World Civ 1 weeks 1-3 (early world, neolithic era, complex society, mesopotamia)
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Neolithic Era - time period
11,000-4000 bc
what is meant by prehistorical?
before there were written records starting 1500 bc
neolithic revolution
new stone age shifting away from hunting gathering to farming
why did we shift to agriculture? (3 things)
1. end of the ice age - world warmer
2. population growth
3. decrease in old animal food sources
first crop planted, where and when?
rice in the fertile crescent around 10,000 BC
- yangze and huang valley
how did sedentary agriculture change social life?
- decreased privacy
- arguments
- idea of owning private property
what was the earliest metal?
copper
what is pastoral nomadism?
Moving from place to place herding livestock for life
what were the 3 patterns of pastoral nomadic migration? where were those patterns found (only 2)
1. circular
2. attitudinal (up + down): up with normal weather, down with colder weather
3. north -> south: north w/ warm, south with cold
who were the scythians?
nomadic tribes who were skilled on horseback, tribal clan familial horizontal loyalty, viewed each part of the clan as connected - all responsible for each other's actions
BARBARIC!
900 bc - 3rd century bc
what is significant about the steppe?
strip of grassland in inner asia with horses, horses were first domesticated here
- able to survive particularly well because they could dig with hoof to find food and also they are able to sweat, so run for a long time
how were women viewed in the clan?
women actually were important to pastoral nomadism and their fathers required payment (a good sum) for her valuable contribution (and therefore loss once married) to the clan
also received protection from clan if husband hurt her
describe social stratification within pastoral nomadic groups
little differences in wealth and power
chiefs
divided sometimes due to clan mentality
who were shamans?
people within nomadic tribes that serve as connections to the spirit world and have means for negotiating with it
biggest cultural contribution of nomads?
pants! people used to only wear robes before pastoral nomads came up with pants (from riding horses, needed functional clothing)
what was the relationship of nomads to other civilizations? what do nomads provide? what do they get?
usually symbiotic
nomads provide animals, meat, wool
given grain in return
what were the first towns/villages?
Jericho and Catalhyouk
what is the significance of jericho?
it is the first city with walls, meaning there was enough structure for someone to tell people to build them and for those people to listen
significance of catalyhouk?
also a first city near a volcano with fertile soil and OBSIDIAN!
who were the bantu people?
Agriculturally based tribe that interacted with many other tribes across Africa, subsequently bringing new diseases to people with little immunity. They displaced, absorbed, and eliminated the gathering and hunting peoples.
what are the dates for the watershed of the .... millenium?
4-3000 bc
what happens during the second wave of transformation and what era does it happen during?
introduction of the plow and irrigation during the watershed of the fourth millenium
what was the next significant metal after copper?
BRONZE!
what was the growth of cities dependent on?
sewage disposal
cities usually stopped growing at ~40,000 ppl because of inability to dispose of more waste than that
why did people move to cities?
hope of justice
what is meant by complex society?
usually sedentary agriculture societies
- sedentary agriculture
- surplus
- urbanization
- specialization
- stratification
- trade
what is meant by indo-european?
language tree encompassing many of the early languages spanning across europe and asia, as far as india
who was otzi the iceman?
