Upper Limb
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
What makes up the shoulder girdle?
Clavicle, scapula, + their connection to the manubrium
Where can you find the only bone to bone contact in the shoulder girdle?
Clavicle and sternum
Pectoral girdle bones
Clavicle and scapula
Purposes of the clavicle
A strut that suspends the upper limb and allowing freedom of motion
Protects neurovascular bundle that supplies the upper limb
Transmits force from the arm to the axial skeleton.
What happens if the clavicle is fixed?
Enables elevation of ribs during active respiration
Clavicular fracture
Caused by indirect force to the clavicle due to impacts to the outstretched hand or falls directly on the shoulder.
How does a clavicular fracture present?
Lateral 1/3 and Mid 3rd of the clavicle is pulled up due to the SCM pulling it up
Clavicular fracture intervention
Surgical intervention = putting a plate on the split clavicle to attach the bone together and help with bone growth
Scapula
Has 3 fossae that provides muscular attachment
Angles, borders, and spine also provide multiple attachment points
Actions of the scapula
Elevation, depression, protraction, retraction, upward/lateral rotation, downward/medial rotation
What are the 3 components of the AC joint?
Superior acromioclavicular joint
Coracoclavicular ligament
Coracoacromial ligament
AC Joint separation
Caused by a direct blow to the shoulder or falling on outstretched hand. Lateral (acromial end) tents upward.
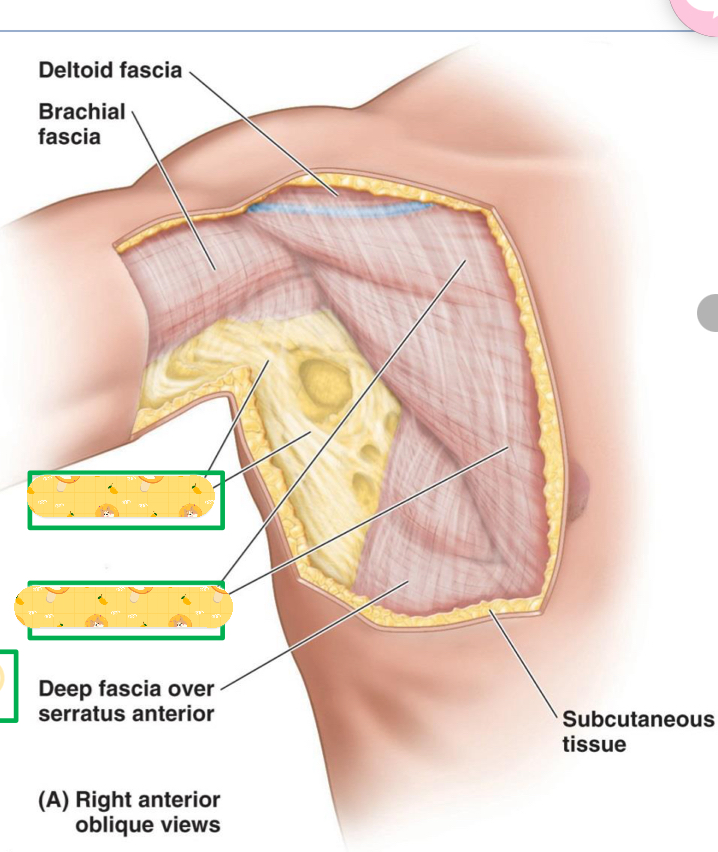
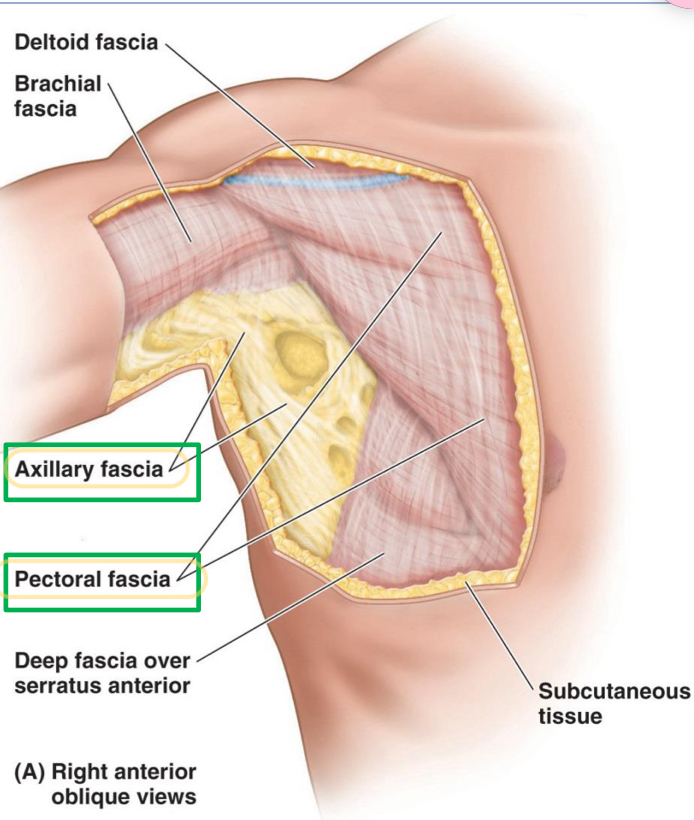
Name these 2 structures
Axillary fascia
Pectoral fascia
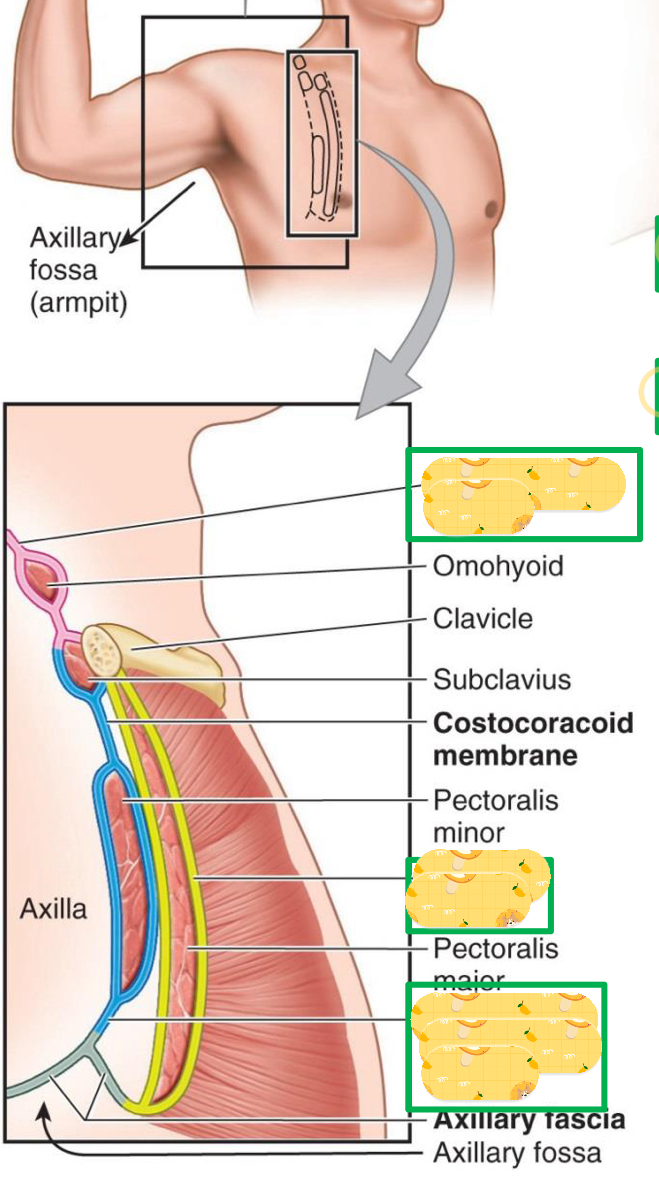
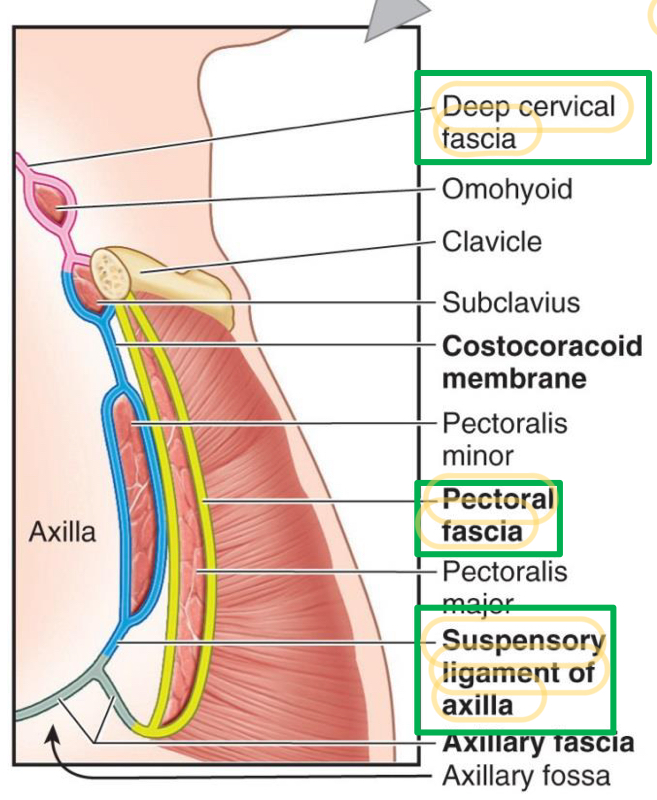
Name these structures found in the axillary fossa
Deep cervical fascia
Pectoral fascia
Suspensory ligament of axilla
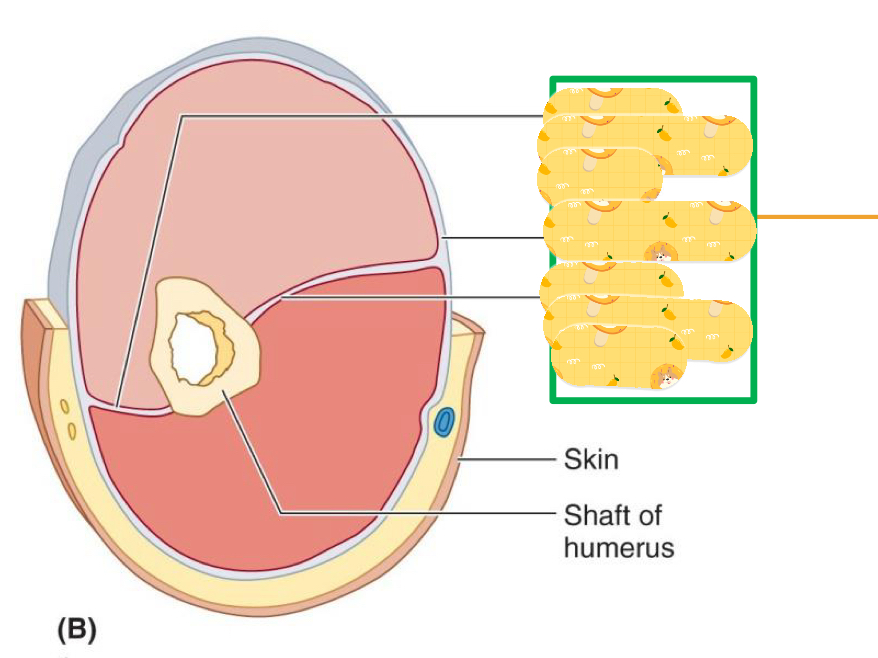
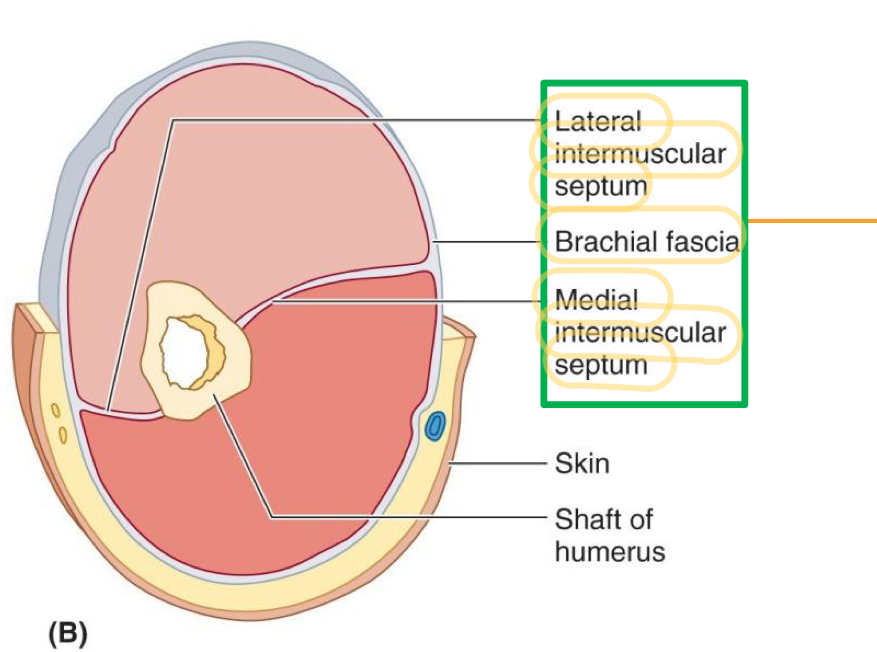
Name these structures
Lateral intermuscular septum
Brachial fascia
Medial intermuscular septum
Superficial veins of the arm
Cephalic vein (lateral)
Basilic vein (medial)
The cephalic and basilic vein communicates via?
The median cubital vein
Where is the common site of venipuncture?
Median cubital vein
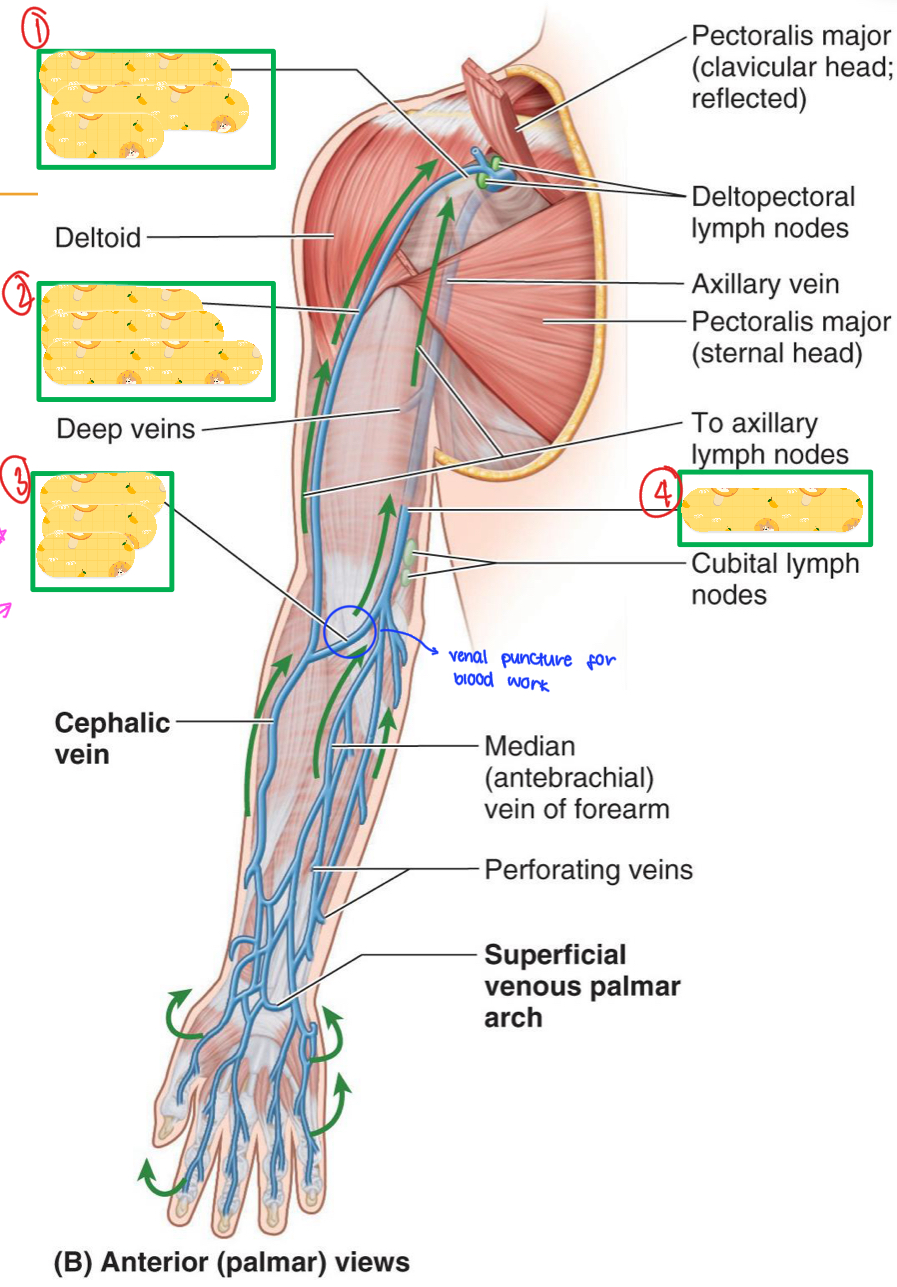
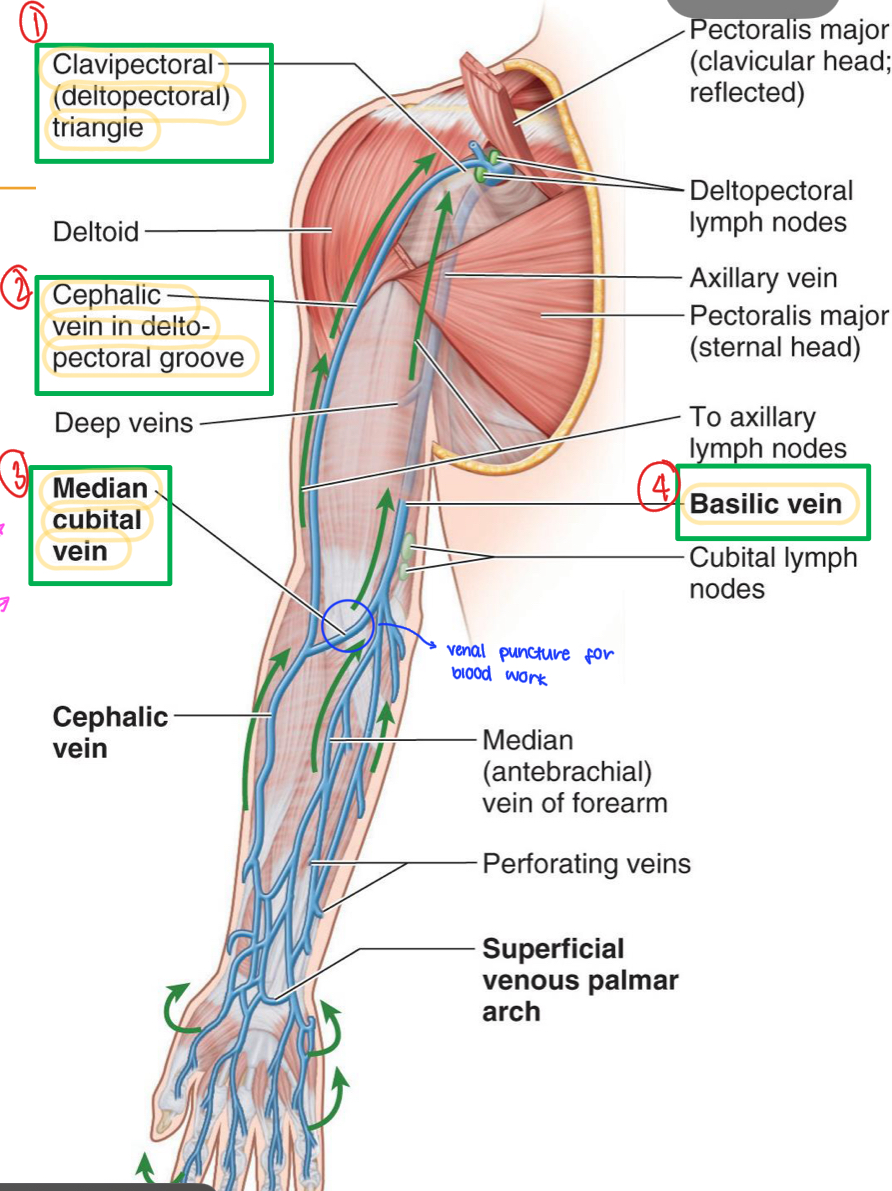
Name these structures
Clavipectoral (deltopectoral) triangle
Cephalic vein in deltopectoral groove
Median cubital vein
Basilic vein
What are the muscles in the Anterior Thoracoappendicular?
