Genetics -USBT JWK
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Genetics
a field of biology devoted to understanding how characteristics are transmitted from parents to offspring
Heredity
the transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring
Trait
genetically determined variant of a characteristic, such as flower color
Self-Pollination
pollen is transferred from the anthers of a flower of the stigma
True-Breeding
pure for a trait always produce offspring with that trait when they self-pollinate
P Generation
The parental generation in a genetic cross.
F1 Generation
offspring of the P generation, the first full filial generation
F2 Generation
offspring of the F1 generation, the second filial generation
Dominant
factor named because it masked , or dominated, the factor for the other trait in the pair
Recessive
factor that seemingly vanished , or is hidden, the by another factor. Can often reappear in later generations/
Law of Segregation
factors (alleles) separate independently of one another during the formation of gametes if they are located on separate chromosomes.
Law of Independent Assortment
Genes separate independently from one another in meiosis
Allele
each of two or more alternative forms of gene
Genotype
an organisms genetic makeup
Phenotype
an organisms appearance or expression of a characteristic
Homozygous
both alleles of a pair are alike
Heterozygous
when two alleles in the pair are different
Probability
the likelihood that a possible future event will occur in any given instance of the event
Monohybird Cross
a cross in which only one characteristic is tracked
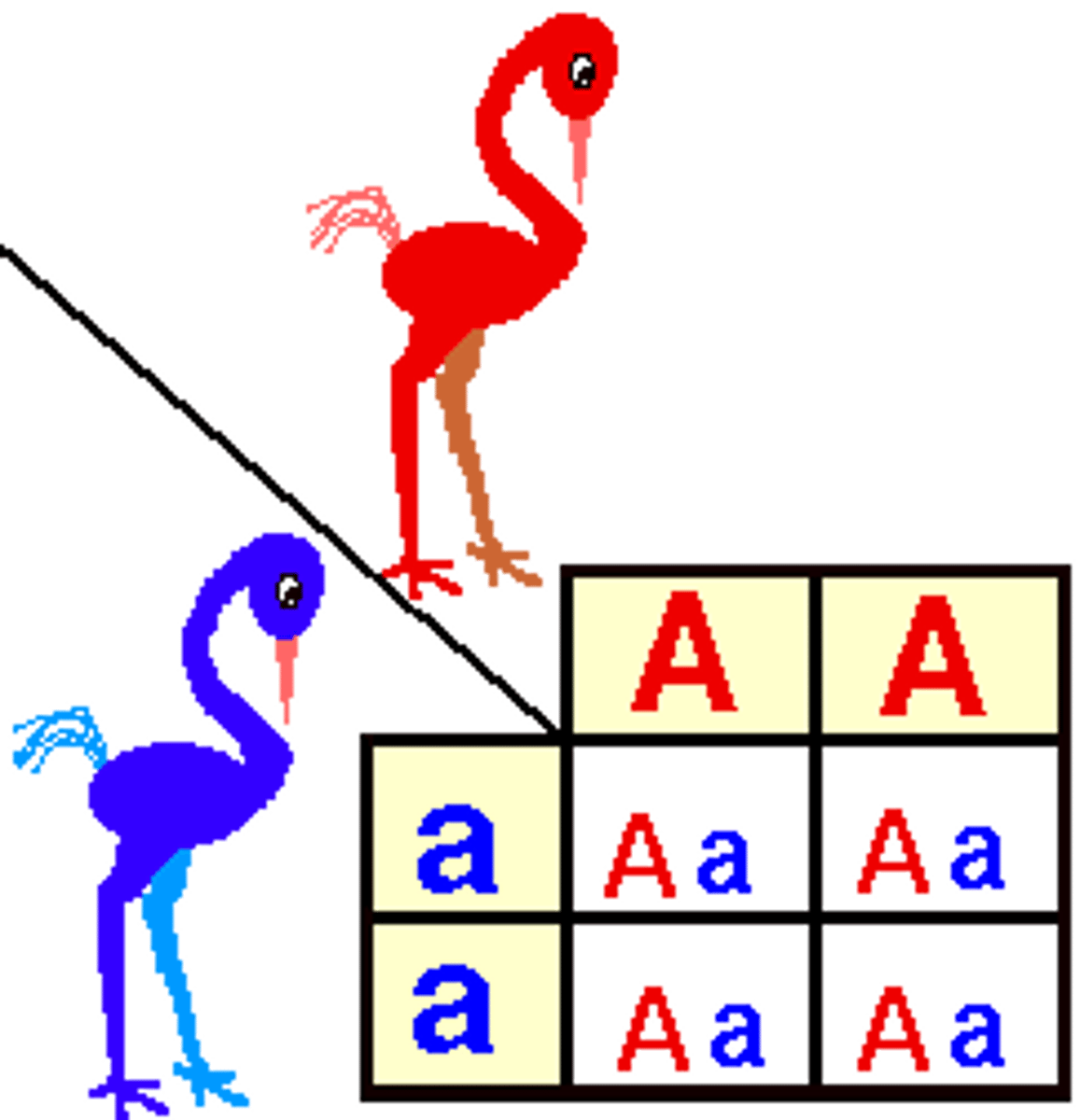
Punnet Square
diagram to aid in predicting the probable distribution of inhered traits in the offspring
recessive allele
represented by a lower case letter
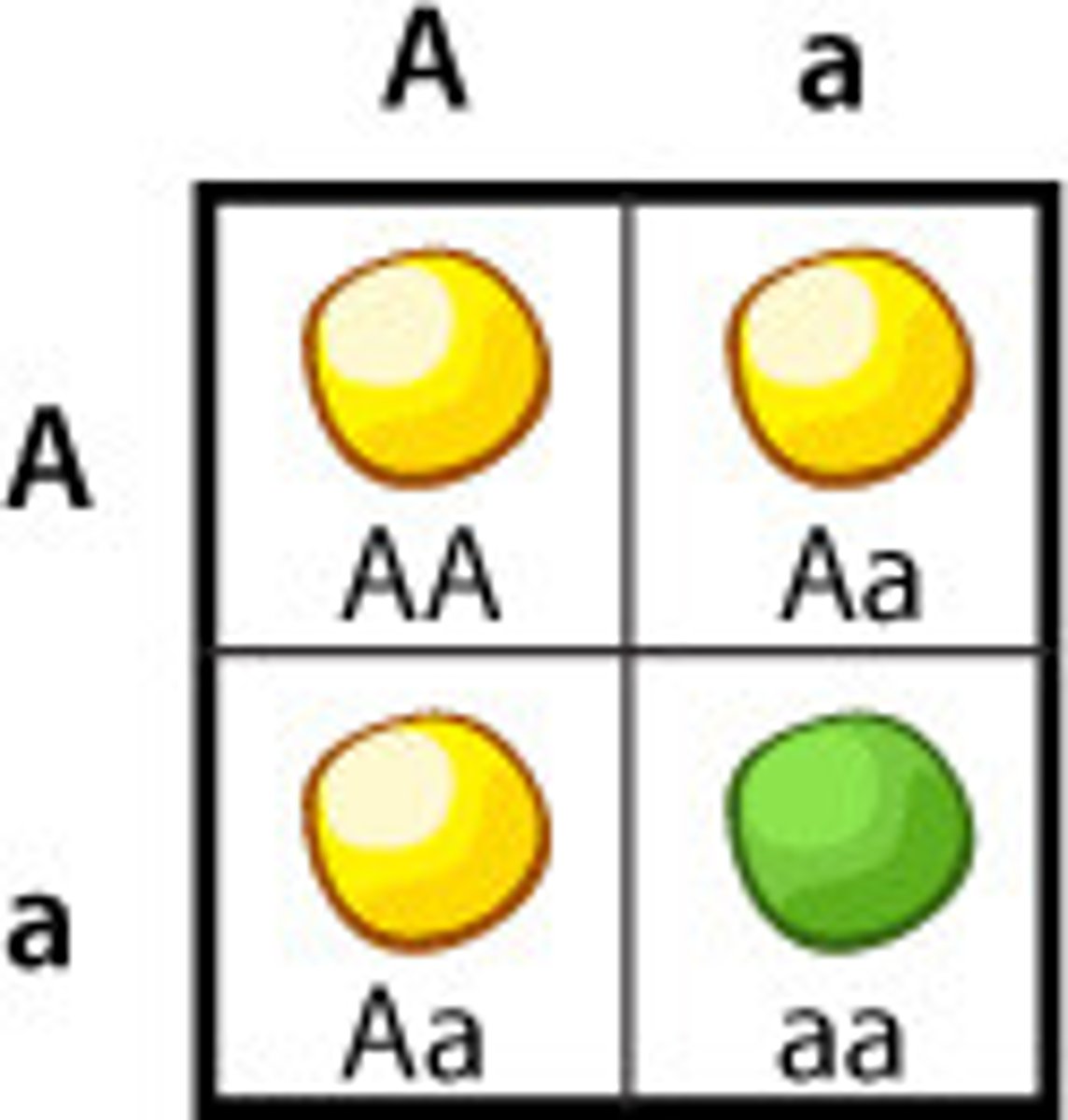
Testcross
