AP Micro Unit 6 - Market Failure and the Role of the Government
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
1
New cards
Socially Efficient Market Outcomes
* The optimal distribution of all resources in society while taking into account all internal and external benefits
* Occurs where Marginal Social Benefit (MSB) = Marginal Social Cost (MSC)
* Occurs where Marginal Social Benefit (MSB) = Marginal Social Cost (MSC)
2
New cards
Marginal Social Benefit (MSB)
* The additional benefit received by all members of society due to the consumption of an additional unit of a good or service
* Slopes downwards because of diminishing marginal utility
* Slopes downwards because of diminishing marginal utility
3
New cards
Marginal Social Cost (MSC)
* The additional cost incurred by all members of society due to the consumption of an additional unit of a good or service
* Slopes upwards because of opportunity cost
* Slopes upwards because of opportunity cost
4
New cards
Socially Optimal Quantity
* MSB = MSC
5
New cards
Market Failure
* When there is a quantity above or below the market equilibrium of the socially optimal quantity and we are either overproducing or underproducing
* We will either have excess benefit or excess costs
* We will either have excess benefit or excess costs
6
New cards
Externality
* A third-person side effect of an economic decision that impacts someone other than the original decision-maker
7
New cards
Negative Externality
* A situation that results in the external costs to others, causing the marginal social costs (MSC) to be higher than the marginal private costs (MPC)
* Government can solve this issue with a per-unit tax to mitigate external costs and force the firm to produce the socially optimal quantity
* Examples: smoking, factory that produces pollution
* Government can solve this issue with a per-unit tax to mitigate external costs and force the firm to produce the socially optimal quantity
* Examples: smoking, factory that produces pollution
8
New cards
Negative Externality (graph)
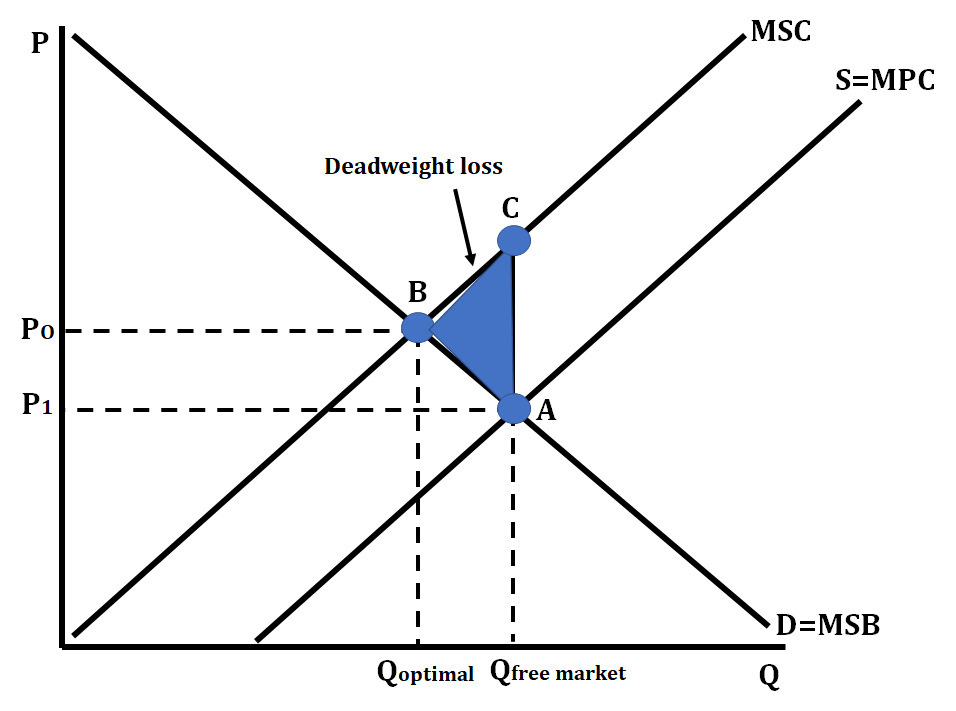
9
New cards
Positive Externality
* A situation that results in external benefits for others, causing the marginal social benefit (MSB) to be higher than the marginal private benefit (MPB)
* Government can solve this with a per-unit subsidy to force the firm to produce at the socially optimal quantity
* Examples: vaccines, education
* Government can solve this with a per-unit subsidy to force the firm to produce at the socially optimal quantity
* Examples: vaccines, education
10
New cards
Positive Externality (graph)
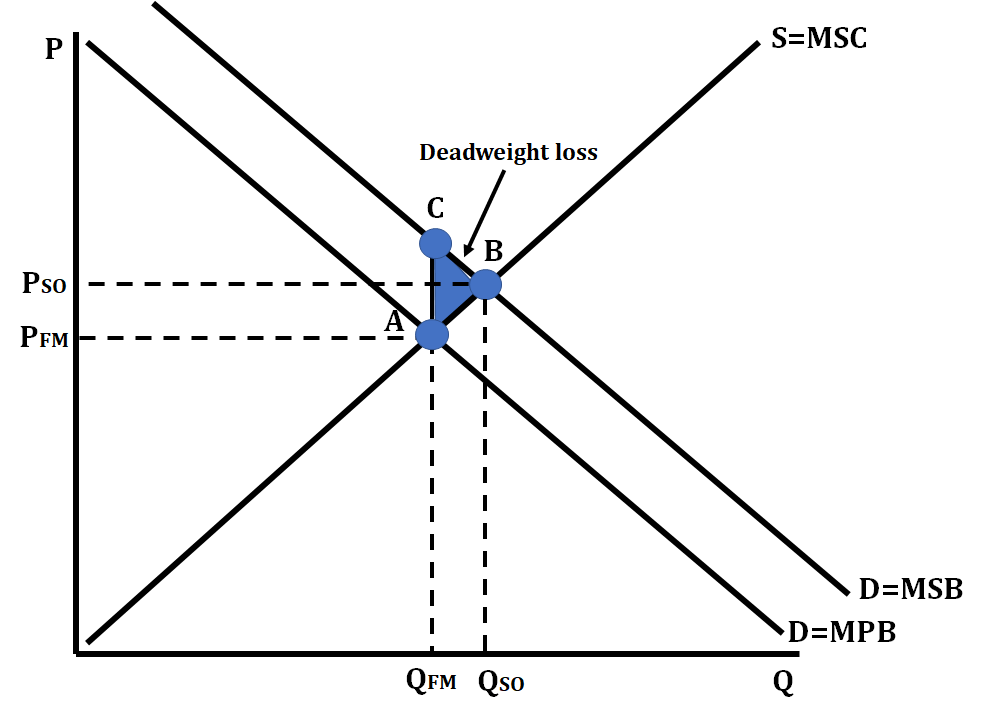
11
New cards
Marginal Private Cost (MPC)
* The additional cost to the firm for producing one more unit
