MMSC402 Body Fluid Analysis Final
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Typical urine pH
4.5-8.0
Typical urinary protein excretion
<150 mg/day
pH commercial strip method
double indicator combinations
protein commercial strip method
protein accepts hydrogen ions from indicator dye
heme/RBCs commercial strip method
Oxidation of chromogen while hydrogen peroxide is reduced
Leukocyte esterase commercial strip method
Hydrolyzes ester on reagent pad then azo coupling reaction form azo dye
Nitrite commercial strip method
diazotization of nitrite followed by azo coupling reaction
glucose commercial strip method
Double sequential enzyme reaction using glucose oxidase oxidizes glucose to hydrogen peroxide which reacts with chromagen
ketone commercial strip method
react with nitroprussideb
bilirubin commercial strip method
coupling of bilirubin with diazonium salt
urobilinogen commercial strip method
Ehrlich's reaction based on reaction of urobilinogen with p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde
Ascorbic can affect what four things?
blood, bilirubin, glucose, and nitrite readings by removing reactant from reaction sequence
Clinitest cannot detect….
reducing substances like sucrose
hemosiderin visualized with
prussian blue stain
urinary cast formation enhanced by..
acidic pH, urinary stasis, increase in solute concentration of the ultrafiltrate, and increase in the quantity of plasma proteins
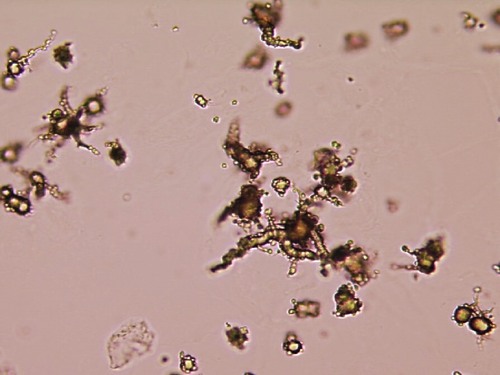
identify
ammonium biurate
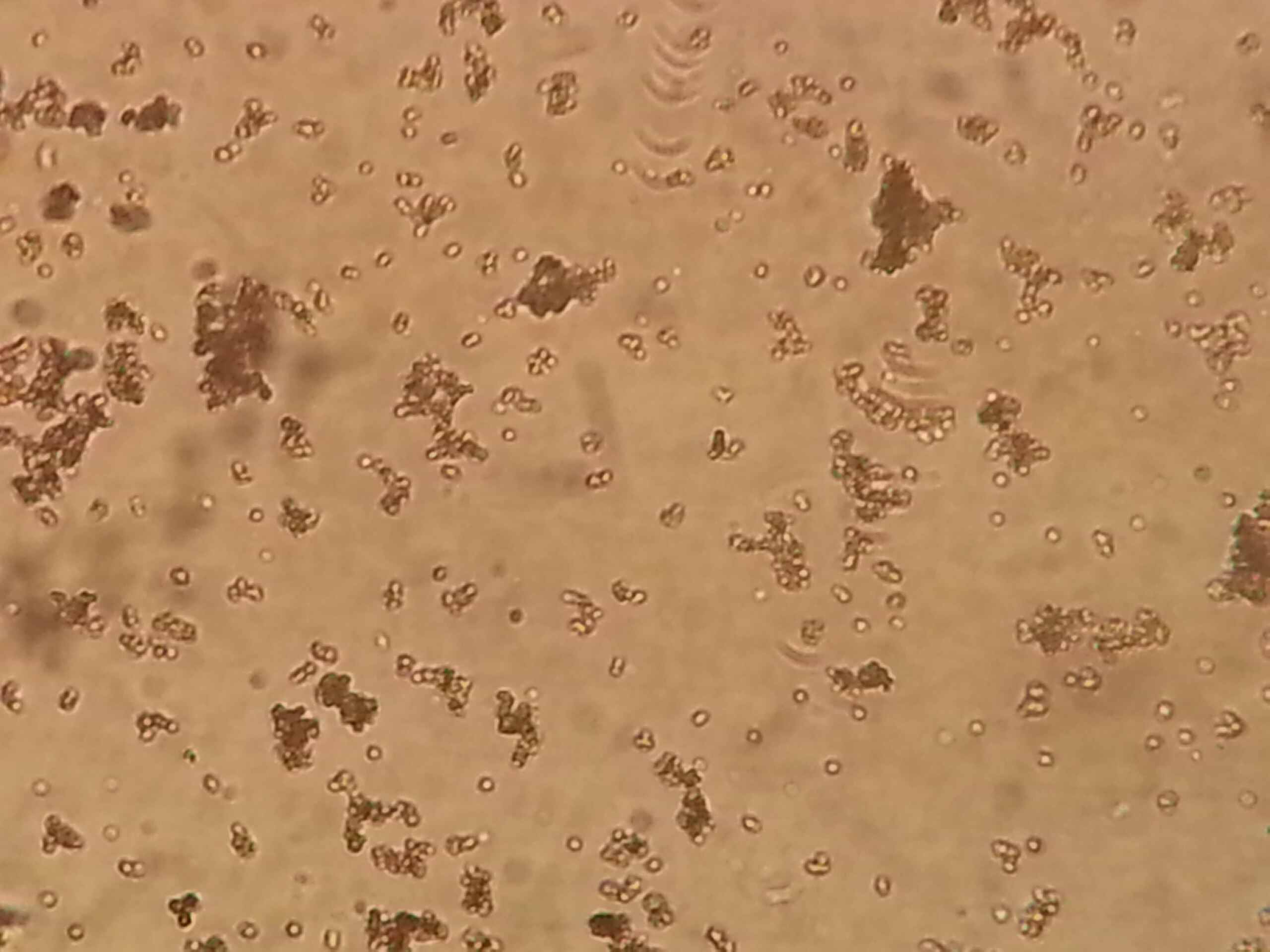
identify
amorphous urates
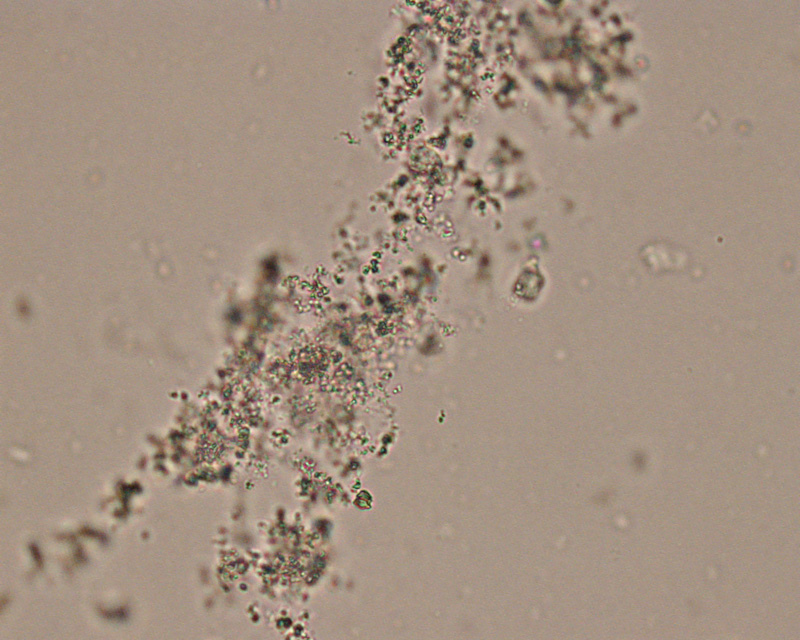
identify
amorphous phosphates
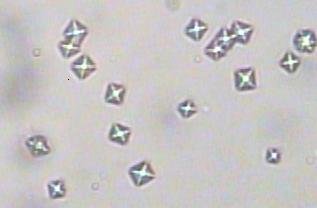
identify
calcium oxalate

identify
cystine
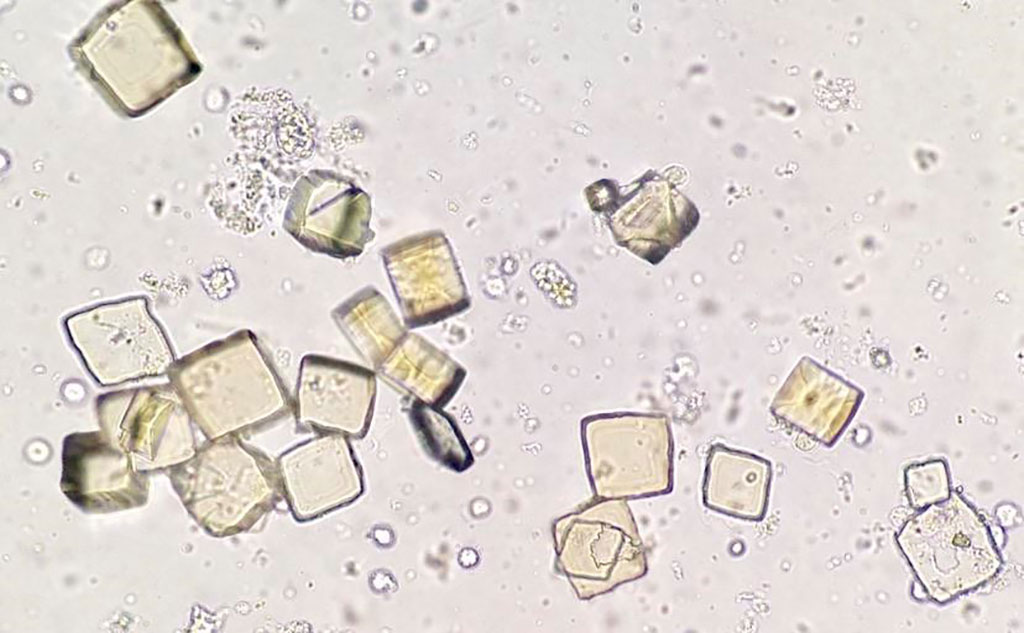

identify
uric acid
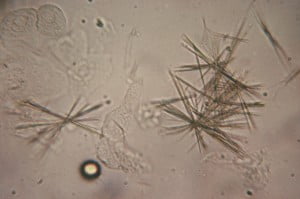
identify
sulfas
What disorder occurs after a bacterial infection of the skin or throat?
