Full cell biology set
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Explain how gas exchange happens in the lungs?
Transfers oxygen to the blood and remove carbon dioxide from it
Use alveoli for diffusion
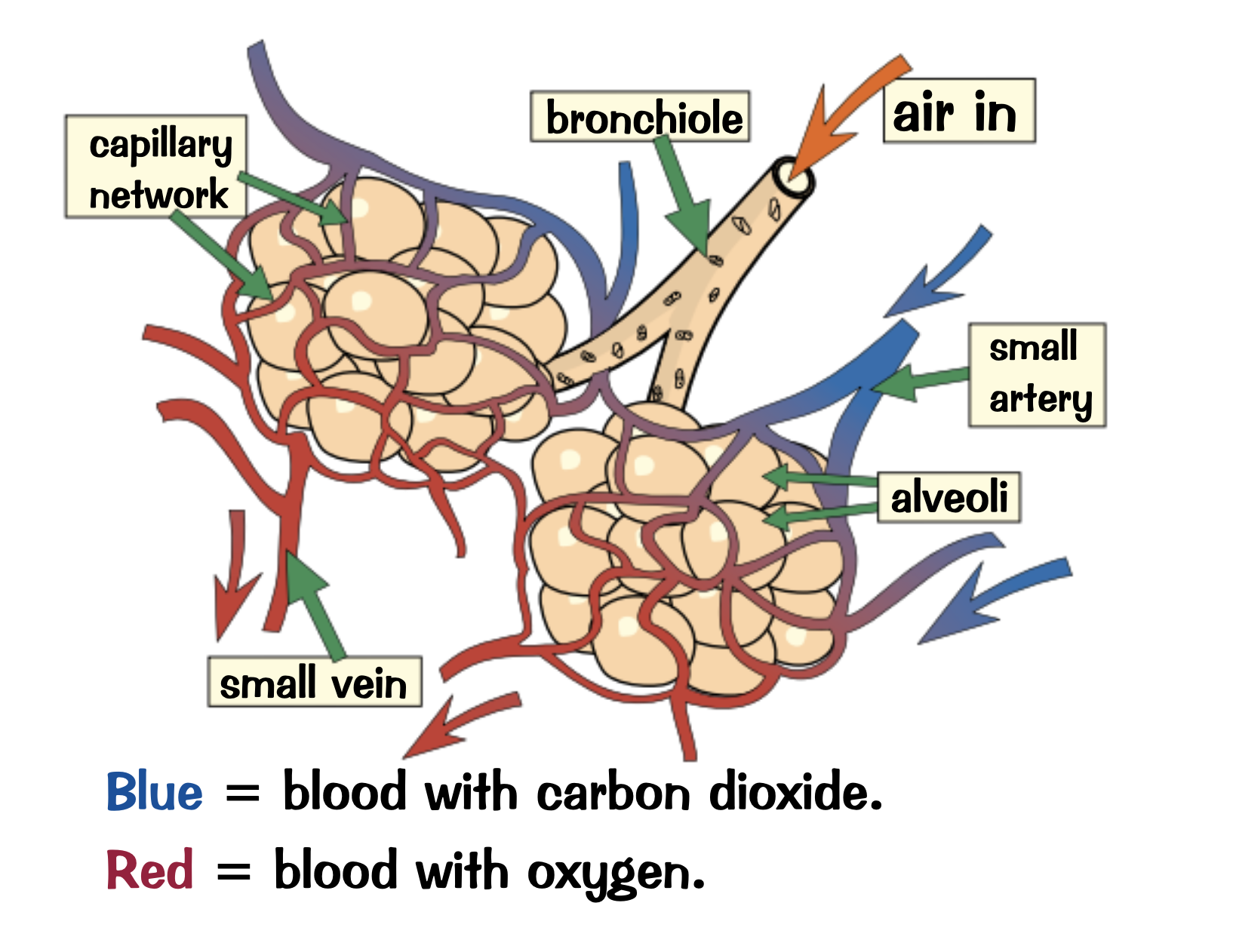
How are the alveoli specialised to maximise diffusion?
Large surface area
Moist lining for dissolving gases
Very thin walls
A good blood supply
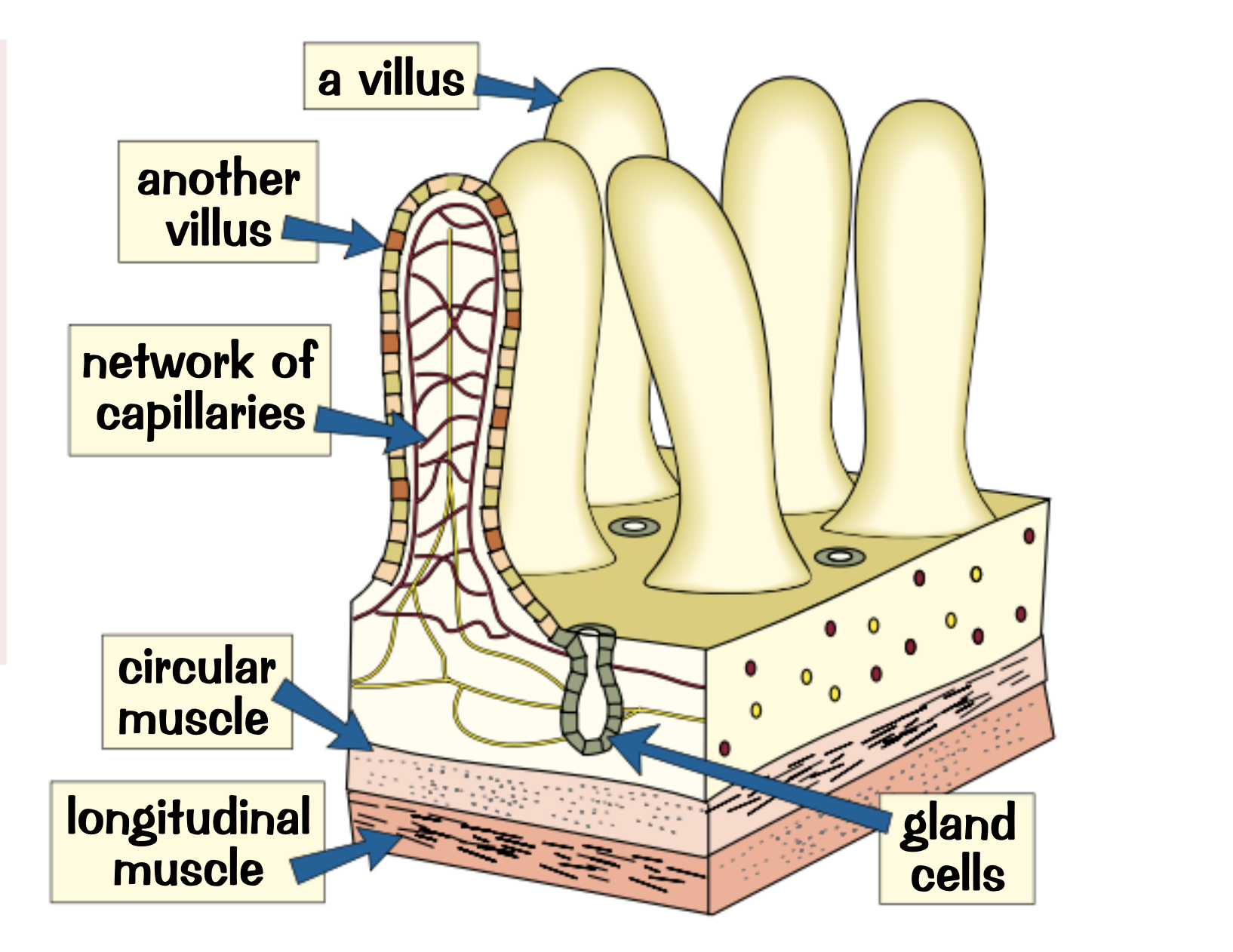
Where are the villi found and what are they used for?
