Properties of Waves
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
In a transverse waves, what direction are the oscillations?
The oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer.
In longitudinal waves, what direction are the oscillations?
The oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer.
What is the purpose of waves?
Waves transfer energy from one place to another.
What is the amplitude?
The maximum displacement of the wave (m)
What is the wavelength?
The distance between 2 equivalent parts of the wave (one oscillation)
What is the trough of a wave?
The bottom of a wave.
What is the time period of a wave?
The time it takes for one complete oscillation.
What is the frequency of a wave?
The number of complete waves passing a point each second. Measured in hertz (HZ)
What are examples of transverse waves?
Electromagnetic waves (radiowaves, X-rays,microwaves,visible light etc), waves on a string or wire, ripples in water,
How do you calculate the time period of a wave?
Time period = 1/ frequency
What are examples of longitudinal waves?
Sound, some shock waves, waves on a slinky
Describe the movement of particles in longitudinal waves
The surface air pushes air molecules away which push adjacent air molecules which push adjacent air molecules etc.. They show areas of compression and rarefaction (an area of reduced pressure)
What is a mechanical wave?
A wave that causes oscillations of particles in a solid, liquid or gas and must have a medium to travel through. Can be longitudinal or transverse.
What is an electromagnetic wave?
A wave that causes oscillations in electrical and magnetic fields. All electromagnetic waves are transverse.
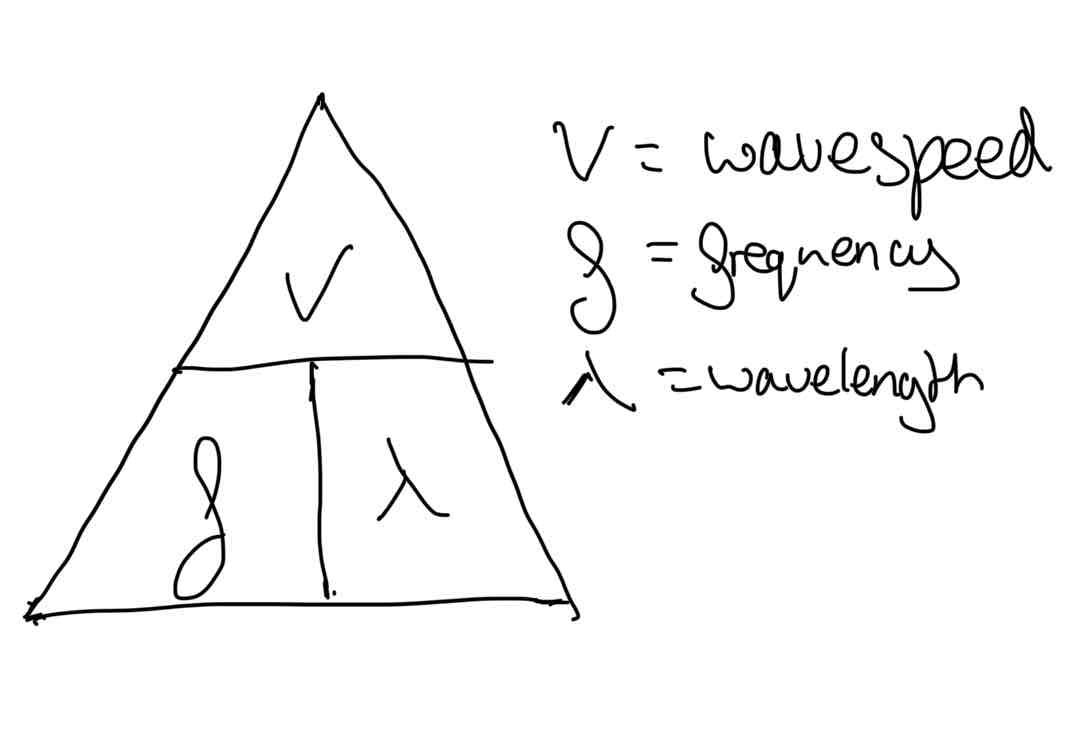
How do you calculate wave speed?
Wave speed (m/s) = frequency (Hz) x wavelength (m/s)