Acute glomerulonephritis
What category of renal disorders are immune mediated and result from toxic substances induced by immune complex formation?
Glomerular renal disease
Which of the following disorders is the major cause of nephrotic syndrome in adults?
Membranous glomerulonephritisis
What features characterize nephrotic syndrome?
Proteinuria, edema, hypoalbuminemia, and hyperlipidemia
Generalized loss of proximal tubular function is a characteristic of
Fanconi’s syndrome
Eosinophiluria, fever, and skin rash are characteristic clinical features of
Acute interstitial nephritis
Which of the following hereditary diseases results in the accumulation and excretion of large amounts of homogentisic acid
Alkaptonuria.
CSF has higher levels of what three things compared to plasma?
Sodium, chloride, magnesium
CSF has lower concentration of what three things compared to plasma?
Potassium, calcium, protein
Normal recumbent pressure of CSF
50-180 mm Hg
Normal albumin level of CSF
<9
Normal CSF protein
15-45 mg/dL
Normal CSF IgG
0.30-0.70
Normal CSF glucose
50-80 mg/dLWh
When is CSF glucose diagnostically significant?
When it is decreased
Thoracentesis refers specifically to the removal of fluid from the
pleural cavity
A glucose concentration difference greater than 30 mg/ dL between the serum and an effusion is associated with
Rheumatoid arthritis
A transudate has a WBC count less than____ cells/uL while an exudate has anything higher than this
1000 cells/uL
A transudate has a fluid/serum protein ratio less than____ while an exudate has anything higher than this
0.5
A transudate has a fluid/serum lactate dehydrogenase ratio less than____ while an exudate has anything higher than this
0.6
When is serous glucose diagnostically significant?
Only when it is decreased
Which of the following substances will not increase the turbidity of synovial fluid?
A. Fat
B. Crystals
C. Hyaluronate
D. White blood cells
Hyaluronate - will increase viscosity but not turbidity
viscosity of synovial due to
hyaluronate
Differentiation of synovial fluid crystals, based on their birefringence, is achieved using
Compensated polarizing microscopy
Synovial fluid should have what two things the same as plasma?
Glucose and uric acid
How does synovial fluid vary from serum?
¼ to ½ total protein and immunoglobulins
Group I noninflammatory synovial fluid characterized by
high viscosity, <3000 WBCs/uL, <25% neutrophils, <20 mg/dL glucose, yellow color
Group II inflammatory synovial fluid characterized by
low viscosity, 2000-100000 WBCs/uL, >50% neutrophils, >20 mg/dL glucose, yellow-white color
Group III septic synovial fluid characterized by
low viscosity, 10,000-100,000 WBCs/uL, >75% neutrophils, >40 mg/dL glucose, yellow-green color
Group IV hemorrhagic synovial fluid characterized by
decreased viscosity, >5000 WBCs/uL, >25% neutrophils, <20 mg/dL glucose, red-brown color
normal serous fluid volume
0.1-3.5 mL
zinc levels of semen can be used to detect function of
prostate gland
fructose levels of semen can be used to detect function of
seminal vesicles
normal sperm concentration
20-250 million sperm/mL
normal pH of semen
7.2-7.8
normal pH of vaginal secretions
3.8-4.5
odor of potassium hydroxide test caused by
trimethylamine
potassium hydroxide test diagnostic of what bacterial condition
bacterial vaginosis
Lactose intolerance caused by the lack of sufficient lactase primarily presents with
osmotic diarrhea
The daily amount of fat excreted in the feces is normally less than
7.0 g
what compound is produces the normal color of feces
urobilins
secretory diarrhea is characterized by
increased solute secretion by intestine that draws water and electrolytes into the intestines
osmotic diarrhea is characterized by
increased osmotically active solutes drawing water and electrolytes into intestine
secretory diarrhea is characterized by what fecal osmolality
<20 mOsm/kg
osmotic diarrhea is characterized by what fecal osmolality
>20 mOsm/kg
how is the apt test used to differentiate fetal and maternal blood in a newborn’s stool
dilute sodium hydroxide added to stool that will degrade the maternal but not fetal hemoglobin
fecal carbohydrate clinitest uses what reaction
copper reduction principle to detect reducing sugars
secretory diarrhea caused by
enterotoxin-producing organisms, damage to mucosa due to drugs or disease
osmotic diarrhea caused by
maldigestion, malabsorption