Money and Banking Ch. 14 Flashcards
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
What are the three entities that influence the money supply?
The fed
Banks
Depositors & Borrowers
the government agency that oversees the banking system and is responsible for the conduct of monetary policy; in the United States, the Federal Reserve System
Central bank
Of the three entities that influence the money supply, which is the most important?
The central bank (federal reserve system)
The Fed’s conduct of monetary policy involves actions that affect its ______,
balance sheet
What are the two liabilities on the fed’s balance sheet?
currency in circulation
reserves
An increase in the currency in circulation or reserves will to an:
a. increase in the money supply
b. decrease in the money supply
c. increase in the money demand
d. decrease in the money demand
A
What are the 3 equations for Monetary base?
Currency + Reserves
Currency + (RR+ER)
Currency + Vault Cash + Deposits at Fed
The amount of currency in the hands of the public is referred to as
Currency in circulation
Currency held by institutions is a liability for what entity?
The fed
IOUs from the fed that promise to pay the bearer back. The fed pays off IOUs with other IOUs.
Federal Reserve Notes
Federal reserve notes are liabilities to which entity?
The fed
which of the following is NOT a liability for the fed?
a. Reserves
b. Federal Reserve Notes
c. Currency in circulation
d. Securities
D
what are the two assets on the fed’s balance sheet?
securities
Loans to financial institutions
What is an example of a “worthy cause” for the fed to spend money on?
economic research
The “securities” category of assets covers the fed’s holdings of securities issued by
a. Congress
b. the US Treasury
c. the Office of Comptroller of Curreny
d. Financial institutions
B; US Treasury
The primary way in which the Fed provides reserves to the banking system is by
purchasing securities
An increase in government or other securities held by the Fed leads to an
a. Increase in the money demand
b. Decrease in the money demand
c. Increase in the money supply
d. Decrease in the money supply
C
An increase in loans from the Fed to financial institutions results in
a. A decrease in the money demand
b. An increase in the money demand
c. A decrease in the money supply
d. An increase in the money supply
D
Which of the following would NOT cause an increase in the money supply?
a. An increase in government securities held by the fed
b. An increase in discount loans from the fed
c. A decrease in bank reserves held at the bank
d. An increase in currency circulation or reserves
C
During normal times, the fed makes loans only to
banking institutions
Government securities dealers who operate out of private banking institutions
primary dealers
Federal reserve purchases and sales of bonds are always done through ________
primary dealers
Suppose the Fed purchases $100 million of bonds from the banking system. What would be the impact on both the banking system (dealer) balance sheet and Fed’s balance sheet?
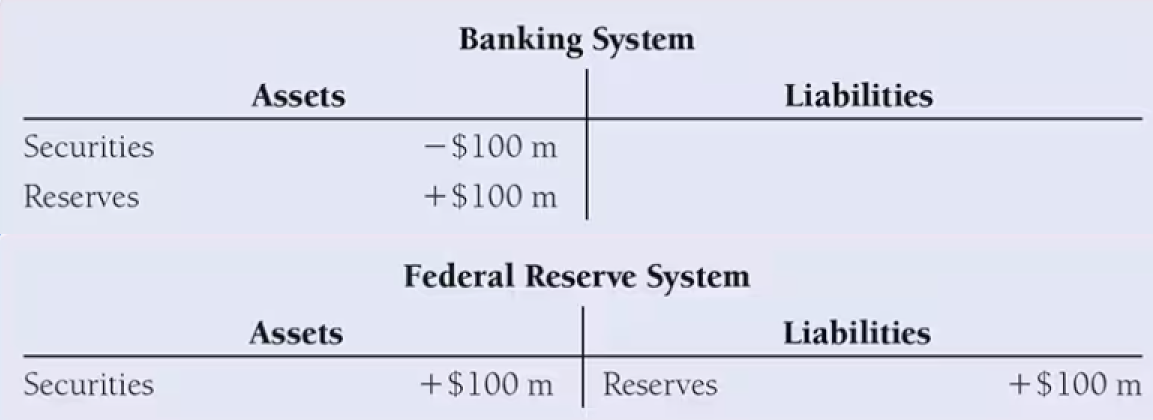
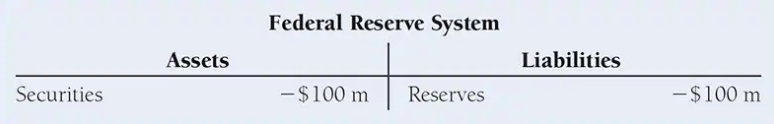
Suppose the Fed conducts an open market sale of $100 million in bonds to a primary dealer, what is the impact on the Fed’s balance sheet?
