E1: cervical spine
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
brachial plexus roots
C5-T1
what are the branches of the brachial plexus?
musculocutaneous
axillary
radial
median
ulnar
(MARMU)
what is the C5 reflex?
biceps brachii
what is the C6 reflex?
brachioradialis
what is the C7 reflex?
triceps
what muscles does C5 control?
deltoid and biceps
what muscles does C6 control?
biceps and wrist extensors
what muscles does C7 control?
triceps, wrist flexors and finger extensors
what muscles does C8 control?
interossei muscles, finger flexors
what muscles does T1 control?
interossi (abduction & adduction)
PAD and DAB
what is the area of sensory for C2 & C3?
subocciput region of head
what is the area of sensory for C4?
trapezius
what is the area of sensory for C5?
lateral shoulder
lateral elbow crease
what is the area of sensory for C6?
lateral forearm
1-2 digits
what is the area of sensory for C7?
arm and 3rd digit
what is the area of sensory for C8?
4-5th digits
what is the area of sensory for T1?
medial elbow crease
which C-spine special test assesses for nerve root compression by seeing if there is radiating pain?
spurling
which C-spine special test:
relief of symptoms from an upward distracting force indicates foraminal compression of nerve root
distraction
which C-spine special test:
flexing hip/knee then extending knee that results in pain in or radiating to legs indicates meningeal irritation/infection
Kernig
which C-spine special test:
flexing the neck and hip that results in pain reduction indicates meningeal irritation
Brudzinski
which C-spine special test:
hyper flexion of the C-spine that results in a shocking sensation down the spinal cord indicates myelopathy or multiple sclerosis
Lhermitte's
which C-spine special test:
flicking the fingernail that results in index finger and thumb flexion indicates a long-tract spinal cord involvement in the neck
Hofffman
AABCDS mnemonic for reading C-spine radiology
Adequacy
Alignment
Bone
Cartilage
Disc
Soft tissue
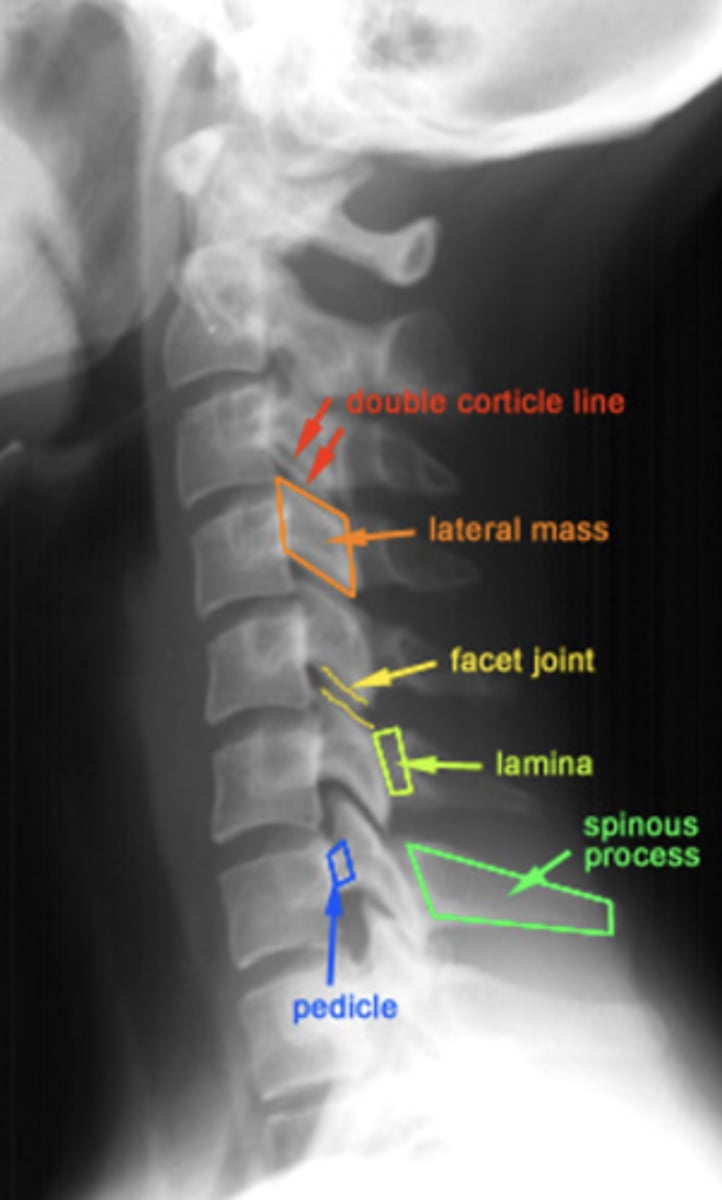
what are the C-spine radiographic landmarks?