Pectoralis Major, Pectoralis Minor, Subclavius, Serratus Anterior
Origin: clavicle, sternum, and costal cartilages
Insertion: intertubercular groove
Action: Adduction, Humerus medial rotation, scapular protraction.
Clavicle = flexes humerus
Sternocostal = extends humerus from flexion
Innervation: Lateral pectoral nerve (clavicle) and medial pectoral nerve (sternocostal)
Pectoralis Major
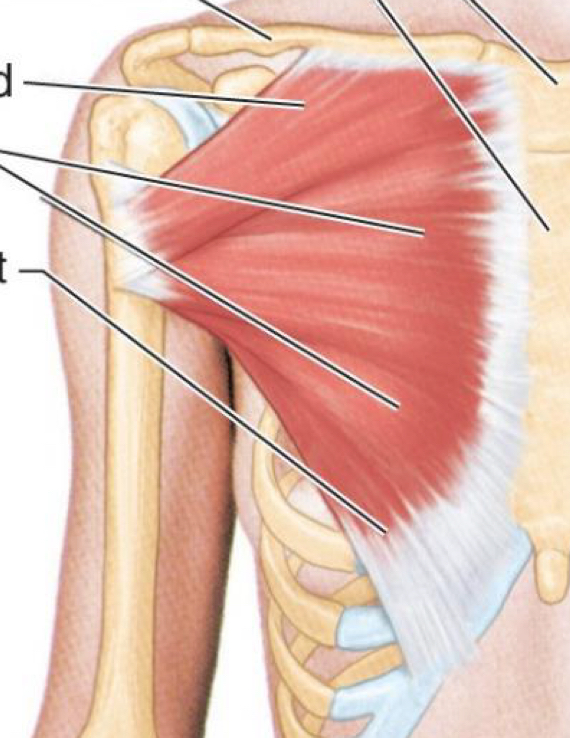
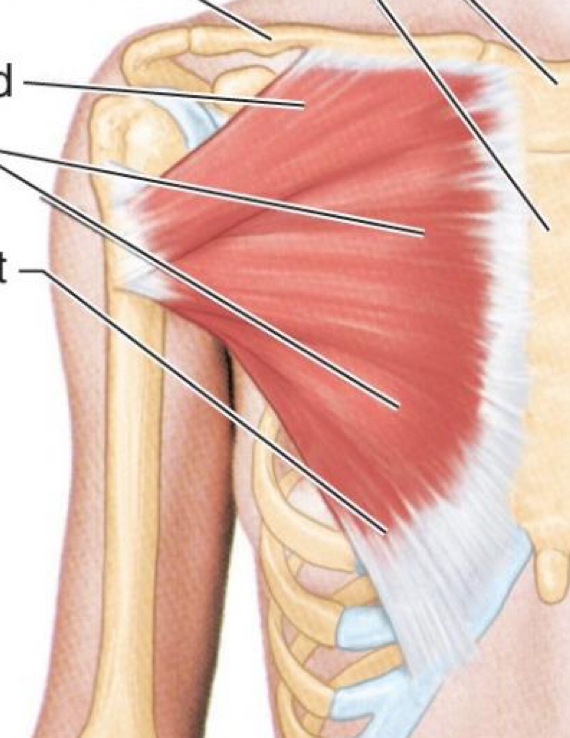
What muscle is this?
Pectoralis Major
Origin: ribs 3-5
Insertion: coracoid process
Action: depresses shoulder girdle, protracts and stabilizes scapula, assists in forced inspiration
Innervation: Medial Pectoral Nerve
Pectoralis minor
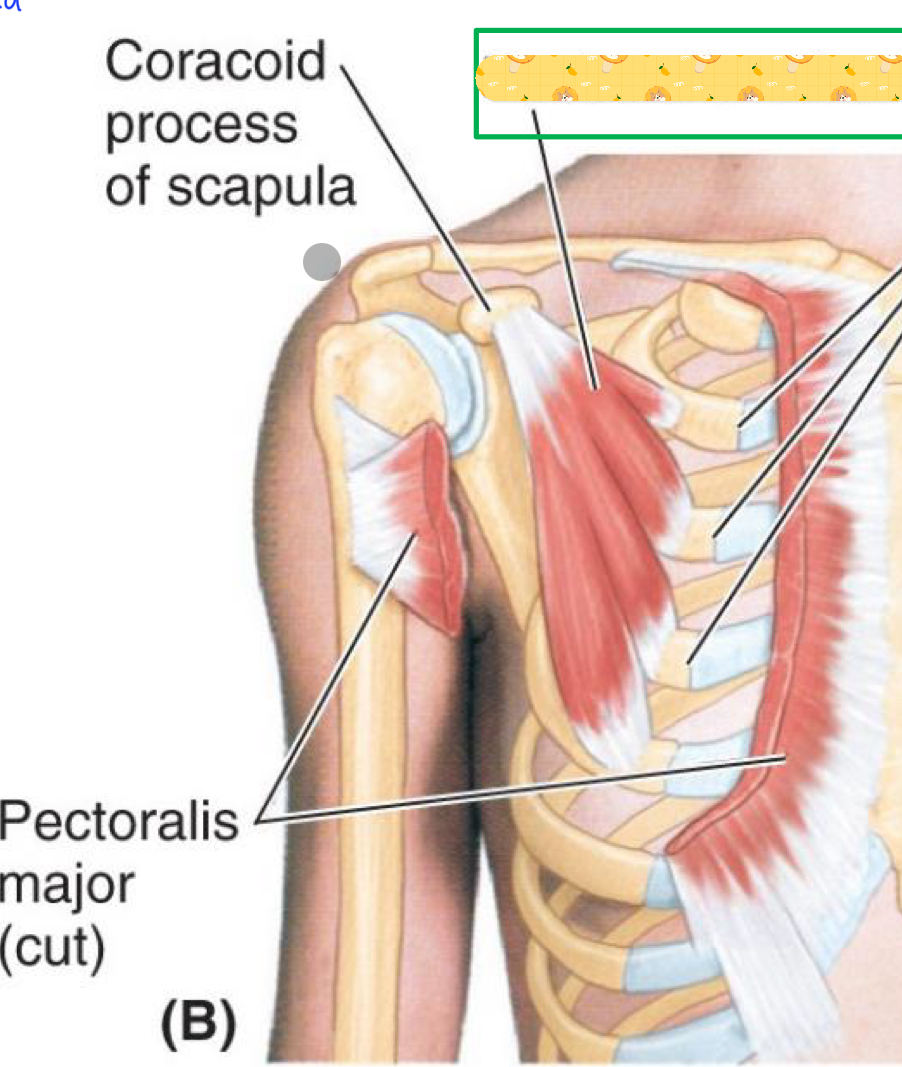
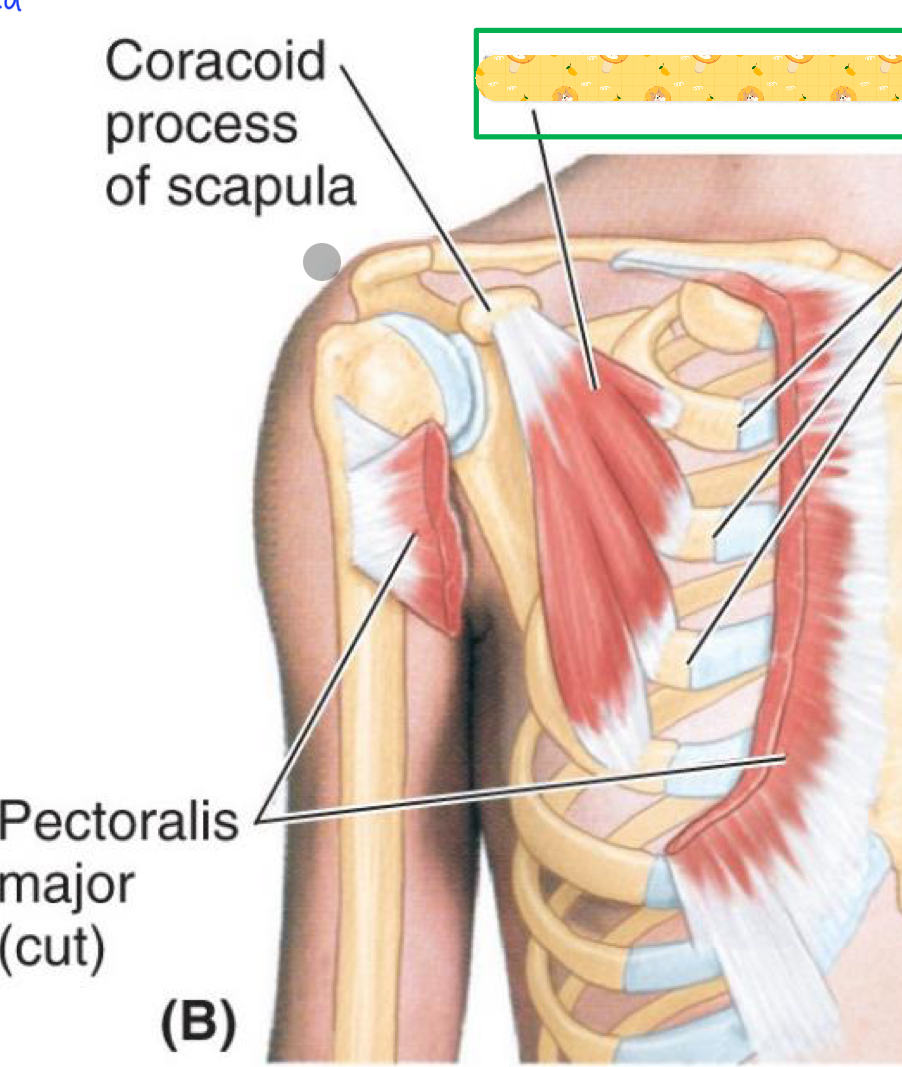
Name this muscle
Pectoralis minor
Origin: costal cartilage (1st rib)
Insertion: clavicle
Action: Anchors and depresses clavicle
Innervation: subclavius nerve
Subclavius
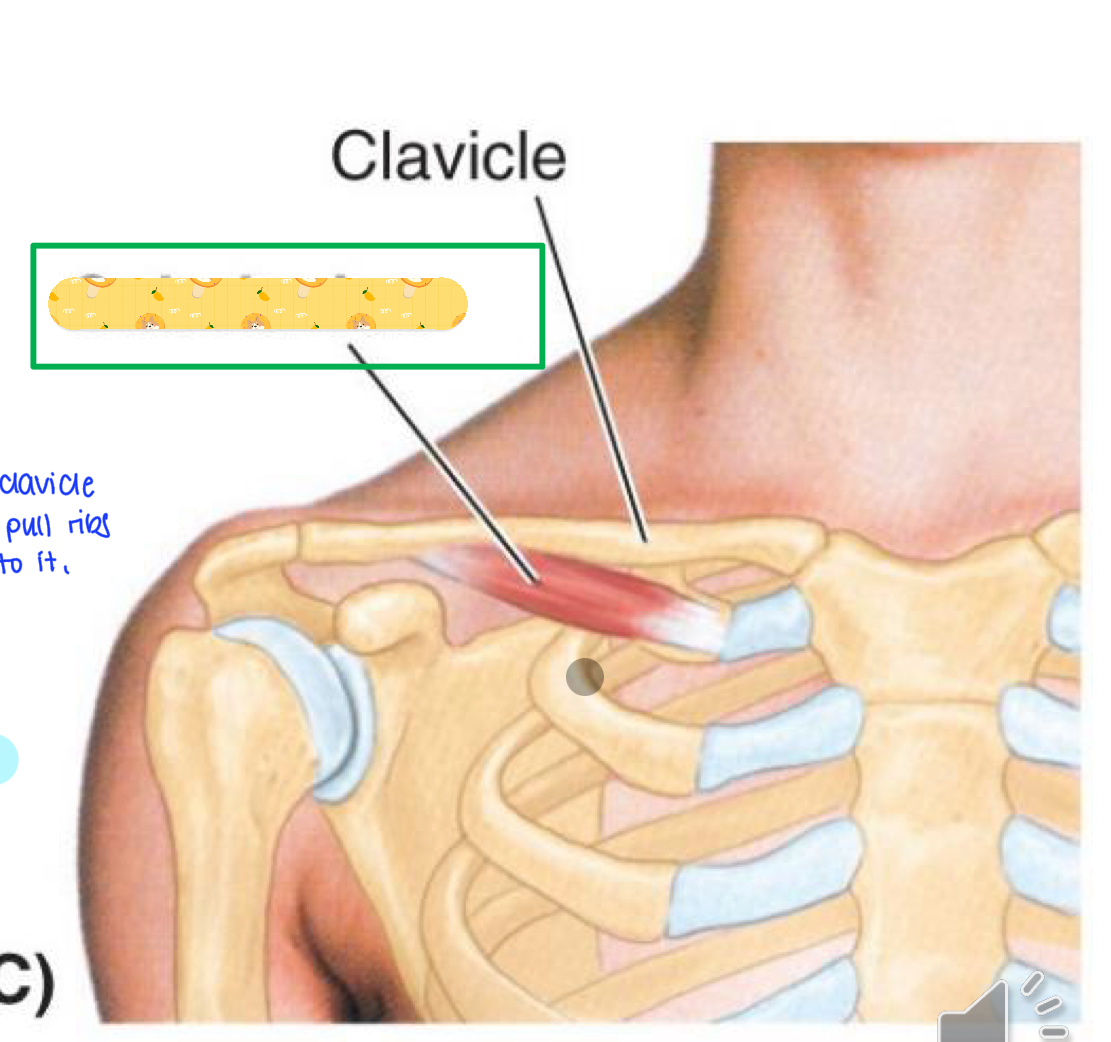
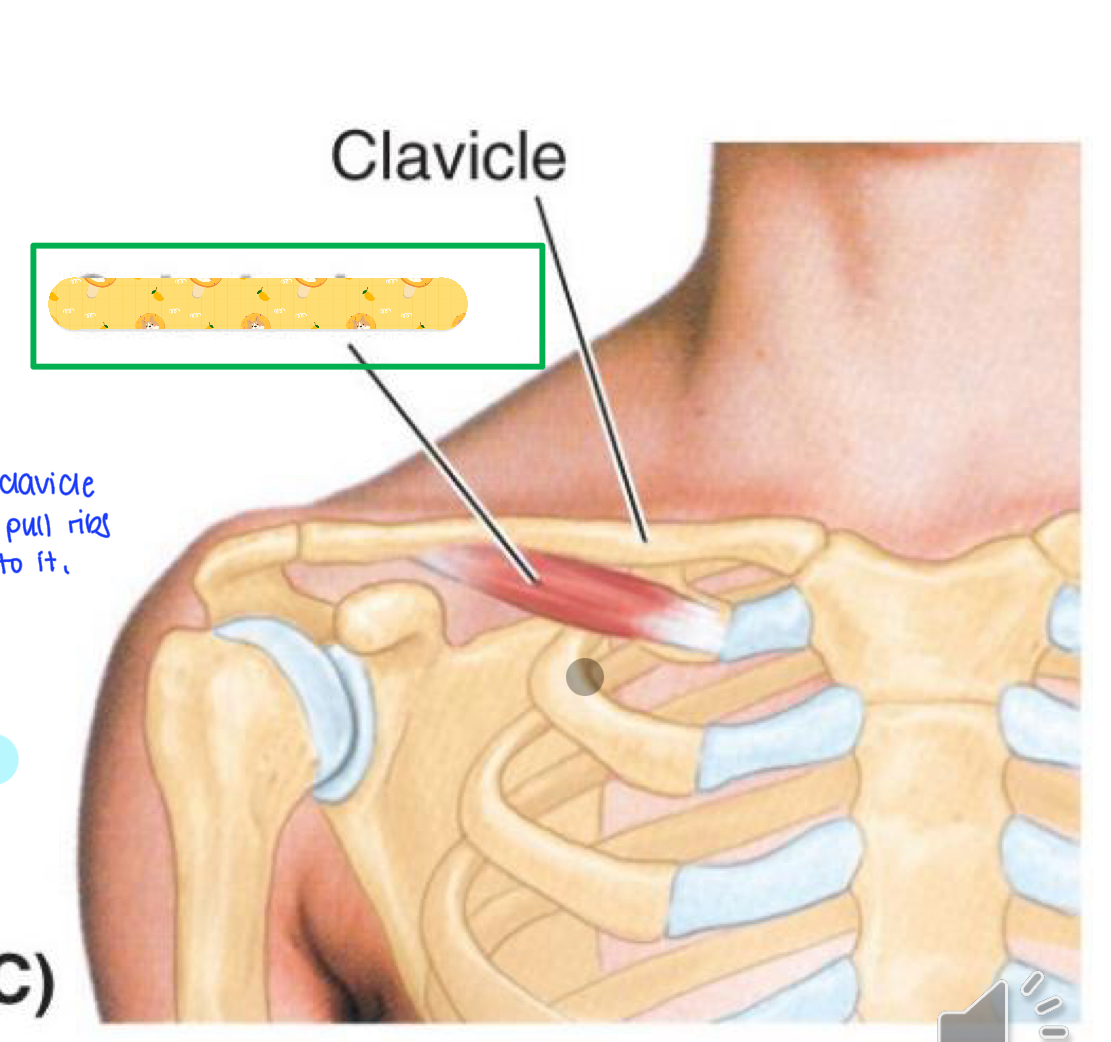
Name this muscle
Subclavius
Origin: Ribs 1-8 (lateral aspect)
Insertion: scapula (medial border)
Action: protracts, lateral rotation, secures scapula against thoracic wall
Innervation: Long thoracic nerve
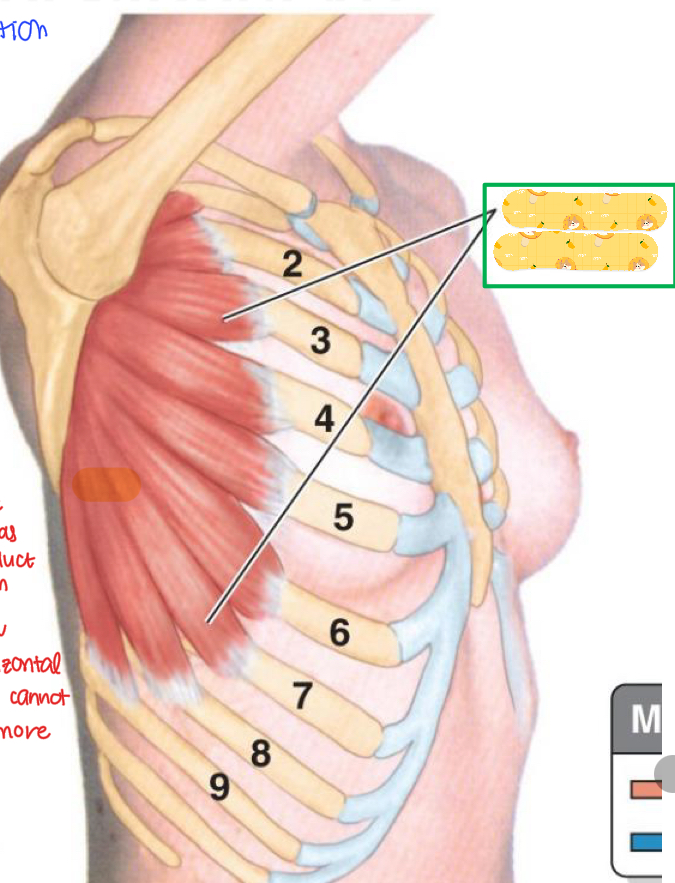
Serratus anterior
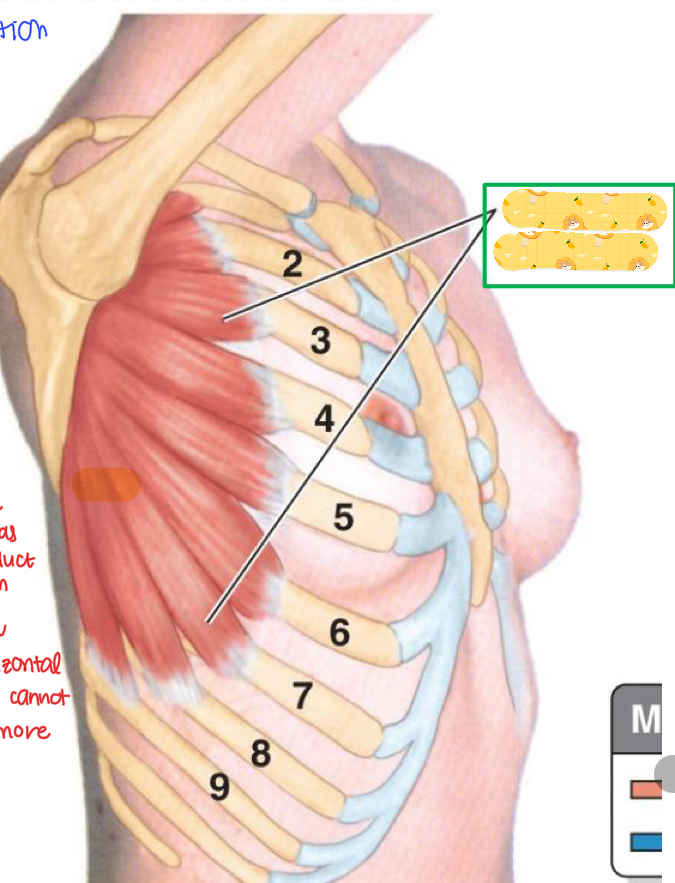
Name this muscle
Serratus anterior
When serratus anterior is paralyzed, what happens to the scapula?
