bio final
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:40 PM on 5/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
1
New cards
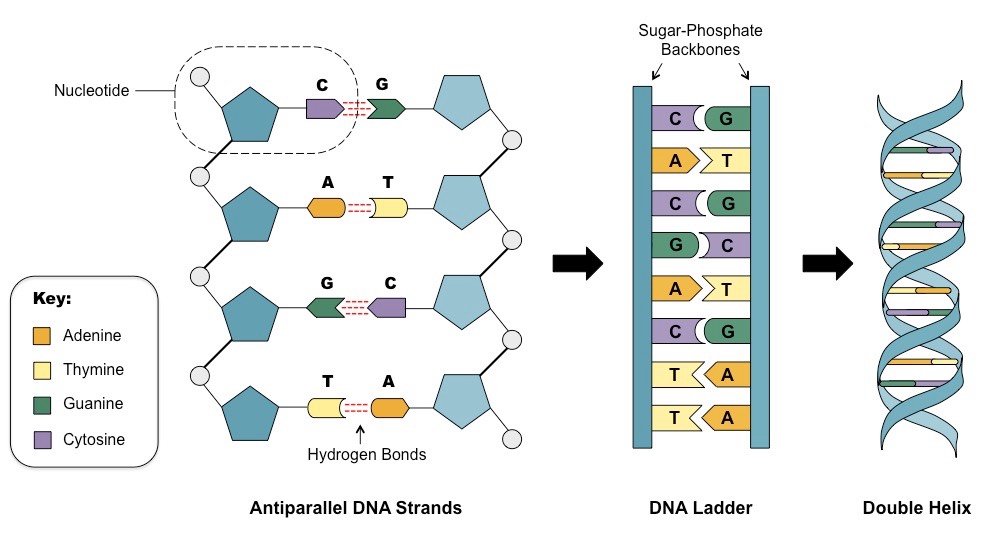
What is DNA, what does it stand for, and what is the structure of DNA? Label the diagram.
genetic material. stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. structure is a double helix
2
New cards
Draw and label the parts of a nucleotide.
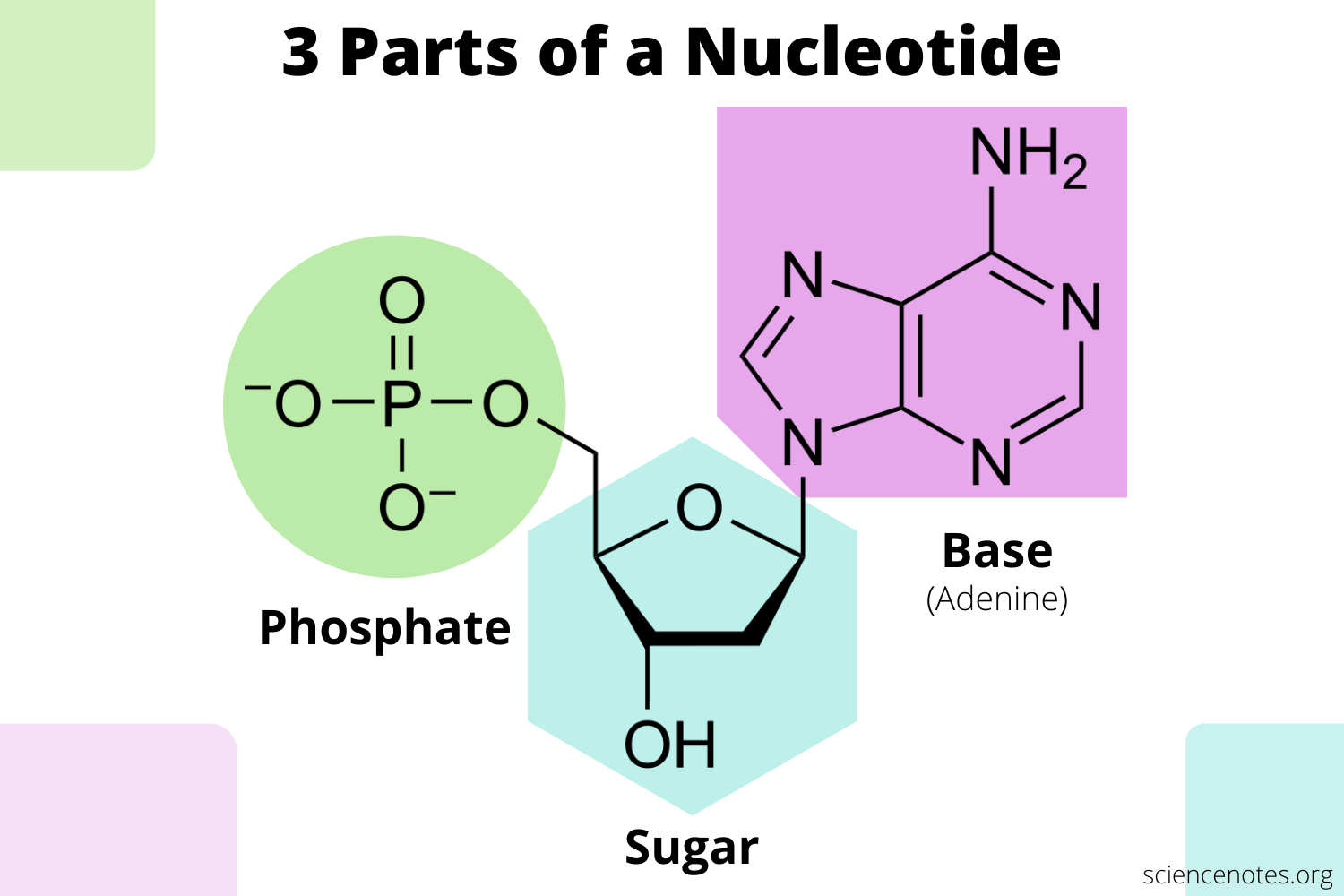
3
New cards
What are the base pairings for DNA? For RNA?
* dna → adenine with thymine; guanine with cytosine
* rna → adenine with uracil; guanine with cytosine
* rna → adenine with uracil; guanine with cytosine
4
New cards
Describe the following types of gene mutations: substitution, deletion, and inversion.
* substitution: substitutes a base for another
* deletion: deletes a base
* inversion: base segment breaks off and reattaches within the same chromosome, but in reverse orientation
* deletion: deletes a base
* inversion: base segment breaks off and reattaches within the same chromosome, but in reverse orientation
5
New cards
What is replication?
in nucleus. uses dna.
1) the opening of the double helix and separation of the dna strands
2) the priming of the template strand
3) and the assembly of the new dna segment
results in two identical strands of dna
1) the opening of the double helix and separation of the dna strands
2) the priming of the template strand
3) and the assembly of the new dna segment
results in two identical strands of dna
6
New cards
What is transcription?
nucleus. uses dna.
1) initiation: helps eukaryotic rna polymerase recognize promoter sequences
2) elongation: rna polymerase unwinds dna and adds nucleotides to the 3’ end of the rna chain
3) termination: when the rna polymerase encounters the termination signal, the rna transcript is released