T/F The fed has more control over the monetary base than over reserves
True
When the Fed does not conduct open market operations, a shift from deposits to currency will affect the reserves in which entity?
a. the banking system
b. the federal reserve system
c. the nonbank public
d. all of the above
A; the banking system
When the Fed does not conduct open market operations, a shift from deposits to currency will not affect:
a. the reserves of the banking system
b. the quantity demanded of funds
c. the checkable deposits of the nonbank public
d. the monetary base
D; monetary base will not be affected
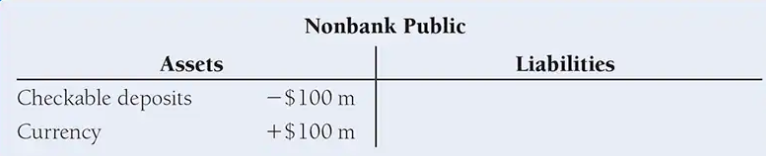
Suppose that during the Christmas season, the public withdraws $100 million in cash. The effect on the T-account of the nonbank public is
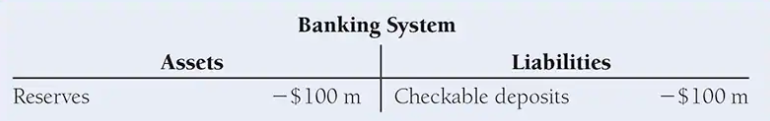
Suppose the public withdraws $100 million in cash. The effect on the T-account of the banking system is
Suppose that the public withdraws $100 million in cash. The effect on the T-account of the Federal Reserve System is

Which of the following is true regarding the monetary base?
a. It’s more stable than reserves
b. It fluctuates wildly with public demand for loans
c. It is determined entirely by commercial banks
d. it can randomly fluctuate
A
How will an increase in public desire for cash affect the monetary base?
No effect; reserves are affected

The fed makes a $100 million dollar loan to the banking system. What is the impact on the T-accounts for both entities?

Two important items that affect monetary base but are not controlled by the fed:
Float
Treasury deposits at the fed
represents the time difference between when a check is deposited and when the funds are actually available in the recipient's account
Float
Float is affected by:
Treasury deposits at the fed are affected by:
Random events
US treasury actions
The amount of open market purchases/sales is completely controlled by
the fed placing orders with dealers (banking system)
Formula for Nonborrowed monetary base:
MBn = MB + BR
Monetary base + borrowed reserves from the Fed
The process whereby, when the Fed supplies the banking system with $1 of additional reserves, deposits increase by a multiple of this amount.
Multiple deposit creation
A bank cannot safely make a loan for an amount greater than the
a. Excess reserves
b. Required reserves
c. Amount of reserves in circulation
d. Amount of their securities
A; excess reserves
Bank A is thinking about using its excess reserves to either make loans or purchase securities. Which choice will have a greater effect on deposit expansion?
Both have the same effect
The only time when deposit creation or contraction will stop is when:
A) The reserve requirement is increased
B) The money multiplier equals one
C) Excess reserves are zero (no reserves to continue the chain)
D) Banks hold more required reserves than needed
C; excess reserves are zero
Multiple deposit expansion can be stopped by:
a. deposits that are kept in currency rather than deposits
b. banks choosing to hold onto their excess reserves
c. excess reserves being zero
d. all of the above
D
The money supply is _____ related to the nonborrowed monetary base .
positively
The money supply is ______ related to the level of borrowed reserves, BR, from the Fed.
positively
The money supply is _____ related to the required reserve ratio rr
negatively
reserve requirements have become a more important factor in the determination of the (2)
money multiplier
money supply
The money supply is ____ related to the amount of excess reserve holdings.
negatively
Holding excess reserves constant, the money supply is _____ related to currency holdings.
negatively
If nonborrowed monetary base increases, what will happen to the money supply?
a. Increase
b. Decrease
A (more monetary base for deposit creation)
If required reserve ratio increases, what will happen to the money supply?
a. Increase
b. Decrease
B (less multiple deposit expansion)
If borrowed reserves increases, what happens to the money supply?
a. Increase
b. Decrease
A (more monetary base for deposit creation)
If excess reserves increases, what will happen to the money supply?
a. Increase
b. Decrease
B (less loans and deposit creation)
If currency holdings increases, what will happen to the money supply?
a. Increase
b. Decrease
B (less multiple deposit expansion)
any increase in the monetary base and deposits leads to ___ (more/less) excess reserves
more
What is the equation for currency outstanding? (Cv)
Currency in circulation + Vault Cash
What are the 2 equations for finding M1?
