bio 2 test 1 ch1-8
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
186 Terms
element
substance that cannot be broken down to other ssubstances by chem rxn
when elements form chem bonds, they create
molecules n compounds
molecules
group of elements bonded tg
ex) o2
compounds
2 or more diff types of elements bonded tg
how many of 92 elements are essential to life
20-25%
trace elements (less than 0.01% mass)
required in minute quantities
STRONG IMPACT
ex) B, Cr, Cu (protein), Fe (blood)
4 elements essential to life (96% of body)
drives neurons/mucles
oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen
toxic elements
too much of certain element=toxic
ex) Ar inc= cancer
atom
smallest unit of matter that retains properties of element
subatomic particles
neutrons, protons, electrons
atomic nucleus
neutrons+protons
neutron mass = proton mass measurements
identical, measured in daltons or amu
mass #
protons + neutrons
Li- atomic #=3, mass= 6.94, what is neutron#
4
energy
capacity to cause change
potential energy
energy that matter has due to location
electron’s potential energy
farthest from nucleus (ELECTRON SHELL) = most PE
high PE, low KE
at the top
low PE, high KE
close to ground
what determines the chemical behavior of an atom?
the distribution of electron chells
valence electrons
in outermost shell= valence shell
chemically inert
full valence shell
no sharing/giving electrons
ex) noble gases
atoms w incomplete valence shells form what
share/give electrons= IONIC/COVALENT bonds
covalent bonds
share electrons
electrons count for both valence shells
single, double, triple bonds
electronegativity
ex) h2
electronegativity
atom’s attraction for electrons
stronger electroneg=greedy= pulls atoms to itself
IN COVALENT BONDS
UP & RIGHT
nonpolar covalent bonds
share electrons equally
STROGNEST= need lotta energy to break
polar covalent bonds
1 atom more electroneg= electrons not shared equally
ionic bonds
strip electrons from bonding partner
attraction of cation and anion
TRANSFER elections (IONS)
EASY TO BREAK
weak chemical bonds
NEED in life
reversible= advantage
weak chemical bonds includes
H+ bonds
Van der Waals interations
bonds btwn ionic compunds dissolved in water
H+ bonds
H atom attracted to electroneg atom
POLAR COVALENT BONDS
Van der Waals Interactions
not constantly sharing election
attracted to those closest
occur by chance if E are asymm
LEAST ENERGY to break= TEMP BONDS
gecko using ___ to stick their feet to tree
van der waals interactions
what determines how molecule interact
molecular shape and charge
ex) receptor shapes
molecular shape/function
small diff= diff cell activity
ex) T n estrogen exact same except extra H+ in estrogen
what gives water its emergent properties
H+ bonds (particial - and + charge)
water’s 4 emergent properties for life*
cohesion/adhesion
moderate temp
expand when freezing
versatile solvent
polarity of water
allow to interact w other h2o or diff substances
cohesion= high surface tension
h+ bond of water to water= hard to break surface of liquid
water moderating temp
water absorbs heat from warm air
release stored heat to cooler air
heat
thermal energy TRANSFERRED from 1 matter to another
WARM to COOL
heat transfer
measured by CALORIES
calories
amount of heat required to raise temp of 1g of ater by 1 degree C
why does water resists changes in temp
high specific heat (1 cal/g/degree C)
ex) metal pan heats faster than h2o in pot
why does water have high specific heat
H+ bonds
water’s high specific heat
heat absorbed=h+ bonds break
heat released=h+ form
less temp change near oceans
heat of vaporization
heat a liquid must absorb for 1g to convert to gas
evaporative cooling
liquid evaporates, surface cools
ex) sweat= heat transfers to h2o from skin, h2o evaporates
water expands upon freezing
H+bonds in ice= ordered/tighter= less dense
water: solvent of life
grape solvent bc h+ bonds & partical +/-
aqueous solution
water=solvent
ionic compounds dissolved in h2o
each ion is surrounded by HYDRATION SHELL
charge of hydrophillic