results in mrna
1) initiation: helps eukaryotic rna polymerase recognize promoter sequences
2) elongation: rna polymerase unwinds dna and adds nucleotides to the 3’ end of the rna chain
3) termination: when the rna polymerase encounters the termination signal, the rna transcript is released
results in mrna
7
New cards
What is mrna processing?
in nucleus. uses mrna.
1) 5’ end gets a modified nucleotide cap. 3’ end gets a poly-a tail (protection as it goes through the cell)
2) introns (toss) are removed to produce mrna (keep exons)
3) to make a functional molecule that performs & looks correct for its job
results in rna
1) 5’ end gets a modified nucleotide cap. 3’ end gets a poly-a tail (protection as it goes through the cell)
2) introns (toss) are removed to produce mrna (keep exons)
3) to make a functional molecule that performs & looks correct for its job
results in rna
8
New cards
What is translation?
in ribosomes. uses rna.
1) initiation: brings together mrna, trna bearing the first amino acids of the polypeptide and two subunits of a ribosome
2) elongation: amino acids are added one by one to the preceding amino acids
3) termination: when the ribosome reaches a stop codon in mrna, ribosomes binds with a release factor (protein), everything starts disassembling
results in polypeptide/ protein
1) initiation: brings together mrna, trna bearing the first amino acids of the polypeptide and two subunits of a ribosome
2) elongation: amino acids are added one by one to the preceding amino acids
3) termination: when the ribosome reaches a stop codon in mrna, ribosomes binds with a release factor (protein), everything starts disassembling
results in polypeptide/ protein
9
New cards
Name and explain the 3 steps of PCR. What is PCR used for?