double cortical line
lateral mass
facet joint
lamina
pedicle
spinous process
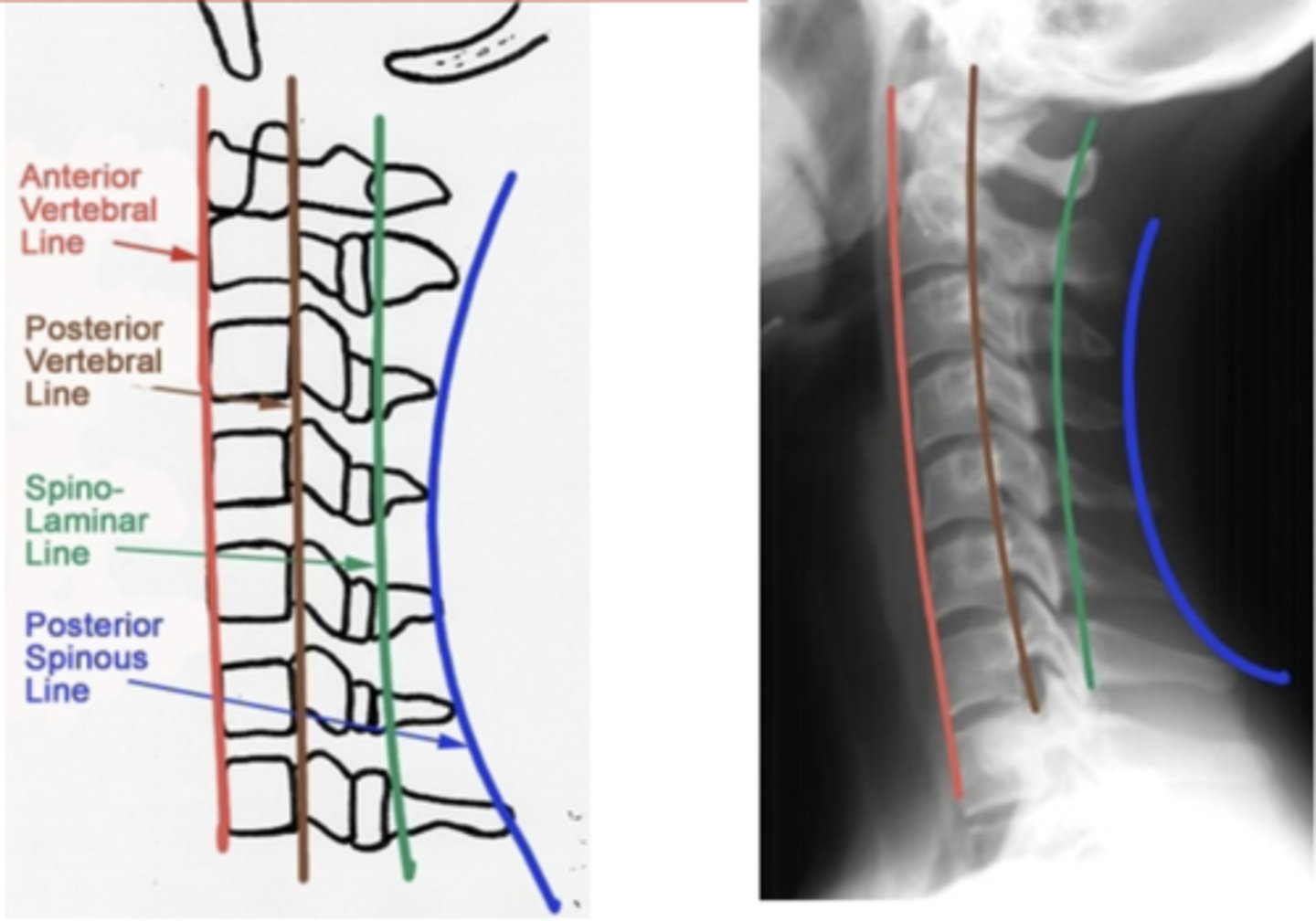
C-spine lateral x-ray landmark lines
if one of the spinous processes is displaced to one side on an AP c-spine view, a ______ should be suspected
facet dislocation
What is a Fuch's view?
modified Water's view to demonstrate the odontoid tip
what is Swimmer's view?
lateral view of the c-spine that allows for assessment of vertebral alignment and apophyseal joints (cervicothoracic junction)
dull aching uni/bilateral neck pain (suboccipital) that is referred to the head that appears upon awakening and symptoms of dizziness, weakness, N/V, blurred vision and photophobia increase throughout the day
cervical headache (cephalgia)
what is seen on physical exam of a cervical headache?