12
New cards
Marginal Private Benefit (MPB)
* The additional benefit obtained by producing one more unit
13
New cards
Public Good
* Non-excludable and non-rivalrous
* An economic good that is provided by the government in the public sector because the free market has failed to produce them
* A kind of market failure because the free market fails to produce essential goods/services that society needs and wants
* There is little, if any, profit made by supplying these goods, so the government must
* An economic good that is provided by the government in the public sector because the free market has failed to produce them
* A kind of market failure because the free market fails to produce essential goods/services that society needs and wants
* There is little, if any, profit made by supplying these goods, so the government must
14
New cards
Free-Rider Problem
* An individual who benefits from using a public good without paying for it
* Problem because many will consume more than their fair share of the costs
* Public goods are non-excludable, so no one can be barred from the benefits of the public goods
* Solutions: Find ways to punish free-riders or tax all citizens that are eligible to use the public good and use tax revenue to fund the public goods (but that can lead to exclusion, and it no longer becomes a public good)
* Problem because many will consume more than their fair share of the costs
* Public goods are non-excludable, so no one can be barred from the benefits of the public goods
* Solutions: Find ways to punish free-riders or tax all citizens that are eligible to use the public good and use tax revenue to fund the public goods (but that can lead to exclusion, and it no longer becomes a public good)
15
New cards
Non-Exclusion
* Everyone can use the good and those who do not pay cannot be excluded from enjoying the benefits
16
New cards
Non-Rivalry (Shared Consumption)
* One person’s consumption of the good does not reduce the usefulness of the good to others
17
New cards
Common Goods
* Non-excludable but rivalrous
* Common resources with limited amounts available
* Can become victim of the Tragedy of the Commons
* Common resources with limited amounts available
* Can become victim of the Tragedy of the Commons
18
New cards
Tragedy of the Commons
* Consumers act in their own self interest and over-consume
19
New cards
Low-Congestion Goods
* Excludable but non-rivalrous
* AKA club goods
* You can be excluded from using the good, but it doesn’t impact the usefulness for others
* AKA club goods
* You can be excluded from using the good, but it doesn’t impact the usefulness for others
20
New cards
Private Goods
* Excludable and rivalrous
21
New cards
How many public goods should the government fund?