* used to replicate copies of a specific dna sequence in a few hours
1. denaturation of the template into single strands
2. annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis
3. extension of the new DNA strands from the primers
1. denaturation of the template into single strands
2. annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis
3. extension of the new DNA strands from the primers
10
New cards
What is gel electrophoresis? What is it used for?
* a laboratory method used to separate mixtures of DNA, RNA, or proteins according to molecular size
* used to determine genetic disorders, identity or individuals
* used to determine genetic disorders, identity or individuals
11
New cards
What is a GMO? Name and explain 2 benefits and 2 disadvantages to their use and propagation.
* genetically modified organisms
* benefits: 1) development of disease-resistant plants 2) can degrade environmental pollutants
* disadvantages: 1) immuno-suppression 2) antibiotic resistance
* benefits: 1) development of disease-resistant plants 2) can degrade environmental pollutants
* disadvantages: 1) immuno-suppression 2) antibiotic resistance
12
New cards
What is a clone? How are clones produced?
* genetically identical copies of genes or entire organisms
* an unfertilized egg is taken from an animal and the nucleus is removed. the nucleus from a cell of an egg to be cloned is inserted and stimulated to divide
* an unfertilized egg is taken from an animal and the nucleus is removed. the nucleus from a cell of an egg to be cloned is inserted and stimulated to divide
13
New cards
What is the outcome of meiosis?
division of a diploid parent cell into haploid progeny
14
New cards
What happens during each of the phases of Meiosis?
* Prophase I → homologs pair up. crossing over
* Metaphase I → independent assortment
* Anaphase I → homologs separate & chromosome # is halved (diploid → haploid)
* Telophase I → chromosomes have finished moving to opposite ends of the cell
* Prophase II → the phase that follows after meiosis I, or after interkinesis if present
* Metaphase II → the centromeres of the paired chromatids align along the equatorial plate in both cells
* Anaphase II → sister chromatids separate. separation doesn’t affect ploidy
* Telophase II → final outcome is four cells, each with half of the genetic material found in the original
* Metaphase I → independent assortment
* Anaphase I → homologs separate & chromosome # is halved (diploid → haploid)
* Telophase I → chromosomes have finished moving to opposite ends of the cell
* Prophase II → the phase that follows after meiosis I, or after interkinesis if present
* Metaphase II → the centromeres of the paired chromatids align along the equatorial plate in both cells
* Anaphase II → sister chromatids separate. separation doesn’t affect ploidy
* Telophase II → final outcome is four cells, each with half of the genetic material found in the original
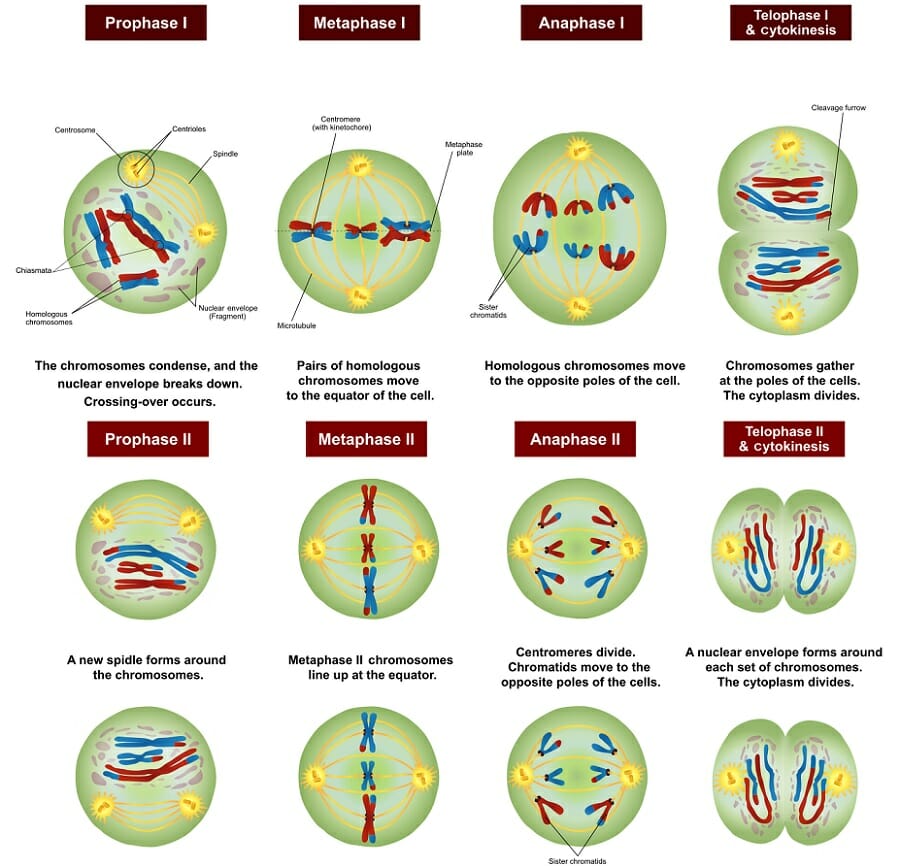
15
New cards
Define the following and include chromosome number for each in humans:
* haploid (n): half of diploid. only gametes
* dipoid (2n): full set of chromosomes. humans → 46. only somatic cells
* dipoid (2n): full set of chromosomes. humans → 46. only somatic cells
16
New cards
Explain how gametogenesis differs in males and females.