an individual of unknown dominant genotype is crossed with a homozygous recessive individual
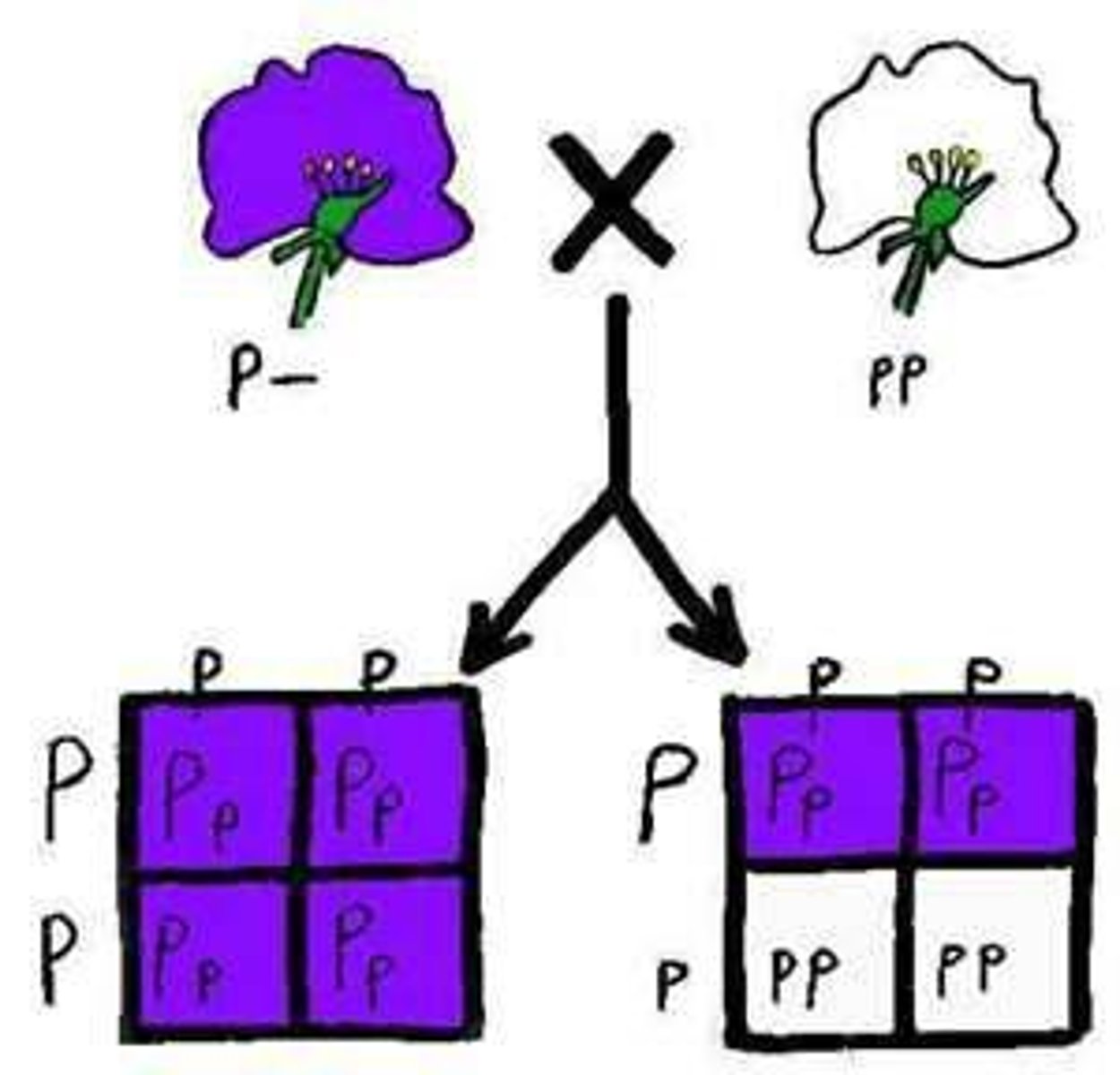
Genotypic Ratio
the ratio of genotypes that appear in the offspring of a cross
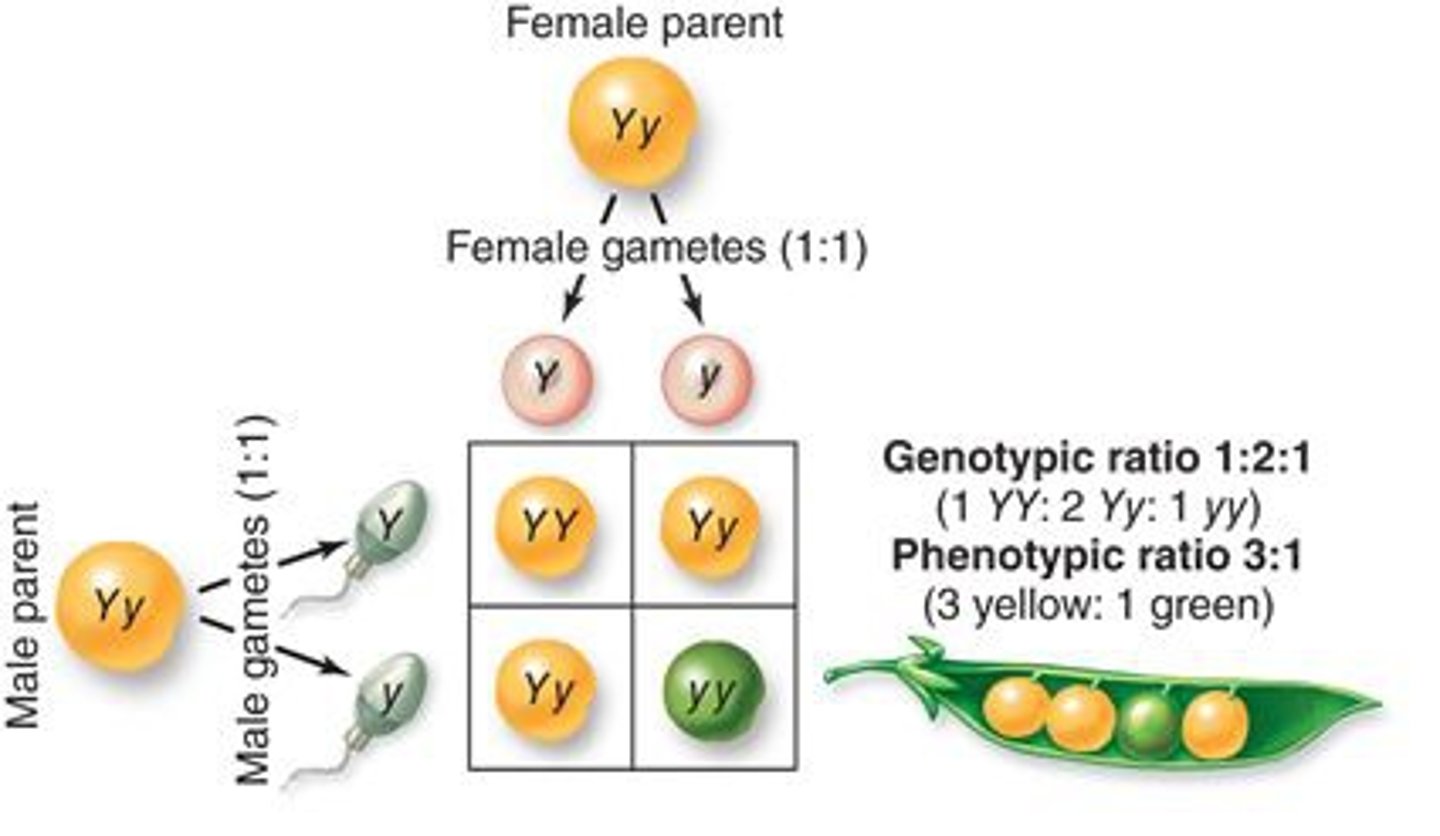
Phenotypic Ratio
the ratio of phenotypes produced by a cross
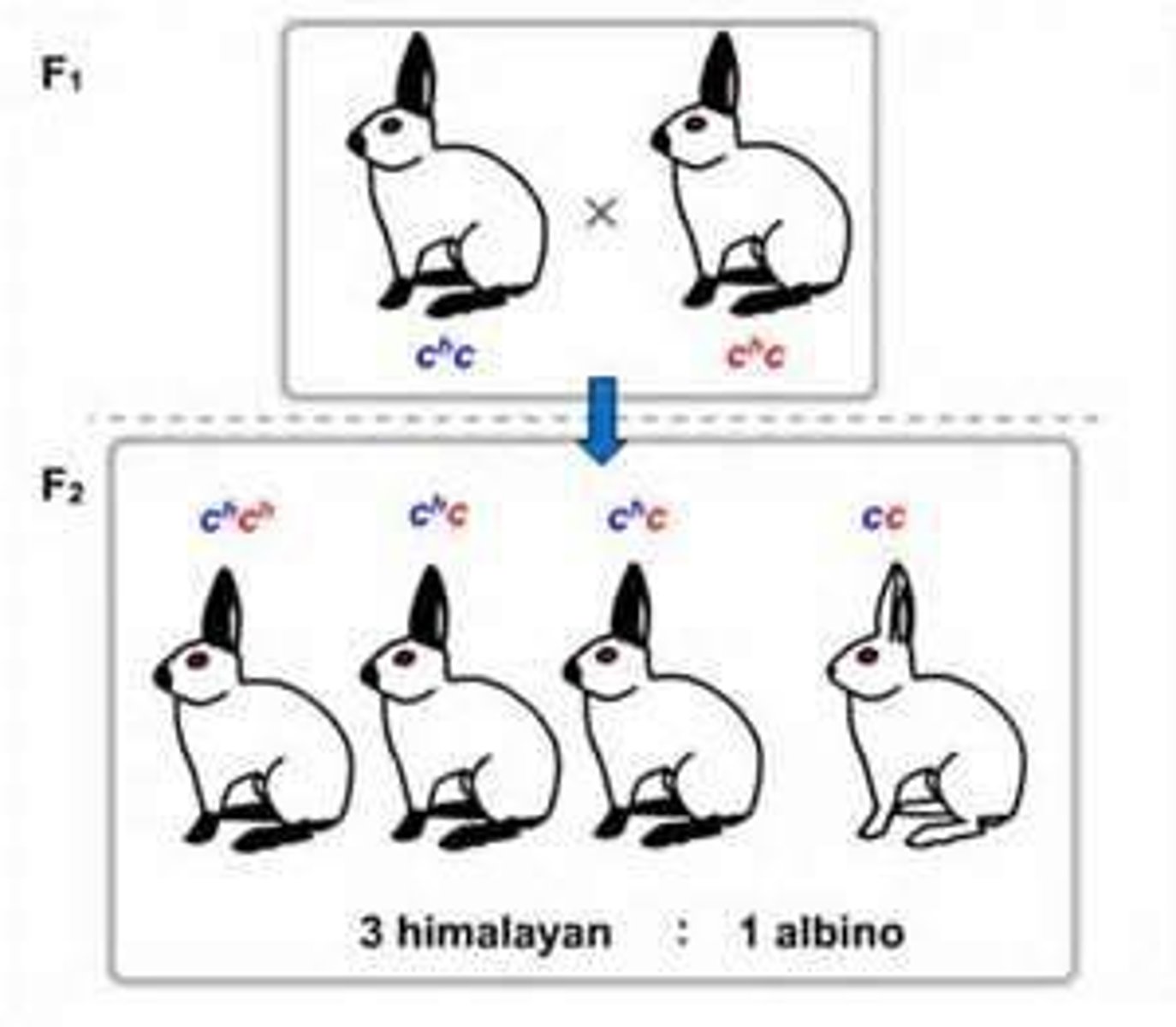
Complete Dominance
a relationship, one allele was completely dominant over another
