Chapter 20: Cancer
Cancer: Understanding the disease
- Cancer is a complex and diverse group of diseases characterized by the abnormal growth and division of cells.
- It is caused by genetic mutations that disrupt the normal cell cycle and regulation mechanisms, leading to uncontrolled proliferation.
- Cancer cells can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body through a process called metastasis.
- There are over 100 different types of cancer, classified based on the affected cell or tissue types, such as breast, lung, prostate, colon, or blood cancers like leukemia.
- There are numerous types of cancer, which can develop in different organs, tissues, and systems of the body.
- The specific type of cancer is determined by the location where the abnormal cell growth originates.
- The most common types of cancer include:
Carcinomas:
Carcinomas are cancers that develop in epithelial tissues, which are the tissues that line the surfaces and cavities of organs.
Examples of carcinomas include lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, colon cancer, and skin cancer (such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma).
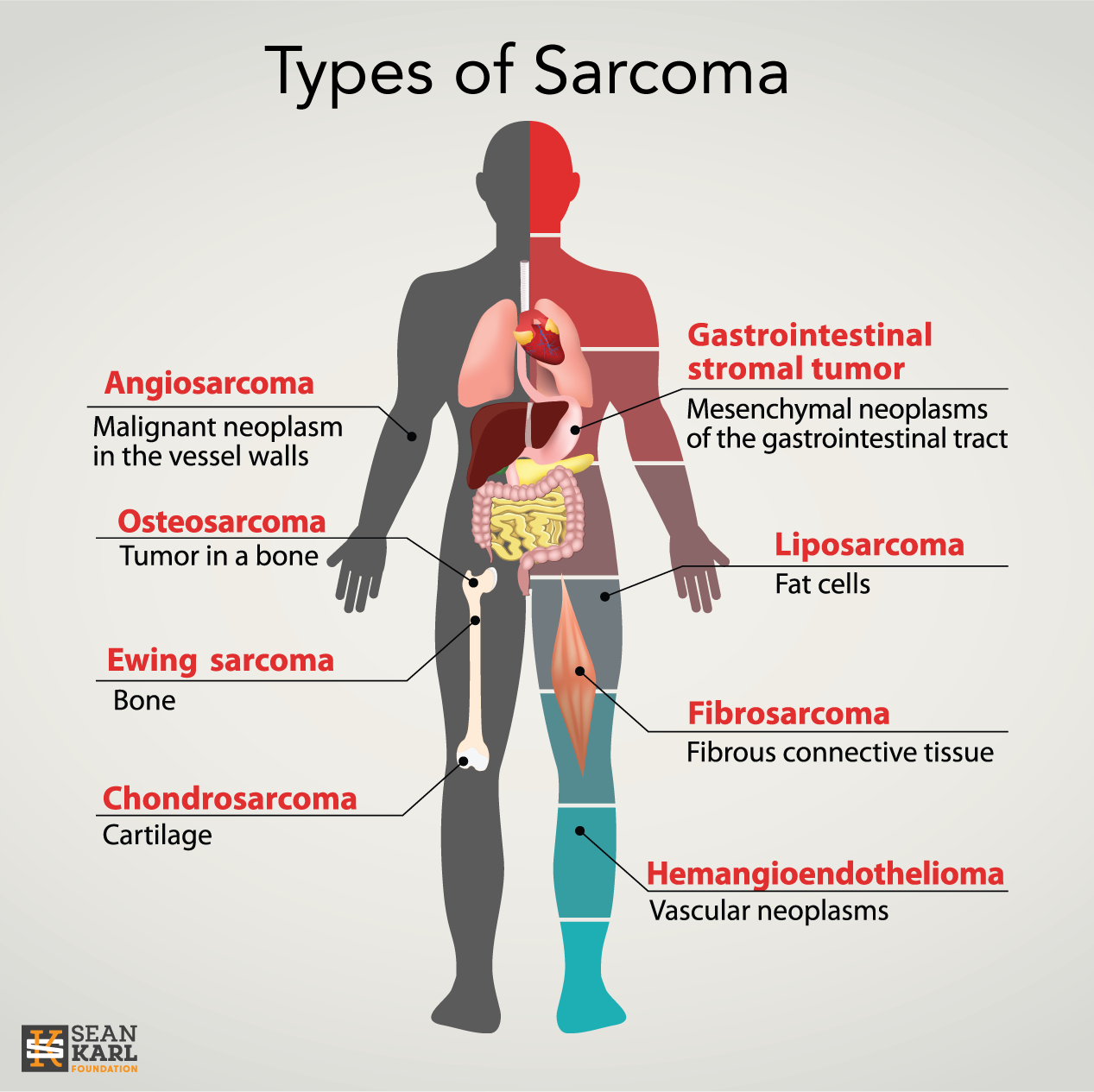
Sarcomas:
Sarcomas are cancers that arise from connective tissues, including bone, muscle, cartilage, and fat.