males do it their entire lives, while females are already made when they are born (finite)
17
New cards
Who is the Father of Genetics?
Gregor Mendel, an australian monk
18
New cards
Define and give an example of the following terms: gene, allele, and trait.
* gene: a charitable factor that has a specific characteristic
* allele: alternate forms of a gene, use letters to represent
* trait: phenotypic characteristic of an organism
* allele: alternate forms of a gene, use letters to represent
* trait: phenotypic characteristic of an organism
19
New cards
What does it mean if a trait is considered dominant? What does it mean if a trait is considered recessive?
if dominant, a trait that covers over, or dominates, another form of that trait. if recessive, the trait of an organism can be masked by the dominant form of a trait
20
New cards
Explain the difference between homozygous and heterozygous
* homozygous → same allele (DD or dd)
* heterozygous → different allele (Dd)
* heterozygous → different allele (Dd)
21
New cards
How are alleles represented for a homozygous dominant trait? Homozygous recessive trait? Heterozygous trait?
DD; dd; Dd
22
New cards
Explain the difference between codominance and incomplete dominance. Give an example of each.
* codominance: alleles are equally dominant. stripes or polka dots
* incomplete dominance: one allele isn’t completely dominant. blending of alleles
* incomplete dominance: one allele isn’t completely dominant. blending of alleles
23
New cards
Define polygenic traits and provide an example.
one trait is characterized by the interaction of several genes. ex: human skin color (6 genes), human eye color (3 genes)
24
New cards
What are karyotypes used for? In other words, what type of information can they give you?
chromosome mapping. can show chromosomal abnormalities, sex, and # of chromosomes
25
New cards
What genetic disorder is Trisomy 21 commonly known as? How does this disorder occur?
down syndrome. occurs when a person has an extra copy of chromosome 21
26
New cards
What is a pedigree, and what do the symbols represent? What does a shaded symbol represent?
a chart that can help trace a trait or disease in a family. box: males; circle: female. shaded means it carries the trait
27
New cards
Explain the Oxygen Revolution and why it was important to the evolution of complex life on Earth.
cyanobacteria produced O2 via photosynthesis about 200 bya; algae and plants followed. aerobic respiration could now take place → more atp is made. different types of organisms could now evolve
28
New cards
What were the first organisms on Earth like?
performed anaerobic respiration (no O2) and heterotrophs
29
New cards
What evidence did Darwin use to support his theory of evolution by natural selection?
fossil evidence, biogeographical evidence, and anatomical evidence
30
New cards
What is an adaptation? Give an example.
any trait that aids the chances of survival and reproduction of organisms. ex: fur, feathers, fat, long legs, camouflage
31
New cards
Explain speciation. What factors lead to speciation?
the forming of a new and distinct species due to evolution. factors are geographical barrier, natural selection, and genetic drift
32
New cards
Compare and contrast analogous, homologous, and vestigial structures. Which ones can be used to support evolution and which ones cannot?
