Chapter 5 - Perception, individual decision making & creativity
What is perception?
@@Perception@@: process by which individuals organize and interpret their sensory impressions in order to give meaning to their environment.
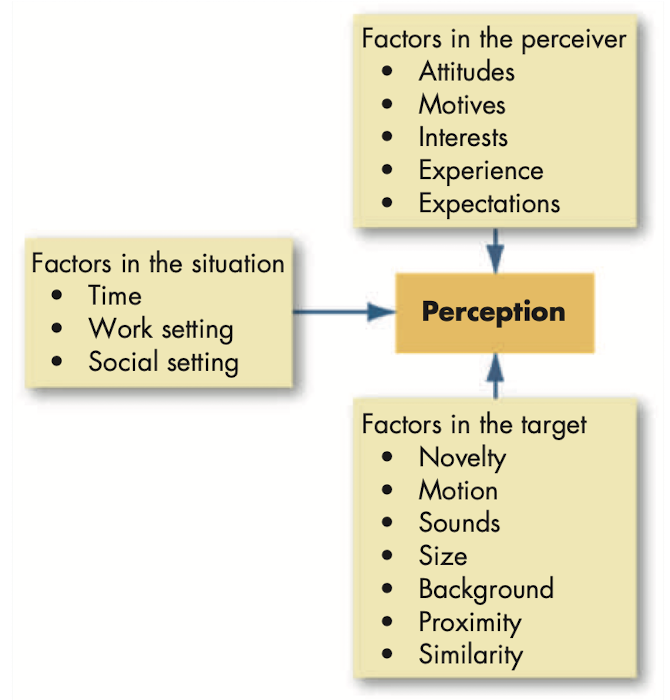
Person perception: making judgements about others
@@Attribution theory@@: attempt to determine whether an individual’s behavior is internally or externally caused.
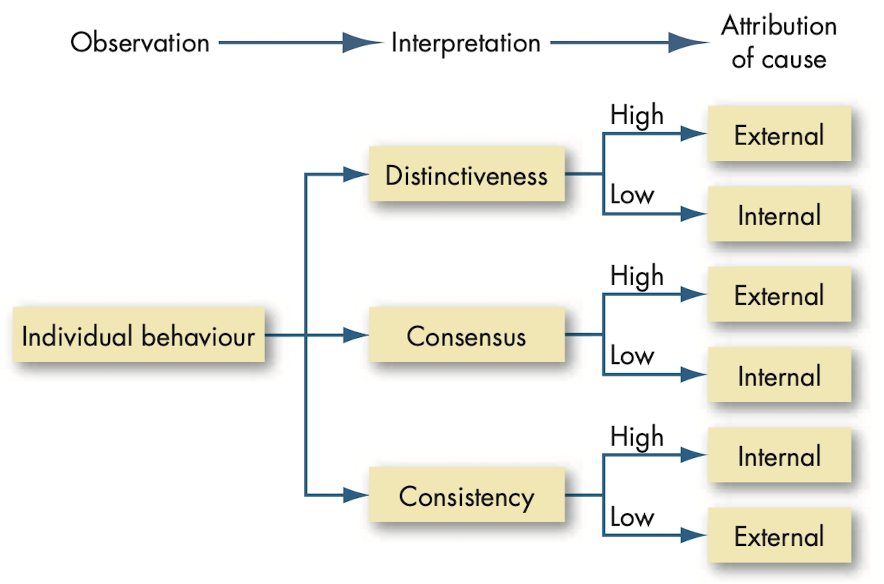
@@Fundamental attribution theory@@: tendency to underestimate the influence of external factors and overestimate the influence of internal factors when making judgements about the behavior of others.
@@Self-serving bias@@: tendency for individuals to attribute their own success to internal factors and put the blame for failures on external factors.
Frequently used shortcuts in judging others
- @@Selective perception@@: tendency to selectively interpret what one sees on the basis of one's interests, background, experience and attitudes.
- @@Halo effect@@: tendency to draw a general impression about an individual on the basis of a single characteristic.
- @@Contrast effects@@: evaluation of a person’s characteristics that is affected by comparisons with other people recently encountered who rank higher or lower on the same characteristics.
- @@Stereotyping@@: judging someone on the basis of one’s perception of the group to which that person belongs.
Specific applications of shortcuts in organizations
- Employment interview → perceptual judgements are made that are often inaccurate.
- Performance expectations → if a manager expects great things from her workers, they are likely to meet their expectations.
- @@Self-fulfilling prophecy@@: situation in which a person inaccurately perceives a second person and the resulting expectations cause the second person to behave in ways consistent with the original perception.
- Performance evaluation can be problematic because many shortcuts and subjectiveness is used.
The link between perception and individual decision-making
- @@Decisions@@: choices from among to or more alternatives.
- @@Problem@@: discrepancy between the current state of affairs and some desired state.
Decision making in organizations
- @@Rational decision making@@
- Rational: characterized by making consistent, value maximizing choices within specified constraints.
- Rational decision making model: decision making model that describes how individuals should behave in order to maximize some outcome.
- Define the problem
- Identify the decision criteria
- Allocate weights to the criteria
- Develop the alternatives
- Evaluate the alternatives
- Select the best alternative
- @@Bounded rationality@@: process of making decisions by constructing simplified models that extract the essential features from problems without capturing all their complexity.