Monetary base + checkable deposits
or
Monetary base x money multiplier
The Feds Balance Sheet
Assets
1.
2.
Liabilities
3.
4.
US Govt Securities
Discount loans
Currency in Circulation
Reserves (vault cash and deposits at fed)
What is the impact of open market operations?
Who is the customers of open market operations?
changes the level of reserves in the banking system
banking system
The fed uses _____ to make purchases and payments in their operations
checks/electronic entry
Suppose the fed does a 1 billion dollar open market purchase of securities. What would be the impact on both the Fed’s balance sheet and the banking system?
(don’t worry about deposit multiplier)
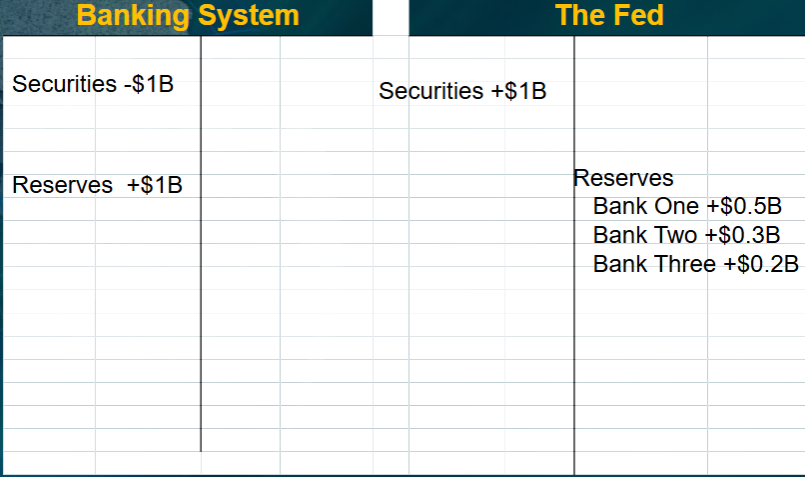
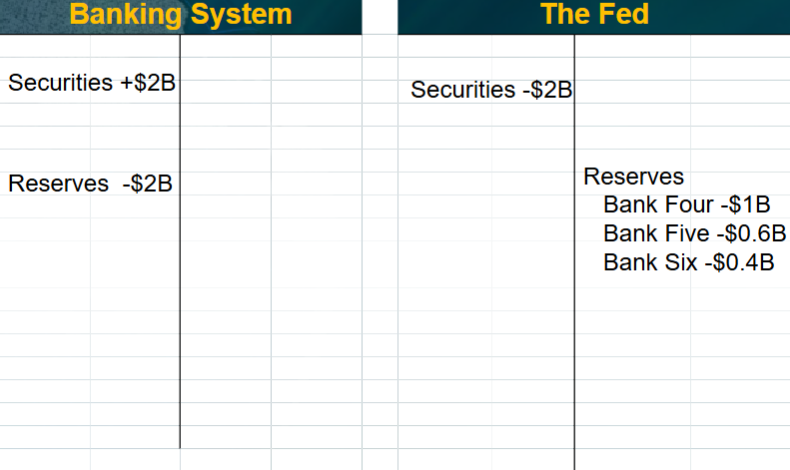
Suppose the fed does a 1 billion dollar open market sale of securities. What would be the impact on both the Fed’s balance sheet and the banking system?
(don’t worry about deposit multiplier)
What is the equation for simple deposit multiplier?
1 / reserve ratio
What is the equation for change in reserves?