* analogous: have a similar structure but no ancestry involved; due to convergent evolution (same function, different structure). provides evidence for evolution
* homologous: body parts arising from the same embryonic tissues; due to divergent evolution (same structure, different function). provides evidence for evolution
* vestigial: structures that have no function in the living organism. provides evidence for evolution
* homologous: body parts arising from the same embryonic tissues; due to divergent evolution (same structure, different function). provides evidence for evolution
* vestigial: structures that have no function in the living organism. provides evidence for evolution
33
New cards
Explain why mules and ligers are not considered to be distinct species.
they are infertile and can’t breed together
34
New cards
What is artificial selection? Give an example.
humans choosing the traits they determine to be advantageous or preferable
35
New cards
Explain Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium. MAKE SURE YOU CAN SOLVE HWE PROBLEMS USING THE EQUATION!
a population’s genetic variation will remain constant with no disturbances in population. (make sure to solve for homozygous recessive first!)
36
New cards
What do the variables p and q refer to in the Hardy-Weinberg Equation?
p → frequency of dominant allele
q → frequency of recessive allele
q → frequency of recessive allele
37
New cards
What do the variables p2, 2pq, and q2 refer to in the Hardy-Weinberg Equation?
p2 →homozygous dominant
2pq → heterozygous
q2 →homozygous recessive
2pq → heterozygous
q2 →homozygous recessive
38
New cards
Define all the parts of a cladogram – sister taxa, clade, and derived character.
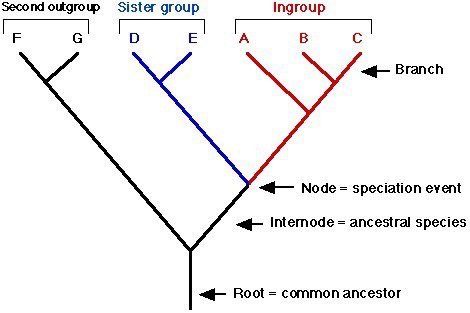
39
New cards
What is a dichotomous key and how is it used to classify organisms?
an important scientific tool, used to identify different organisms, based on the organism's observable traits. consists of a series of statements with two choices in each step that will lead users to the correct identification
40
New cards
Is a virus considered to be a living organism? Why or why not?
no. aren’t made of cells, they can't keep themselves in a stable state, they don't grow, and they can't make their own energy
41
New cards
What is binomial nomenclature? Who developed this method of naming organisms?
two word naming system made by Carolus Linnaeus
42
New cards
What are the levels of classification from broadest (most inclusive) to most specific (least inclusive)?
domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
43
New cards
Complete the chart to explain the following plant adaptations.
* phototropism: growth of an organism in response to a light stimulus. will grow towards the light. ex: plant bending towards window
* gravitropism: the growth response of a cell or an organism to gravity. roots will grow towards gravity and the stem will grow away from gravity
* thigmotropism: the directional growth of a plant, in response to the stimulus of direct contact. ex: venus fly traps and vines growing on buildings
* gravitropism: the growth response of a cell or an organism to gravity. roots will grow towards gravity and the stem will grow away from gravity
* thigmotropism: the directional growth of a plant, in response to the stimulus of direct contact. ex: venus fly traps and vines growing on buildings
44
New cards
Complete the chart about the 6 kingdoms of life.
* archaebacteria: unicellular, prokaryotic, autotrophic and/or heterotrophic, no peptidoglycan in the cell wall. unusual group of lipids make up the cell membrane
* eubacteria: multicellular, prokaryotic, autotrophic and/or heterotrophic, “true bacteria”
* protista: most are unicellular, some are multicellular or colonial cellular, eukaryotic, autotrophic and/or heterotrophic, some cell walls contain cellulose. some have chloroplasts.
* fungi: multicellular except yeast, eukaryotic, heterotrophic, cell walls have chitin. many are decomposers.
* plantae: multicellular, eukaryotic, autotrophic, cell walls have cellulose.
* animalia: multicellular, eukaryotic, heterotrophic, no cell walls or chloroplasts
* eubacteria: multicellular, prokaryotic, autotrophic and/or heterotrophic, “true bacteria”
* protista: most are unicellular, some are multicellular or colonial cellular, eukaryotic, autotrophic and/or heterotrophic, some cell walls contain cellulose. some have chloroplasts.
* fungi: multicellular except yeast, eukaryotic, heterotrophic, cell walls have chitin. many are decomposers.
* plantae: multicellular, eukaryotic, autotrophic, cell walls have cellulose.
* animalia: multicellular, eukaryotic, heterotrophic, no cell walls or chloroplasts
45
New cards
Give an example of a biotic factor and give an example of an abiotic factor.
* biotic factor: soil & animal dung
* abiotic factor: water temperature
* abiotic factor: water temperature
46
New cards
What are three types of symbiotic relationships? Give an example of each.