Scapular winging since serratus anterior is no longer holding the scapula down.
Posterior thoracoappendicular muscles
Trapezus, Latissimus dorsi, Rhomboids, Levator Scapulae
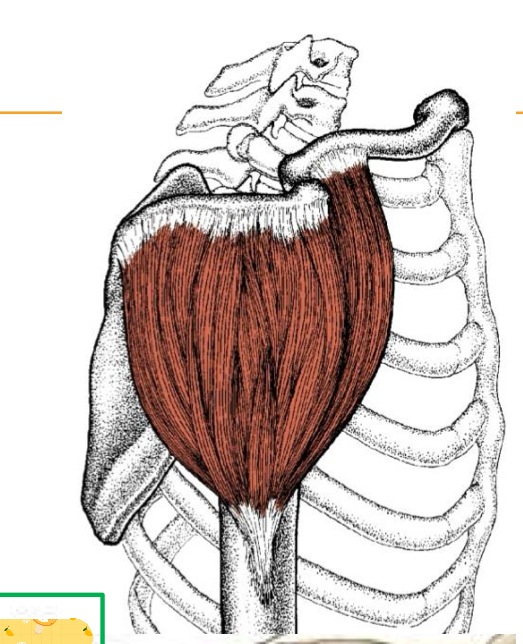
Origin: Superior nuchal line, ligamentum nuchae, spinous processes (C7- T12)
Insertion: Clavicle, acromion process, scapular spine
Action: Elevation, retraction, scapular rotation, and neck extension
Innervation: Accessory nerve and Sensory nerve (C2, C3)
Trapezius
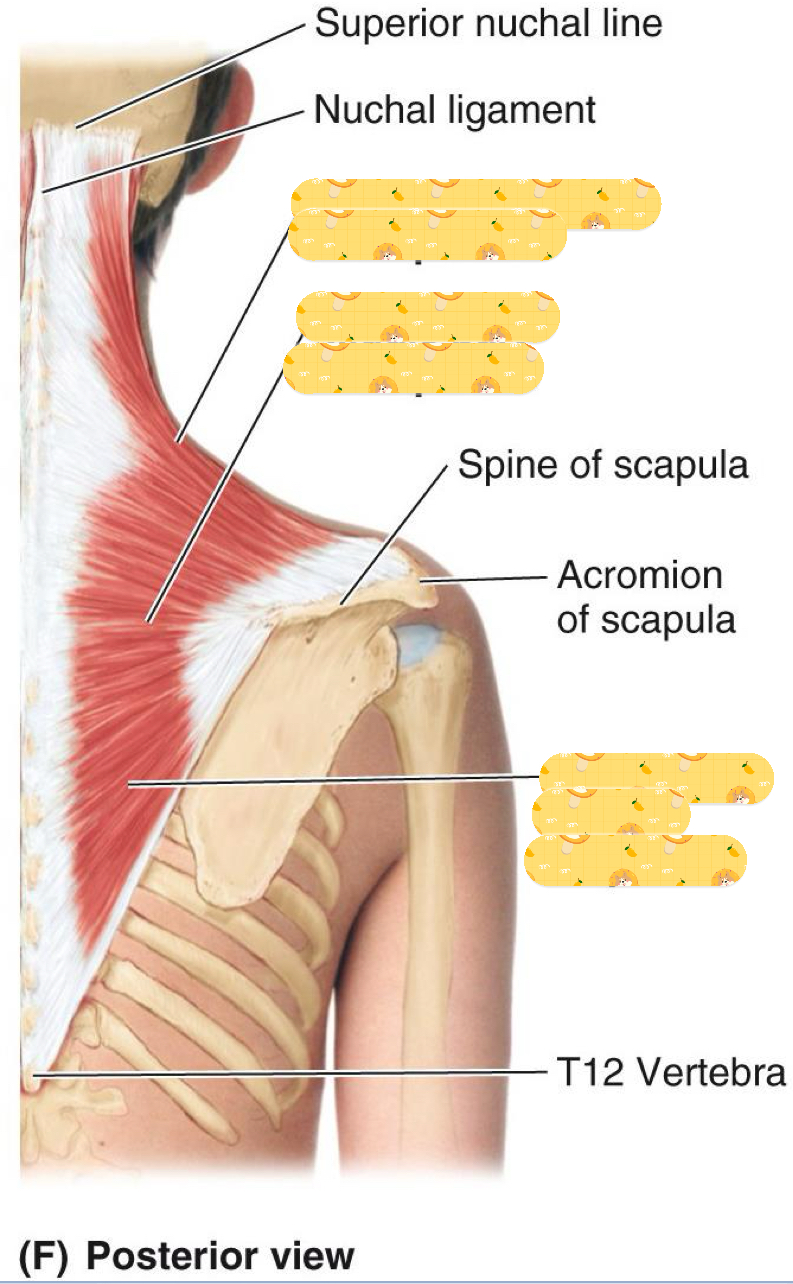
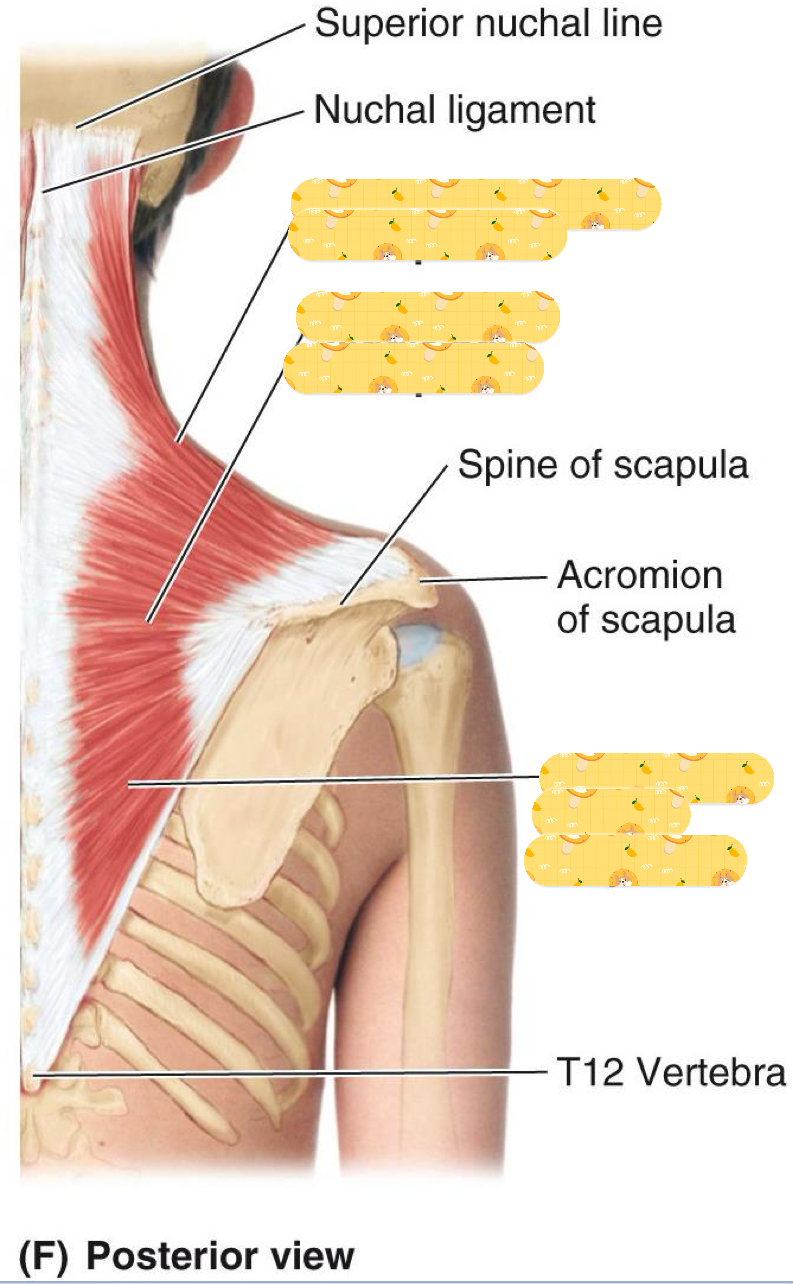
Name this muscle
Trapezius
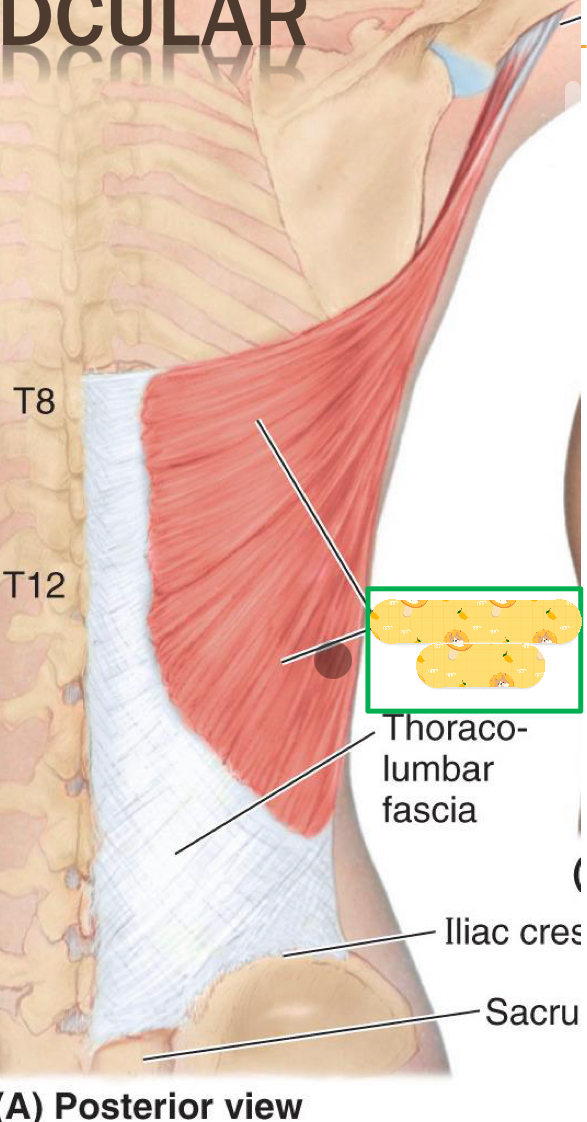
Origin: spinous processes (T6-T12), Iliac crest, Inferior ribs
Insertion: humeral intertubercal groove
Action: Humeral extension, adduction, and medial rotation
Innervation: Thoracodorsal nerve
Latissimus dorsi
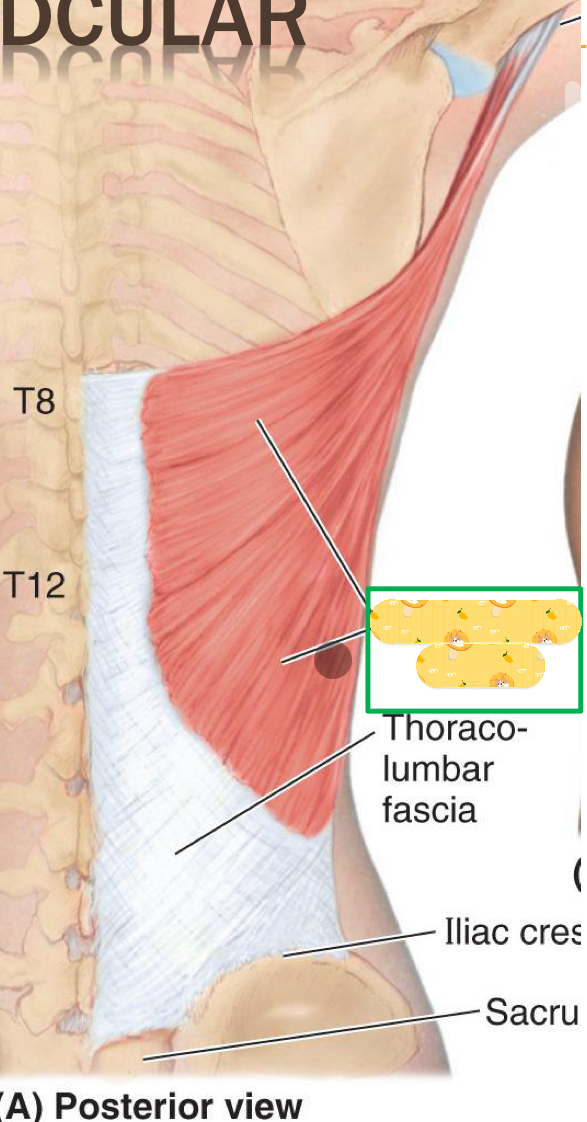
Name this muscle
Latissimus dorsi
Origin:
Minor - nuchal ligament and spinous process
Major - spinous processes T12-T5
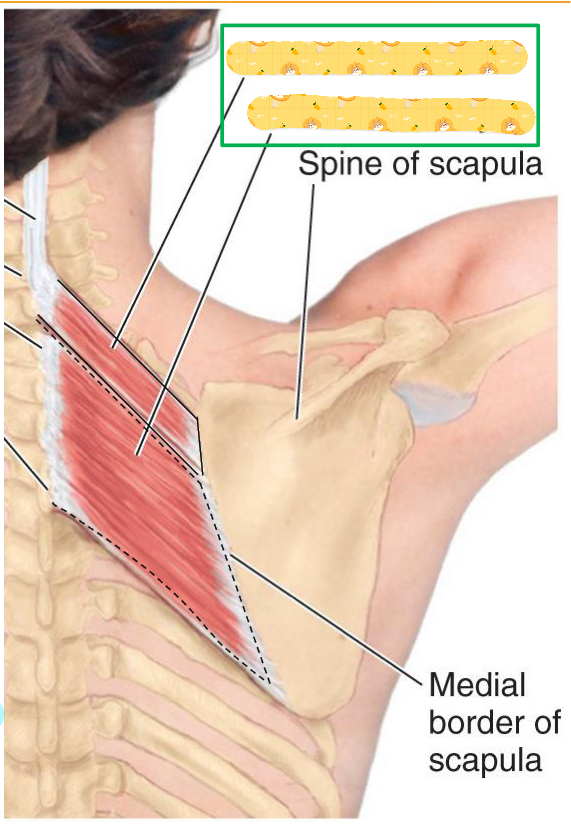
Insertion: scapula (medial border)
Action: Retracts, medially rotates, and fixes scapula to thoracic wall
Innervation: Dorsal scapular nerve
Rhomboids
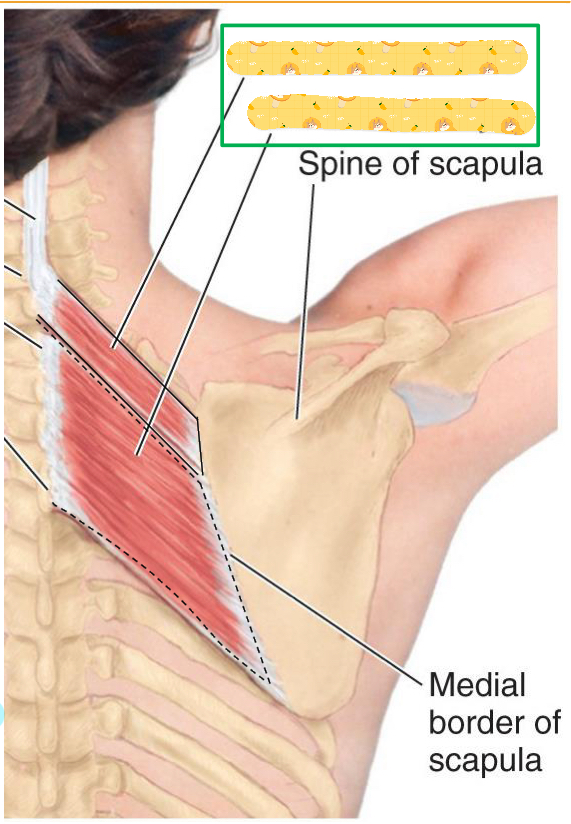
Name this muscle
Rhomboids
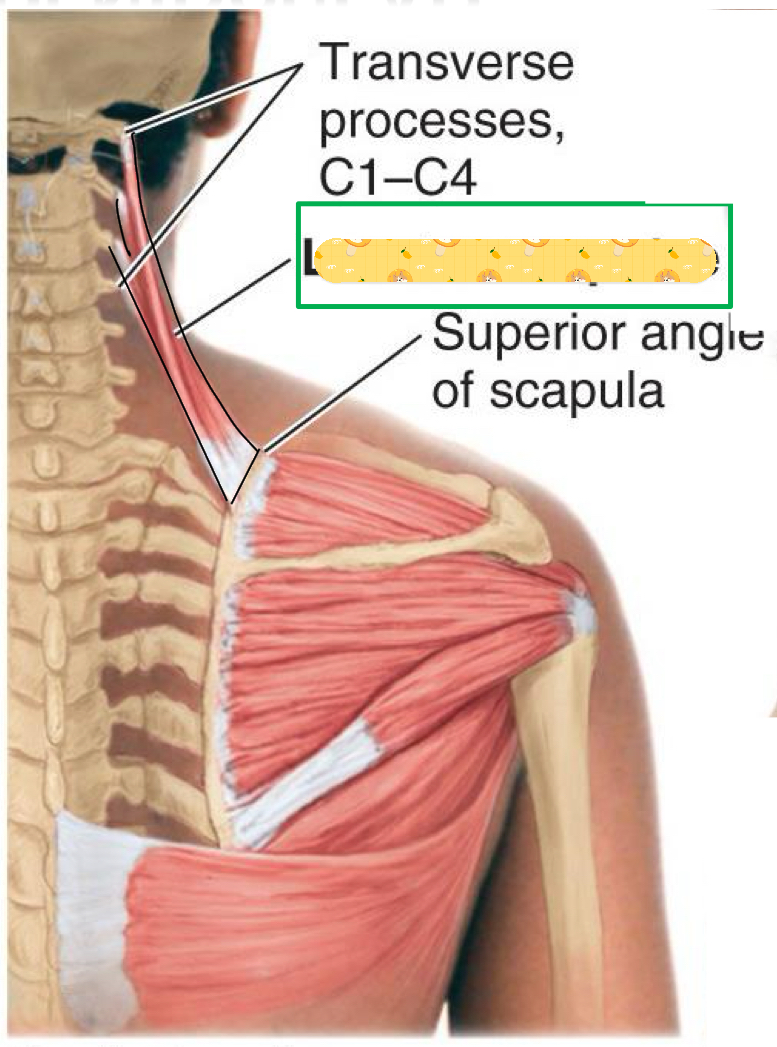
Origin: Transverse processes of C1-C4 Vertebrae
Insertion: scapula (superior angle)
Action: Scapular rotation and elevation
Insertion: Dorsal scapular nerve & cervical nerve