man's body from 3350ish bc that was extremely well preserved in ice
he had a copper axe
evidence of disease under his nails
last feast with meat fat and grains
what rivers were part of mesopotamia? where is modern day mesopotamia?
tigris and euphrates in modern day iraq
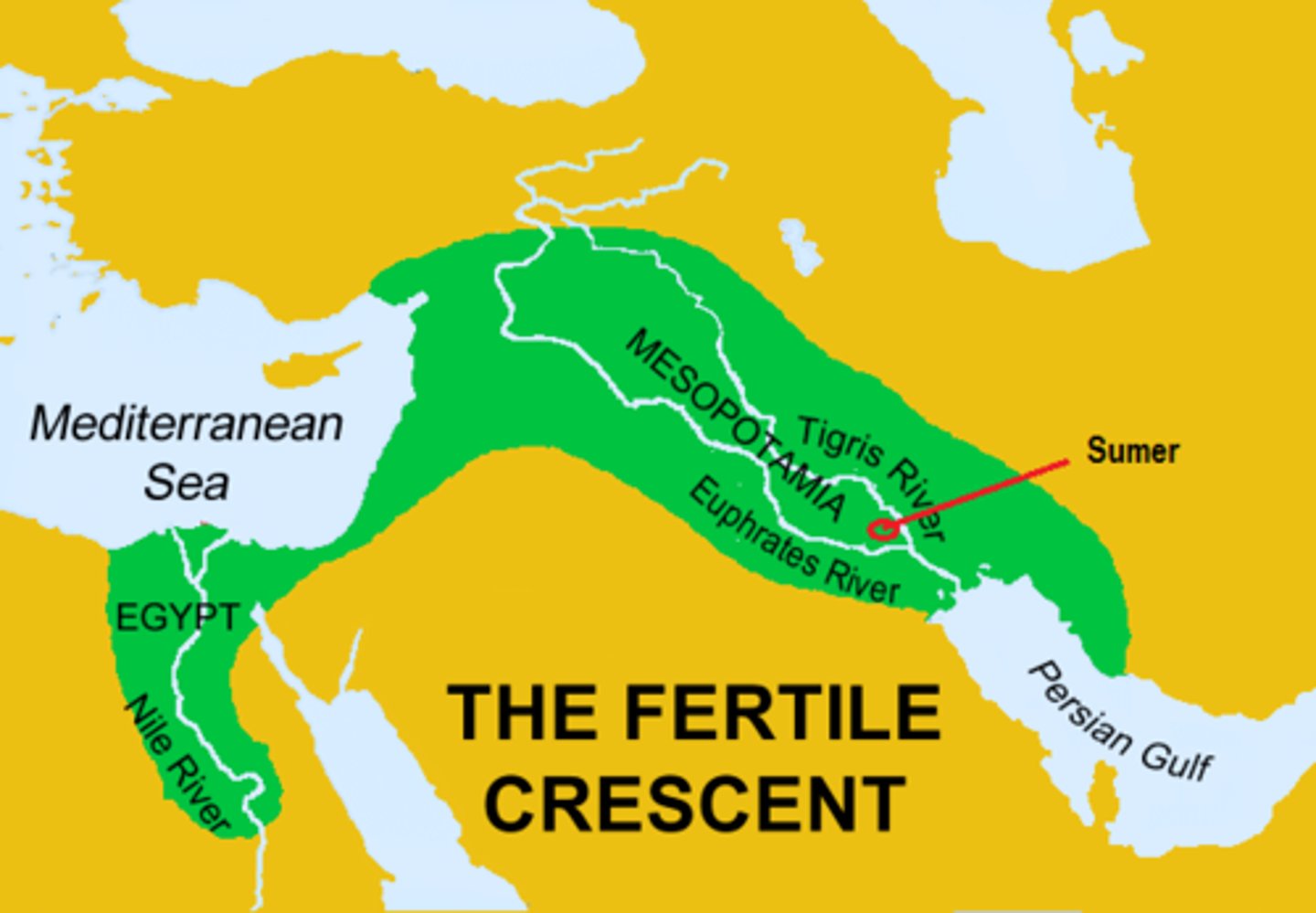
what were mesopotamia's signficant geographical features?
1. not a lot of rain --> necessary irrigation, but good silty soil
bad though because floods destroy irrigation system
2. mountains preventing awareness of oncoming attack --> sense of vulnerability
what was the first complex society in mesopotamia? what is a city of that society
Sumer! with city of uruk
what was sumer's contribution?
cuneiform
what material was used for cuneiform writing?
clay tablets that proved to be durable and last till today
who were the first writers?
priests and religious leaders
what is the most likely reason writing became needed?
for land deeds, taxes, laws, ideas, and intellectual traditions
what is sumer's political legacy?
city-states
what is a city state?
a city and its surrounding lands functioning as an independent political unit
what things did sumeria export?
crops (grain), textiles (made of cotton + wool)
what things did sumeria import?
timber, lapuz lazuli, bronze
what is lapuz lazuli?
The Sumerians were willing to travel great distances to mine lapis lazuli, traded for lapis lazuli with independent centers on the Iranian plateau
found in afghanistan
what winds allowed for sea trade? where did trade first begin within sumeria?
monsoon! across persian gulf to indian ocean
what was the relationship between kings and priests in mesopotamia?
priests give kings divine sanction
priests also needed (as first writers) to enable king to collect taxes
how did kings rise to power?
temporary leadership role made longer by doing some accomplishment like winning a battle or fixing a problem
what was mesopotamia's religion like?
polytheistic
how are gods portrayed in mesopotamia? how are they viewed?
with human characteristics, but they are much more feared than loved
the geography of mesopotamia breeds what type of outlook on life?
pessimistic outlook because of flooding , attacks and overall uncertainty of life
what is the epic of gilgamesh?
The world's first Great literary work - sumerian poem recounting the adventures of a hero (king of uruk)
what is a ziggurat? what did it imply? what was god's response?
Sumerian temple - tower of babel
idea that gods were located upward
offered food to gods there
psalm where god says : if i were hungry I would not tell you lol
what was an empire of later mesopotamia?
Akkadian empire
who was the leader of the akkadian empire? when did he rule?
sargon, 2334 - 2315
what were major contributions of the akkadian empire?
1. professional standing army
2. multiethnic empire what sargon united
how did sargon set the pattern for the establishment of future empires?
kill the leader but leave everything else the same
how did kings increase their power over time?
taking ownership of land from temples
being in control of the economy and trade
judicial functions: king gets law delivered from god
king = high priest
what mesopotamian empire existed around 1800 bc?
Babylonian empire, came after akkadian
who was the leader of the babylonian empire?
Hammurabi 1792-1750 bc

what was hammurabi most known for?
lex talionis : eye for an eye, tooth for a tooth
idea that punishment should fit the crime
what mesopotamian group existed around 1600 bc?
hittites
what did the hittites do?
irst to extensively use chariots in battle, became part of war technology
where were chariots first developed?
in the steppe
what mesopotamian group existed from 1000-612 bc?
the assyrians
what did the assyrians do?
ditched bronze to use iron
dominated all the way to egypt with iron and calvary forces