Chem. KAP - Bonding
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Force of attraction that holds atoms or ions together to form a compound
Chemical Bond
What is the attractive bond between?
Nucleus of one atom/ion and the electron cloud of another atom/ion.
What rule is chemical bonding driven by? What does that rule mean?
Chemical bonding is driven by the octet rule, which states atoms lose, gain, or share VALENCE electrons to achieve the electron configuration of the closest noble gas.
Unfilled or partially filled valence orbitals are ______
Inherently Unstable
What does it mean to be unstable?
Possess high potential energy
How is stability reached?
Reducing potential energy
Bond type is determined by
Valence electrons of participating atoms
Name the bond: transfer of electrons between a metal and nonmetal
Ionic
Name the bond: Sharing of electrons between nonmetals/metalloids
Covalent
Name the bond: electron sea between metal atoms
Metallic
An atom that loses electrons to achieve an octet will form a
Cation
An atom that gains electrons to achieve an octet will form a
Anion
Ionic compounds involve
Metal ion and nonmetal ion; may also involve polyatomic ions
Anions and cations are attracted to each other by
electrostatic forces
What are electrostatic forces
Coulombic forces
Forces of attraction between oppositely-charged ions
Ionic bonds
What are Coulombic charges
Charges between two charged forces
How do you write those equations for chemistry?
Ion formation of Element 1 + Ionic formation of Element 2 —> Combination of Elements —> Element Name
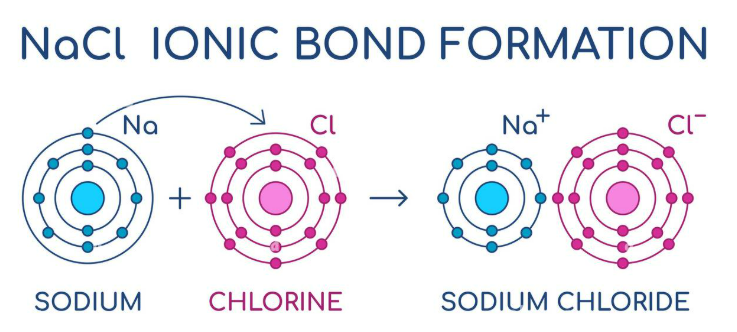
What is a lattice?
3-D system of points showing the positions of ions that make up the ionic compound.
T/F: A lattice is used for all bonds?
False—it’s only used for ionic bonds
The electrostatic (Coloumbic ions) between ions are very ____.
Strong
Because the electrostatic (Coloumbic ions) between ions are very strong, ionic compounds are found in nature as
Crystalline solids
Because the electrostatic (Coloumbic ions) between ions are very strong, ionic compounds have
High melting and boiling points
Because the electrostatic (Coloumbic ions) between ions are very strong, ionic compounds are
hard, rigid, brittle (shatters not flatten)
What does it mean if something is brittle?
Shatter not flatten
Ionic compounds will conduct ___ when ____
Ionic compounds will conduct electricity when molten or aqueous (dissolved in water)
The smallest particle of a ionic compound is a
formula unit
The formula unit is the smallest particle of which kind of compound?
Ionic
Electrolyte
substance that conducts electricity when molten or in solution
What are Coloumbic Forces saying basically?
Opposites attract/pull, likes push
Why does the ionic compound have to be either dissolved in water or molten to conduct electricity? In other words, why won’t the dry salt conduct?
Charged particles must be in motion for the substance to conduct electricity. In the solid form, the ions are held in place and cannot conduct electricity. Molten/dissolved = not held in place so they CAN conduct at that point.
Metals characteristically have few ___ in their highest energy levels
Metals characteristically have few electrons in their highest energy levels
Because metals characteristically have few electrons in their highest energy levels, metals have
vacant orbitals (typically d and/or p orbitals)
The vacant orbitals can be ____, allowing valence electrons to ____. This is known as the ____.
The vacant orbitals can be occupied, allowing valence electrons to travel freely throughout the metal. This is known as the electron sea.
The electrons in metallic bonds are ____.
Delocalized
What do we mean we say the electrons in metallic bonds are delocalized?
We are saying they do not belong to any one nucleus
This chemical bonding results from the attraction between nuclei of metal atoms and the surrounding sea of electrons
Metallic
What is the reason for the high thermal and electrical conductivity of metals?
The freedom of electrons to roam in metals
T/F: Metals are lustrous (think metalloids)
True
Why are metals lustrous/shiny? (think metalloids)
They absorb a wide range of light frequencies.
T/F: Metals are malleable (think metalloids)…and what does that term mean?
True; can be hammered into thin sheets
T/F: Metals are ductile…and what does that term mean?