Levator scapulae
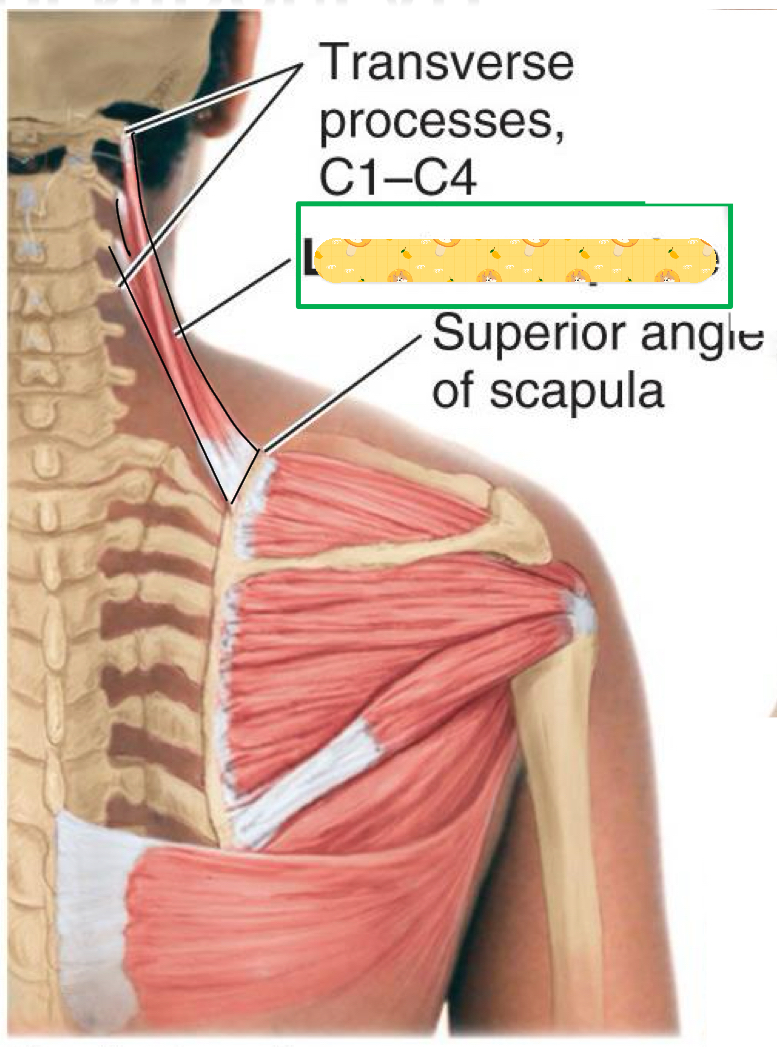
Name this muscle
Levator scapulae
Scapulohumeral muscles
Deltoid, Teres major, Rotator cuff muscles (SITS)
Origin: Clavicle, acromion, and spinous process
Insertion: deltoid tuberosity
Action: Shoulder flexion, extension, medial rotation, lateral rotation, abduction, and stabilizes shoulder
Innervation: Axillary nerve
Deltoid
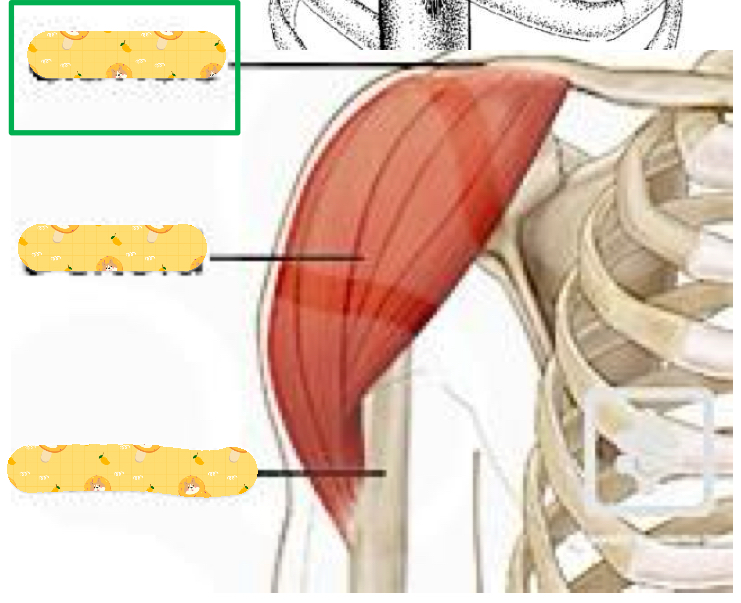
Name these structures
Clavicle, deltoid, humerus
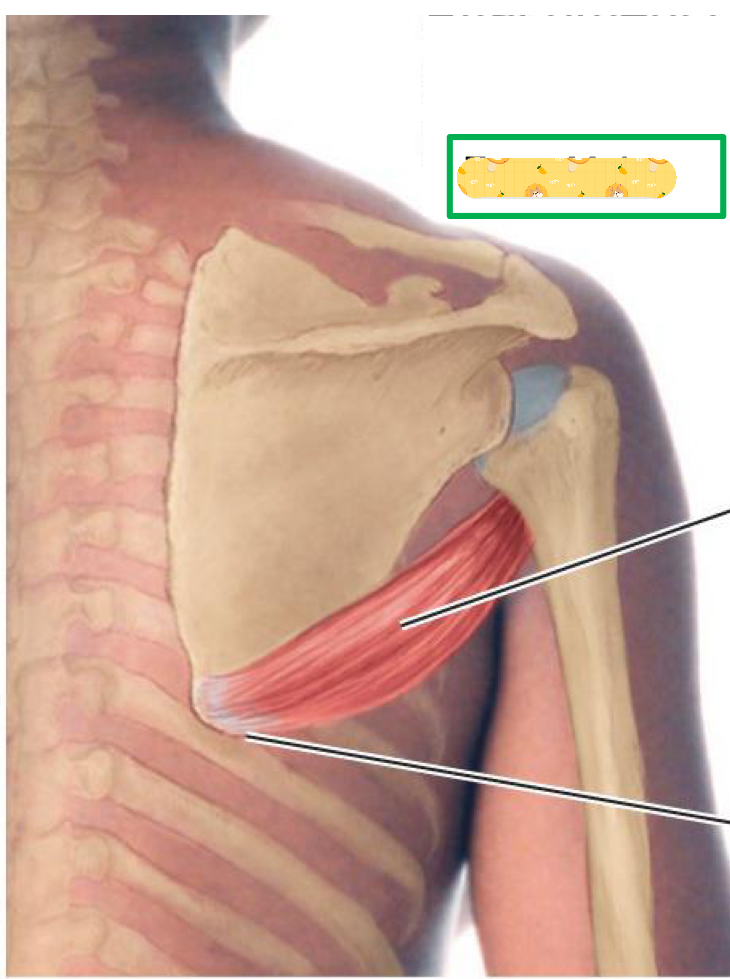
Origin: inferior angle of scapula
Insertion: intertubercular groove
Action: Arm adduction, medial rotation, and stabilizes GH joint during abduction
Innervation: Lower subscapular nerve
Teres Major
Rotator cuff muscles
Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres minor, Subscapularis
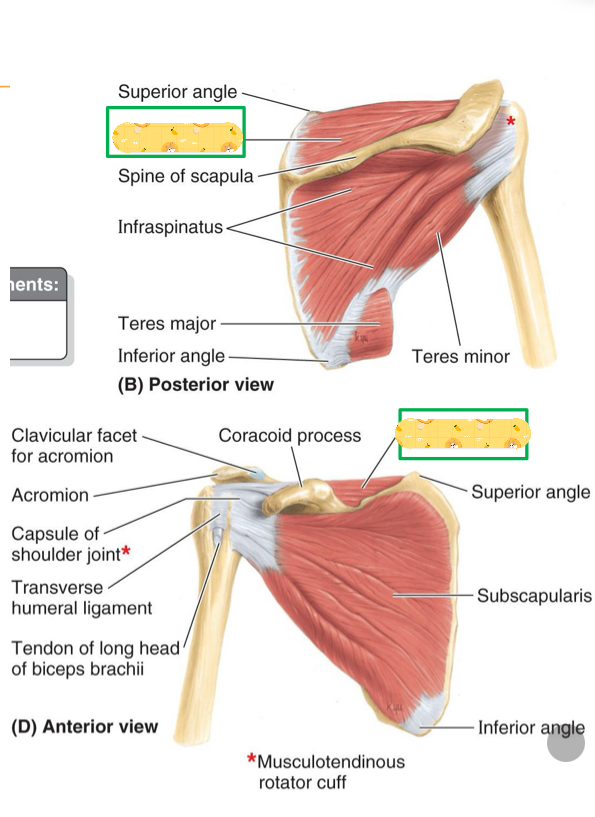
Origin: Supraspinous fossa of scapula
Insertion: Greater tubercle
Action: Initiates arm abduction, stabilizes glenohumeral joint
Innervation: subscapular nerve
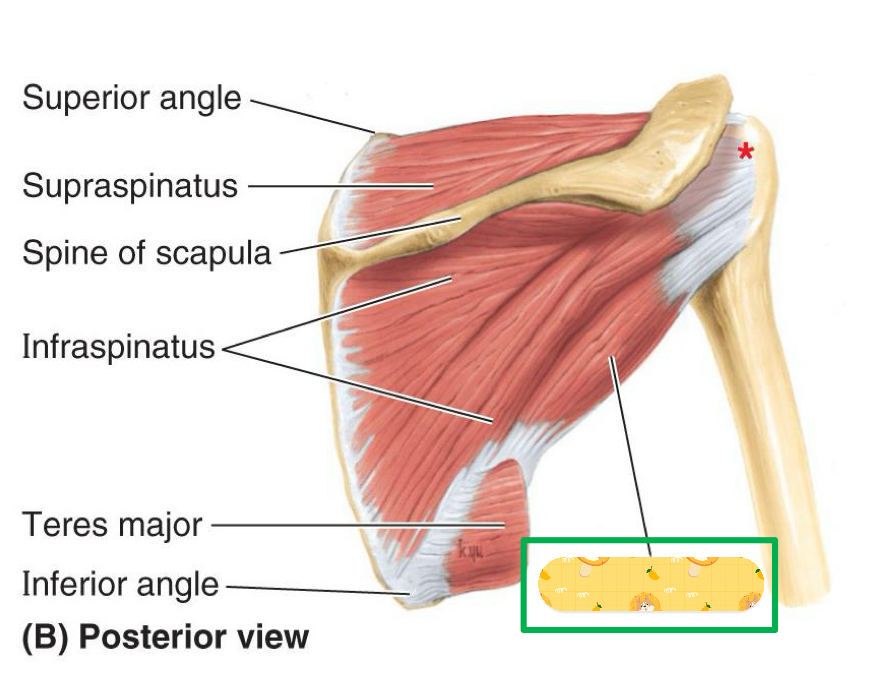
Supraspinatus
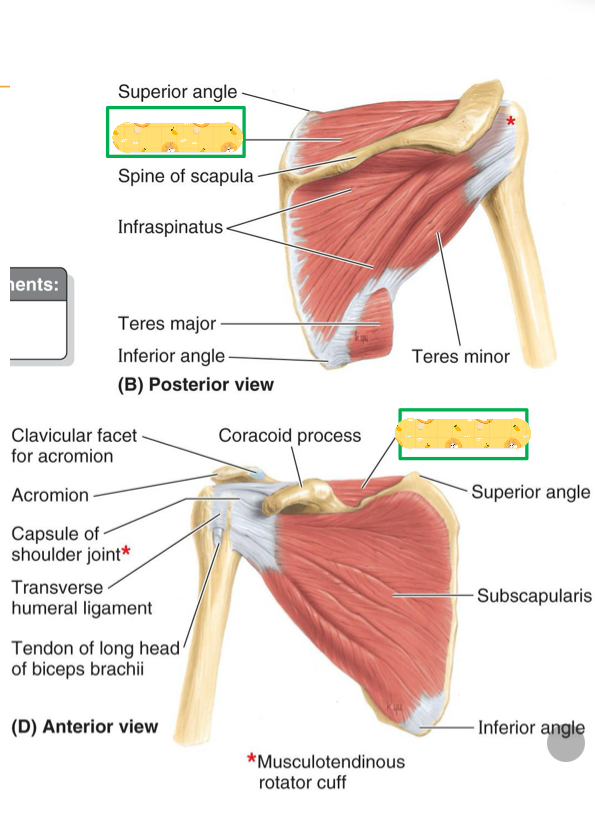
Name this muscle
Supraspinatus
Origin: infraspinous fossa of scapula
Insertion: Greater tubercle
Action: Arm lateral rotation, stabilizes GH joint
Innervation: Suprascapular nerve
Infraspinatus
Rotator cuff injuries
Caused by repetitive-type throwing activities
First appears as Tendonitis but continuous activity leads to tear due to overuse and no healing time.
