WEEK 1 - TUTOR
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What are the 7 components of a Complete Blood Count (CBC)?
1. total protein (plasma protein, total solids)
2. White blood cell count (WBC)
3. Red blood cell count (RBC)
4. Hemoglobin (Hgb, Hb)
5. Hematocrit (Act or PCV)
6. Blood smear evaluation
7. RBC indices (MCV, MHC, MCHC)
What is the function of hemoglobin?
Carry oxygen
What 3 values measure RBC mass?
RBC count, hemoglobin, hematocrit
What is the purpose of the RBC indicies (MCV, MHC, MCHC)?
To describe RBC features such as size, amount of Hgb, and concentration of Hgb
What is a differential count?
How many of each WBC type is present out of 100 WBC's
What does MCV stand for?
mean corpuscular volume (mean SIZE)
What does MCH stand for?
mean corpuscular (cell) hemoglobin
What does MCHC stand for?
mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration
What is MCV measuring and what is the unit used?
the average size or volume of RBC
unit is femtoliters (fl)
What is MCH measuring and what is the unit used?
amount of hemoglobin (weight or mass) in average RBC
unit is picograms (pg)
RARELY USED
What is MCHC measuring and what is the unit used?
concentration of hemoglobin in the average RBC
unit is grams/deciliter (g/dl)
What is clinical chemistry?
measuring of the chemical components of body fluids, most commonly blood (serum or plasma)
other fluids can include: abdominal or thoracic fluid, cerebral spinal fluid (CSF), saliva, sweat, etc.
What does a clinical chemistry give us information on?
metabolism, function, or injury of various organs
commonly: liver, kidneys, pancreas, energym edocrine, acid-base, etc.
What do you get from a red top tube? (serum or plasma)
serum
What do you get from a tiger top tube? (serum or plasma)
serum
What do you get from a green top tube? (serum or plasma)
plasma
What tubes can be used for a clinical chemistry?
red (serum), tiger top (serum), green (plasma)
What is serum?
fluid portion of blood that sits on top of the RBCs once a red/tiger top is spun down
Whats is plasma?
fluid portion of blood that sits on top of RBCs once a green, purple, or blue top is spun down (tubes that contain an anticoagulant)
What color tubes do not contain an anticoagulant meaning they will clot?
red, tiger top
What color tubes contain an anticoagulant meaning they will not clot?
green, purple, blue
Does serum or plasma contain fibrinogen and clotting factors?
plasma DOES, serum DOES NOT
What does morphology mean?
appearance
What does appearance include?
size, shape, color, inclusions
What do mammalian RBCs look like?
biconcave discs, anuclear
What is the largest mammalian RBC and larger area of central pallor?
canine
What is the lifespan of a canine RBC?
110-120 days
What are characteristics of a PORCINE blood sample? (size, central pallor, lifespan)
smaller size, little to no central pallor, lifespan is 70-98 days
What are characteristics of a FELINE blood sample? (size, central pallor, lifespan)
smaller to variable size, little to no central pallor, lifepsan 65-76 days
Why are feline blood cells more susceptible to injury?
fragile hemoglobin
What morphology is common among felines?
rouleaux ("coin stack" of multiple RBC)
What are characteristics of a EQUINE blood sample? (size, central pallor, lifespan)
smaller size, little to no central pallor, lifespan: 140-150 days
What morphology is common in equine blood?