Examples of sarcomas include osteosarcoma (bone cancer), rhabdomyosarcoma (muscle cancer), and liposarcoma (fat cancer).
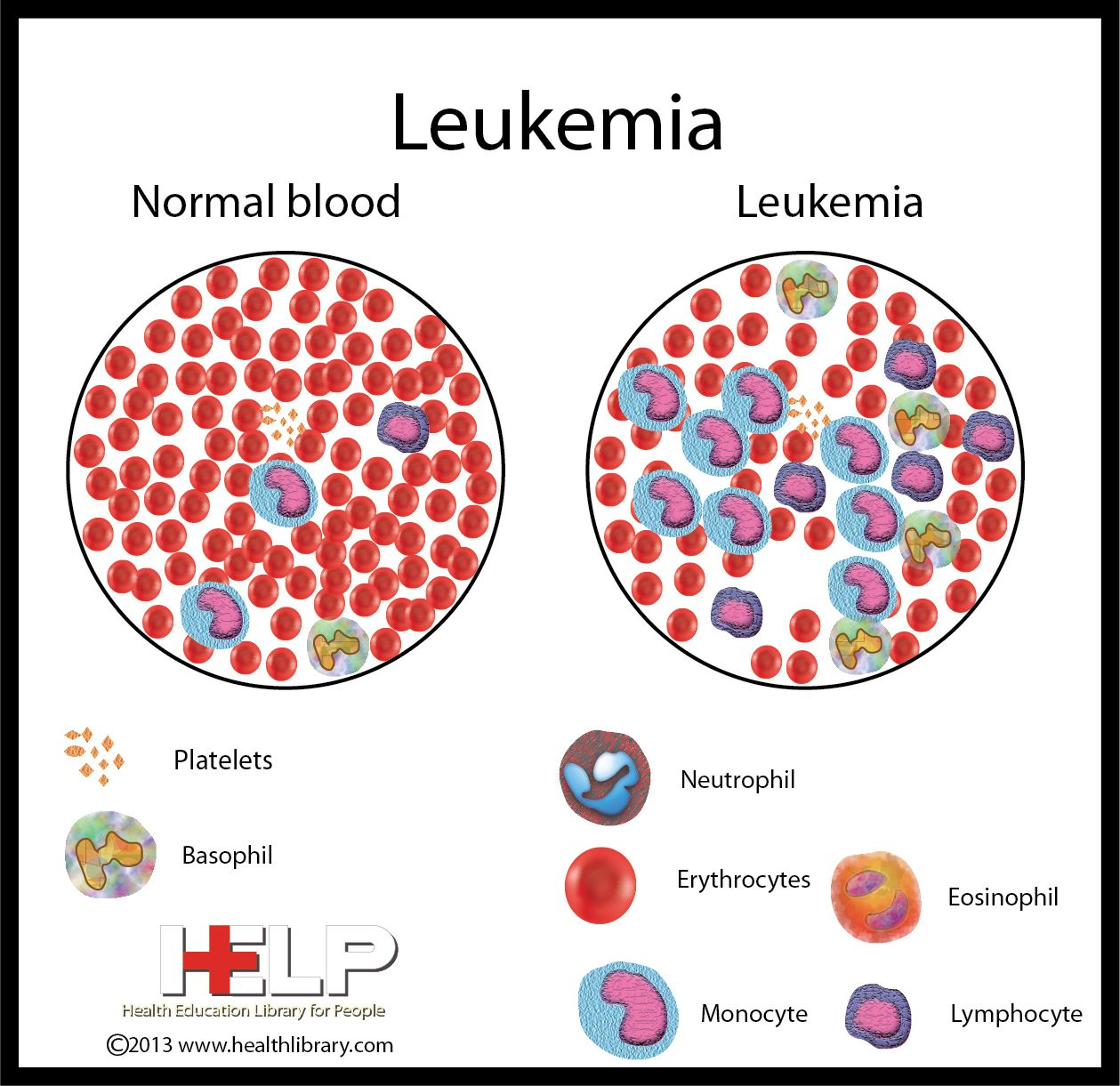
Leukemias:
Leukemias are cancers that affect the blood and bone marrow, resulting in abnormal production of white blood cells.
Examples of leukemias include acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