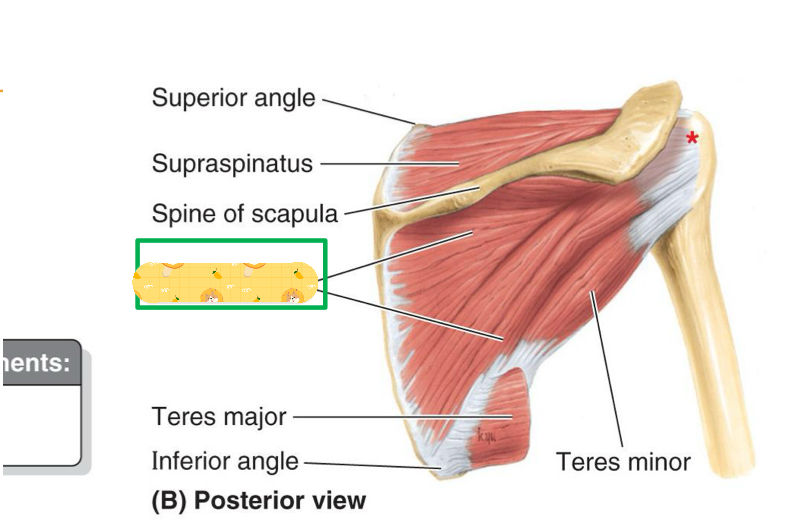
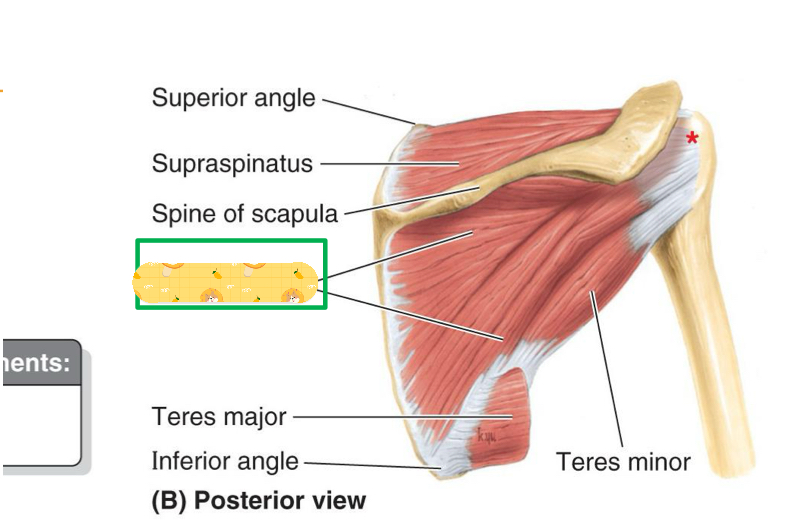
Name this muscle
Infraspinatus
Origin: Lateral border of scapula
Insertion: Greater tubercle
Action: Arm lateral rotation, stabilizes GH joint
Innervation: Axillary nerve
Teres minor
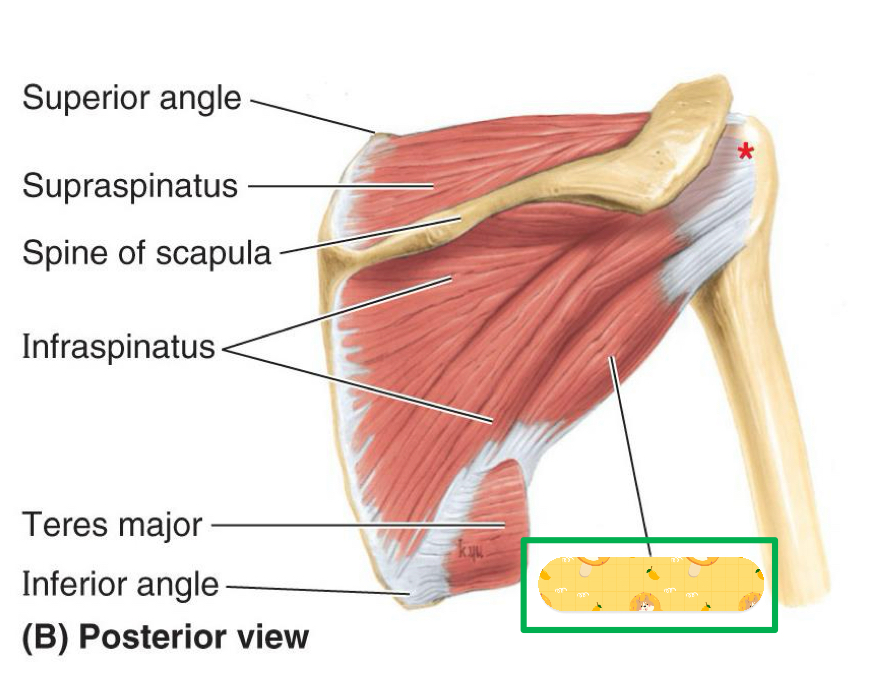
Name this muscle
Teres minor
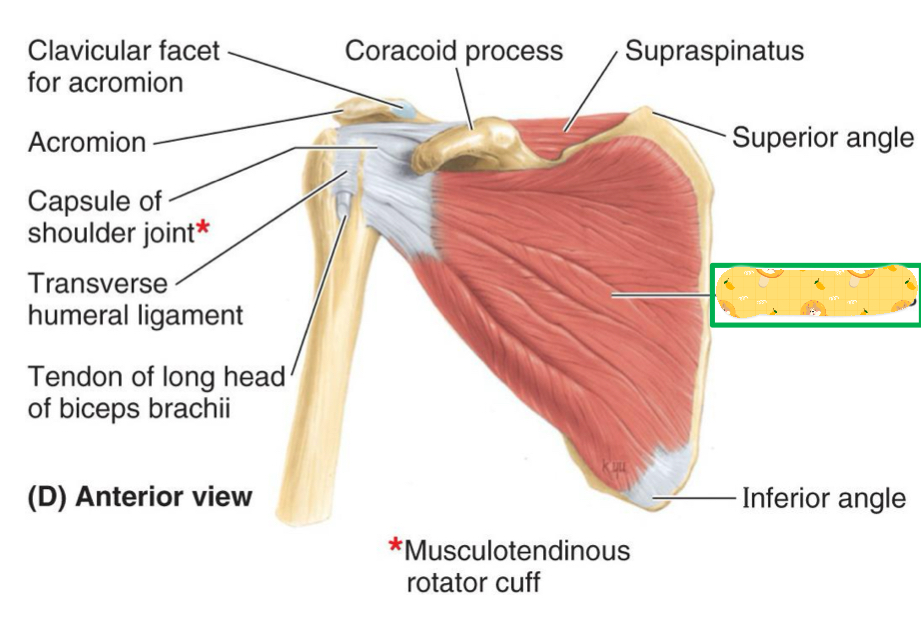
Origin: subscapular fossa of scapula
Insertion: Lesser tubercle
Action: Arm medial rotation, stabilizes GH joint
Innervation: Subscapular nerve
Subscapularis
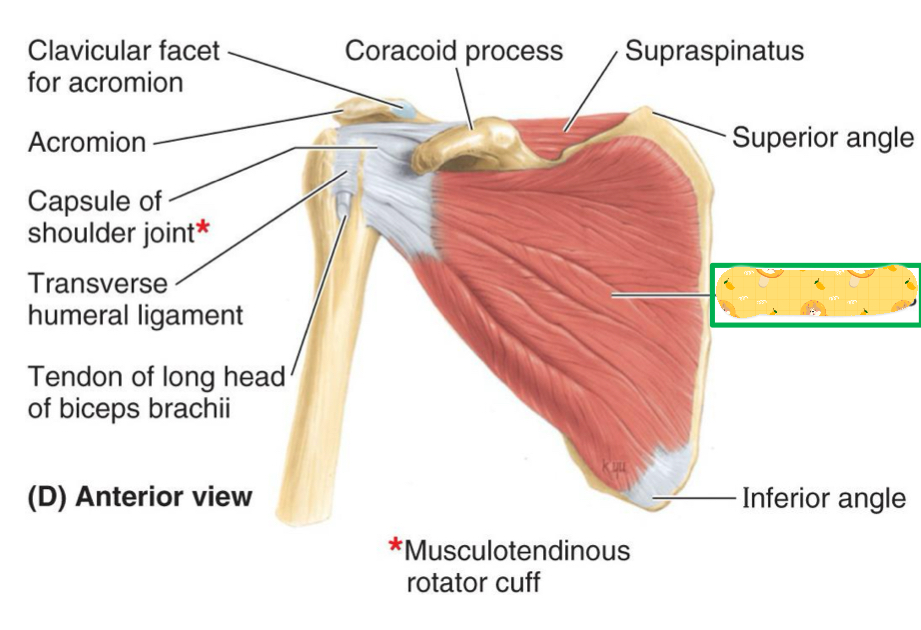
Name this muscle
Subscapularis
Rotator Cuff injuries
Caused by repetitive-type throwing activities
First appears as tendonitis but leads to tear from continuous activities due to overuse and no time for healing.
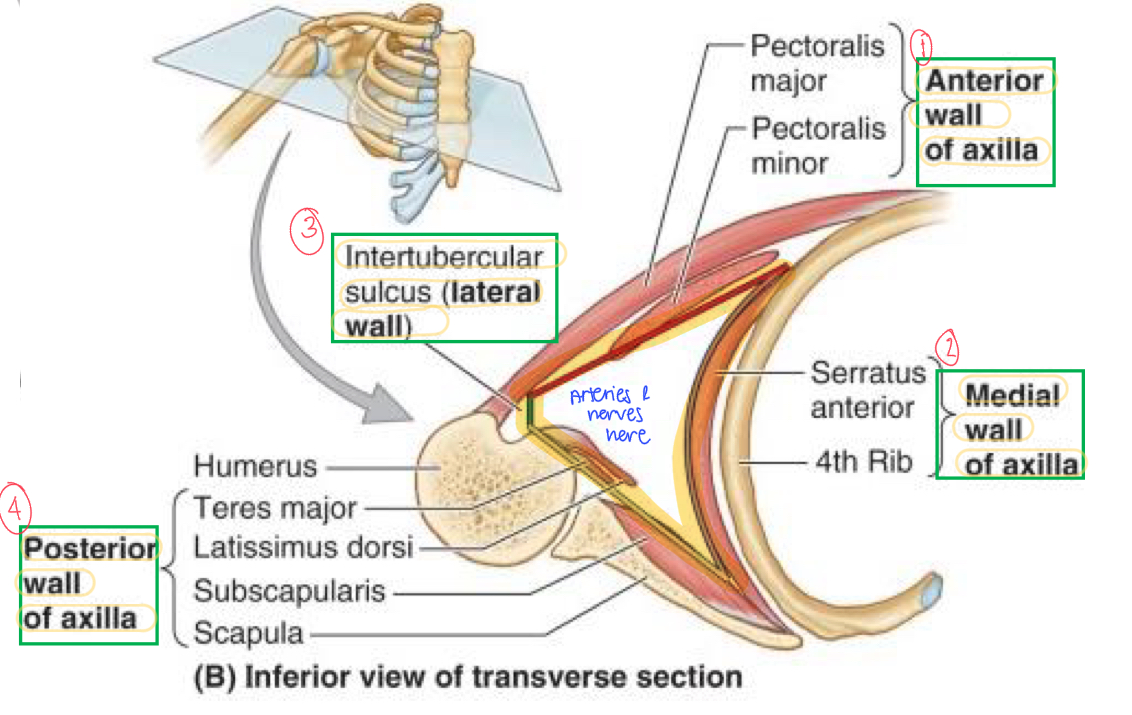
Axillary boundaries
Apex, Base, Ant. Wall, Post. Wall, Medial Wall, Lateral Wall
Apex contains…
1st rib & clavicle
Base contains…
Axillary fascia
Ant. Wall contains…
Pec major & fascia
Post. Wall contains…
Scapula, subscapularis, teres major, & lats.
Medial wall contains…
Thoracic wall, serratus anterior (ribs 1-4)
Lateral wall contains…
Intertubercular groove
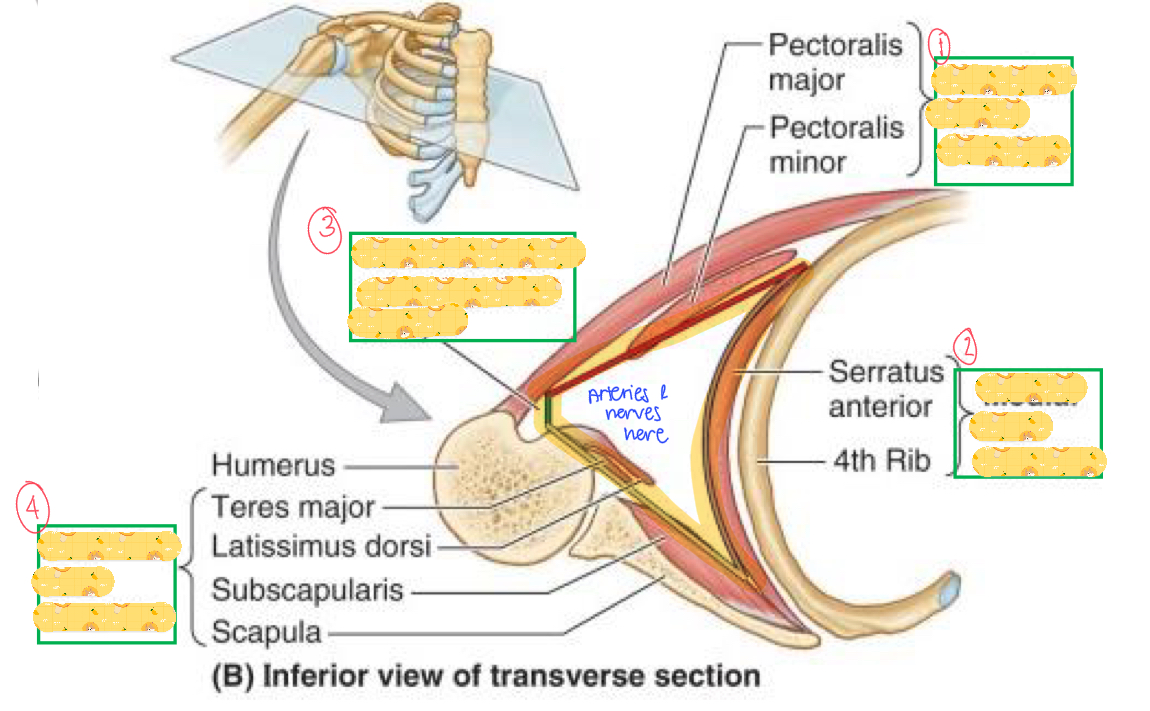
Name these structures
Anterior wall
Medial wall
Intertubercular sulcus (lateral wall)
Posterior wall
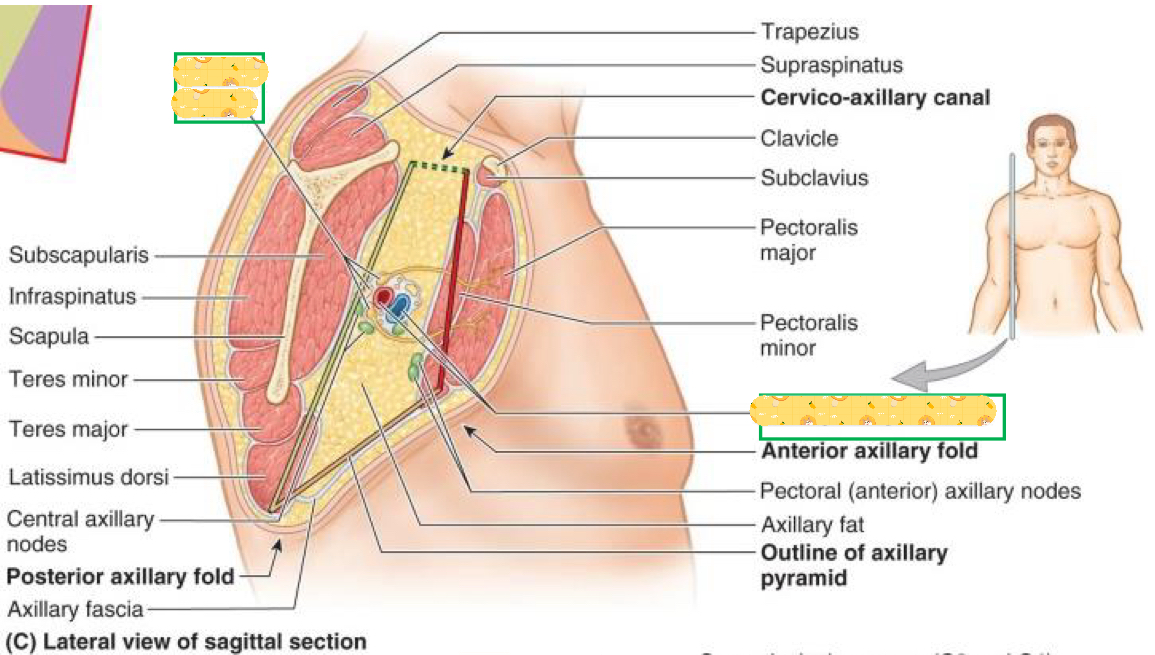