Found in the small intestine to increase diffusion and active transport of nutrients
How are the villi adapted to maximise diffusion and active transport?
Millions of villi
Increase the surface area to maximise absorption
A single layer of surface cells
a very good blood supply
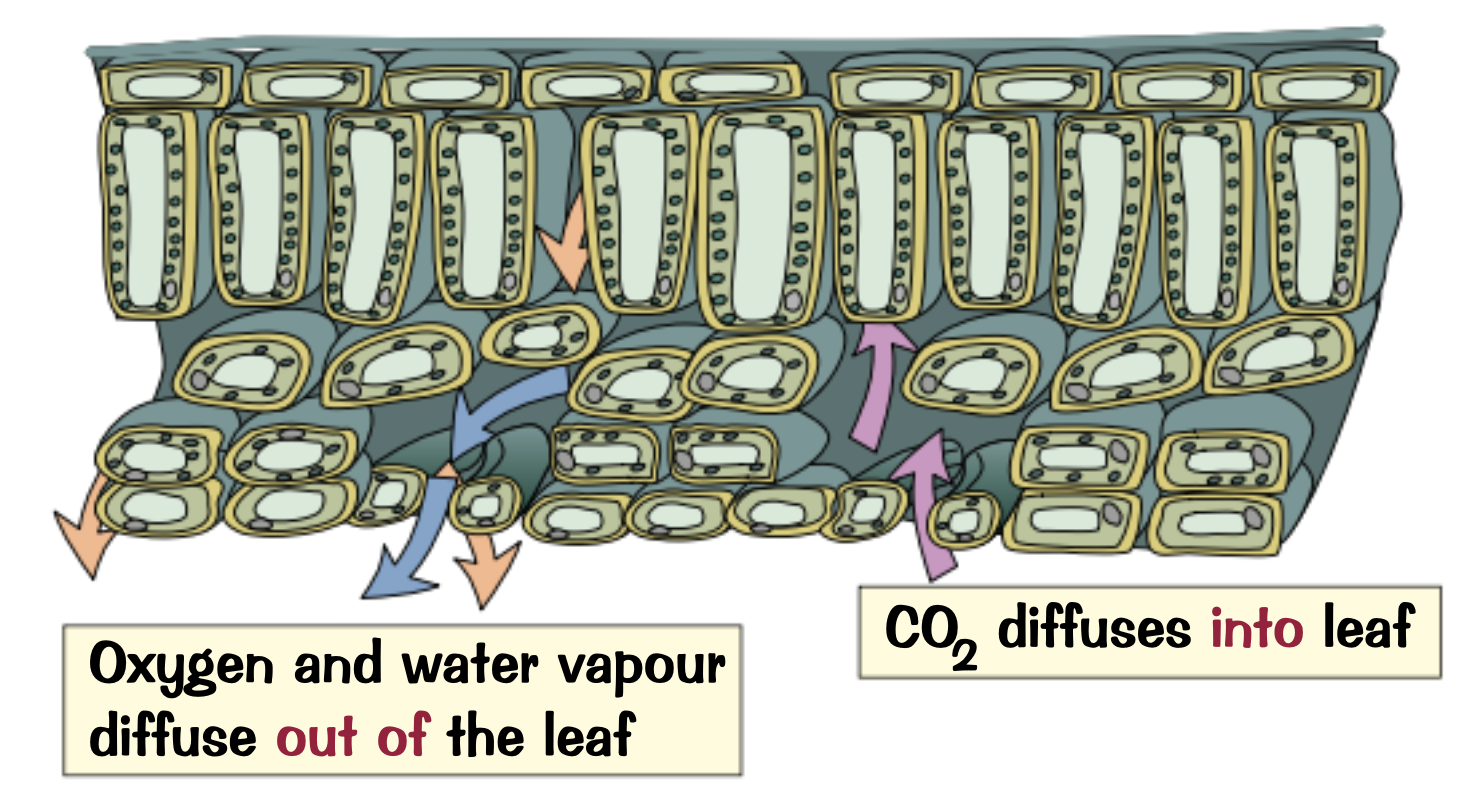
What is diffusion used for on a plants leaves?
carbon dioxide diffuses into the air spaces within the leaves and then into the cells where photosynthesis happens
What are the exchange surfaces on leaves called?