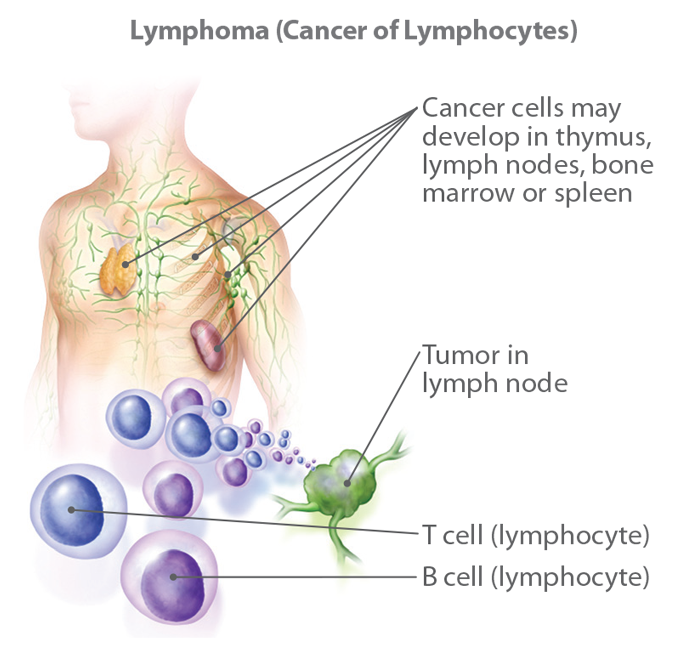
Lymphomas:
Lymphomas are cancers that begin in the lymphatic system, which includes lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow.
Examples of lymphomas include Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL).
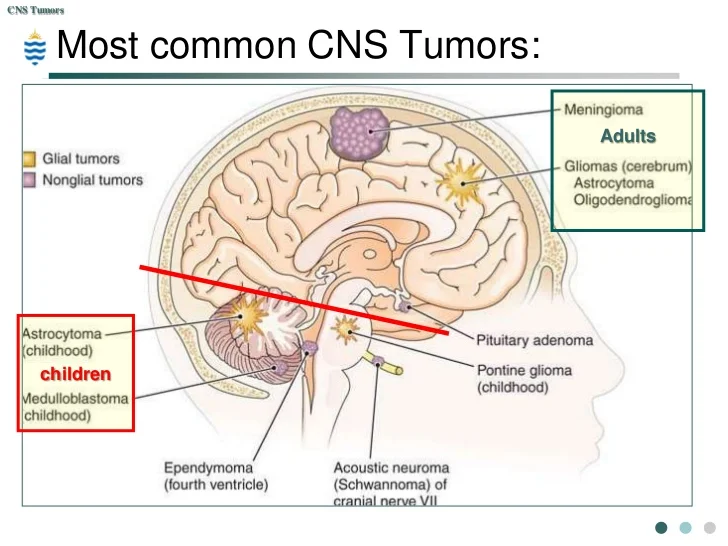
Central Nervous System (CNS) Cancers:
- CNS cancers occur in the brain or spinal cord.