↓ ROM and tenderness in suboccipital region
poor posture
weakness of scapulothoracic muscles and deep neck flexors
what is the treatment for cervical headaches?
- posture re-education training
- exercise (stretching suboccipitals) → McKenzie exercises > chin tucks
- analgesics
- behavioral changes → regular sleep/meals, stress reduction
neurogenic pain associated with a cervical nerve root or roots +/- associated numbness, weakness or loss of reflexes
cervical radiculopathy herniated cervical disk
what is the cause of cervical radiculopathy in young pts?
herniation of a cervical disk that entraps the root as it enters the foramen
what is the cause of cervical radiculopathy in older pts?
combo of foraminal narrowing d/t vertical settling of the disk space and arthritic involvement of the uncovertebral (facet) joint
what are risk factors for cervical radiculopathy from a herniated cervical disk?
cigarette smoking
frequent heavy lifting
diving
what are symptoms associated with a herniated cervical disk?
- neck pain w/ radicular pain, numbness and paresthesia in UE distribution
- HA
- muscle spasms
- weakness, lack of coordination, changes in handwriting & grip strength
- trunk/leg dysfunction, bowel/bladder changes
what is seen on physical exam of a herniated cervical disk?
reduced cervical lordosis
↓ AROM
pain in the shoulder/arm with extension/rotation
+ Spurling's test
possible + Babinski's reflex
what are diagnostic tests for herniated cervical disks?
radiographs → areas of spondylosis/degenerative involvement of disk or facet joint
MRI/CT w/ contrast → confirms dx
EMG/NCV → differentiates radiculopathy from peripheral neuropathy
what is the treatment for a herniated cervical disk?
spontaneous resolution in 2-8 wks
anti-inflammatory meds
PT
muscle relaxants
cervical ESI
what should be avoided with a herniated cervical disk?
narcotics and cervical manipulation
degenerative disk disease in the cervical spine produced by bony spur growth, buckling or protrusion of the ligamentum flavum causing narrowing of the neural foramen and stenosis of the spinal canal
cervical spondylosis (cervical stenosis)
which condition has symptoms of chronic pain that worsen w/ upright activity, ↓ AROM of the cervical spine, HA that originate in the neck, irritability, fatigue, sleep problems and radicular pain in the UEs?
cervical spondylosis (stenosis)
what is seen on physical exam of cervical spondylosis?
tenderness along lateral neck or spinous processes
limited/painful ROM
myelopathy → flexion produces shock that travels down spine
Hoffman & Babinski reflex
clonus
hyperrflexia
what is seen on a lateral x-ray of cervical spondylosis?
bony reactive changes w/ osteophytes anteriorly, posteriorly or at facet joints
what is seen on AP view of cervical spondylosis?
anterior subluxation of one vertebra onto the vertebra below
where are degenerative findings of cervical spondylosis most common?
C5-6 and C6-7 disk spaces
what is the treatment for cervical spondylosis?
NSAIDs
doxepin/amitryptiline → for sleep
rehab
steroid injection
surgery → decompression, laminectomy, discectomy
AVOID narcotics
narrowing of the spinal canal due to wear and tear (disc degeneration/inflammation) that leads to spinal cord compression causing sympotms of limited ROM of spine, morning stiffness of neck, neck pain/tenderness, tingling/numbness, difficulty walking, wide-based gait and coordination problems
cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM)
what are physical exam findings of cervical spondylotic myelopathy?
tenderness along lateral neck/spinous processes
↓ ROM w/ shock-like symptoms
ataxia
hyperrflexia
+ Hoffman & Babinski
+ Lhermitte's sign
what is the treatment for cervical spondylotic myelopathy?
electrotherapeutic modality → control pain
immobilization
ROM exercises
isometric & cervical stabilization exercises
surgical decompression/fusion → intractable pain + neuro findings
cervical sprain (ligamentous injury) from hyperextension of the neck then flexion (commonly MVA rear-end collision)
whiplash
muscle strain of the neck that is caused by > pillows and working at computers
cervical strain
what are the symptoms associated with cervical sprain/strain?
most common → nonradicular, nonsocial neck pain anywhere on the base of the skull
SCM/trap pain that is worse w motion
occipital HA
irritability, fatigue, sleep disturbances, diff concentrating
what is seen on physical exam of a cervical sprain/strain?
