Chapter 4: Enzymes
Enzymes
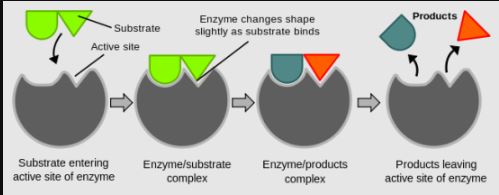
Are ^^biological catalysts^^ made of ^^proteins^^. They ^^alter the rate of chemical reactions^^ without being chemically changed at the end of reaction and are specific nature.
Enzyme-Catalysed Reaction:
- %%Amylase%% digests starch.
- %%Cellulase%% digests cellulose (only in plants not in humans).
- %%Protease%% digests proteins.
- %%Lipase%% digests fats.
Characteristics of Enzymes:
- Speed up chemical reactions.
- Required in minute amounts.
- Are specific.
Factors affecting Enzyme Activity:
- %%pH%%: they work ^^best at optimum pH^^. As pH ^^moves away from the pH scale the rate of reaction decreases^^. A ^^change in pH causes the shape of active site to change.^^
- %%Temperature%%: works ^^best at optimum temperature^^. At a temperature ^^above optimum temperature the enzyme denatures.^^
- %%Enzyme and Substrate concentration%%: as the ^^substrate concentration increases the rate of reaction increases to an initial point to make reaction constant^^ + Increase in enzyme concentration increases rate of enzyme reaction.
Lock and Key hypothesis: