PAD- Carlson
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Make sure to memorize the dosing!!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)?
a condition where narrowed arteries cause reduced blood flow to the outer parts of your body (peripherals)
What causes narrow arteries in PAD?
plaque build up
What part of the body is most commonly effected by PAD?
a. legs
b. heart
c. brain
d. arms
a. legs
What are the risk factors for PAD?
HISTORY OF SMOKING
age
black ethnicity
HTN
Diabetes
Hyperlipidemia/ Artherosclerosis
In the early stages of PAD, what are the symptoms, if any?
asymptomatic in the early disease
What is the MAIN symptom of PAD? Describe this symptom.
Intermittent claudication
discomfort, pain, or numbness in affected lower extremities during physical activity
resolves w/in 10 min of rest
What is the name of the test used to diagnose PAD?
Ankle-brachial index (ABI)
What is the nonpharm treatment for PAD?
smoking cessation
exercise
30-45 min, 3x a week
What are some ways to quit smoking?
non-pharm: counseling, programs
pharm: nicotine replacement therapy, bupropion, varenicline
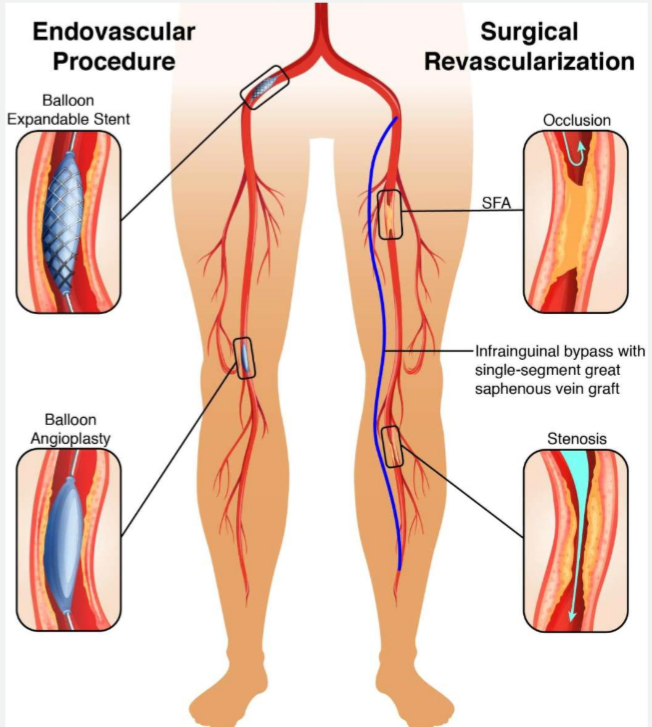
If nonpharm tx doesn’t work, what can we do for PAD?
revascularization
basically we physically open up that narrow artery
PAD is a form of ASCVD. What pharm tx is recommended for management of hyperlipidemia?
high intensity statin
What are the 2 high intensity statins and their dosing?
Atorvastatin 40, 80 mg
Rosuvastatin 20, 40 mg
For HTN management, what is the recommended 1st line therapy and bp goal?
1st line therapy- ACEIs/ARBs, thiazides, CCBs
bp goal- <130/80 mmHg
What is the target HbA1c for diabetes management?
a. <4%
b. <5%
c. <6%
d. <7%
d. <7%
For Asymptomatic and Symptomatic PAD which of the following is recommended/reasonable?
a. thrombolytics
b. antiplatelet therapy
c. anticoagulant therapy
d. ACEIs/ARBs
b. antiplatelet therapy
What are the 2 options for antiplatelet therapy for PAD?
Aspirin
Clopidogrel (if can’t take aspirin)
What is the dosing for Aspirin for PAD?
KNOW
75-325 mg PO daily
What is the dosing for Clopidogrel (Plavix) for PAD?
KNOW
75 mg PO daily
MOA, Contraindications, and ADRs of Aspirin:
not that important
MOA: bind COX enzymes, prevent formation of TxA2
Contraindications: hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, active bleeding
ADRs: GI bleeding/ulcer/upset, and dyspepsnia
MOA, Contraindications, and ADRs of Clopidogrel:
not that important
MOA: blocks P2Y12 component on ADP receptors= reduce platelet aggregation
Contraindications: active bleeding
ADRs: GI bleed, angioedema, TTP (rare)
Should anticoagulants be used to reduce the risk of CV event in PAD? What is the one exception to this?
NOOOOOOO
one exception: rivaroxaban—-special conditions
When is rivaroxaban indicated in PAD?
FOLLOWING REVASCULARIZATION
Rivaroxaban MUST be combined with what in PAD?
Aspirin!!!
Rivaroxaban CANNOT BE GIVEN ALONE!!!
What is the dosing for Rivaroxaban+ Aspirin?
Rivaroxaban 2.5 mg PO BID in combo w/ Aspirin 75-100 mg PO daily
In PAD, Rivaroxaban can only be taken if you have a low or high bleeding risk?
low
What is recommended in addition to antiplatelet therapy in patients with PAD for INTERMITTENT CLAUDICATION?
Cilostazol
Cilostazol is stopped at ____ weeks if NO SYMPTOMATIC IMPROVEMENT is seen.
12 weeks!
Is Pentoxifylline recommended for Intermittent claudication treatment?
no