- Examples of CNS cancers include glioblastoma, meningioma, and medulloblastoma.
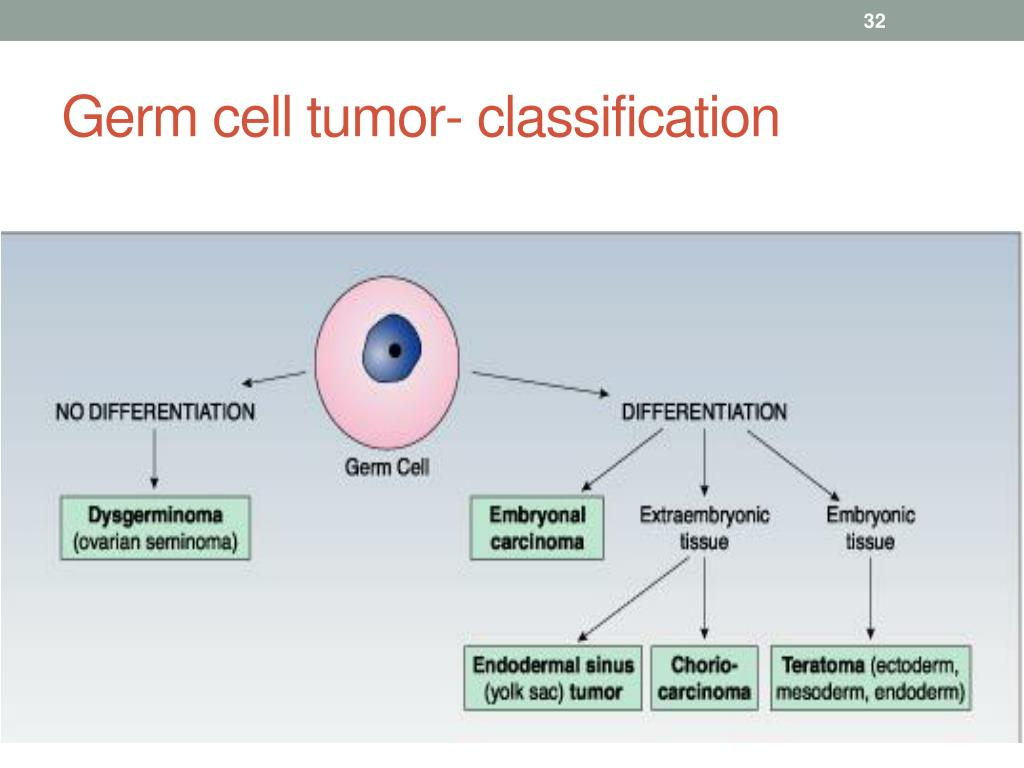
 Germ Cell Tumors:
Germ Cell Tumors:
Germ cell tumors are cancers that arise from cells that produce eggs or sperm.
Examples of germ cell tumors include testicular cancer and ovarian cancer.
Neuroendocrine Tumors (NETs):
NETs are cancers that develop in the cells of the neuroendocrine system, which is responsible for producing hormones.
Examples of NETs include carcinoid tumors and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs).
Others:
- There are numerous other types of cancer that affect specific organs and tissues, such as liver cancer, kidney cancer, bladder cancer, pancreatic cancer, and thyroid cancer.