paraspinal tenderness
limited AROM
pain at extremes of motion
normal neuro exam
what is the treatment for cervical sprain/strain?
soft collar immobilization
NSAIDs
muscle relaxants → Robin, Flexeril, Skelaxin
PT
ice & heat
what should you suspect for ALL patients who complain of neck pain?
cervical fx
when do cervical fxs occur?
high-energy trauma (MVA, falling, diving)
when are cervical fxs missed?
pts who have closed head injury (CHI), unconscious or intoxicated
- most commonly upper & lower c-spine areas
what condition has symptoms of severe neck pain, paraspinous muscle spasms, point manual tenderness, pain w/ radiculopathy and global sensory/motor deficits?
cervical fracture
what is the most important x-ray view for a multiply injured patient?
cross-table lateral view of the c-spine (include C1-T1)
what is the treatment for cervical fractures?
immobilize!
immediate IV steroids → methylprednisone
fracture of C1 from axial compression w hyperextension, hyperflexion or forced lateral flexion commonly seen in football players/contact sports and divers
Jefferson/atlas burst fracture
what x-ray views should you get to evaluate a Jefferson fx?
AP
lateral → eval for atlantal ligament disruption & occipitoatlantal dislocation
open-mouth
what is the treatment for a Jefferson fx?
stable → hard collar immobilization
unstable → rigid halo immobilization & C1-2 arthrodesis
what does an odontoid (C2) fracture result from?
forceful flexion, extension and/or rotational injury
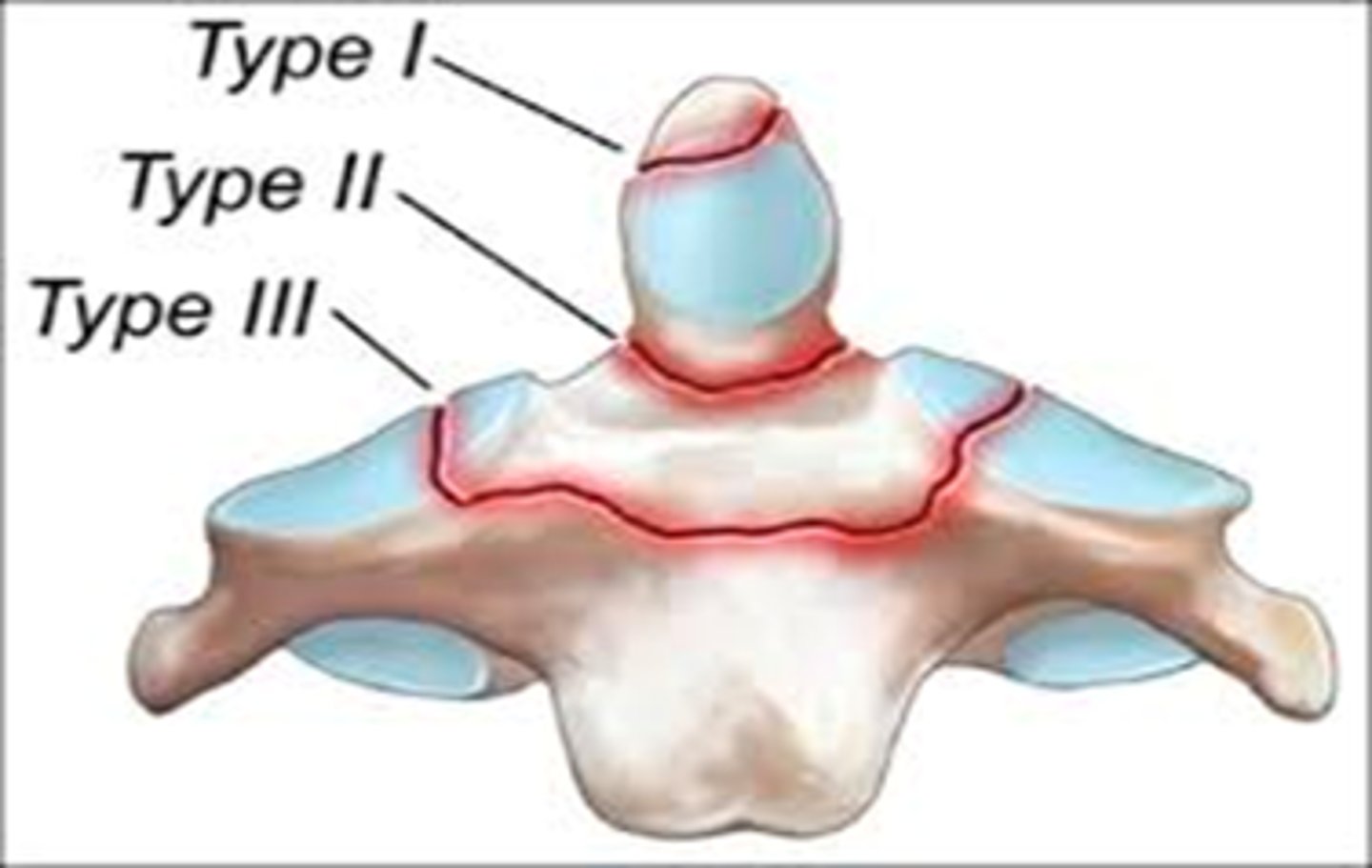
what are the 3 types of an odontoid fracture?