Name these structures
Brachial plexus
Axillary artery and vein
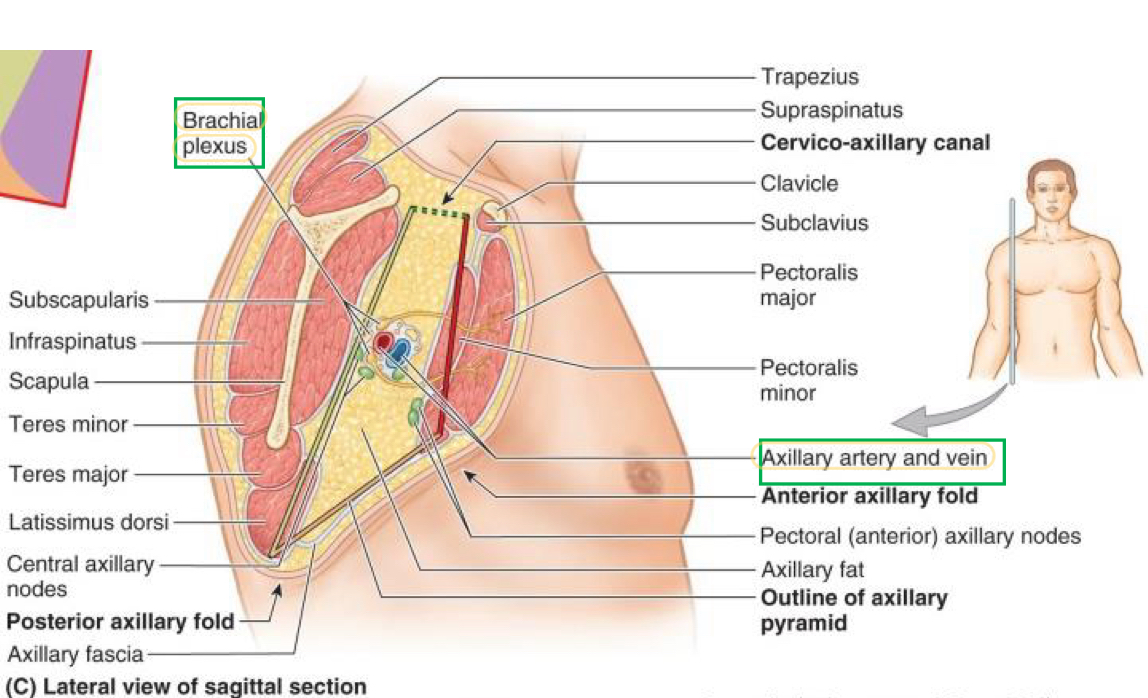
Axilla contents
Axillary vein & branches
Axillary artery & branches
Lymph vessels & nodes
Brachial plexus
Axillary sheath
A dense sheath that encloses all the contents of the axilla
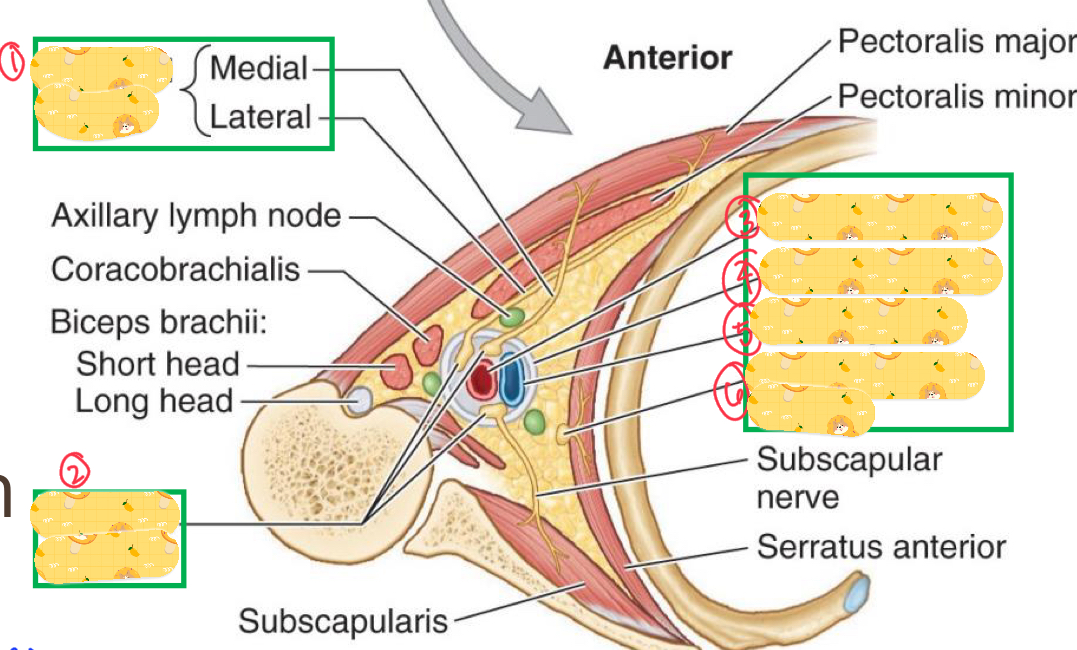
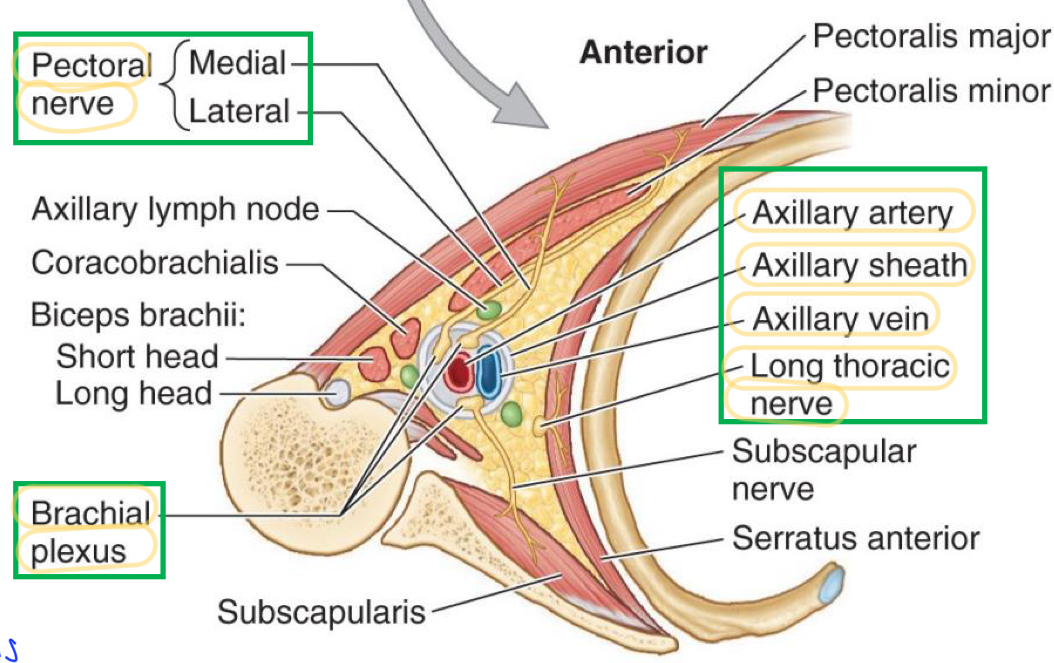
Name these structures
Pectoral nerve
Brachial plexus
Axillary artery
Axillary sheath
Axillary vein
Long Thoracic nerve
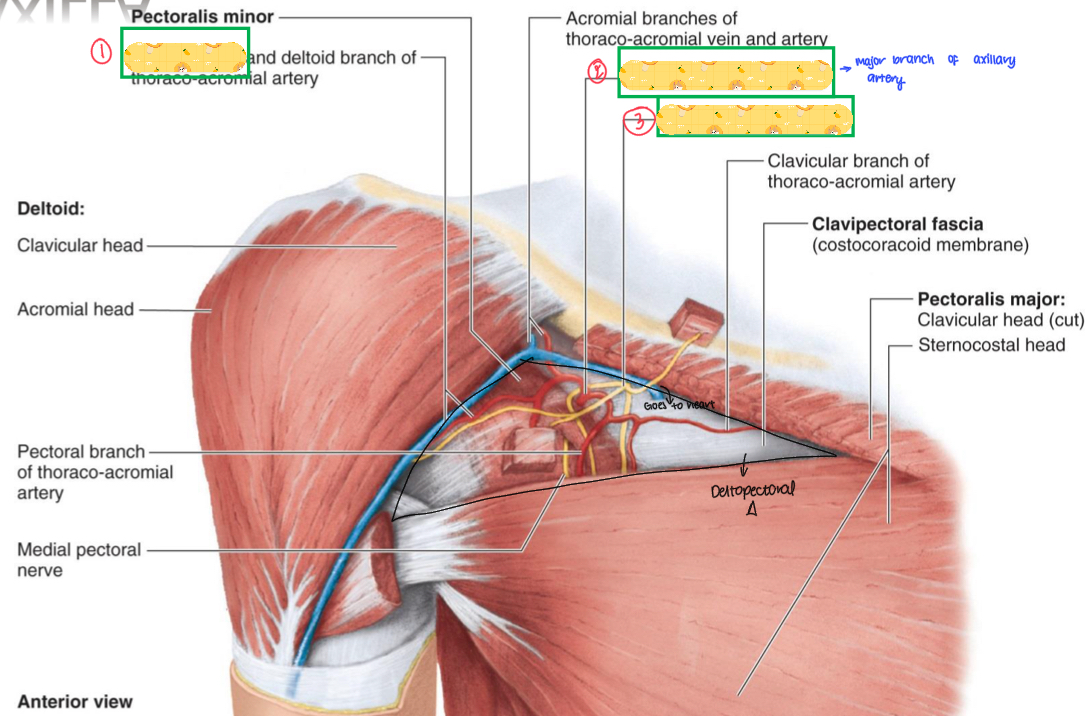
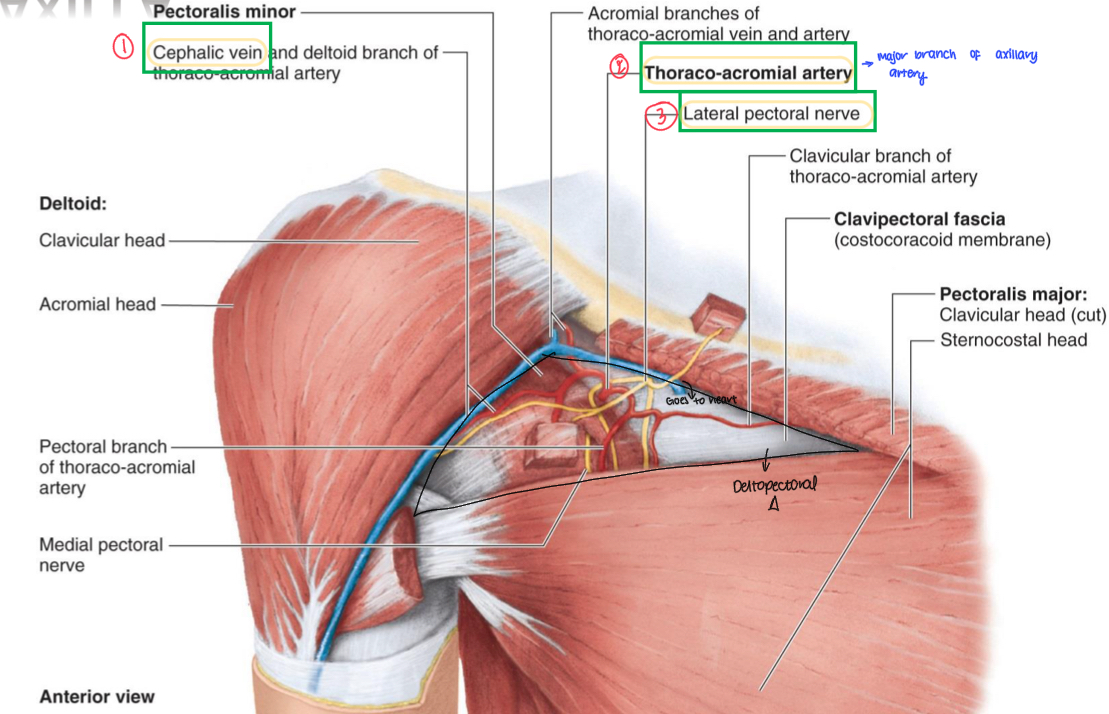
Name these structures
Cephalic vein
Thoracoacromial artery
Lateral pectoral nerve

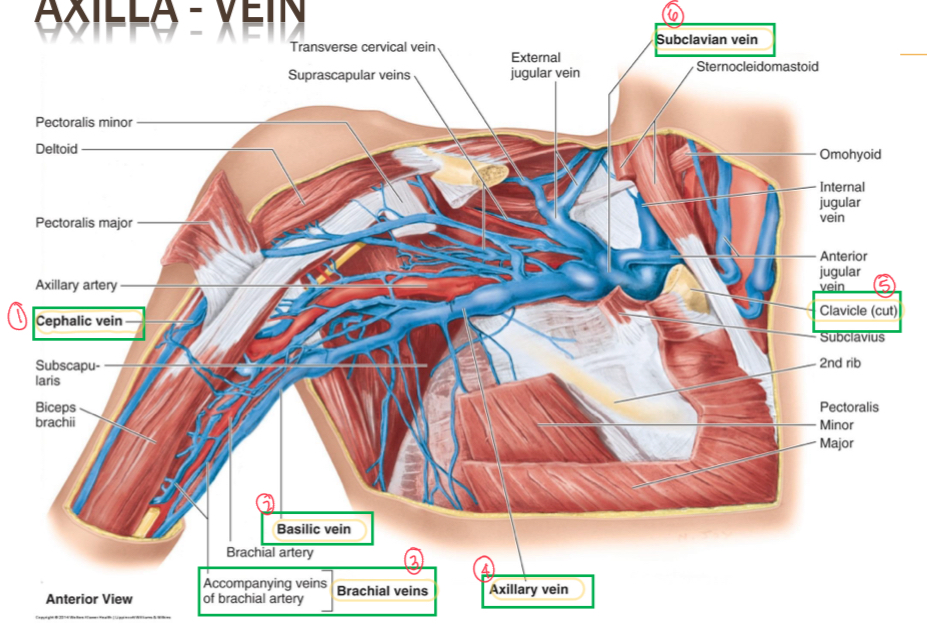
Name all the axillary veins
Cephalic vein
Basilic vein
Brachial veins
Axillary vein
Clavicle
Subclavian vein
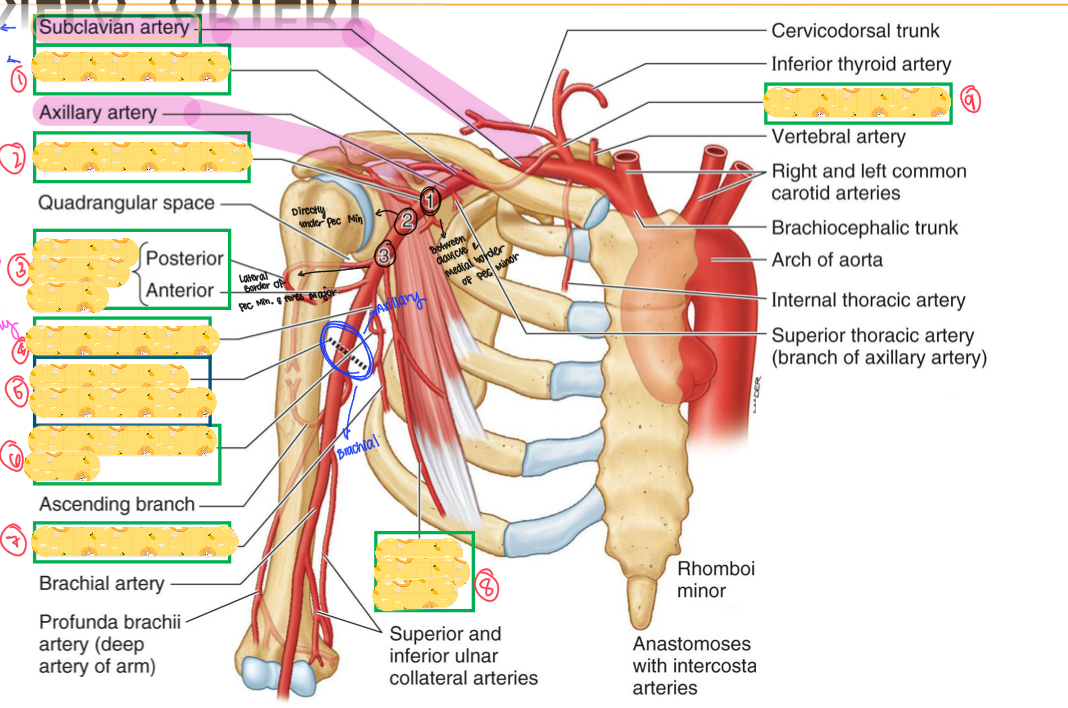
Name all these structures
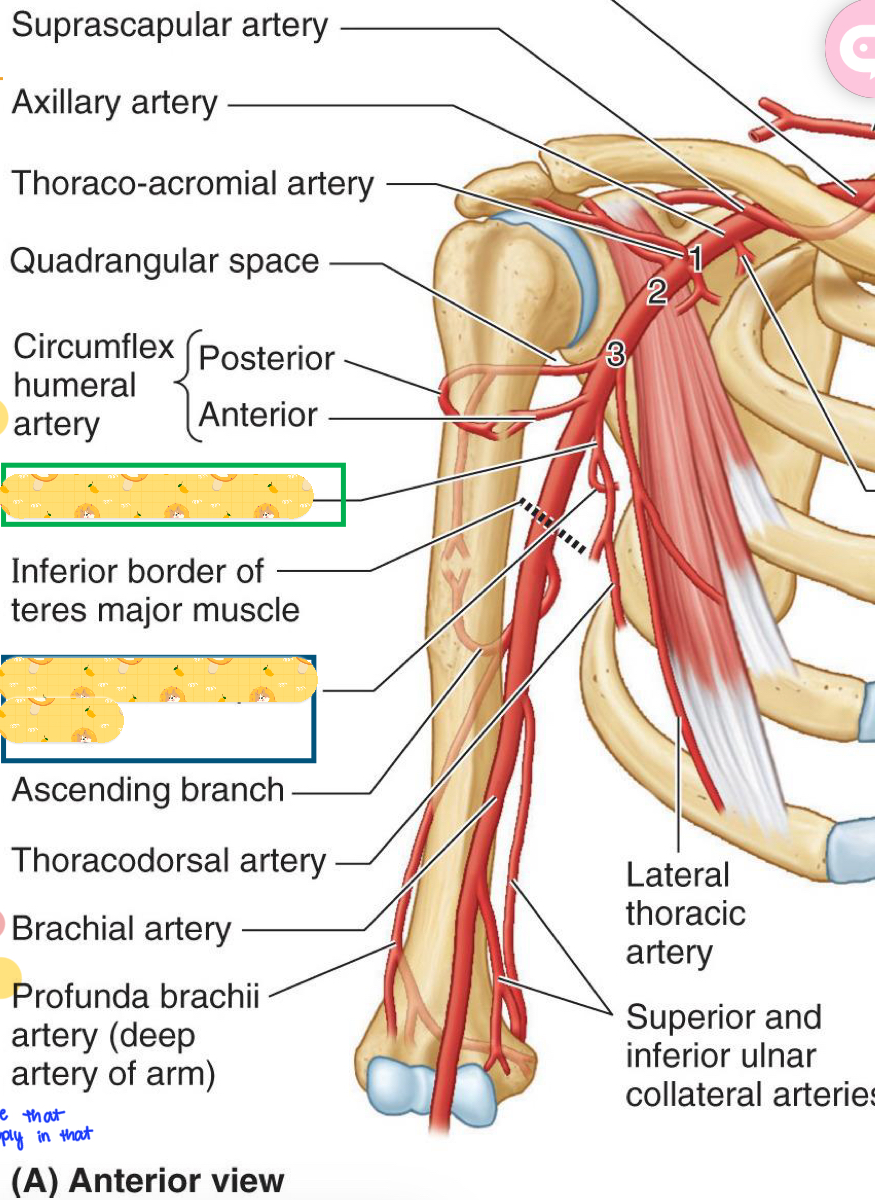
Suprascapular artery
Thoracoacromial artery
Circumflex humeral artery
Subscapular artery
Inferior border of teres major
Circumflex scapular artery
Thoracodorsal artery
Lateral thoracic artery
Thyrocervical artery
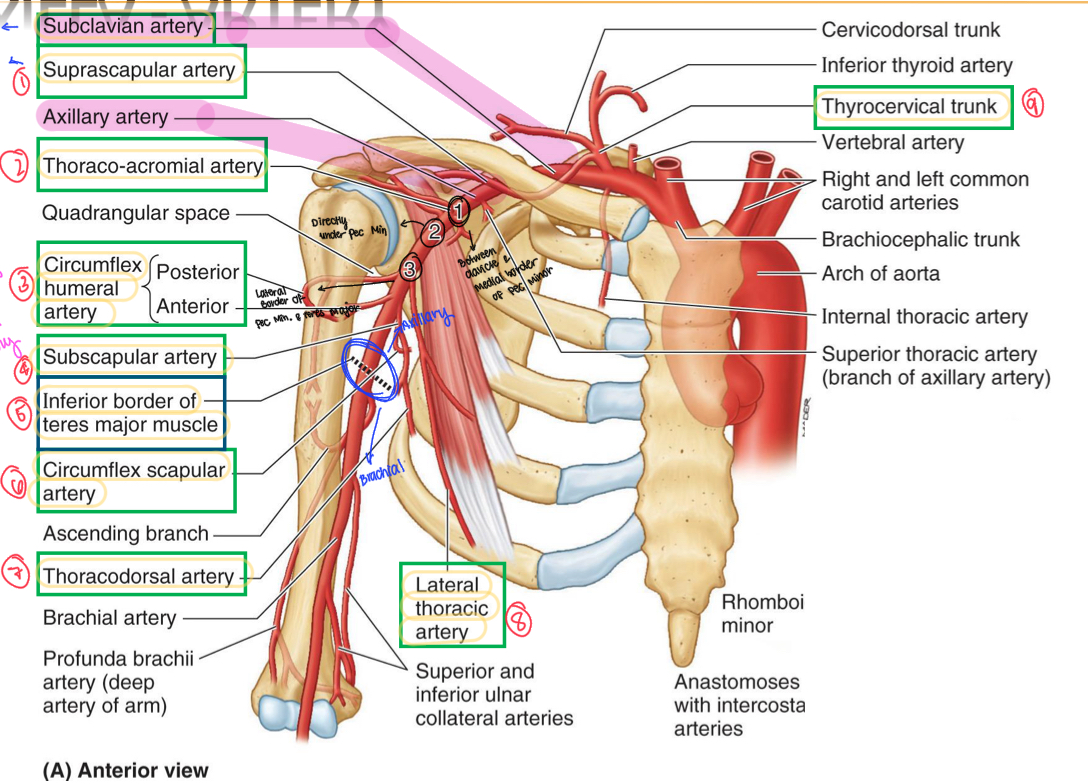
Starts from the 1st rib to medial border of pec minor
Is found inferior, medial, posterior to axillary vein
Contains the superior thoracic artery (supplies 1st and 2nd costal spaces and serratus anterior)
Axillary 1