Stomata
What diffuses out of stomata and why?
Oxygen and water vapour because they are the products of photosynthesis
Explain what guard cells are and where they are found?
Controls the size of stomata by opening or closing them to control a plants water lose in comparison to its water absorption in the roots. Found inside of stomata
How are leaves adapted to maximise diffusion?
stomata
flattened shape to increase surface area
walls of cells act as an exchange surface
air spaces inside the leaf increase area increasing chances of carbon dioxide absorption
How does water loss occur through the stomata?
the water vapour evaporates from cells inside the leaf
it escapes by diffusion because the concentration gradient is lower outside than inside the leaf
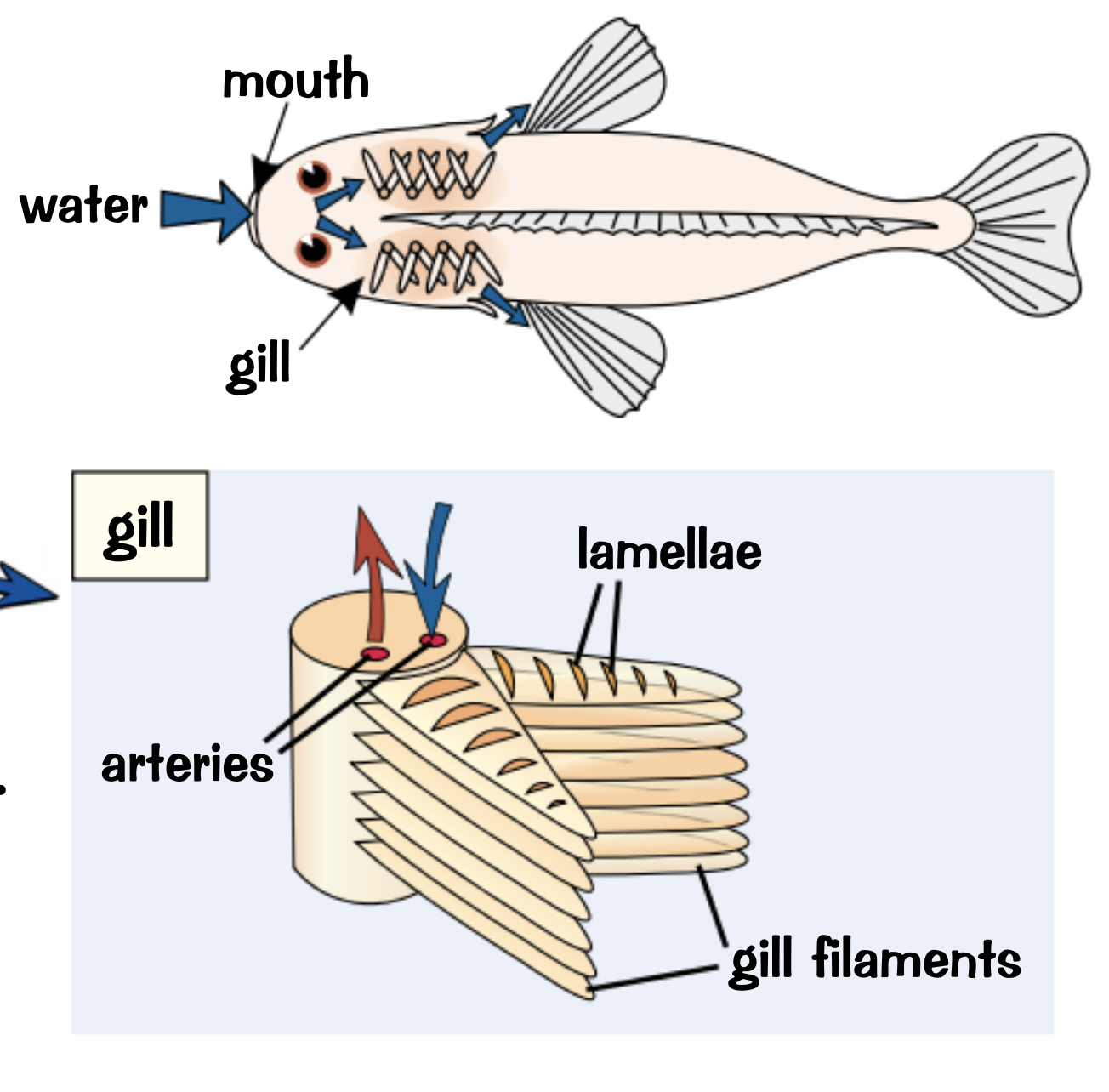
What are the exchange surfaces on fish?
Gills
What and how substances are exchanging through the gills of a fish?
Water enters the fish through its mouth and passes out through the gills. As this happens oxygen diffuses from the water into the blood in the gills and carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the water
How are the gills adapted to maximise diffusion?
Gil filaments: increase the surface area
Lamellae: further increase the surface area by covering the filaments
Lots of blood capillaries: speed up diffusion
thin surface layer of cells: minimise the distance of diffusion
Blood vs water flow directions: blood flows through the lamellae in one direction and water flows in the opposite direction to maintain the concentration gradient
Oxygen concentration in the water is always higher than in the blood
Give 2 examples of organisms exchanging substances with their environment.
Oxygen and carbon dioxide are transferred between cells and the environment during gas exchange
Urea diffuses from your cells into the blood plasma for removal from the body by the kidneys
What affects an organisms ability to exchange substances with its environment?