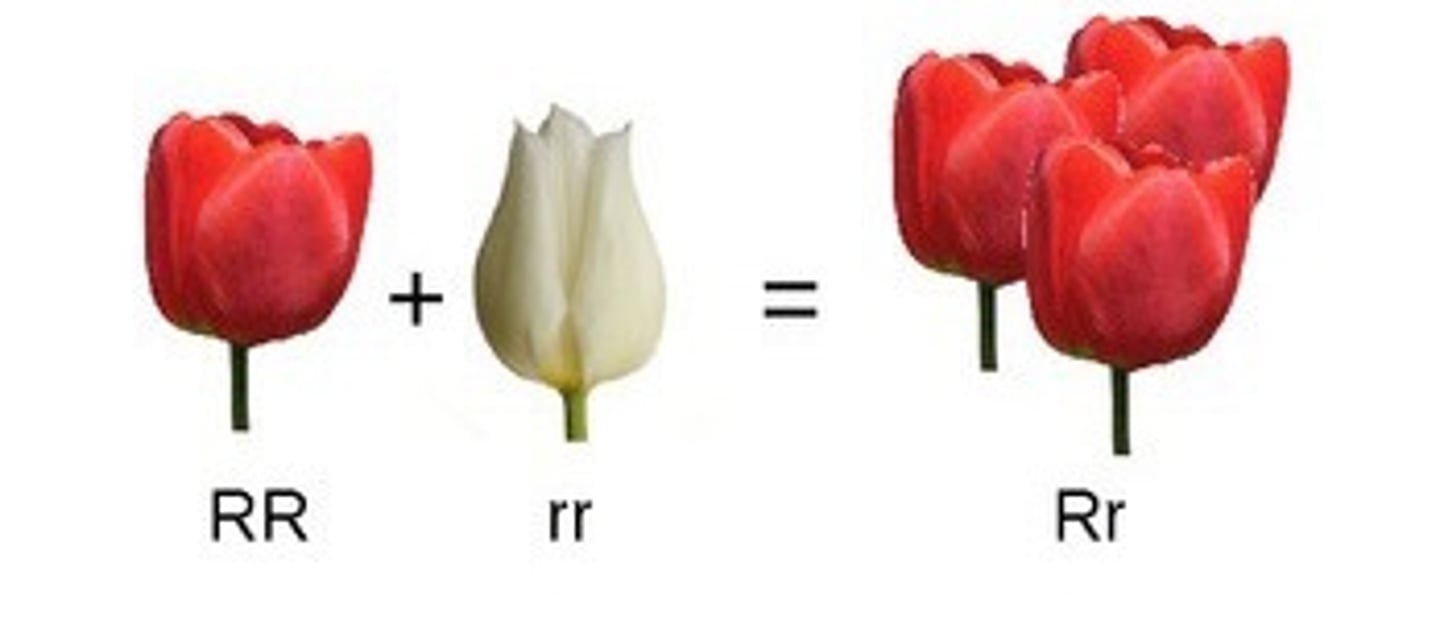
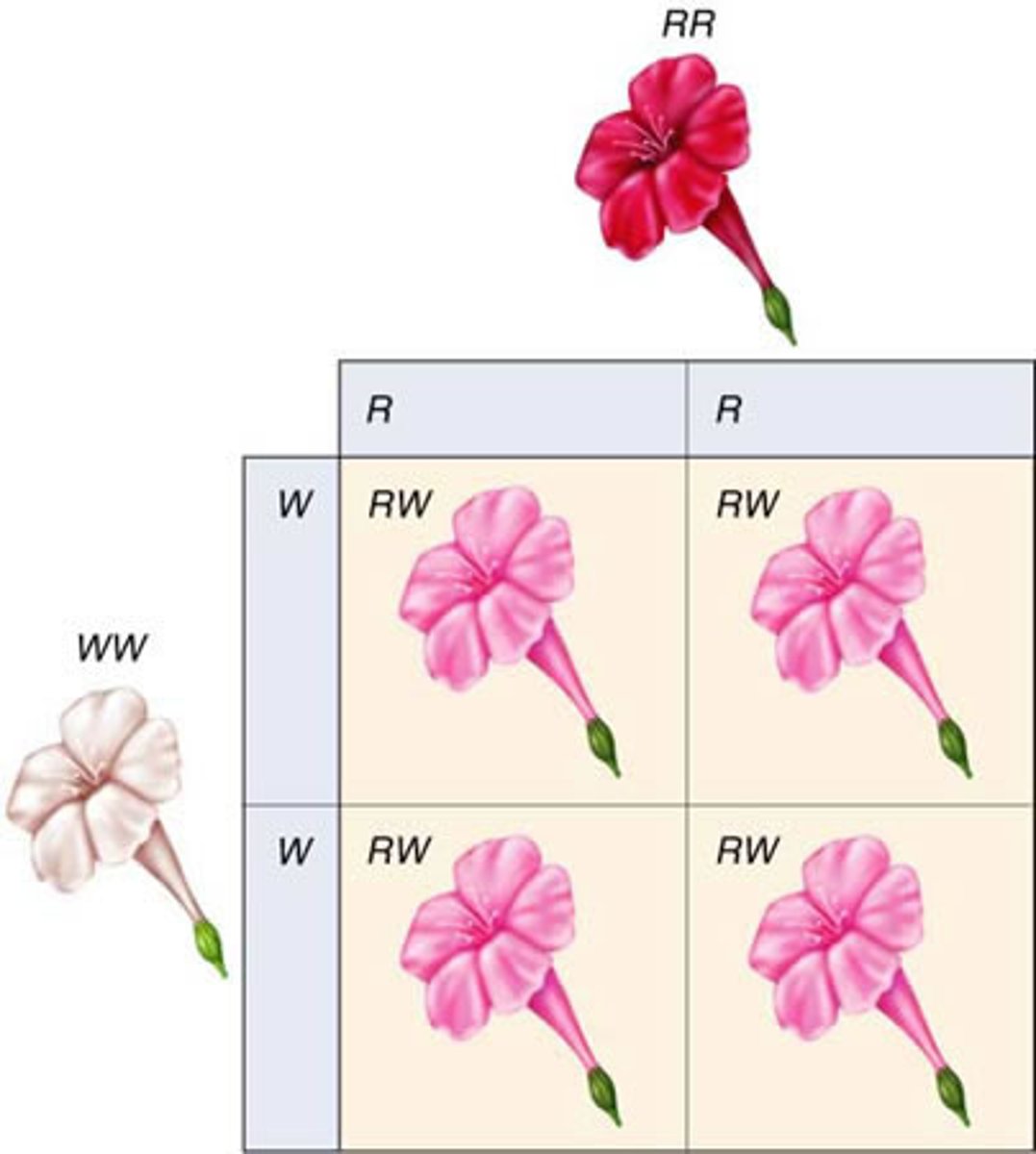
Incomplete Dominance
the F1 offspring will have a intermediate (blend) phenotype in between the parents
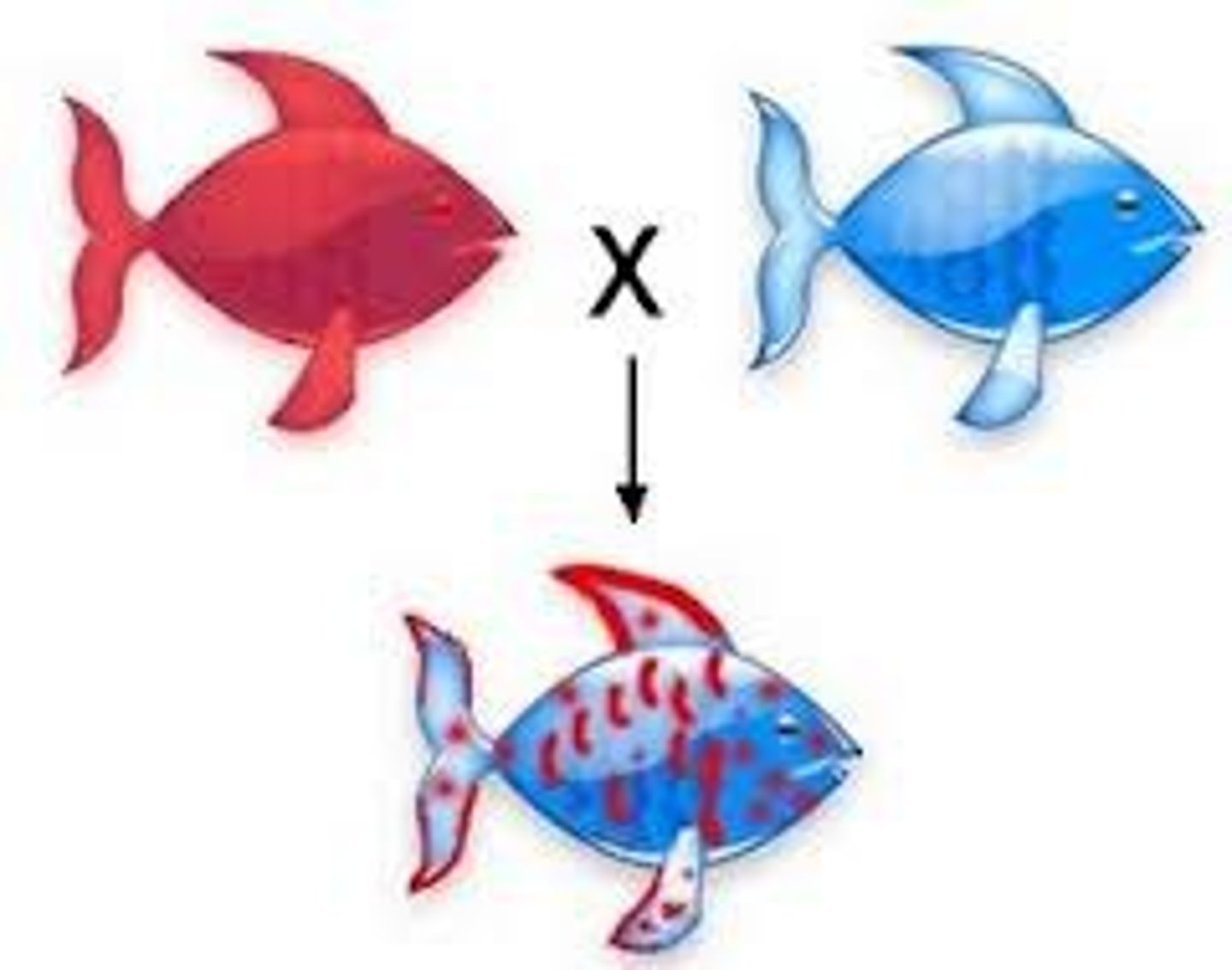
Codominance
occurs when both alleles for a gene are expressed in a heterozygous offspring
Dihybrid Cross
is a cross in which two characteristics are tracked
Multiple Alleles
genes with 3 or more alleles. i.e. blood type
polygenic
characteristics that are influence by several genes. i.e. skin color.
genetic disorder
diseases or disabling conditions that have a genetic basis.
Pedigree
a diagram used to show how a trait is inherited over several generations.
sex-linked trait
a trait coded for on the sex chromosomes (X or Y)