type 1 = rare, avulsion injury of alar ligament w oblique fx at tip of dens
type 2 = MC, base of dens
type 3 = fx of dens to body of C2
the distance from the dens to the C1 body
predental space
what is the normal predental space in adults and children?
adults = < 3 mm
children = < 5 mm
what is indicated if the predental space is increased?
fx of odontoid process or disruption of transverse ligament
what is the treatment for an odontoid fx?
type 1 = externally immobilized
type 2 = reduction using traction & halo immobilization
type 3 = traction reduction & halo immobilization
what fracture results from forceful flexion?
flexion teardrop fx
what are the radiographic findings of a flexion teardrop fracture?
large wedge oof the anterior aspect of affected vertebra
fracture of C7 caused by flexion
Clay-Shoveler's fx
what are the radiographic findings of a Clay-Shoveler's fx?
avulsion of posterior aspect of spinous process
- usually incidental finding
what are traumatic causes of cervical spine dislocation?
MVA
diving
blunt trauma
what are atraumatic causes of cervical spine dislocation?
RA
down's syndrome
what are symptoms associated with cervical spine dislocation?
neck pain after trauma
muscle weakness or paresthesia
what is seen on physical exam of cervical spine dislocation?
spinous process "step off"
check C4-T1 motor
check reflexes & sensory
what are the best radiographic views for eval of cervical spine dislocation?
AP & lateral
what is the treatment for cervical spine dislocation?
cervical HALO
emergent ortho/neurosurgeon consult
< 50% anterior subluxation of one vertebra on another
unilateral facet dislocation
> 50% anterior subluxation of one vertebra on another accompanied by widening of the interspinous & interlaminar spaces
bilateral facet dislocation
what does an atlanto-occipital dislocation result from?
hyperextension, distraction &/or rotational injury w excessive force on the ligaments most commonly from a MVA
what are consequences of an atlanto-occipital dislocation?
brainstem dysfunction
cranial nerve deficits
death
the distance for the occiput to the atlas should not exceed ___
5 mm
what are the 3 types of atlanto-occipital dislocation?
type 1 = anterior dislocation (MC)
type 2 = pure longitudinal dislocation
type 3 = posterior dislocation
what is the treatment for atlanto-occipital dislocation?
tx of choice = halo immobilization w posterior occipital-cervical fusion
type 2&3 = gentle reduction w/ 2-5 lbs weights
traction is CI in type 1
what is the cause for a Hangman's fx (C2)?
spondylolisthesis of the axis d/t bilateral fx of pars interarticularis C2
what fx results from hyperextension with secondary flexion (tears PLL & disc) most commonly from a MVA
Hangman's fx (C2)
what is seen on radiographs of a Hangman's fx?
subluxation
what is the study of choice for a Hangman's fx?
CT → delineates fx pattern
what is the treatment for a Hangman's fx?
C2-3 fusion w open reduction of facet dislocation
- anterior C2-3 interbody fusion
- posterior C1-3 fusion
what are causes for atlanto-axial subluxation?
RA
Down's syndrome
what are x-ray findings of atlanto-axial subluxation?
asymmetric lateral aspects on odontoid view
↑ predental space
cervical spine trauma may be cleared clinically if which preconditions are met?
- fully alert & oriented
- no drugs or alcohol
- no neck pain
- no abnormal neurology
- no significant other distracting injury
can the cereal spine be cleared if there is no bruising or deformity, no tenderness and a pain free range of active movements?
yes
which condition has symptoms of neck discomfort w motion, stiffness, loss of function, ↓ ROM, joint effusion & deformity?
cervical osteoarthritis
what is the treatment for cervical osteoarthritis?
NSAIDs
ROM exercises
ortho/neurosurgeon consult
a condition where the neck muscle contract involuntarily, causing the head to twist/turn to one side?
torticollis (aka skeletal wry neck or "cock robin")