Surface area:volume ratio
Why don’t single celled organisms need exchange surfaces?
Gases and dissolved substances can diffuse directly into the cell across the cell membrane
large surface area compared to their volume,
substances can be exchanged across the membrane to supply the volume of the cell
Why do multicellular organisms need exchange surfaces?
smaller surface area compared to their volume
not enough substances can diffuse from their environment to supply their whole volume
Require exchange surfaces to increase the surface area for diffusion to allow enough of the necessary substances to pass through
How are exchange surfaces adapted to maximise effectiveness?
thin membrane: substances have a shorter distance to diffuse
Large surface area: lots of substances can diffuse at once
Animals → high blood supply: diffuse in and out of the blood faster
Ventilation in gas exchange surfaces: moves the air in and out of surface to allow more of the requires substance
What is active transport used for?
to transport substances against a concentration gradient: from a lower to a higher concentration gradient
What are root hair cells used for?
providing a larger surface area for a plant to absorb water and mineral ions from the soil
What do plants need mineral ions for?
Growth
Why can’t root hair cells use diffusion?
The concentration of the minerals is usually higher in the root hair cells than in the soil around them
How is active transport used in plants?
To absorb minerals from a very dilute solution against a concentration gradient.
Where does a plant receive the energy for active transport?
from respiration
Where is active transport used in humans?
In the gut when there is a lower concentration of nutrients in the gut than in the blood.
When does diffusion occur in the gut?
When there’s a higher concentration of glucose and amino acids in the gut than in the blood
How does the gut being able to do diffusion and active transport useful?
Allows nutrients to be transported into the blood with or against a concentration gradient
What is the definition of osmosis?
the movement of water particles across a partially permeable membrane from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration
What is a partially permeable membrane?
A membrane with small holes in it to allow tiny molecules to pass through it
How does osmosis work?
Water molecules pass through both ways of the membrane because water molecules move around randomly all the time
Because there are more water molecules on one side than the other, there’s a steady net flow of water into the region with fewer water molecules
This causes the stronger sugar solution to get more dilute
Explain an experiment to observe how sugar solutions affect plant tissue.
Cut up a potato into identical cylinders and get 2 beakers with different sugar solutions. One should have pure water and another should have a very concentrated sugar solution
Measure the mass of the cylinders and then leave one cylinder in each beaker for about 24 hours
Take them out and dry them with a paper towel and measure their masses again
If the cylinders have drawn in water with osmosis, they’ll have increased in mass, and if water has been drawn out the mass will have decreased
What is the independent variable for the experiment to observe how sugar solutions affect plant tissue due to osmosis?
The concentration of the sugar solution
What is the dependant variable for the experiment to observe how sugar solutions affect plant tissue due to osmosis?
The potato cylinders mass
What are the main controlled variables for the experiment to observe how sugar solutions affect plant tissue due to osmosis?
same volume of solution
Same temperature
Same time in solution
same type of sugar used
What are some possible errors for the experiment to observe how sugar solutions affect plant tissue due to osmosis?
if the potato cylinders weren’t fully dried, the excess water would give it a higher mass
if water evaporated from the beakers, the concentrations of the salt solutions could change
How could you reduce the effect of possible errors for the experiment to observe how sugar solutions affect plant tissue due to osmosis?
Repeating the experiment and calculating the mean percentage change at each concentration
What is the definition of diffusion?
the spreading out of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Where and why does diffusion happen?
In solutions and gases because the particles in these substances are free to move around
How does the concentration gradient affect the rate of diffusion?
The bigger the concentration gradient the faster the rate of diffusion
How does temperature affect the rate of diffusion?
Higher temperatures will increase the rate bow diffusion because the particles have more energy and move around faster
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Holds the cell together and allows different particles in and out of the cell
What substances can move in and out the cell membrane through diffusion?
dissolved substances
What particles can and can’t enter the cell membrane through diffusion?
can: glucose, amino acids and water
can’t: startch and protein
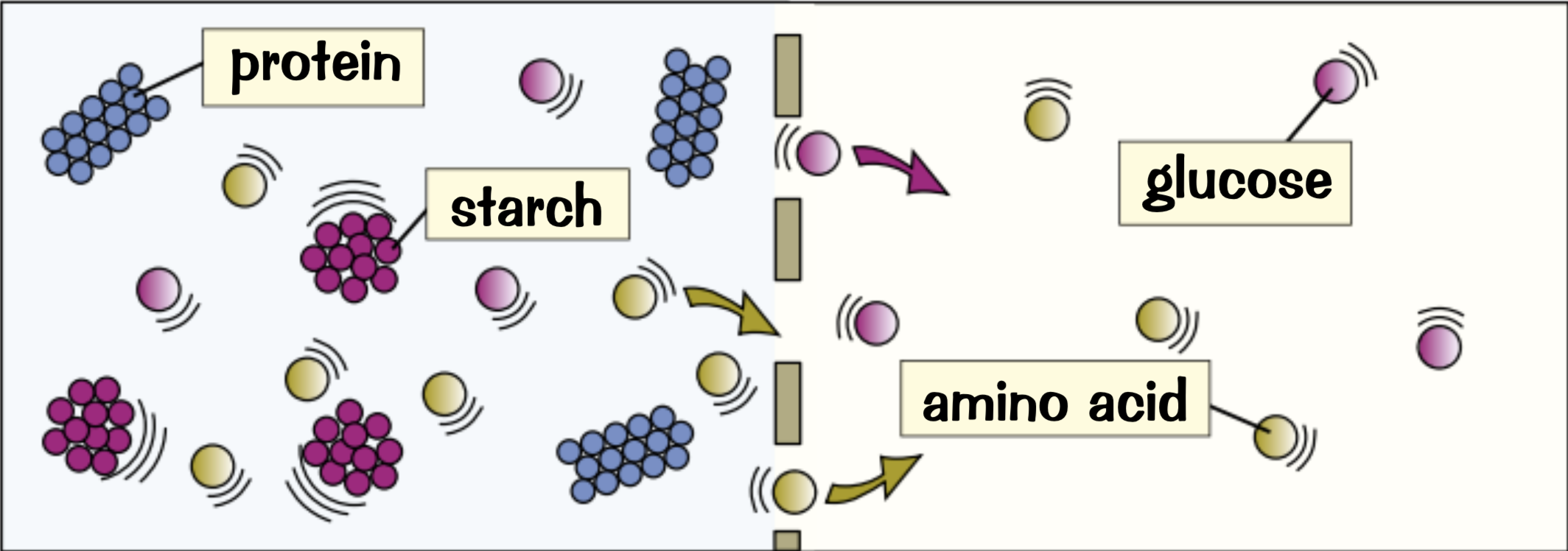
How does diffusion through a cell membrane work?