charged or partically charged
charge of hydrophobic
no charge
create barriers
only want other hydrophobes
organic chem
study of compounds w carbon
ex) living organisms, macromolecules
carbon bonds
form large, complex molecules w covalent bonds
4 VALENCE ELECTRONS= variety of combos
hydrocarbons
hydrogen & carbon
in fats (adipose tissue)
isomers
compounds with same molecular formula but diff structure/properties
structural isomers
cis-trans isomers
enantiomers
structural isomers
same molecules but diff covalent arrangements of their atoms (diff branching)
cis-trans isomers
same molecules but same covalent bonds but diff spatial arrangements
cis: same side
trans: opp sides
enantiomers
same molecules but mirror images
important in pharm/toxicology
show sensitivity to subtle changes
organic molecules’ distintive properties depend on
carbon skeleton and R-group
functional groups
coponents of org molecules in chem rxn
arrangment give molecules its properties
High macromolecule makes up most/ DA WORKERS
Proteins
Where are macromolecules unique properties arise from
orderly arrangements of their atoms
who is not a macromolecule, why
Lipids
NO REPEAT MONOMERS
Who r true polymers, why
Carbs, proteins, nucleic acids
MONOMERS REPEAT
BUILT N BROKEN DA SAME
proteins that speed up chem rxns
enzymes
dehydration rxn
BOND monomers by LOSING water
hydrolysis
BREAK polymers by ADDING water
what make up lipids
hydrocarbons + alcohol
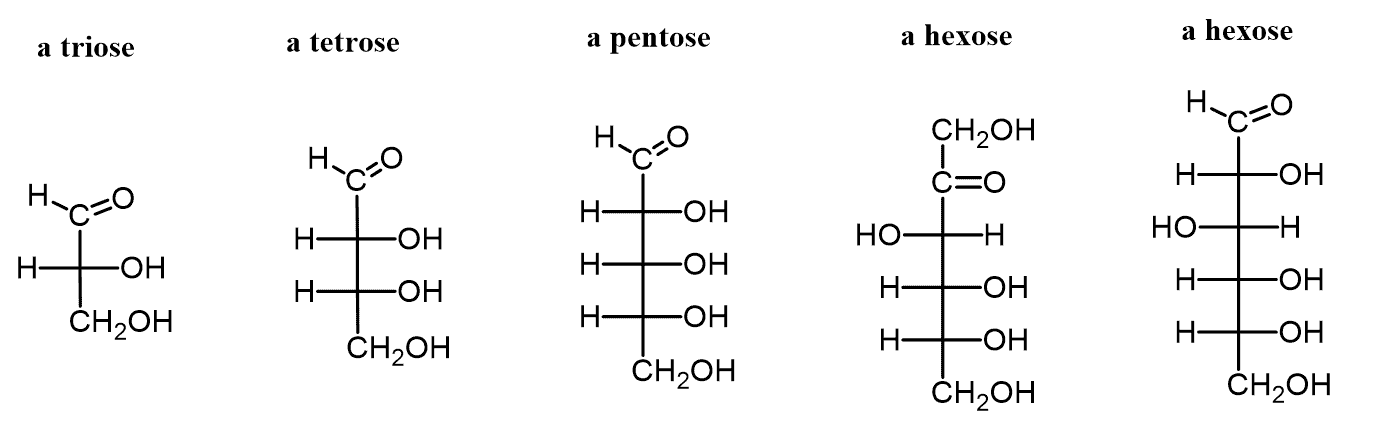
how are monosaccharides classified?
location of carbonyl group (C=O) AND # of carbons in carbon skeleton
SAME STRUCTURE, DIFF DEPEND ON CARBONYL GROUP
why do sugar have lots of energy/main source of fuel
carbon bonds
break to give energy
glycosidic linkage
covalent bond in sugars
monomer (glucose)+monomer (glucose)
determents of polysaccharides shape/function
monomers + position of glycosidic linkage
polysaccharide storage in plants
STARCH
UNBRANCHED
made of glucose monomers line, no branching
where do plants store starch
as GRANULES in CHLOROPLASTS n plastids
what is the simplest form of starch
amylose
UNBRANCHED
amylopectin
somewhat branched starch= ENZYMES attach to break= give energy
storage polysacc in animals
glycogen
BRANCHED
where is glycogen stored
liver and muscles
need energy to break toxins/move muscles
hydrolysis of glycogen releases what
glucose when sugar is needed
cellulose
polysacc of glucose
STRENGTH in CELL WALLS= hard to digest
glycosidic linkages of cellulose
beta= orientation of glucose
STR8 N UNBRANCHED= strong
easy for glucose’s hydroxyl (OH-) to H+ bond to cellulose’s hydroxyl (trans)
alt OH- crates parallel stack
glycosidic linkages of starch
alpha
HELICAL= soft/squishy
easy to access glucose
easy for glucose’s hydroxyl (OH-) to H+ bond to starch’s hydroxyl (cis)
enzymes that hydrolyze alpha bond in starch, cant hydrolyze ___?
beta linkages in cellulose
how does celluose break down if enzymes cant do it?
passes as insoluble fiber
some microbes use enzymes
chitin
provides structural support for cell walls of FUNGI n insects’ EXOSKELETON
unifying feature of lipids
mix poorly w water
3 biologically important lipids
fats, phospholipids, steroids
2 monomers of fats
GLYCEROL n FATTY ACIDS
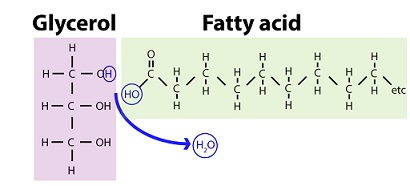
glycerol
1 of 2 lipid monomers
3 carbon alc w hydroxyl (OH) group attached to each carbon
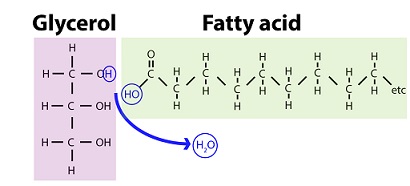
fatty acids
1 of 2 lipid monomers
carboxyl (C=O) group attached to long carbon skeleton
carbon skeleton varies in length & H+
ester linkage creating glycerol+fatty acid
triacylglycerol
How can the fatty acids in a fat be diff from each other
Did length n diff saturation of H+ n C
#H+ in saturated fatty acids
Max # of H+
Solid @ room temp
Most animal fats
Unsaturated fatty acids
Have 1 or more double bonds
Liquid @ room temp
Plant & fish fats
Hydrogenation
Converts unsaturated fats to saturated fats by adding H+
Diet rich in saturated fats contributes to
Cardiovascular disease
Hydrogenating vegetable oils creates
Unsaturated fats w TRANS double bonds