* mutualism: +/+. ants, acacia trees, and butterfly caterpillars
* commensalism +/0. phoretic mites on damselflies
* parasitism: +/-. heartworms and humans
* commensalism +/0. phoretic mites on damselflies
* parasitism: +/-. heartworms and humans
47
New cards
What are keystone species? Provide an example.
species that keep an ecosystem together. ex: beavers and prairie dogs
48
New cards
Explain the four trophic levels in an ecosystem. Explain how each level obtains energy. Explain what type of consumers (herbivore, carnivore, omnivore, and detritivores) would be at each level.
* producers: obtain energy from the sun
* primary consumers: obtain energy from producers. usually herbivores
* secondary consumers: carnivores or omnivores that obtain energy from primary consumers
* tertiary consumers: carnivores or omnivores that obtain energy from secondary consumers
* apex/quaternary consumers: carnivores that obtain energy from tertiary consumers
* decomposers: detritivores and decomposers that obtain energy from decomposing organisms
* primary consumers: obtain energy from producers. usually herbivores
* secondary consumers: carnivores or omnivores that obtain energy from primary consumers
* tertiary consumers: carnivores or omnivores that obtain energy from secondary consumers
* apex/quaternary consumers: carnivores that obtain energy from tertiary consumers
* decomposers: detritivores and decomposers that obtain energy from decomposing organisms
49
New cards
What is the average ecological efficiency of most ecosystems? In other words, how much energy gets passed from one trophic level to the next? Why is the number so low?
10%. 90% is lost to the environment
50
New cards
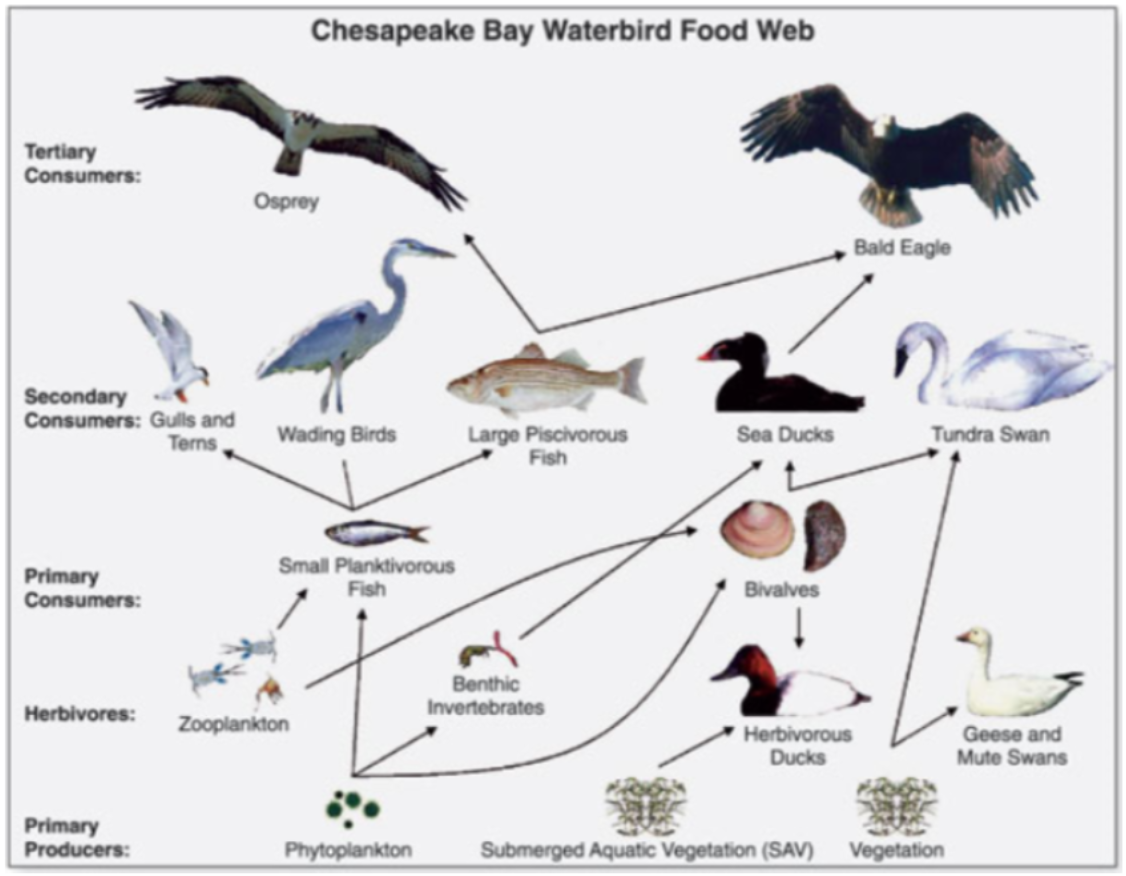
How would this food web be impacted if the small planktivorous fish were removed?