Superior thoracic artery
Found in Axillary 1
Supplies 1st and 2nd costal spaces and serratus anterior

Name this structure
Superior thoracic artery
Found medial to and posterior to pec minor
Inferior, medial, and posterior to axillary vein
Contains the thoracoacromial artery and lateral thoracic artery
Axillary 2
Trunk/artery that has 4 branches: acromial, deltoid, pectoral, and clavicular
Thoracoacromial artery
Artery found along the lats
Border of pec minor
Supplies pec muscles, axillary lymph nodes and breast, & serratus anterior
Lateral thoracic artery
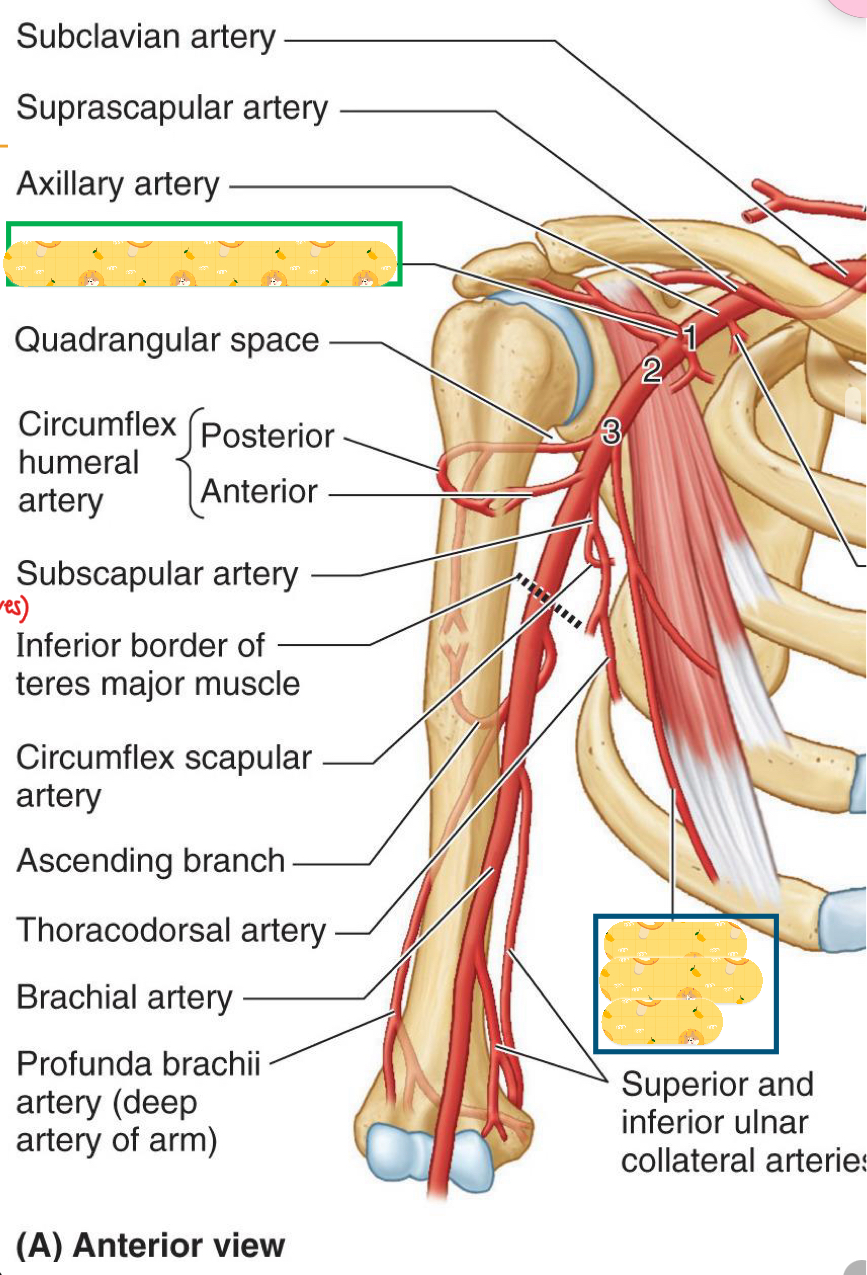
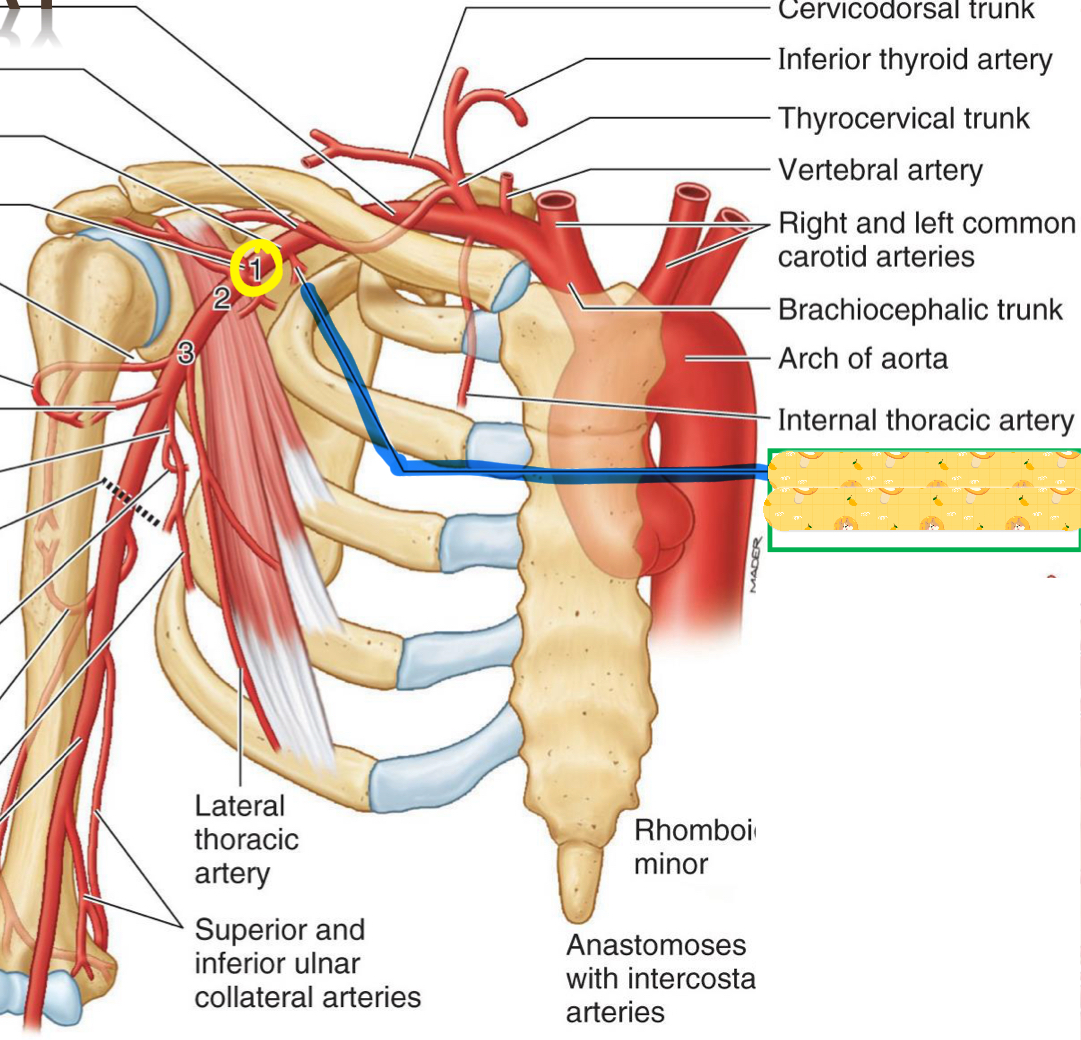
Name these structures
Thoracoacromial artery
Lateral thoracic artery
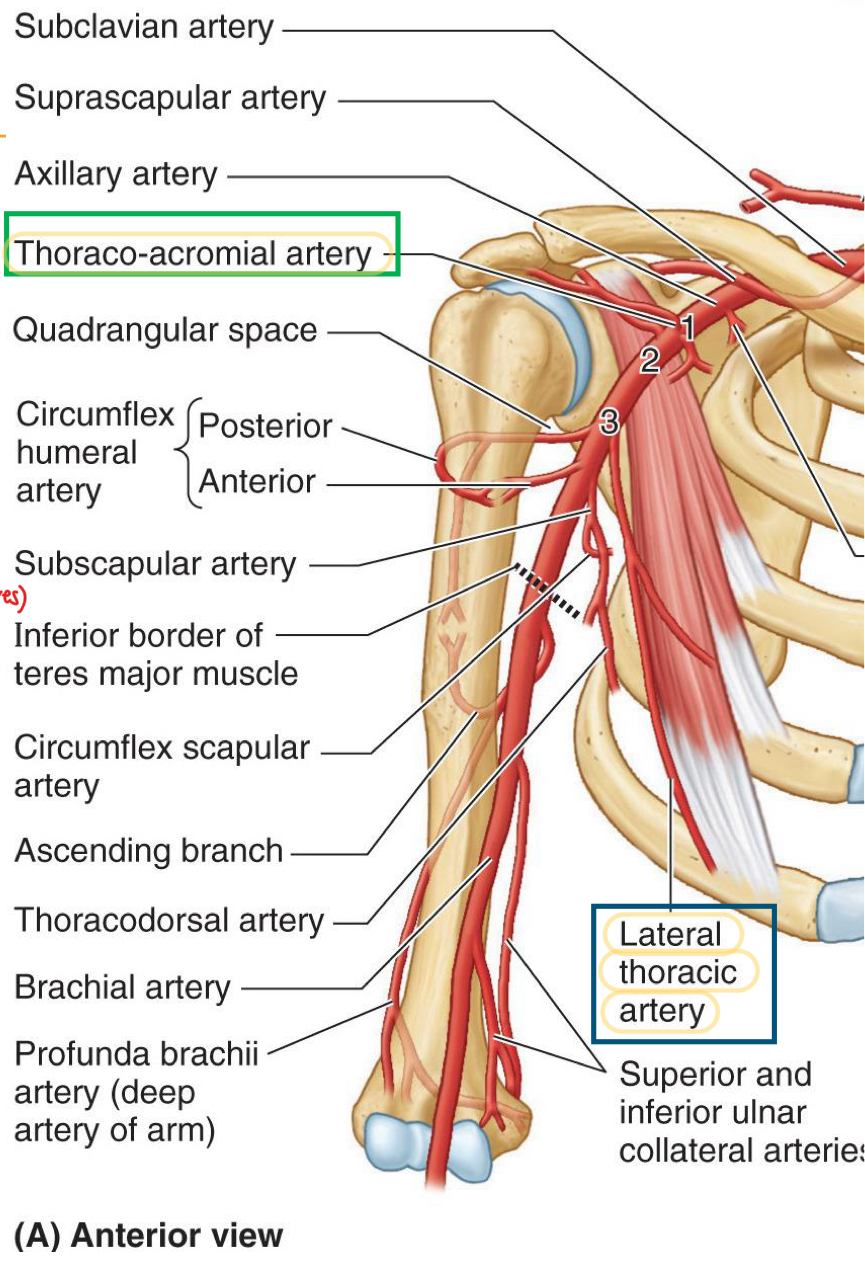
Starts from the lateral border of pec minor to inferior border of teres major
Contains the subscapular artery, which divides into circumflex scapular artery
Also contains the thoracodorsal artery and anterior & posterior circumflex humeral arteries.
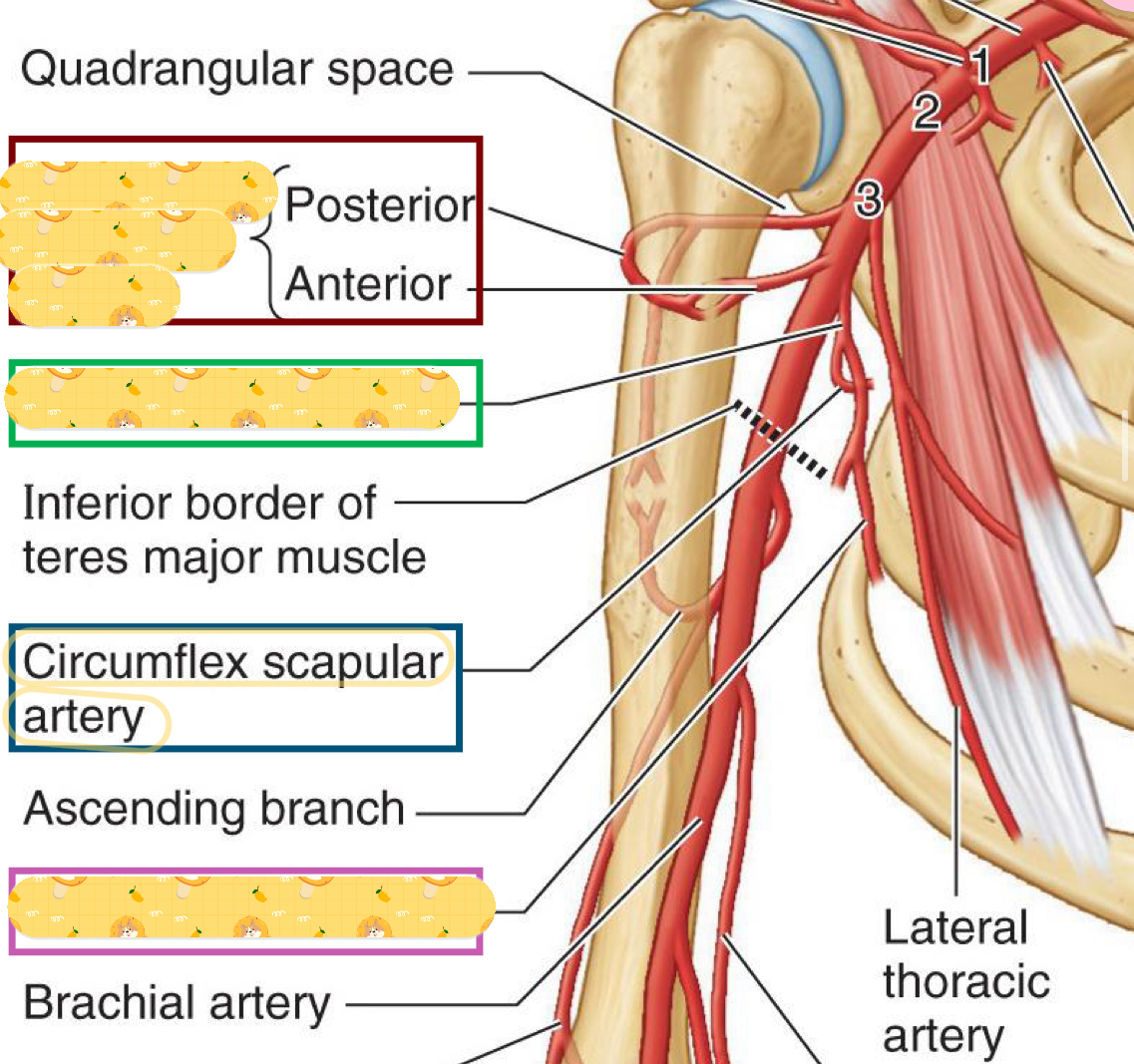
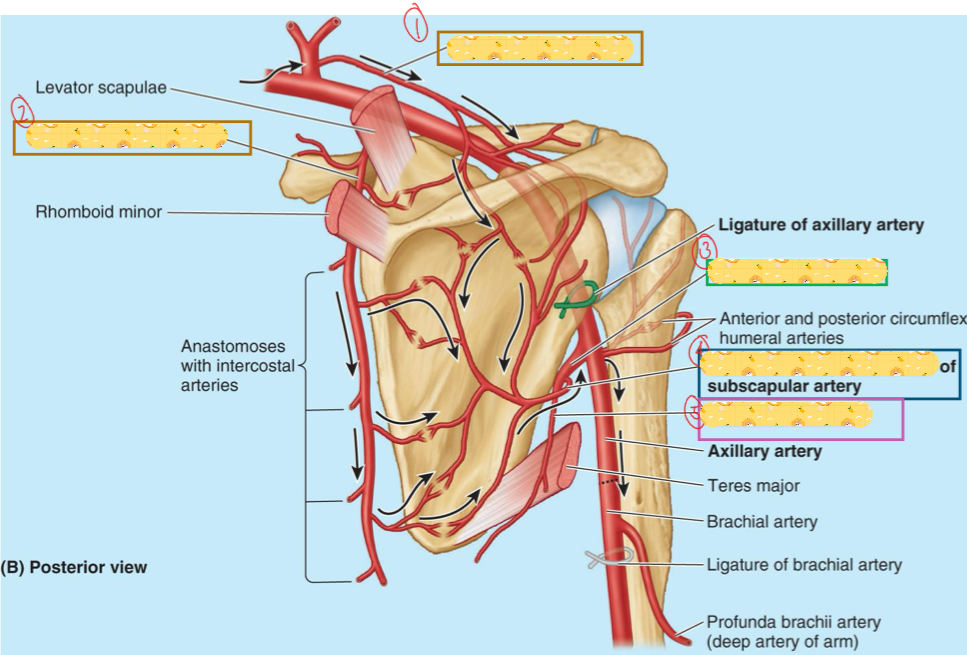
Where you will find the quadrangular space
Axillary 3
Found in axillary 3, along the lateral border of subscapularis to posterior axillary wall
Subscapular artery
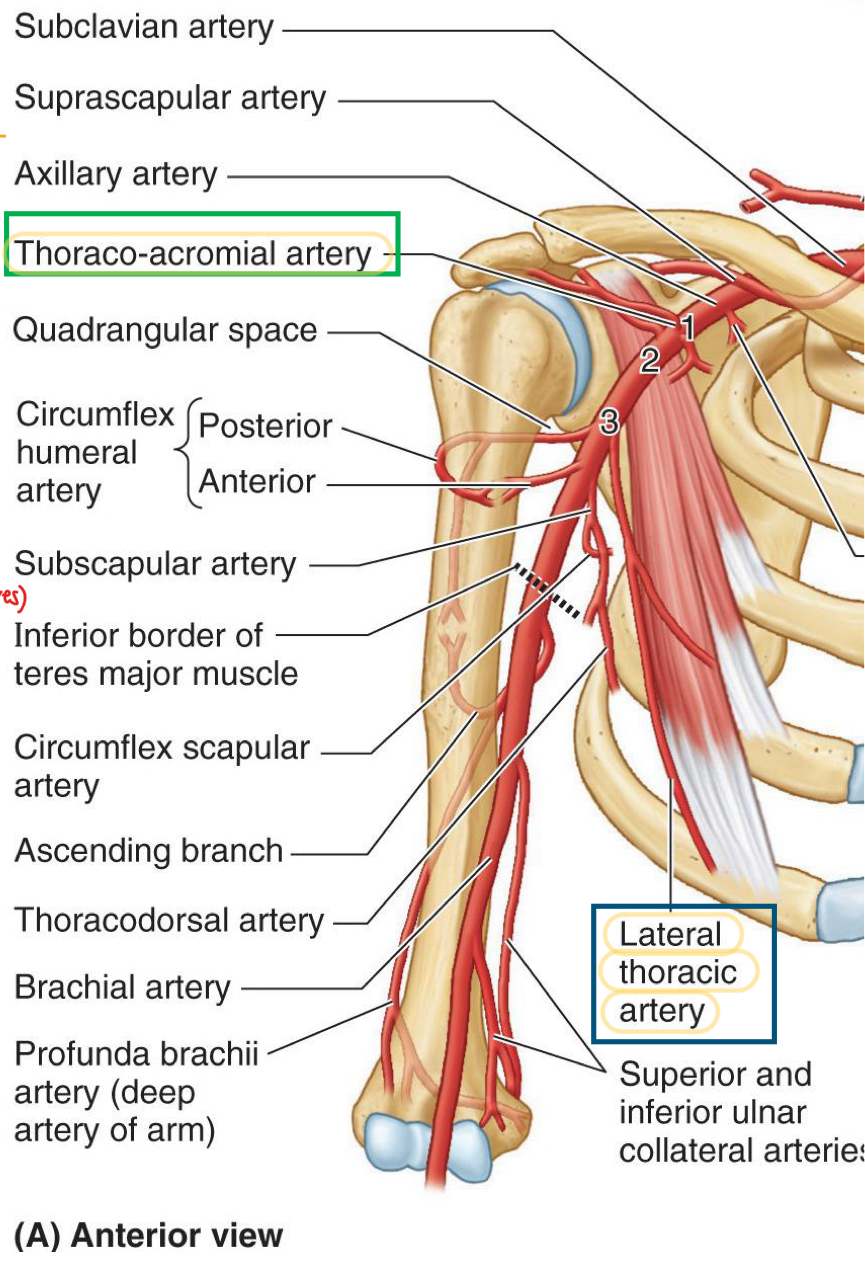
Divides from the subscapular artery and passes posterior along lateral border of subscapularis.