particles flow from a higher concentration gradient ( more particles ) to a lower concentration gradient ( less particles )
Diffusion works in both directions, but if there are a lot more particles on one side the net movement is from that side
The larger the surface area of the membrane the faster the rate of diffusion because more particles can move through at once
What is the definition of differentiation?
the process by which a cell changes to become specialised to its job
What are stem cells?
Undifferentiated cells that can divide to create more stem cells to be specially based on the instructions received
Where are stems cells found?
In early human embryos
Why are stem cells found in early human embryos exciting?
have the potential to turn into any kind of cell
Name 2 places stem cells can be found.
Early human embryos and bone marrow
How are cells created with stem cells for medical research?
Stem cells are grown in a lab to produce clones which are differentiated into specialised cells that are used in medicine or research
How are adult stem cells used to cure disease?
Stem cells from bone marrow from a healthy person can be specialised into blood cells to replace faulty ones in a sick person
How are embryonic stem cells used for patients with diabetes?
Insulin-producing cells are created from differentiation of embryonic stem cells that replace faulty cells
What is therapeutic cloning in terms of stem cells?
Embryo produced with the same genetic information as the patient so stem cells produced for patient won’t be rejected by the body
What is a risk of using stem cells in medicine?
Stem cells can become contaminated with a virus in the lab and passed on to the patient making them sicker
Explain the different views of the use of stem cells in medicine.
Some people believe embryonic stem cells shouldn't be used because they have the potential for human life
Others think curing diseases for people who is suffering is more important than the rights of embryos
Some believe its fine because the embryos used are often unwanted from fertility clinics and would otherwise be destroyed
Some believe scientists should focus on finding other sources of stem cells to prevent the further use of embryos
Where are stem cells found in plants?
Meristems
How are stem cells from meristems used?
To produce clones of whole plants quickly and cheaply
to grow more rare plant species
to grow crops of identical plants that have desired features for farmers e.g disease resistance props
What does a cultured medium contain that bacteria needs to grow?
Carbohydrates , minerals proteins and vitamins
Give 2 examples of cultured mediums that can grow bacteria
nutrient broth solution or solid agar jelly
What will you see when bacteria has cultured on an agar plate?
visible colonies on the surface of the jelly or evenly spread out bacteria on the surface
Describe the method to culture bacteria on an agar plate.
Use an inoculating loop to transfer microorganisms to the agar plate.
Close the agar plate in a Petri dish and wait for bacteria to grow
What is the max temp cultures of microorganisms are kept at ,at schools? Why?
25*c to prevent the growth of harmful pathogens that require higher temperatures
Why are cultures incubated at higher temperatures in industrial conditions?
To allow the bacteria to grow faster
Explain how to investigate the effect of antibiotics on bacterial growth.
Place paper discs soaked in different types or concentrations of antibiotics on an agar plate that has an even coverage on bacteria. Leave some space between the discs
The antibiotics will diffuse into the agar jelly. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria that aren’t affected by the antibiotic will continue to grow around the discs, but non-resistant strains will die, leaving an inhibition zone.
Used a control disc soaked in sterile water to ensure that any difference between the growth of bacteria around control disc and antibiotic discs is due to the effect of the antibiotic alone.
Leave the agar plate for 48 hours at 25*c
The more effective the antibiotic is against bacteria, the bigger the inhibition zone will be
What is an inhibition zone?
a clear area left behind where bacteria has died
How do you prevent contamination or development of harmful pathogens when culturing or using cultured bacteria?
Sterilise the Petri dish and culture medium before use to kill any unwanted microorganisms
Sterilise inoculating hoop in a flame before using it to transfer bacteria to the culture medium
Lightly tape Petri dish lid after transferring bacteria to stop microorganisms from the air getting in
store Petri dish upside down to stop condensation falling onto the agar surface.
How do you know which antibiotic was most effective at killing bacteria?
Based on the area of the inhibition zone. The bigger the inhibition zone the better the antibiotic was.
How do you calculate the size of an inhibition zone?
Calculate the area of the circle.
What is the process of binary fission?
The circular DNA and plasmids replicate
The cell gets bigger and the circular DNA strands move to opposite poles of the cell
The cytoplasm begins to divide and new cell walls begin to form
The cytoplasm divides and two daughter cells are produced. Each daughter cell has one copy of the circular DNA but can have various numbers of plasmids
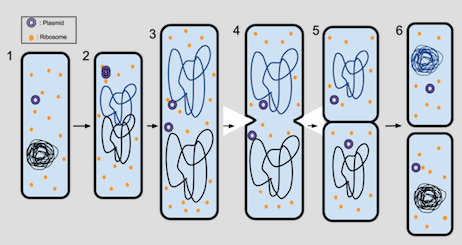
What conditions do bacteria cells need to divide quickly?
warm environment and lots of nutrients
What type of cells can reproduce through binary fission?