rouleaux ("coin stack" of multiple RBCs
What are characteristics of a BOVINE blood sample? (size, central pallor, lifespan)
smaller size, little to no central pallor, lifespan 160 days
What are characteristics of a OVINE blood sample? (size, central pallor, lifespan)
smaller size, no central pallor, lifespan unknown
What are characteristics of a CAPRINE blood sample? (size, central pallor, lifespan)
smallest mammalian RBC, about 1/2 the size of canine, no central pallor, lifespan is 125 days
What are characteristics of a CAMELID (llamas, alpacas, camels) blood sample? (size, central pallor, lifespan)
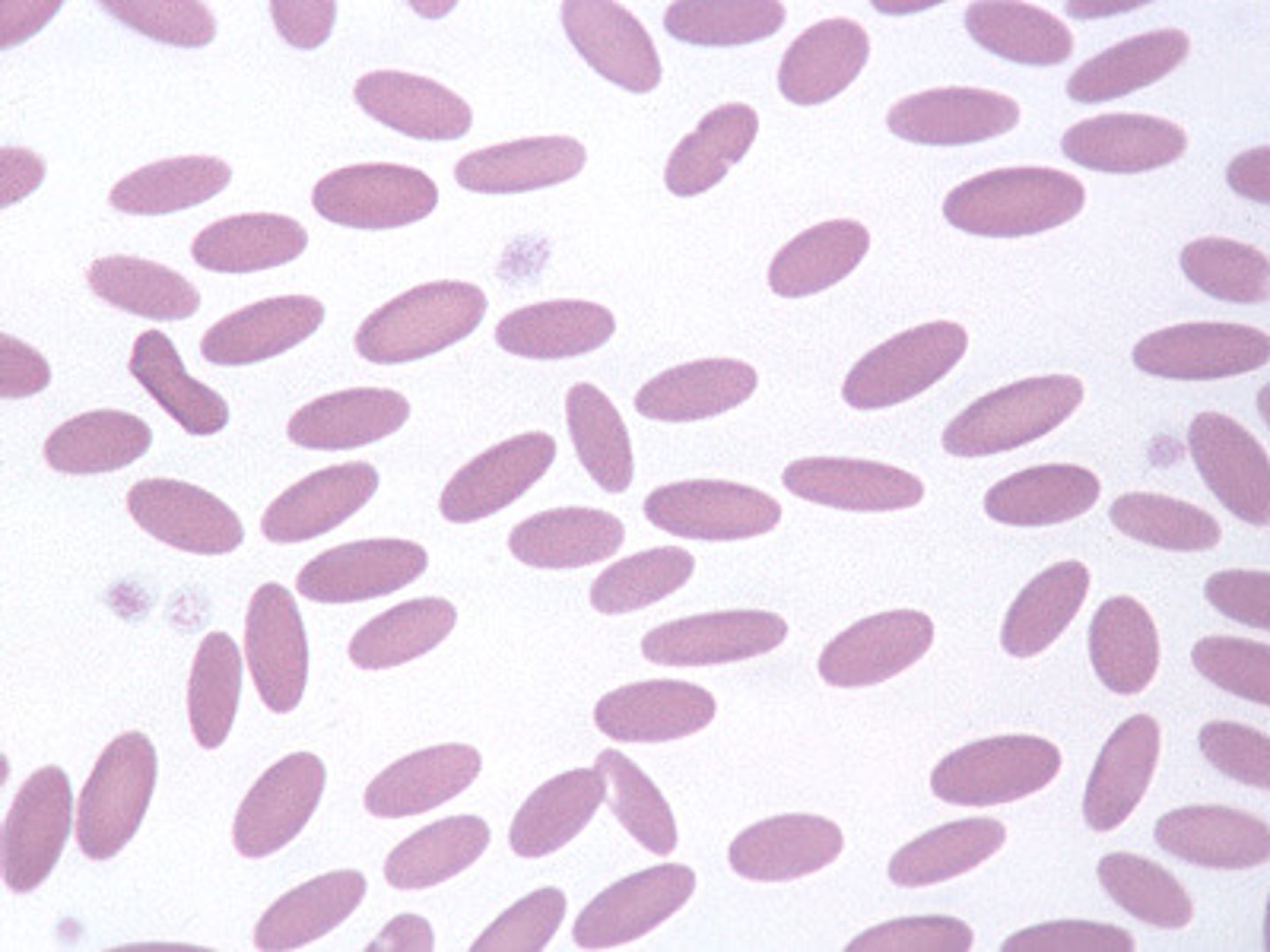
oval shape! lifespan is 60 days
What is higher in camelid species than other species?