zooplankton would increase. large piscrivorus fish, wading birds, gulls and tems populations would decrease due to lack of small planktivorous fish. osprey populations would decrease since they only eat large piscivorous fish.
51
New cards
Explain the process of succession and distinguish between primary and secondary succession.
primary succession: takes the longest. starts with rocks turning to soil. starting from scratch. starts with lichen or mosses. secondary succession: damaged ecosystem but the soil is left intact. less time needed.
52
New cards
Explain the difference between logistic and exponential growth. Draw a graph depicting each.
* logistic growth: occurs with limited resources and population has a slow growth rate until carrying capacity is reached
* exponential growth: occurs when resources are abundant and a population size increase very rapidly
* exponential growth: occurs when resources are abundant and a population size increase very rapidly
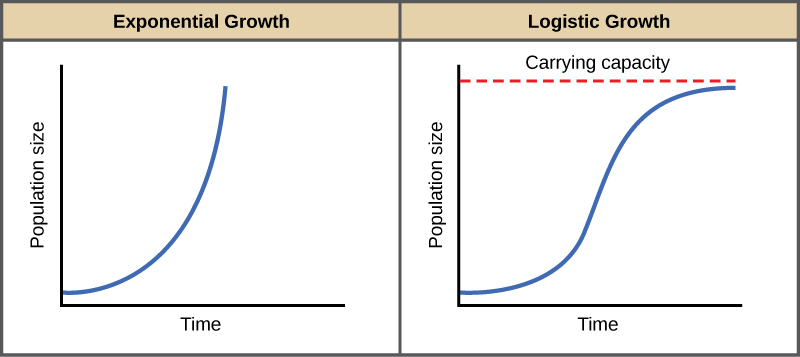
53
New cards
What is the difference between a renewable and non-renewable resource? Give an example of each.
* renewable resources are regenerated as soon or quickly after they are used. ex: coal and oil
* non-renewable resources are regenerated long after they are used. ex: water and solar
* non-renewable resources are regenerated long after they are used. ex: water and solar
54
New cards
Explain the reproductive strategies of organisms with a Type I, Type II, or Type III survivorship.
* type i: late loss, high survivorship throughout life. few amount of offspring
* type ii: constant loss, independent of age. medium amount of offspring
* type iii: early loss, low mortality after maturity. lots of offspring
* type ii: constant loss, independent of age. medium amount of offspring
* type iii: early loss, low mortality after maturity. lots of offspring
55
New cards
Differentiate between density-dependent limiting factors and density-independent limiting factors.
* density-dependent limiting factor: are affected by the number of individuals in a given area (competition, predation, parasitism, disease)
* density-independent limiting factor: are aspects of the environment that can affect a population regardless of its size (unusual weather, natural disasters, human activities)
* density-independent limiting factor: are aspects of the environment that can affect a population regardless of its size (unusual weather, natural disasters, human activities)
56
New cards
Explain the Nitrogen Cycle.
the nitrogen cycle is the process by which nitrogen is converted into different forms that can be used by living organisms. nitrogen fixation is the process by which nitrogen gas is converted into ammonia by bacteria. ammonia is then converted into nitrate by bacteria in a process called nitrification. plants can then assimilate the nitrate and use it to build proteins. when organisms die, decomposers break down the proteins and release ammonia back into the soil. denitrification is the process by which bacteria convert nitrate back into nitrogen gas, which is released into the atmosphere.
57
New cards
In what way are humans most impacting the Carbon Cycle?
breathing, burning fossil fuels, changing land use, and using limestone to make concrete
58
New cards
Explain biomagnification.
occurs when a pollutant moves up a food chain and accumulates in higher concentrations in the bodies of predators.
59
New cards
Explain some ways that humans can help the environment.
sustainable development, protecting umbrella species, and creating conservation acts