Prokaryotic cells


What does the nucleus contain?
genetic material n the form of chromosomes
What is a chromosome?
coiled up lengths of dna
What do chromosomes contain? and what is this part used for
Genes which are used to control the development of different characteristics
How many pairs of chromosomes does the human cell contain?
23 pairs
What is the process when multicellular organisms divide?
mitosis
Why do organisms go through mitosis?
grow
replace damaged cells
What is the result of mitosis?
two new identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes
What is the process of growth and DNA replication In the cell cycle?
Grow and increase the amount of sub cellular structures it has
Duplicates its DNA so there is one copy for each new cell.
The DNA is copied and forms X-shaped chromosomes. Each arm of the chromosome is an exact duplicate of the other
What is the process of mitosis in the cell cycle?
The chromosomes line up at the centre of the cell and cell fibres pull them apart. The two arms of the chromosome go to opposite sides of the cell.
Membranes form around each set of chromosomes. These become the nuclei of the two new cells-the nucleus has divided
The cytoplasm and cell membrane divide
The cell produces two identical new daughter cells.
What is the full process of mitosis?
Duplicates its DNA so there is one copy for each new cell.
The DNA is copied and forms X-shaped chromosomes. Each arm of the chromosome is an exact duplicate of the other
The chromosomes line up at the centre of the cell and cell fibres pull them apart. The two arms of the chromosome go to opposite sides of the cell.
Membranes form around each set of chromosomes. These become the nuclei of the two new cells-the nucleus has divided
The cytoplasm and cell membrane divide
The cell produces two identical new daughter cells.
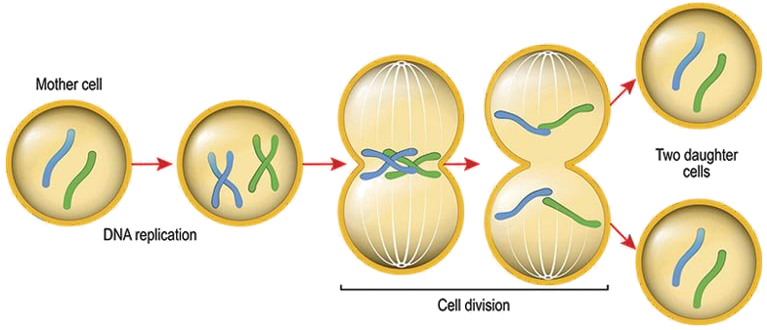
What is differentiation?
the process by which a cell changes to become specialised for its job
How do cells change to become specialised?
They develop different sub cellular structures and turn into different types of cells
In what cells and for how long can cells differentiate?
Animal cells: in the early stages of growth/development
