Chapter 22: Monetary Policy and the Federal Reserve
Barter trading is the trading of goods and services directly for other goods or services, without using money.
One downside of barter is that it tends to be ^^time consuming.^^
One alternative to barter is to use a medium of exchange to facilitate trade. ^^A medium of exchange is an item that is widely accepted as payment for goods and services.^^
Throughout history, metals like silver and gold have been used as a medium of exchange. Metals are durable, can be divided into parts, are in relatively limited supply, and have value in their own right for making jewellery, tools, or other items.
There are three primary functions of money.
- <<First, as mentioned earlier, money serves as a medium of exchange.<<
- <<Second, money serves to establish a common unit of account or measure of how much goods and services cost.<<
- <<The third function of money is as a store of value. A store of value is something that can be saved and used at a later time.<<
The M1 money supply includes money in circulation: cash, demand deposits, travellers checks, and other checkable deposits.
Banks issue checking or savings accounts and use the funds to make consumer, business, and mortgage loans. ^^In this way, banks act as financial intermediaries or brokers between savers and borrowers.^^
A bank's balance sheet is a statement of its assets and liabilities, where assets are the things you own and liabilities are the things you owe.
A bank's total reserves are deposits that it has received but not lent out.
The required reserve ratio (rrr) is the percentage of deposits that a bank must hold as reserves by law.
- The required reserve ratio formula can be expressed as a ratio of the cash that a bank holds in the Federal Reserve to its total deposits.
- For example, if a bank has $100,000 in deposits and is required to hold $5,000 in the Federal Reserve, the bank's reserve ratio would be 1/20 or 5%.
The dollar amount that a bank is required to hold as reserves is called its required reserves.
^^Under a fractional reserve banking system, banks are required to hold only a fraction of their deposits as reserves.^^
Excess reserves are the difference between a bank’s total reserves and its required reserves.
The supply of loans comes primarily from savings accounts. As the interest rate increases, the amount of money people decide to save rises.
- As savings deposits increase, the quantity of money available to lend rises.
- The positive relationship between the interest rate and the quantity of loans supplied reflects the law of supply.
- ^^As the interest rate increases, there is an increase in savings deposits which in turn generates an increase in the quantity of loans supplied to the market.^^
The demand for loans comes from individuals and businesses who want to borrow money.
- When the interest rate that borrowers must pay on loans falls, the total cost of taking out a loan falls.
- Because loans are cheaper when the interest rate is lower, the quantity of loans demanded is negatively related to the interest rate.
- ^^The negative relationship between the interest rate and the quantity of loans demanded reflects the law of demand.^^
The intersection of the supply and demand for loans determines the equilibrium interest rate and quantity of loans made in the market.
- If the interest rate is below equilibrium, the quantity of loans demanded will be higher than the quantity of loans supplied, and there will be a shortage of loans available.
- As interest rates rise, some potential borrowers will decide not to take out loans because they have become more expensive. At the same time, rising interest rates will give people an incentive to increase their savings, so the quantity of loans supplied will rise.
- The shortage will be eliminated as the interest rate rises to its equilibrium level.
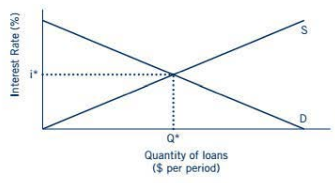
Here the S represents the Supply of loans and the D represents the Demand of loans.
The intersection of the supply and demand for loans determines the equilibrium interest rate (i*) and quantity of loans made in the market (Q*)
At the equilibrium interest rate, all of the borrowers who are willing and able to take out loans at that interest rate are able to obtain loans, and all of the lenders who are willing and able to make loans at that interest rate are able to do so.
The money multiplier tells the maximum amount that the money supply can increase for a given amount of excess reserves loaned out. It is equal to the reciprocal of the required reserve ratio(1/rrr).
- Taking the example of Econobank, the initial increase in deposits was $10 million.
- This means that up to ^^$10 million * (1/.10) = $100 million^^ in new money could be created through the rounds of loans and deposits that started from the initial deposit of $10 million.
- For a $10 million increase in deposits, the money supply can increase by up to $100 million.
- ^^The money multiplier tells us the maximum amount by which the money supply can increase as a result of an increase in deposits.^^
- If people hold some of their money as cash rather than depositing it in their checking accounts or if banks do not lend out all of their excess reserves, the actual increase in the money supply will be less than that predicted by MM.
^^A bank run occurs when a large number of customers withdraw their deposits from the bank because they worry that their bank might fail.^^
Federal Reserve banks hold reserves on deposit and make loans to commercial banks in their district, move cash in and out of circulation, and collect and process checks. The Fed Banks also provide checking accounts for the U.S. Treasury, buy and sell government securities, and supervise commercial banks to make sure they are operating safely and within regulations.
Monetary policy is the use of regulations or actions by the central bank to influence the money supply.
Open market operations are the purchases and sales of federal government securities by the Fed.
The discount rate is the interest rate that the Federal Reserve charges banks for loans.
The federal funds rate is the interest rate that banks charge one another for loans to cover required reserve shortfalls.
When the Fed needs to encourage spending to stimulate employment, the Fed undertakes expansionary monetary policy. Expansionary monetary policy involves actions to increase the money supply, including lowering the discount rate, buying securities, or reducing the required reserve ratio.
The figure below shows the impacts of Expansionary monetary policy:

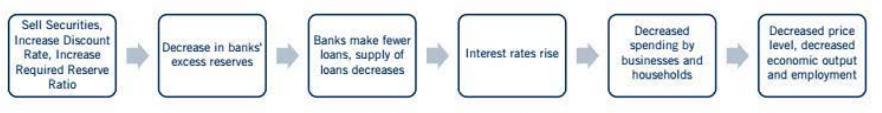
When the Fed needs to encourage price stability in the face of rising prices, it undertakes contractionary monetary policy. Contractionary monetary policy includes actions designed to reduce the money supply, including selling securities, raising the discount rate, and raising the required reserve ratio.
The figure below shows the impacts of Contractionary monetary policy:
^^The primary two missions of the Fed, promoting employment and promoting price stability, are often at odds with one another.^^
- If the Fed uses its monetary policy tools to promote employment and economic growth, it will seek to increase the money supply.
- Increases in the money supply cause reductions in interest rates.
- Falling interest rates spur increased spending as consumers take advantage of lower interest rates by increasing borrowing for new homes, for cars, or for other items.
- Businesses take advantage of lower interest rates by increasing borrowing for investment in new equipment or new buildings.
- These changes will increase demand for goods and services, and may result in increases in the prices of goods and services, which is at odds with the Fed's mission of promoting price stability.
- Alternatively, when the Fed reduces the money supply to combat inflation, it generates increases in interest rates and reductions in borrowing and spending.
- The reductions in spending cause businesses to reduce their levels of employment.