1 / reserve ratio x change in reserves in the banking system
Deposit Creation Practice
Say the Fed buys $100 of securities from the banking system. what would be the real effect on the banking system balance sheet? (use the simple deposit multiplier)
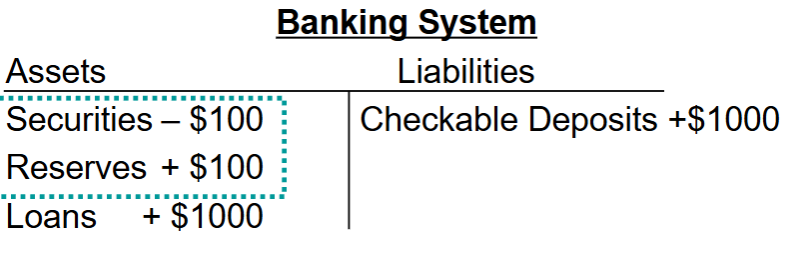
Deposit Creation Practice
Say the Fed makes a $100 loan to the banking system. What would be the real effect on the banking system balance sheet? Assume a reserve ratio of 10%
(use the simple deposit multiplier)
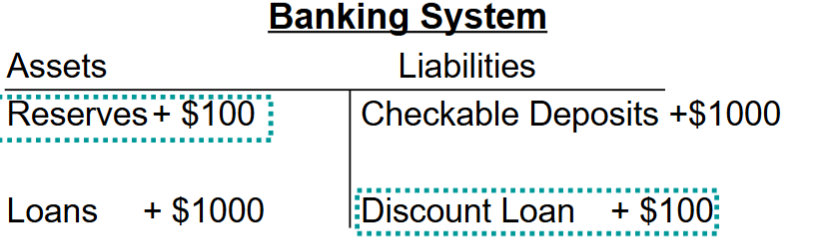
The Simple Deposit Multiplier incorrectly assumes (2)
The public keeps no cash from loan checks
Banks loan out all excess reserves
Monetary base
Determined by:
Money Multiplier
Determined by:
The fed
The fed, banking system, nonbank public
The Money Multiplier depends on these three ratios (name them and their equations)
1.
2.
3.
Currency ratio: C/CD (public)
Excess reserve ratio: ER/CD (banks)
Required reserves ratio: RR/CD (fed)
The true money multiplier equation:
“1 plus the public, divded by the public plus the banks plus the required reserves ratio”

Exercise 1: Simple Deposit Multiplier
Assume an open market purchase of 20 billion, 10% required reserves.
What is the impact on the Fed balance sheet and the Banking System balance sheet?
What is the change in monetary base?
What is the simple deposit multiplier?
What is the change in checkable deposits & total loans?
What’s gonna happen to the money supply?
see image
+20 Billion
10
1 / 0.1 = 10+200 billion
(1/0.1) x 20 = 200increase by 200 billion
Exercise 2: True money multiplier
- The public keeps 200 million in currency
- The public keeps 1000 million in checkable deposits
- Required reserve ratio is 10%
- Banks have 150 million in reserves
What is the excess & required reserves?
What is the money multiplier?
What is M1?
100 required, 50 excess
1000 × 0.1 = 100; 150 - 100 = 5024/7 (kept as a fraction for higher accuracy)
1200
(C + R) x multiplier = (200 + 150) x 24/7
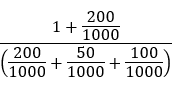
The fed conducts an open market sale of 30 million. The money multiplier is 3.4286.
a. What is the change in monetary base?
b. What is the change in money multiplier?
c. What is the change in M1?
a. -30 million net change (reserves are removed from the banking system in exchange for securities)
b. No change; changes in reserves has no effect on the money multiplier
c. change in M1 = Change in mb x m = -30m x 3.4286 = -102.96 million change
Given the public has:
200m in currency
Currency ratio is 0.2
Excess reserve ratio is 0.05
Required reserve ratio is 0.1
Banks have 150m reserves
Determine the level of checkable deposits in the banking system
Use the CD formula
350/(0.2+0.05+0.1) = 1000m
What is the formula for Checkable deposits?
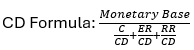
What is the formula for change in Checkable deposits?
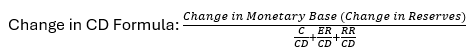
How does the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) make monetary policy?
A) By adjusting tax rates and government spending
B) By setting the federal funds target rate and IORB
C) By controlling stock market regulations
D) By determining international trade tariffs
B; By setting the FFR and IORB
How does the Federal Reserve manage the federal funds rate/target rate using Interest on Reserves (IOR)?
A) By directly lending unlimited funds to banks
B) By changing tax policy to influence bank reserves
C) By using IOR to set a floor that keeps rates from falling too low
D) By setting a ceiling that limits how high rates can rise
C
Monetary base has 3 components
Currency, Vault Cash, Deposits at Fed