Properties that typically contribute to cancerous growth
- They grow (biosynthesize) when they should not, aided by a metabolism shifted from oxidative phosphorylation toward aerobic glycolysis.
- They go through the cell division cycle when they should not.
- They escape from their home tissues (that is, they are invasive) and survive and proliferate in foreign sites (that is, they metastasize).
- They have abnormal stress responses, enabling them to survive and continue dividing in conditions of stress that would arrest or kill normal cells, and they are less prone than normal cells to commit suicide by apoptosis.
- They are genetically and epigenetically unstable.
- They escape replicative cell senescence, either by producing telomerase or by acquiring another way of stabilizing their telomeres.
Tumors
- A tumor is an abnormal mass of tissue that arises from uncontrolled cell division.
- Tumors can be benign or malignant:
Benign Tumors:
- Benign tumors are non-cancerous and do not invade nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body.
- They grow slowly and usually have a well-defined boundary.
- Benign tumors are generally not life-threatening, but they can cause problems if they grow large enough or press on surrounding organs.
Malignant Tumors:
- Malignant tumors are cancerous and have the potential to invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body through a process called metastasis.
- They grow rapidly and can infiltrate surrounding tissues, disrupting their normal function.
- Malignant tumors can be life-threatening and require prompt and appropriate treatment.
Overview on cancer cells
- Most cancers derive from a single abnormal cell.
- Cancer cells contain somatic mutations.
- A single mutation is not enough to change a normal cell into a cancer cell.
- Cancers develop gradually from increasingly aberrant cells.
- Human cancer cells are genetically unstable.
- Cancer cells display an altered control of growth.
- Cancer cells have an altered sugar metabolism.
- Cancer cells have an abnormal ability to survive stress and DNA damage.
- Human cancer cells escape a built-in limit to cell proliferation.
- The tumor microenvironment influences cancer development.
- Cancer cells must survive and proliferate in a foreign environment.
Cancer-critical genes: how they are found and what they do?
- Cancer critical genes, also known as cancer driver genes, are genes that play a key role in the development and progression of cancer.
- These genes undergo genetic alterations, such as mutations or changes in their expression levels, which contribute to the abnormal growth and behavior of cancer cells.
- Identifying cancer critical genes is crucial for understanding the underlying mechanisms of cancer and developing targeted therapies.
Finding Cancer Critical Genes:
- Genomic Studies:
- Large-scale genomic studies, such as whole-genome sequencing and exome sequencing, are performed to analyze the genetic landscape of cancer cells.
- These studies compare the genetic profiles of tumor cells with normal cells to identify genetic alterations that are specific to cancer.
- Bioinformatics Analysis:
- Sophisticated bioinformatics tools and algorithms are utilized to analyze the vast amount of genomic data generated from cancer studies.
- These analyses help identify recurrent genetic alterations that are likely to drive cancer development.
- Functional Studies:
- Functional studies, such as in vitro and in vivo experiments, are conducted to validate the role of candidate genes in cancer.
- Techniques like gene knockdown or knockout, overexpression, and cell-based assays are used to assess the impact of gene alterations on cancer-related processes.
Cancer Critical Genes and their Functions:
- Oncogenes:
- Oncogenes are genes that, when mutated or overexpressed, promote cell growth and division.
- They can stimulate cell proliferation, inhibit apoptosis, and enhance cell survival.
- Examples of oncogenes include KRAS, BRAF, HER2, and MYC.
- Tumor Suppressor Genes:
- Tumor suppressor genes regulate cell growth and division and prevent the formation of tumors.
- Mutations or loss of function in these genes can lead to uncontrolled cell growth.
- Tumor suppressor genes promote cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, and apoptosis.
- Examples include TP53 (p53), BRCA1, BRCA2, and PTEN.
- DNA Repair Genes:
- DNA repair genes are involved in maintaining the integrity of the genome.
- Mutations in these genes can impair DNA repair mechanisms, leading to the accumulation of genetic alterations and the development of cancer.