MCHC
What are characteristics of an exotic animals like avian, reptiles, amphibian, and fish blood sample? (size, central pallor, lifespan)
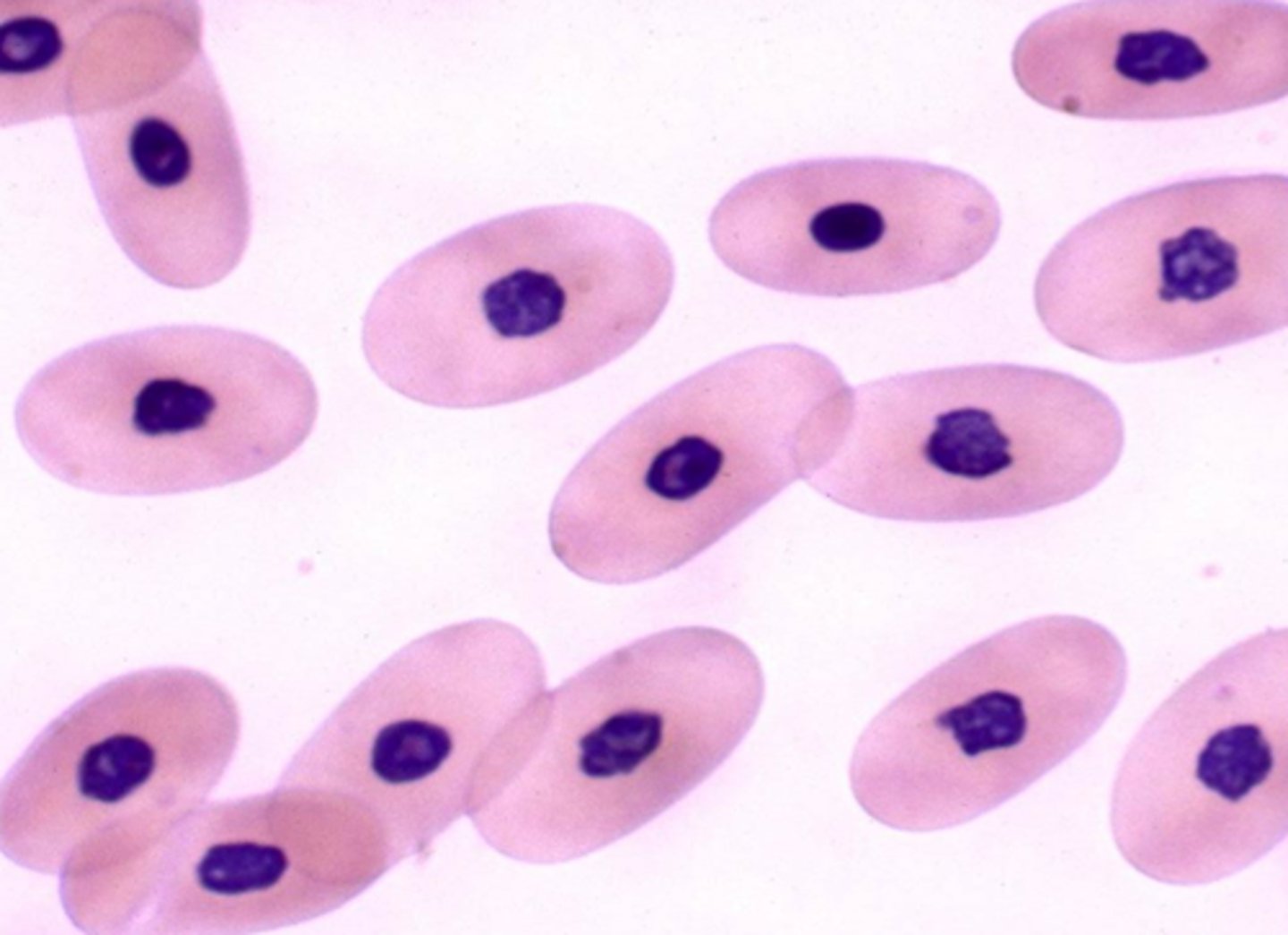
NUCLEATED, all cells are special, lifespan depends on species
What species is this?
camelid
What kind of species does this red blood cell belong to?
exotics red blood cell
What is a hemacytometer?
manual counting system for performing cell counts in various fluids (manual WBC count, manual platelet count)
How many square grids are in a hemacytometer?
9 square grid on both sides
How long does a loaded hemacytometer need to sit for under a humidity chamber?
10 minutes
What objective on the microscope do you use to look at a hemacytometer?
40x objective
What is a reference interval?
an interval of values in which the majority of healthy patient's values lie
What is the purpose of a reference interval?
helps identify abnormalities in sick patients
What phrase should you avoid using when talking about a reference interval or range?
"normal values" may be misleading or confusing
What 3 main variables are used when chosing reference populations?
same species, clinically healthy, age (adult animals older than 1 year old)
What is the shape of reference interval design and what percentage is overlap?
bell shaped, 5%
Are all values outside of reference intervals clinically abnormal?
no! there can be minor changes in values, think about tube used, how the sample was stored, how long until it was tested, etc. this will impact results