True; can be pulled into a wire
in the covalent bond, electrons are shared by the bonding atoms to achieve ____ for the atoms
Octets
compounds that consist of covalently bonded atoms are
Molecular compounds
The smallest particle of a molecular compound
Molecule
The smallest particle in a covalent bond
Molecule
The chemical formula for a molecular compound is the
Molecular formula
nonmetal elements and sometimes metalloids tend to form which kind of bond
Covalent
Because molecular compounds have relatively weak intermolecular forces between molecules, molecular compounds often exist as
gases or vaporize easily at room temperature
Because molecular compounds have relatively weak intermolecular forces between molecules, molecular compounds
Have relatively low melting and boiling points
Because molecular compounds have relatively weak intermolecular forces between molecules, molecular compounds
Are relatively soft if solid
Because molecular compounds have relatively weak intermolecular forces between molecules, molecular compounds
Are usually insoluble meaning they do not dissolve in water
A single covalent bond involves one ___ of electrons and thus includes ___ electrons
A single covalent bond involves one shared pair of electrons and thus includes two electrons
Lewis structures are depictions of molecules that show electrons as
Dots
T/F: In a Lewis Structure, shared pairs of electrons (bonds) are drawn between atoms in the form of lines, unshared/lone pairs are represented by dots on o ne atom only
True
What are the three exceptions for needed # of electrons (N)?
H = 2, Be = 4, B = 6
What do you do if something has a charge?
It depends—
1) If the question asks you to find the ION, add the opposite of the charge under “S” and bracket the final structure with the charge shown in the PT.
2) If the question isn’t asking about the ion, just proceed as normal.
How do you find the number of needed electrons?
N in NASE
How do you find the available number of electrons (# fo valence electrons for each atom)?
A in NASE
How do you find the number of share electrons between atoms?
S in NASE
How do you find the number of unshared pairs needed to get an octet?
E in NASE
What are resonance structures?
Structures that occur wen it is possible to write 2 or more valid Lewis structures for the same molecule or ion.
T/F: Double bonds are shorter than single bonds.
TRUE
Why are the two bonds in ozone the same length?
The actual bonds are delocalized, so the bonds are hybrid. Each bond spends about half its time being single and half its time being double.
What is the difference between Lewis Dot Diagram and Structural Formula?
Lewis shows pairs as dots and does not use lines, structural formula uses them as lines
What does VSEPR theory stand for?
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory
What does VSEPR theory explain?
The 3d shape of molecules
What does VSEPR state?
Because electron pairs repeal each other, the molecular shape results from valence electron pairs position themselves as far apart as possible (109.5 degrees, not 90 degrees like in diagram)
How do you know if you need to alter the “S” in NASE and place brackets around the molecular geometry?
If the provided element has a + or - or if it says it is an ion.
What do lines imply?
Sharing, so covalence
What is electronegativity
The measure of an atom’s ability to attract bonding electrons
WHAT SHOULD YOU DO IN EVERY SINGLE TYPE OF BOND DETERMINING?
Check if the elements being combined are metals/nonmetals!!!!! If they are different, the bond is automatically ionic.
What does it mean if the difference in electronegativity is less than .36?
Nonpolar covalent
What does it mean if the difference in electronegativity is .36-1.7
Polar Covalent
Describe the trends in electronegativity difference in relation to bonds
Large electronegativity difference = ionic bond
Moderate electronegativity difference = polar covalent bond
Little to no electronegativity difference = nonpolar covalent
What are the diatomics?
I—>F, F—>N, H
Where are the bonding pairs of electrons in covalent bonds located?
Between the nuclei of the atoms sharing the electrons
When the pull of each nucleus for the electrons is equally strong, the electrons are shared equally and are located on average halfway between the two nuclei. This is a
nonpolar covalent bond
When the pull of one nucleus is stronger than the other, electrons move towards the more electronegative nucleus. This is a
Polar Covalent Bond
The more electronegative atom requires a ___ charge
Partial Negative
The less electronegative atom requires a
partial positive charge
How do you indicate the partial charges?
The figure 8 type thing with a sign
T/F: Don’t draw dipole lines unless it is polar
True
When drawing, the least electronegative should be in ___
The least electronegative should be in the middle, with the exception of “H”
What is another name for dipoles
Dipole moments
Where do the dipoles point
The more electronegative
T/F: Just because an atom contains polar bonds, doesn’t mean it is a polar molecule
True
Polarity of a molecule depends on
1) The existence of polar bonds (if none of the bonds are polar, the molecule is nonpolar)
2) Shape of the molecule
3) Orientation of the polar bonds
Why are molecules nonpolar even with dipoles?
Dipoles could cancel.
Is water polar or nonpolar and why?
Polar; dipoles don’t cancel
What are the three types of geometries that, assuming equivalent dipoles, would lead to nonpolar molecules even when a bond is polar?
Triatomic linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral
What is a polar bond?
A bond between two non-metals where electrons are shared unequally
In a polar bond, which atom will hold the electrons closer to itself
The more electronegative one
What is a nonpolar bond?
A non-polar bond is a covalent bond where electrons are shared equally?
High melting and boiling points
Ionic and metallic
Conduct electricity when melted
Ionic and metallic
Poor electrical conductors in all phases
Covalent
Many soluble in nonpolar liquids but not in water
Covalent
Low melting and boiling points
Covalent