plant cells: don’t lose the ability
What are differentiated cells used for in mature animal cells?
repairing cells
replacing cells
What are stem cells?
Un differentiated cells
Explain how a sperm cell specialised for reproduction?
function is to get male DNA to female DNA
Long tail and streamlined head help it swim to the egg
Lots of mitochondria to provide energy when needed
Carries enzymes to digest through the egg membrane
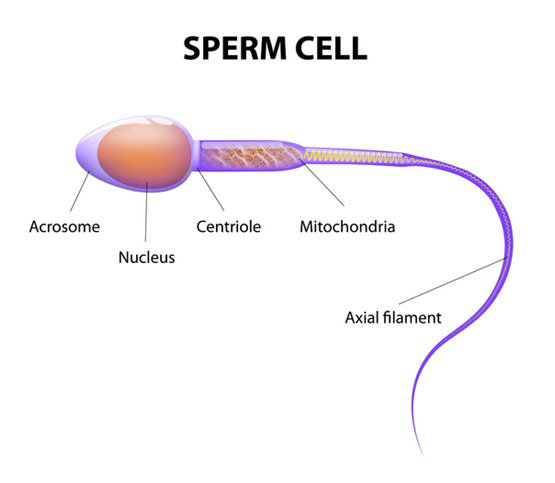
Explain how nerve cells are specialised for rapid signalling
Function is to carry electrical signals from one part of the body to another
They are long, and have branched connections at their ends to connect to other nerve cells
Form a network throughout the body
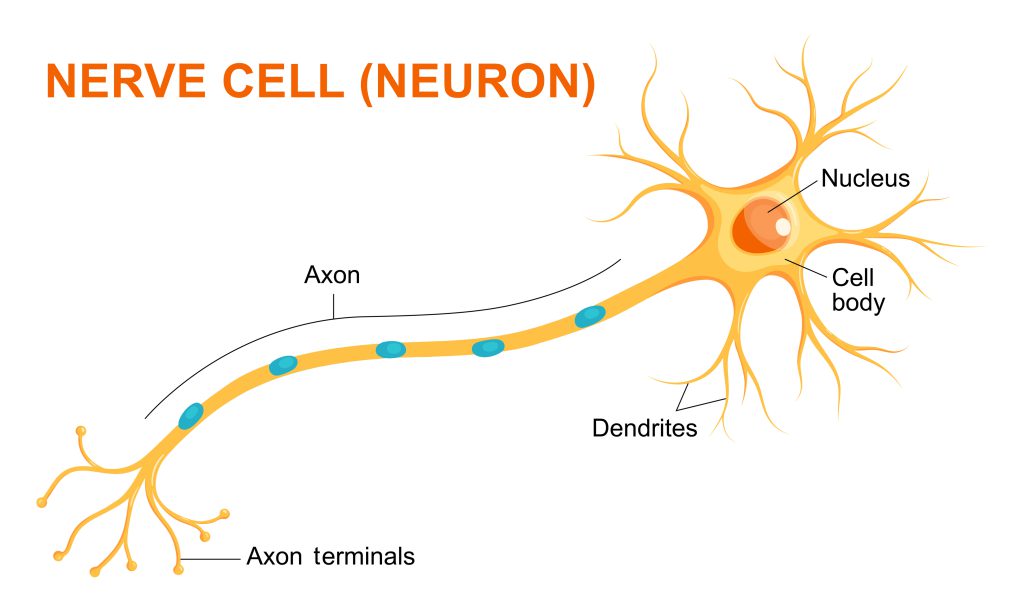
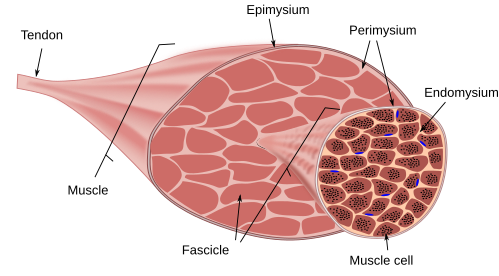
Explain how muscle cells are specialised for contraction
function is to contract quickly
long and contain lots of mitochondria to generate energy needed for the contraction
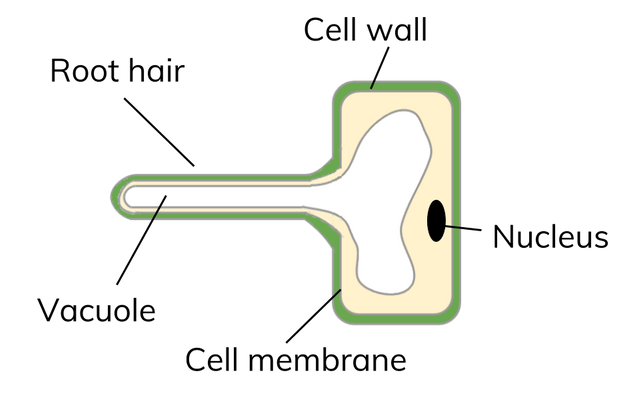
Explain how root hair cells are special for absorbing water and minerals
On the surface of plant roots
grow into long hairs that stick out into the soil
gives the plant a big surface area for absorbing water and mineral ions from the soil
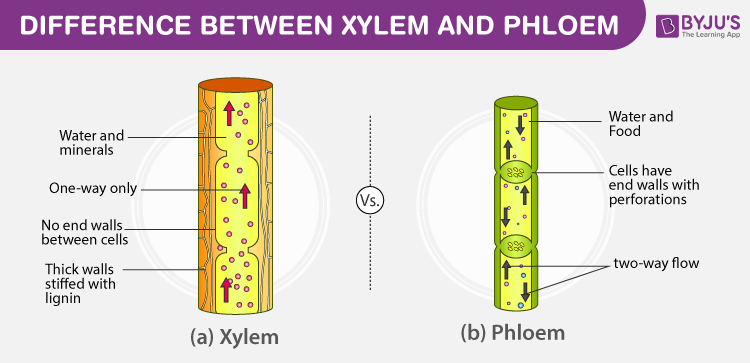
Explain how phloem and xylem cells are specialised for transporting substances
tubes that transport substances such as food and water around plants
to form tubes the cells are long and join end to end
Xylem cells are hollow in the centre
Phloem cells have very very sub cellular structures so that stuff can flow through them
What are the unit conversions on a light microscope?
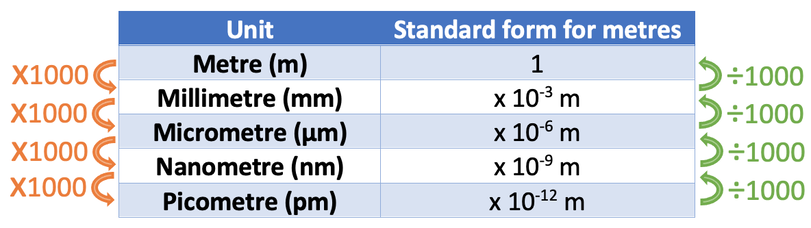
What is the purpose of a light microscope?
Uses light and lenses to form a magnified image of a specimen
Allow us to see individual cells and large sub-cellular structures
e.g nuclei
What is the purpose of an electron microscope?
Uses electrons to form a magnified image of a specimen
Have higher magnification and resolution
See smaller things in detail like
The internal structure of mitochondria and chloroplasts
and tiny sub-cellular structures like ribosomes and plasmids
What is the formula triangle for magnification?