- @@Intuitive decision making:@@ unconscious process created out of distilled experience.
- Common biases and errors in decision making
- @@Overconfidence bias@@: overconfident about our abilities and the abilities of others, usually unaware of it.
- @@Anchoring bias@@: tendency to fixate on initial information, from which one then fails to adequately adjust for subsequent information.
- @@Confirmation bias@@: tendency to seek out information that reaffirms past choices and to discount information that contradicts past judgements.
- @@Availability bias@@: tendency for people to base their judgements on information that is readily available to them.
- @@Escalation of commitment@@: increased commitment to a previous decision in spite of negative information.
- @@Randomness error@@: tendency of individuals to believe that they can predict the outcome of random events.
- @@Risk aversion@@: tendency to prefer a sure gain of a moderate amount over a riskier outcome might have a higher expected payoff.
- @@Hindsight bias@@: tendency to believe falsely, after an outcome of an event is actually known, that one would have accurately predicted the outcome.
Influences on decision making: individual differences and organizational constraints
- Individual differences
- Personality → personality influences our decisions.
- Gender → women tend to spend more time than men analyzing decisions.
- Mental ability → people with higher levels of mental ability are able to process information more quickly and solve problems more accurately.
- Cultural differences → cultural background can definitely influence the way a decision is being made like in the selection of problems, depth of the analysis, etc.
- Organization constraints
- Performance evaluation → managers are strongly influenced in their decision making by the criteria on which they are evaluated.
- Reward systems influences decision makers by suggesting to them what choices are preferable in terms of personal payoff.
- Formal regulations → rules that are set and need to be followed are definitely a constraint in the decisions that can or can not be taken.
- System-imposed time constraints → decisions are often imposed with deadlines, they need to be made before a certain date.
- Historical precedents → choices made today are therefore a result of choices made over the years.
What about ethics in decision making?
- 3 ethical decision criteria
- @@Utilitarian criterion@@: system in which decisions are made to provide the greatest good for the greatest number.
- @@Rights criterion@@: individuals to make decisions consistent with fundamental liberties and privileges, respecting and protecting basic rights of every individual.
- Whistle-blowers: individuals who report unethical practices by their employer to outsiders.
- @@Justice criterion@@: impose and enforce rules fairly and impartially so that there is an equitable distribution of benefits and costs.
- Behavioral ethics: analyzing how people actually behave when confronted with ethical dilemmas.
Creativity, decision making and innovation in organizations
@@Creativity@@: ability to produce novel and useful ideas.
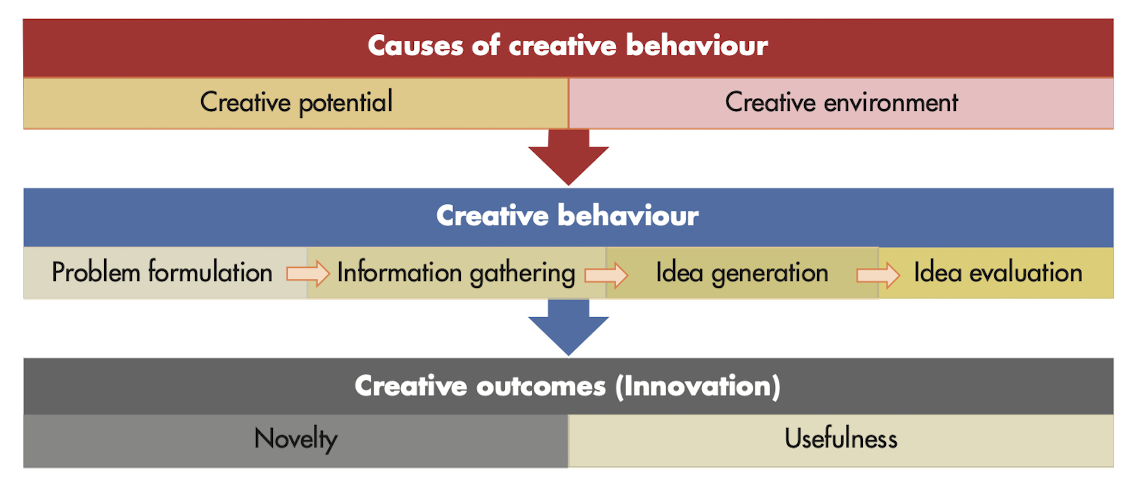
@@Three-stage model of creativity@@: proposition that involves three stages: causes (creative potential and creative environment), creative behavior and creative outcomes (innovation).
- Creative behavior
- Problem formulation: state of creative behavior which involved identifying problem or opportunity that requires a solution that is as yet unknown.
- Information gathering: state when possible solutions to a problem incubate in individuals mind.
- Idea generation: process of creative behavior that involves developing possible solutions to a problem from relevant information and knowledge.
- Idea evaluation: process of creative behavior involving the evaluation of potential solutions to problems to identify the best one.
- Causes of creative behavior
- Creative potential: intelligence is related to creative behavior, expertise is the foundation of all creative work.
- Creative environment: potential is not enough, you need to be in an environment where creative potential can be realized.
- Creative outcomes (innovation): ideas or solutions judged to be novel and useful by relevant stakeholders.