic
External processes such as weathering by wind/water or transporting
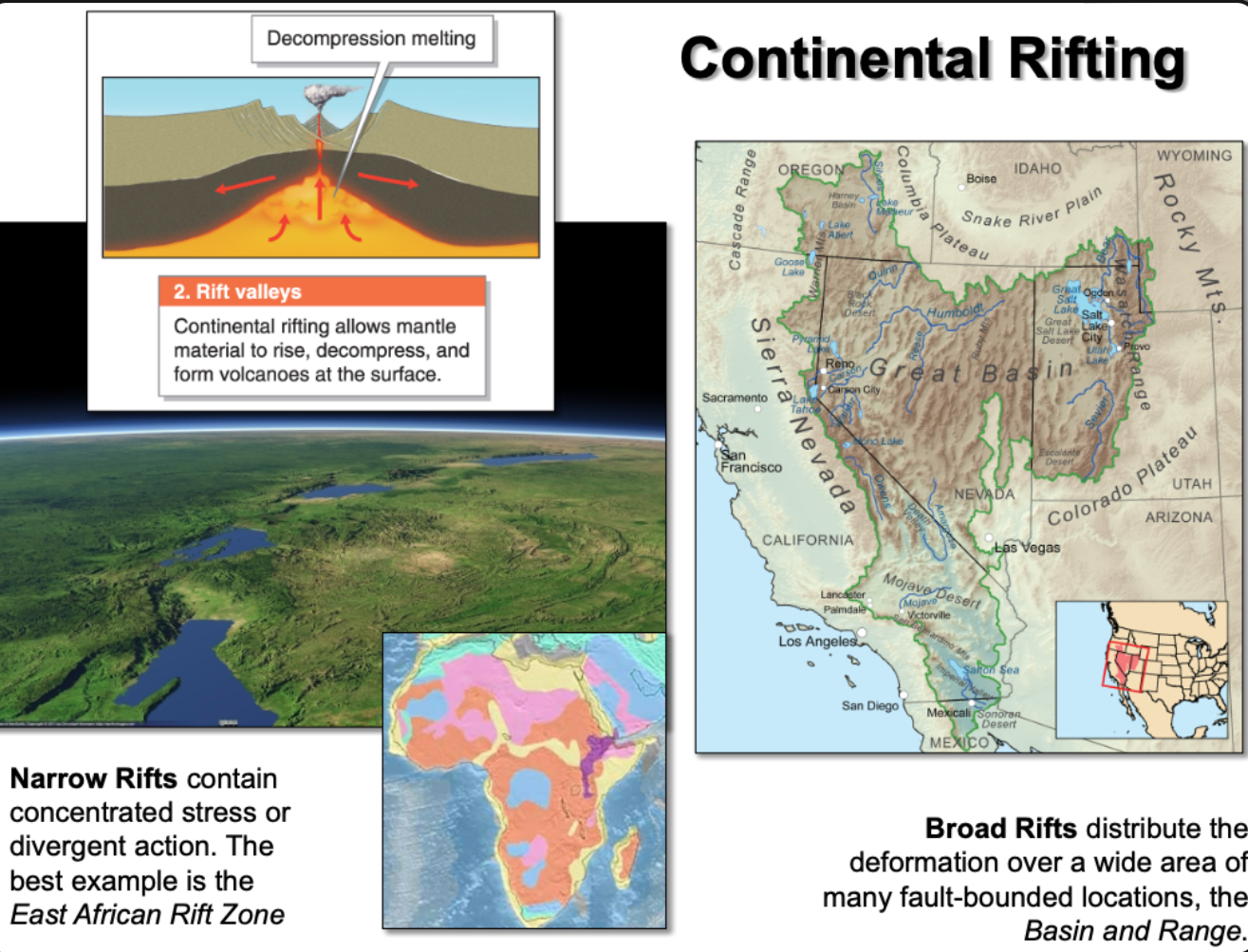
Continental Riftng
Places where the continental crust is extending and thinning (often creates bodies of water)
Collision Zones/Convergent Boundaries
Places where two or more tectonic plates have a net movement toward each other
Orogenesis
The process of building mountains and mountain chains at collision zones/convergent boundaries
Subduction
When plates of different density converge