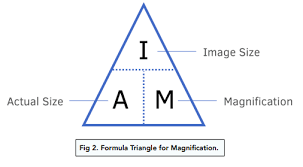
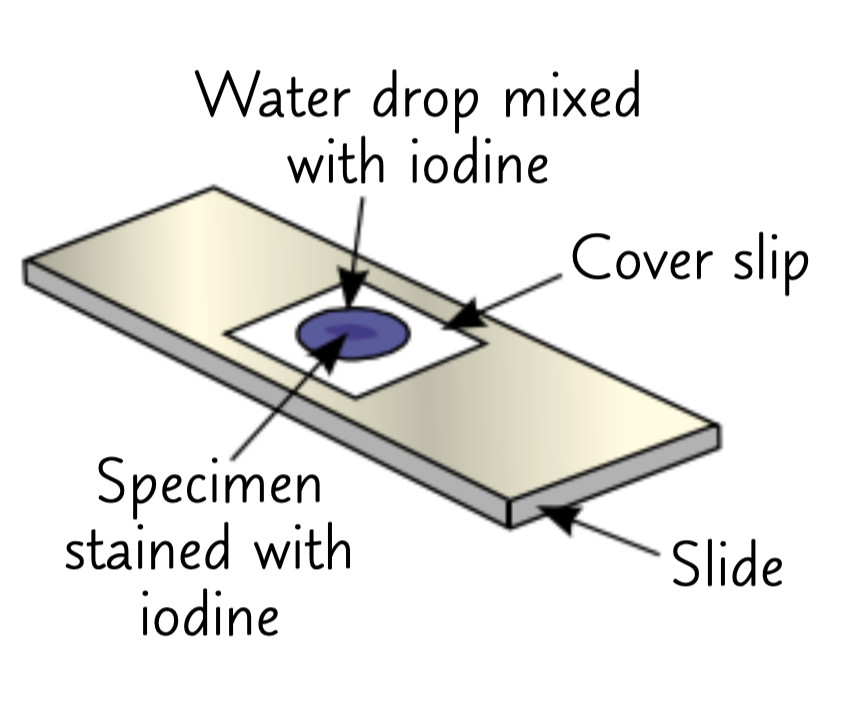
How do you prepare your slide to investigate a specimen on a light microscope? (practical)
add a drop of water to a clean slide
Seperate epidermal tissue from your specimen
Place epidermal tissue on water drop on slide
Add a drop of iodine solution to stain the tissue to highlight them with colour
Place a cover slip on top
How to use a light microscope to look at your slide? (practical)
Clip the slide you prepared onto the stage
Select the lowest powered objective lens
Use the course adjustment knob to move the stage up to just below the objective lens
Look down the eyepiece. Use the course adjustment knob to move the stage down until the image is roughly in focus
Adjust the focus with the fine adjustment knob until you get a clear image of what’s on the slide
If you need to see the slide with greater magnification, swap to a higher powered objective lens and refocus
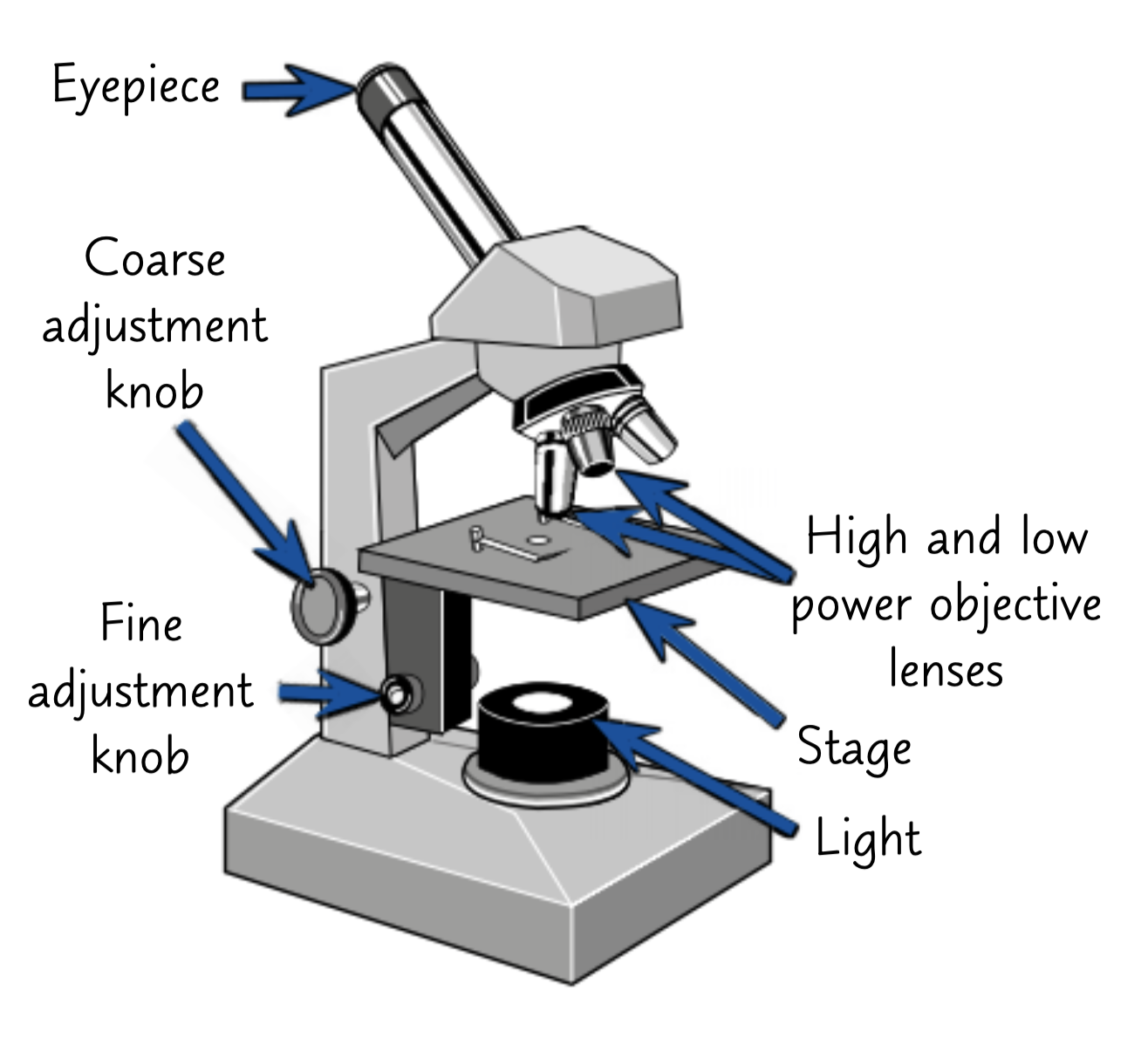
What are the parts and function of a light microscope?
Eyepiece Lens - This is the lens that you look down.
Coarse Focussing Wheel - This moves the stage by a large amount to bring the image into focus (make the image clear and not blurry).
Fine Focussing Wheel - This moves the stage by a small amount to focus the image carefully (make the image clear and not blurry).
Objective Lens - This is the lens next to the specimen that magnifies the image.
Stage - This is where the sample is placed.
Light Source - This can be a lamp or a mirror used to shine light through the specimen.
How do you draw your observations? (practical)
Draw what you see with a sharp pencil
Make sure your drawing takes up at least half the space available that is drawn with clear and unbroken lines
Do not colour or shade
If you are drawing cells, sub cellular structures should be in proportion
Include title and magnification of the image
Label important features of your diagram