- Examples include BRCA1, BRCA2, MLH1, MSH2, and MSH6.
- Epigenetic Regulators:
- Epigenetic regulators control gene expression patterns without altering the DNA sequence.
- Aberrant epigenetic modifications can contribute to cancer development by silencing tumor suppressor genes or activating oncogenes.
- Examples include DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), histone modifiers (e.g., HDACs, HATs), and chromatin remodeling factors.
- Signaling Pathway Genes:
- Genes involved in crucial signaling pathways, such as the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, Wnt/β-catenin pathway, and MAPK pathway, can be critical drivers of cancer.
- Alterations in these genes can result in dysregulated signaling, promoting cell growth, survival, and metastasis.
- Angiogenesis Genes:
- Angiogenesis genes are involved in the formation of new blood vessels, which are essential for tumor growth and metastasis.
- Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors are examples of angiogenesis genes that are often dysregulated in cancer.
Cancer preventions and Treatment: Present and Future
Cancer Prevention:
- Healthy Lifestyle:
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of developing cancer.
- This includes maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, and practicing safe sun exposure.
- Vaccinations:
- Vaccinations can help prevent certain types of cancer.
- For example, vaccines are available to prevent human papillomavirus (HPV) infections, which can lead to cervical, anal, and other cancers, and hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections, which can cause liver cancer.
- Screening Programs:
- Regular cancer screenings can aid in early detection and intervention.
- Screening tests such as mammograms, Pap smears, colonoscopies, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests can detect cancer at an early stage when treatment is often more effective.
- Environmental and Occupational Safety:
- Minimizing exposure to environmental carcinogens, such as pollutants, radiation, and industrial chemicals, can reduce the risk of cancer.
- Ensuring occupational safety measures and following guidelines for hazardous materials handling can also mitigate cancer risks.
Cancer Treatment - Present:
- Surgery:
- Surgical removal of tumors is a common treatment option for localized cancers.
- It aims to remove the cancerous tissue and, in some cases, nearby lymph nodes to prevent the spread of cancer.
- Radiation Therapy:
- Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells or inhibit their growth.
- It can be used as a primary treatment or in combination with surgery or chemotherapy.
- Chemotherapy:
- Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill or slow down the growth of cancer cells.
- It is typically administered systemically, targeting cancer cells throughout the body.
- Targeted Therapy:
- Targeted therapy utilizes drugs or other substances that specifically target cancer cells by interfering with specific molecules or pathways involved in their growth and survival.
- Targeted therapies are often tailored to the genetic or molecular characteristics of the tumor.
- Immunotherapy:
- Immunotherapy harnesses the body's immune system to fight cancer.
- It can stimulate the immune response, enhance immune cell activity, or use engineered immune cells to target and destroy cancer cells.
Cancer Treatment - Future:
- Precision Medicine:
- Precision medicine aims to personalize cancer treatment based on the individual's genetic and molecular profile.
- It involves analyzing the genetic mutations and other molecular alterations in a tumor to guide treatment decisions and identify targeted therapies.
- Immunotherapies Advancements:
- Ongoing research focuses on improving existing immunotherapies and developing new approaches.
- This includes developing better strategies for immune checkpoint inhibitors, adoptive cell therapies, cancer vaccines, and combination therapies.
- Gene Therapy:
- Gene therapy involves modifying a patient's genes to treat or prevent disease.
- In cancer treatment, gene therapy aims to deliver therapeutic genes to cancer cells or modify the patient's immune cells to enhance their anti-cancer activity.
- Nanotechnology:
- Nanotechnology offers potential in cancer diagnosis and treatment.
- It involves the use of nanoparticles to deliver drugs directly to cancer cells, improve imaging techniques, and develop sensitive diagnostic tools.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- AI and machine learning algorithms are being utilized to analyze vast amounts of cancer-related data, identify patterns, and improve diagnosis, treatment planning, and drug development.