Supplies subscapularis, teres major
Anastomosis with dorsal scapular & suprascapular arteries
Circumflex scapular artery
Continuation of subscapular artery
contributes of anastomosis around scapula
Supplies lats (main job of this artery)
Thoracodorsal artery
Branch lateral
Anterior-deep to biceps brachii
Posterior part of this artery is found posterior with axillary nerve in the Quadrangular space
Supplies deltoid (mainly), teres major & minor, and triceps
Anterior and posterior circumflex humeral arteries
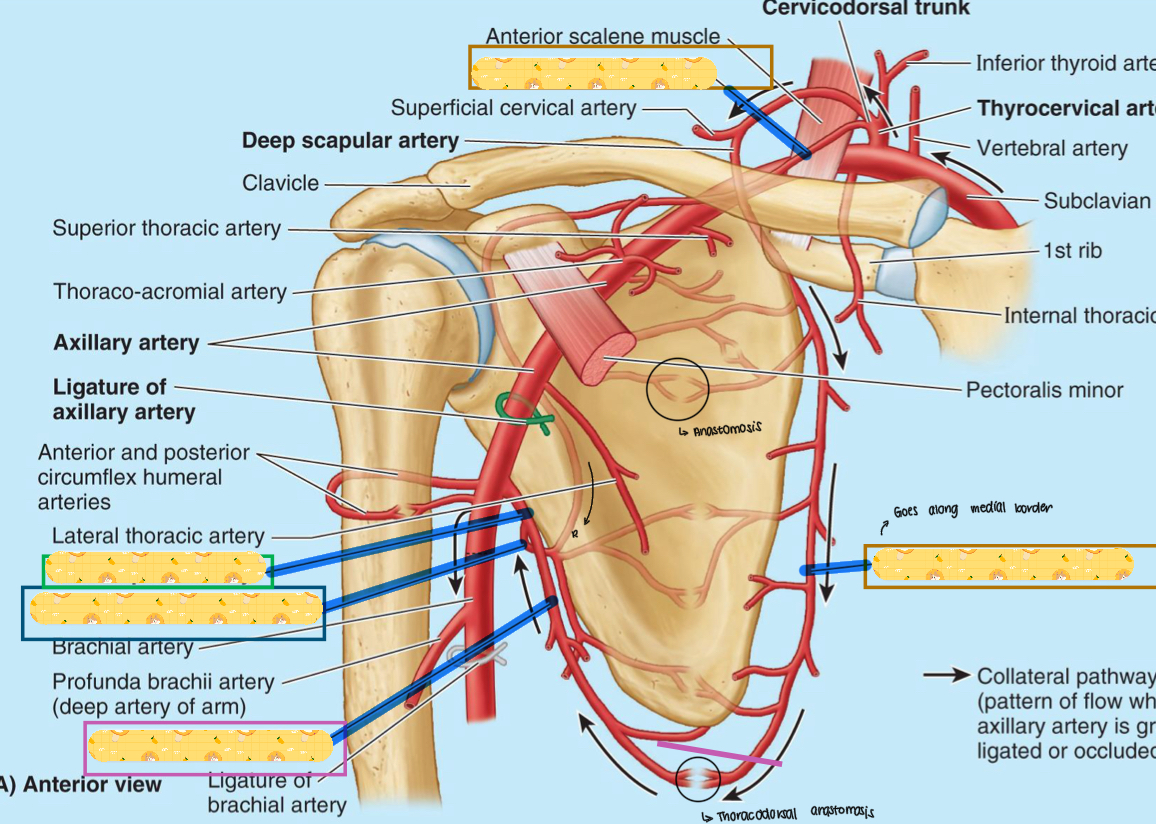
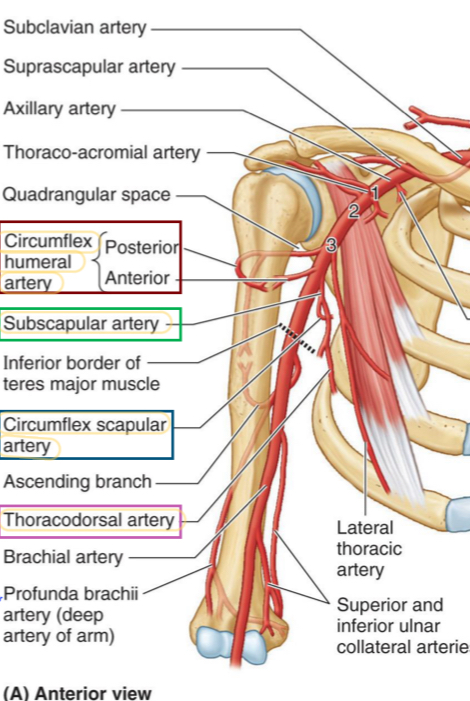
Name these structures
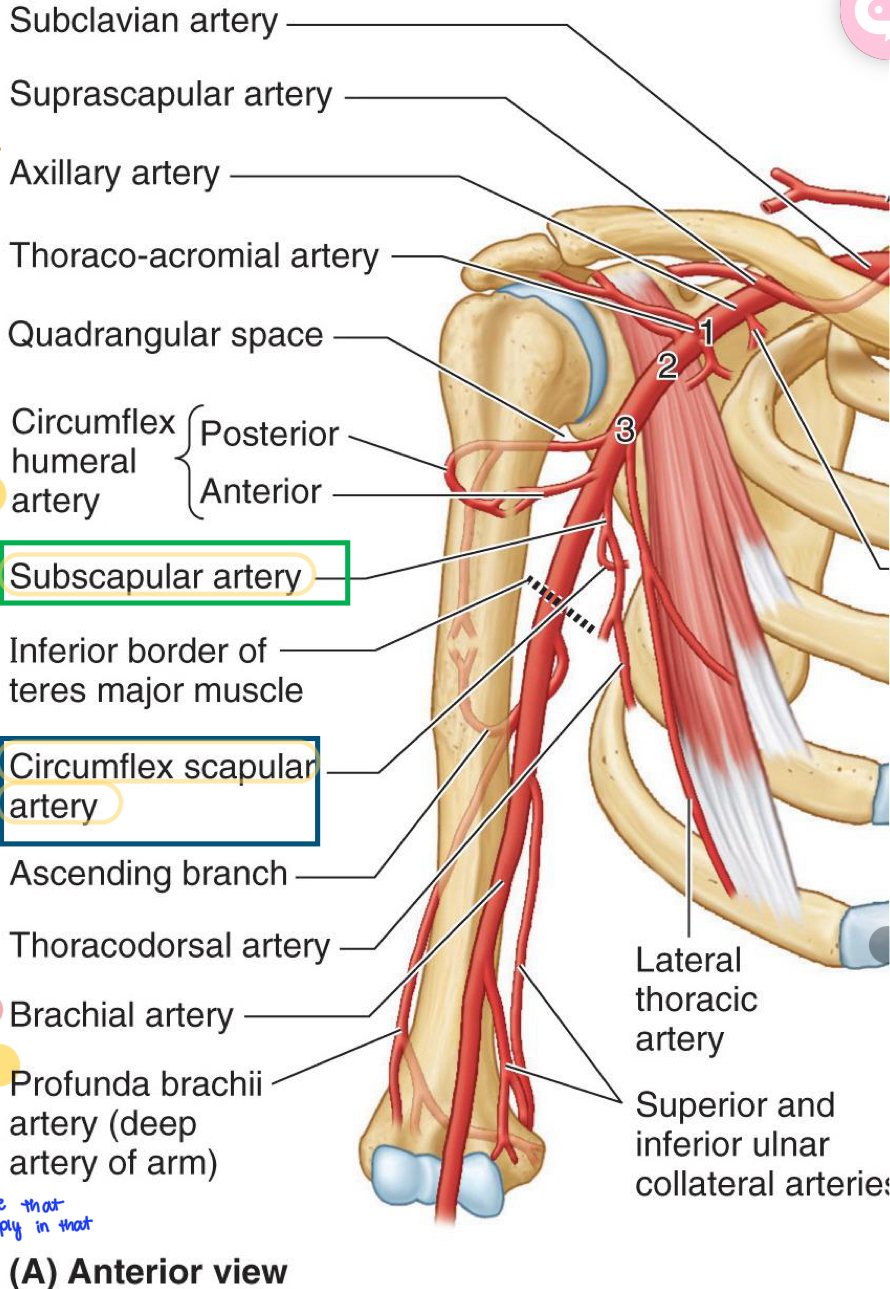
Suprascapular artery
Subscapular artery
Circumflex scapular artery
Thoracodorsal artery
Dorsal scapular artery
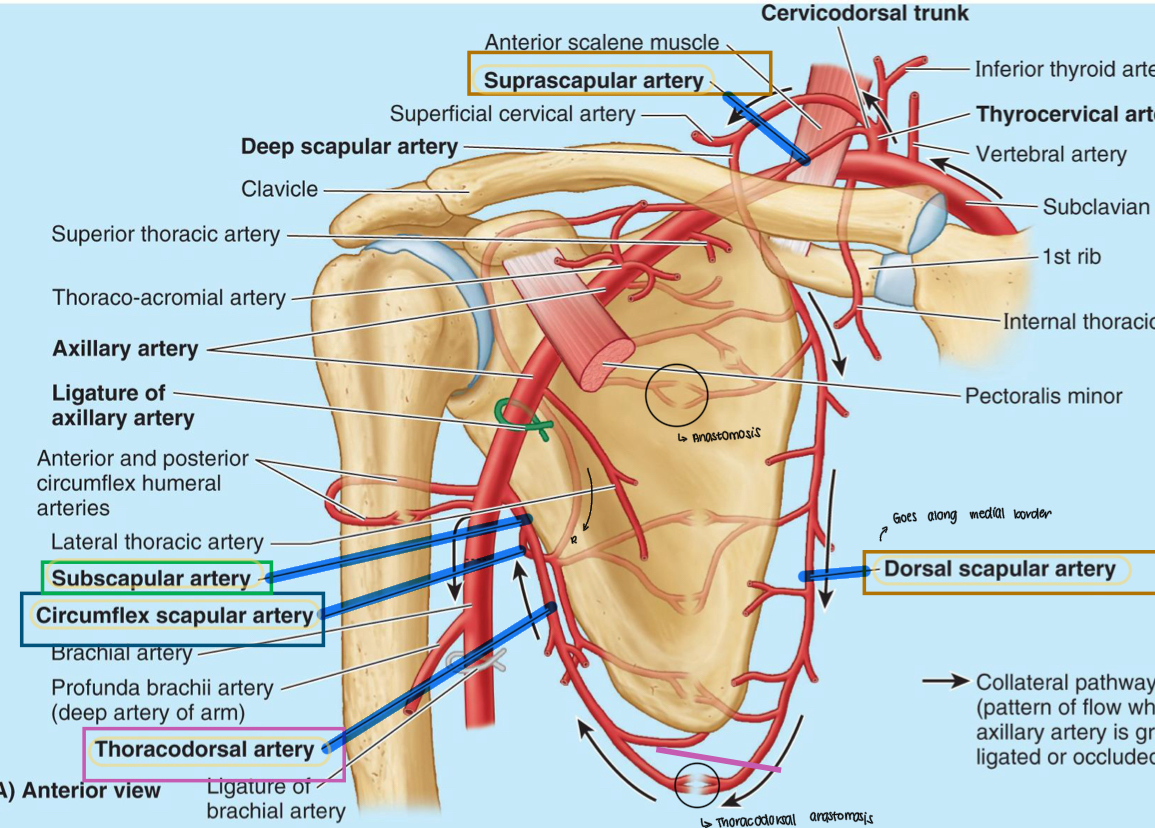
Name these structures
Suprascapular artery
Dorsal scapular artery
Circumflex scapular artery
Thoracodorsal artery
Formed when the anterior rami of spinal nerves combine and then bifurcate to form nerve branches consisting of motor and sensory neurons from 2 or more spinal nerves
Redistribution from an orderly array to apparent disarray
Composed of: 1) mixed somatic motor, 2) somatic sensory, & 3) sympathetic nerve fibers
Nerve plexus
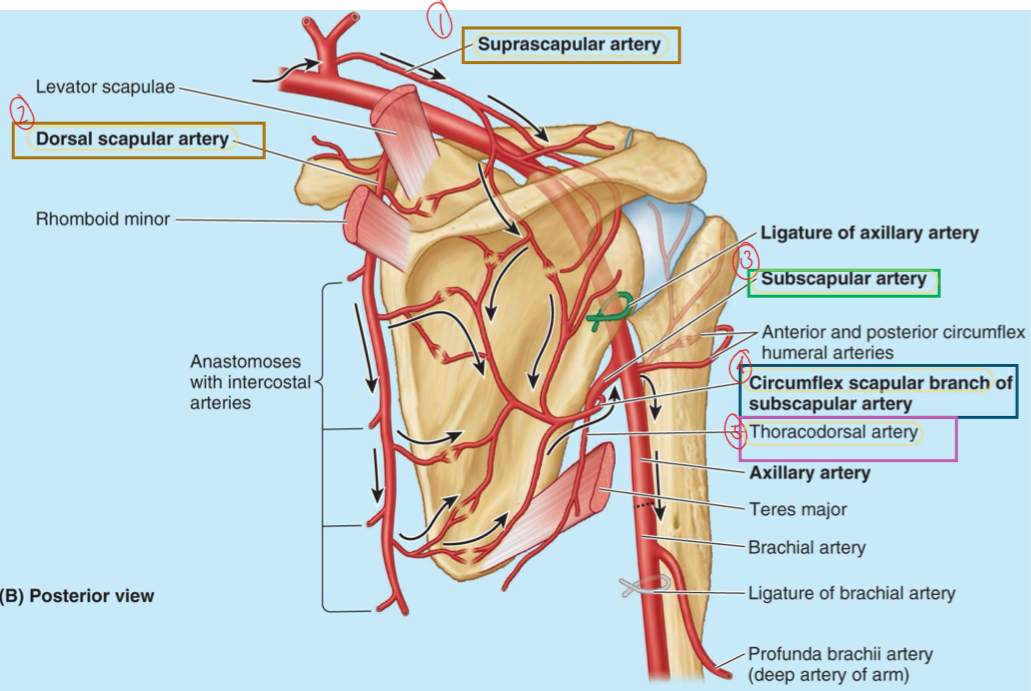
Name these structures
Subscapular artery
Circumflex scapular artery
C5, C6, C7, T1, T2
5 roots of the brachial plexus
Superior, middle, inferior
3 trunks of the brachial plexus
6 divisions