* When MSB = MSC
22
New cards
Government’s Role in the Market
* Tax firms to give money to the government
* Subsidize firms and give them money
* Subsidize firms and give them money
23
New cards
Per-Unit Tax
* A smaller tax on every unit produced
* Essentially a variable cost, so it affects marginal cost and average total cost
* Essentially a variable cost, so it affects marginal cost and average total cost
24
New cards
Lump-Sum Tax
* One time fixed tax
* Essentially a fixed cost, so it only affects average total cost
* Essentially a fixed cost, so it only affects average total cost
25
New cards
Regulating a Monopoly
* The government can set a price ceiling (but if the price ceiling causes the monopoly to make a loss, the monopoly may need a subsidy to continue)
* In this case, the government can compromise and let the monopoly produce where it breaks even, setting a price ceiling there - no need for a subsidy
* In this case, the government can compromise and let the monopoly produce where it breaks even, setting a price ceiling there - no need for a subsidy
26
New cards
Types of Inequality
* Income Inequality
* Looks at how annual earnings are distributed
* Wealth Inequality
* Looks at how assets are distribute
* Looks at how annual earnings are distributed
* Wealth Inequality
* Looks at how assets are distribute
27
New cards
Lorenz Curve
* Graphically represents inequality
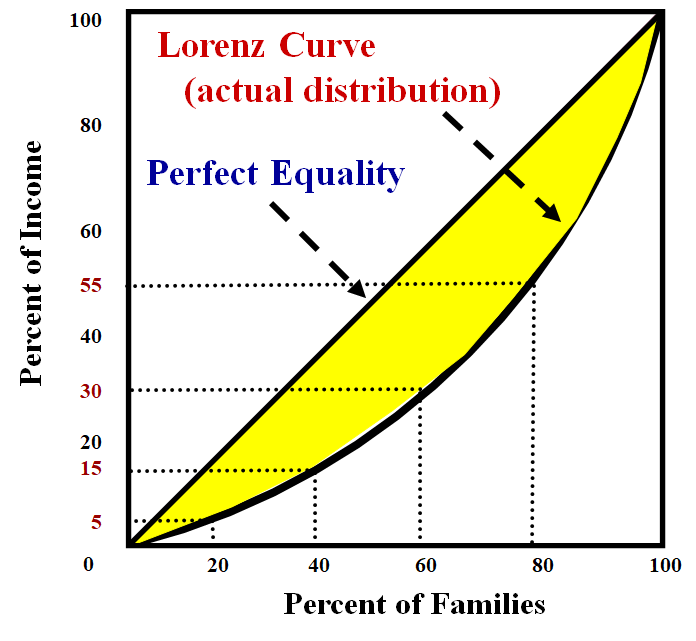
28
New cards
Gini Coefficient
* A numerical measurement of income inequality
* Perfect equality = 0
* Perfect inequality = 1
* A/(A+B)
* Perfect equality = 0
* Perfect inequality = 1
* A/(A+B)
29
New cards
Government solutions to solve income inequality
* Increase amount it taxes wealthier citizens
* Increase transfer payments to the poor
* Government payments to individuals or businesses designed to meet a specific objective rather than pay for goods/resources (welfare)
* Increase transfer payments to the poor
* Government payments to individuals or businesses designed to meet a specific objective rather than pay for goods/resources (welfare)
30
New cards
Types of Taxes
* Progressive taxes
* Take a larger percentage of income from high-income groups than from low-income groups - everyone pays a different % of their income
* A variable tax based on %%
* (ex. Federal Income Tax System in the US based on tax brackets)
* Regressive taxes
* Take a larger percentage of income from low-income groups than from high-income groups - everyone pays the same amount for the tax
* A fixed tax based on $$
* (ex. sales tax)
* Proportional taxes
* Takes the same percentage of income from all income groups - everyone pays a certain % of their income
* A fixed tax based on %%
* Take a larger percentage of income from high-income groups than from low-income groups - everyone pays a different % of their income
* A variable tax based on %%
* (ex. Federal Income Tax System in the US based on tax brackets)
* Regressive taxes
* Take a larger percentage of income from low-income groups than from high-income groups - everyone pays the same amount for the tax
* A fixed tax based on $$
* (ex. sales tax)
* Proportional taxes
* Takes the same percentage of income from all income groups - everyone pays a certain % of their income
* A fixed tax based on %%